3 4 Ratio in Pixels Guide for Photography and Design
Learn how to use the 3:4 aspect ratio in pixels for photography, printing, and design, with common sizes, formulas, and resizing best practices.

Introduction to the 3:4 Ratio in Pixels
The 3:4 ratio in pixels is a key concept in photography, graphic design, and digital imaging, defining the proportional relationship between an image's width and height. Expressed as two numbers separated by a colon—3:4 means that for every three units of width, there are four units of height. This vertical, portrait-friendly format is popular for portraits, print layouts, and mobile-friendly visuals, offering a balanced aesthetic that fits standard photo sizes and viewing expectations.

Choosing the right aspect ratio influences composition, framing, and viewer perception. The 3:4 aspect ratio is a versatile choice, lending itself to professional and creative work across different mediums.
---
Understanding the 3:4 Ratio in Pixel Terms
The proportional relationship can be broken down simply:
- Example 1: Width = 300 px → Height = 400 px
- Example 2: Width = 750 px → Height = 1000 px
Mathematically:
height = (4 / 3) × width
width = (3 / 4) × heightMaintaining this proportion ensures that your image's shape stays consistent, regardless of its size.
---
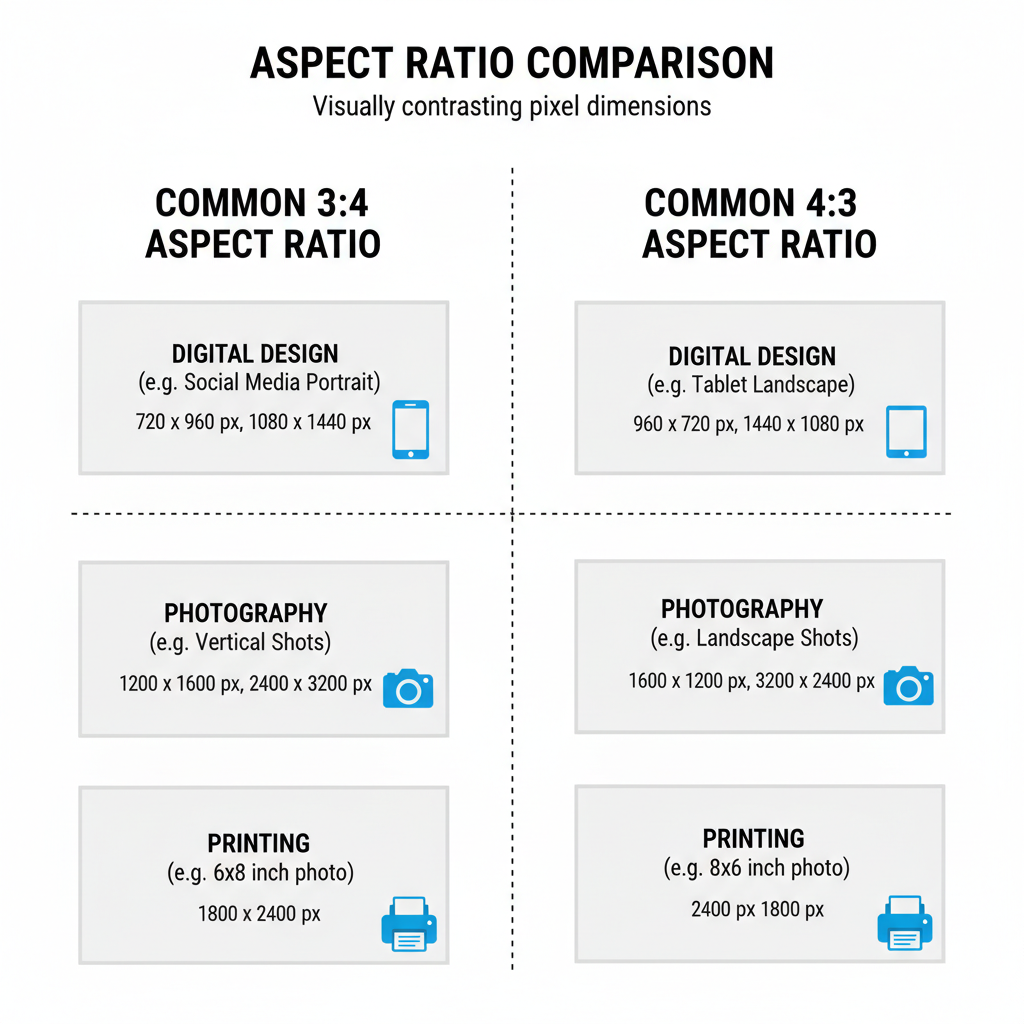
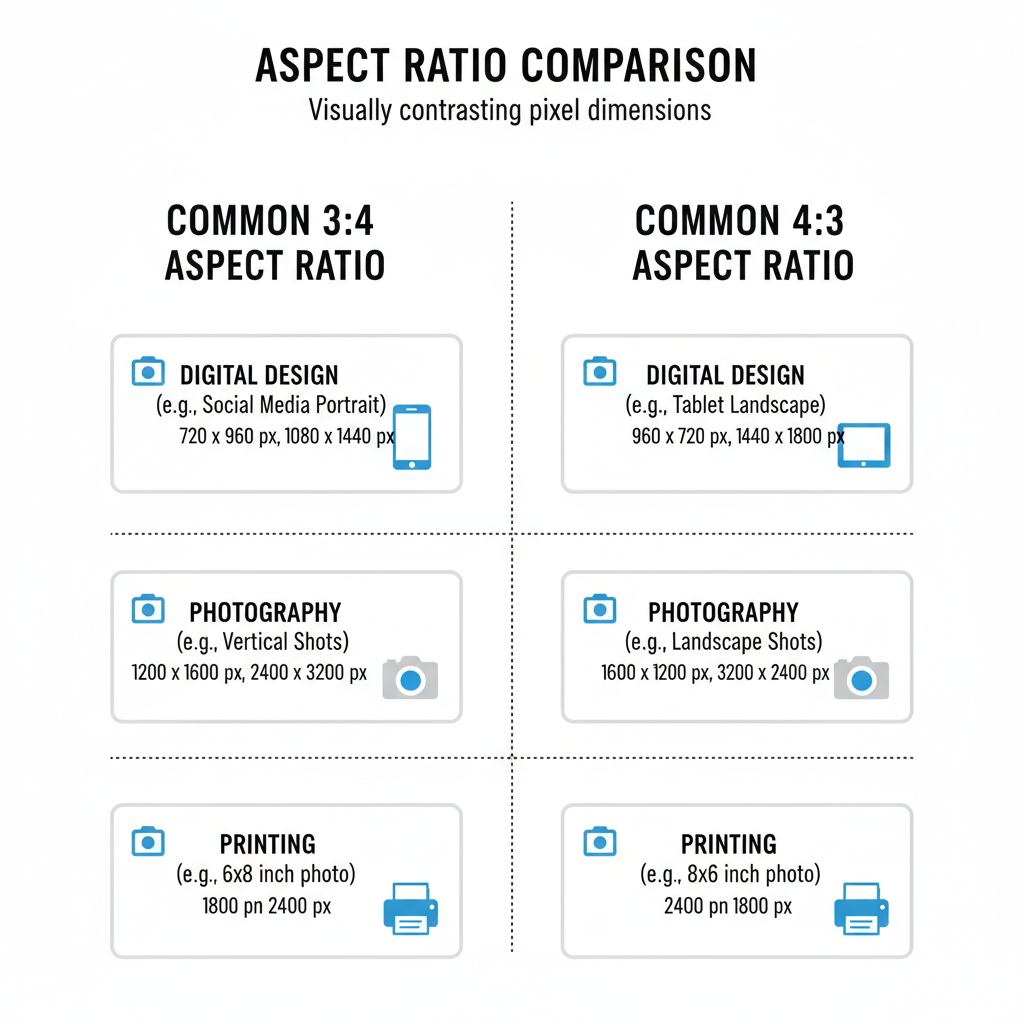
Common Pixel Dimensions for the 3:4 Aspect Ratio
Here are popular pixel dimension sets that perfectly match the 3:4 aspect ratio for digital, print, and web applications:
| Width (px) | Height (px) | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| 600 | 800 | Web portrait image |
| 750 | 1000 | Digital art print |
| 900 | 1200 | Magazine layout |
| 1200 | 1600 | High-res poster |
| 1500 | 2000 | Large portrait photo |
These dimensions can be scaled while maintaining perfect proportions for high-quality results.
