400 Yuan Remote-Controlled 95% Robotic Arm! Shanghai Jiao Tong University Launches Open-Source U-Arm for a Universal, Low-Cost Human-Machine Teleoperation Interface
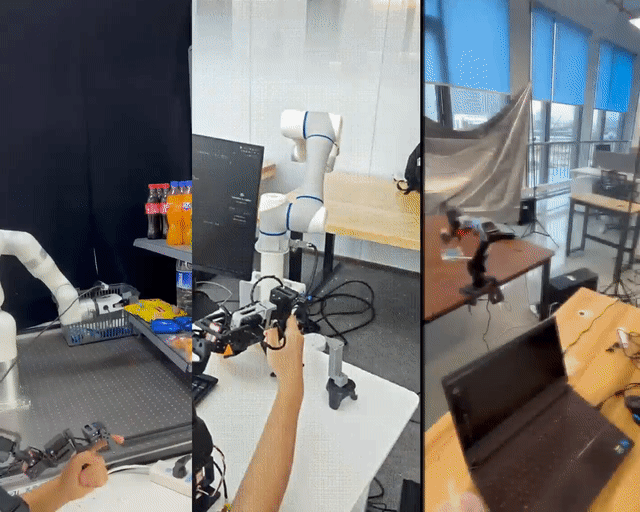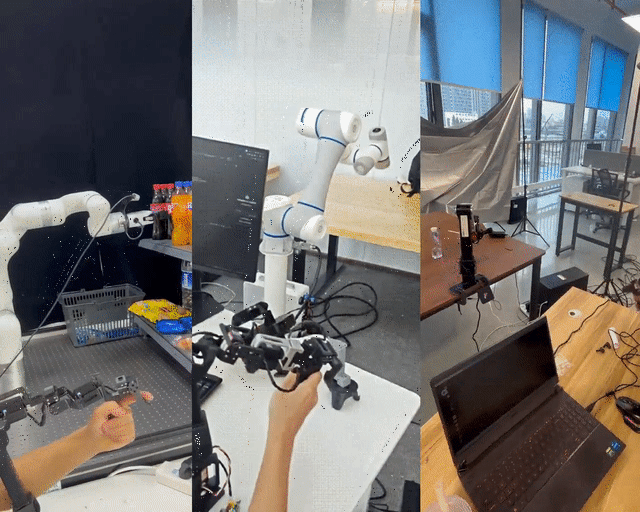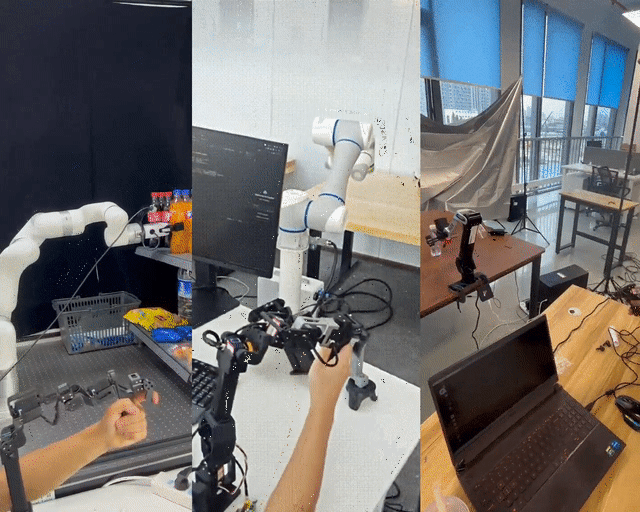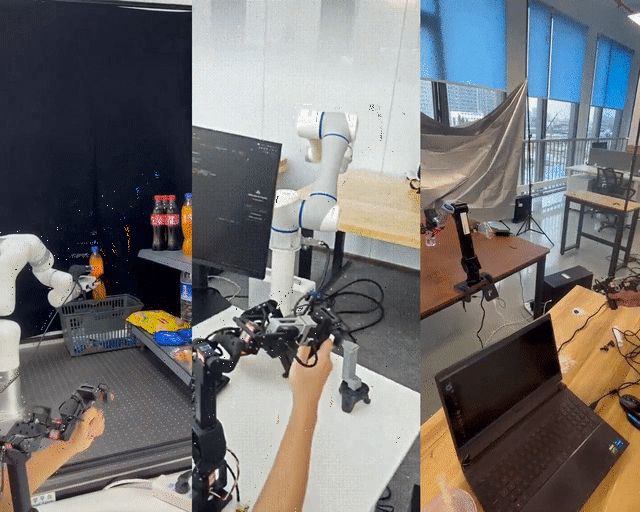
400 RMB Remote-Control Robotic Arm — Shanghai Jiao Tong University’s U-Arm Open-Source Project
Shanghai Jiao Tong University has unveiled LeRobot-Anything-U-Arm, an open-source, low-cost teleoperation system tested successfully on multiple mainstream robotic arms including XArm6, Dobot CR5, and ARX R5.