---
Use Cases Across Photography, Printing, and Digital Design
The 3:4 aspect ratio is ideal for:
- Photography: Natural choice for portraits and vertical compositions.
- Printing: Matches popular print sizes such as 6×8 inches and 9×12 inches.
- Digital Design: Useful for banners, posters, and editorial layouts.
It’s also frequently used in mobile interfaces, where vertical images fit storytelling formats and profile displays.
---
How to Calculate 3:4 Dimensions From Either Measurement
If you know one measurement, calculating the other is straightforward:
Finding Height From Width
Width = 900 px
Height = (4 / 3) × 900 = 1200 pxFinding Width From Height
Height = 1600 px
Width = (3 / 4) × 1600 = 1200 pxThese formulas are easy to apply in editing tools, spreadsheets, or even manual resizing.
---
3:4 Ratio vs 4:3 Ratio: Key Differences
Although 3:4 and 4:3 use the same numbers, the orientation is different:
| Aspect Ratio | Orientation | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| 3:4 | Portrait (vertical) | Portrait photography, posters, art prints |
| 4:3 | Landscape (horizontal) | Computer screens, TV, landscape photography |
Think of 3:4 as the portrait counterpart of 4:3.
---
How to Resize Images Without Losing the 3:4 Ratio
When resizing:
- Open the image in your preferred editor (Photoshop, GIMP, Canva, etc.).
- Lock aspect ratio or enable "Constrain Proportions."
- Adjust dimensions while keeping proportions intact.
- Export in the target pixel size.
Pro tip: Use cropping rather than stretching if your source image does not match the ratio.
---
Recommended Tools for Perfect 3:4 Cropping and Resizing
Some widely used tools for precise aspect ratio management include:
- Adobe Photoshop – Presets for common ratios.
- GIMP – Free with robust ratio features.
- Canva – Intuitive interface with preset templates.
- Pixlr – Web-based editor for quick changes.
- Figma – Excellent for UI layout with fixed dimensions.
All of these tools allow custom ratio settings to preserve proportional accuracy.
---
How 3:4 Affects Visual Composition and Style
Because the 3:4 ratio emphasizes height, it is ideal for:
- Showing full-body portraits
- Capturing tall architecture or nature scenes
- Creating striking editorial layouts with space for headlines or captions
- Focusing attention vertically to direct the viewer’s gaze
This ratio often feels more intimate than wider formats, enhancing vertical storytelling.
---
Best Practices for Selecting Resolution by Medium
Resolution choices should match usage:
Printing:
- Target 300 DPI for crisp output.
- Match pixel size to print size (e.g., 1800×2400 px for 6×8 inches).
Web:
- Optimize for speed without quality loss, e.g., 900×1200 px.
- Save as WebP or optimized JPEG/PNG.
Mobile Apps:
- Consider pixel density and scaling (e.g., 1200×1600 px).
- Use vector graphics for scalability when possible.
Correct resolution ensures professional quality without bloated file sizes.
---
Summary
The 3:4 ratio in pixels is a timeless choice in photography and design, providing a visually pleasing, portrait-oriented proportion. By understanding its math, common sizes, and use cases, plus applying correct resizing methods, you can maintain image fidelity across print, digital, and mobile platforms.
For best results, apply the formulas, use dependable editing tools, and adjust resolution for your intended medium. A consistent 3:4 aspect ratio will make your work stand out with clean, professional presentation—so start applying it confidently in your next project.