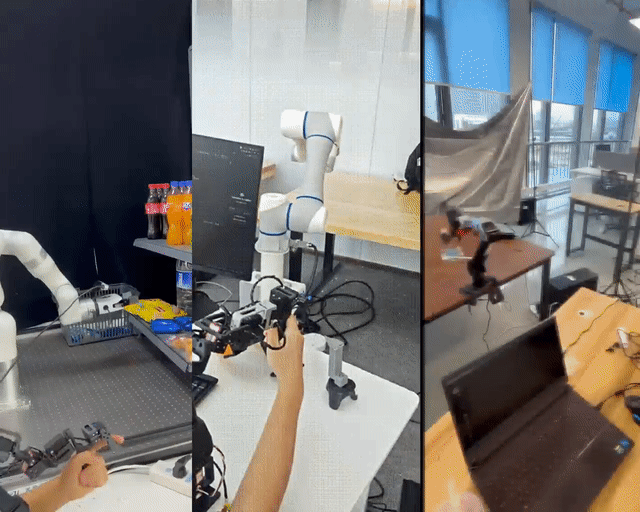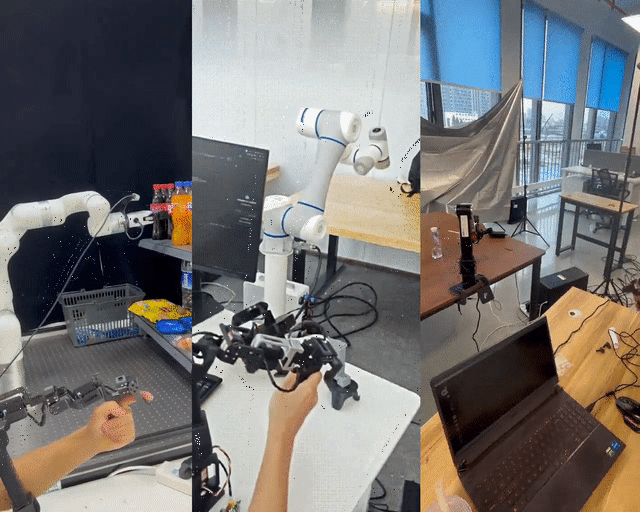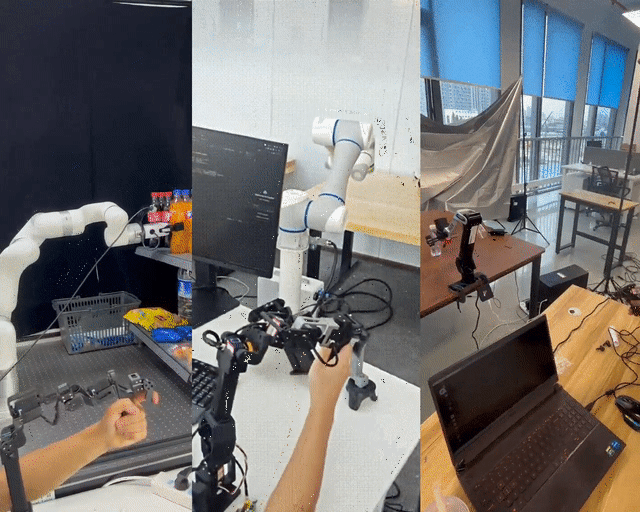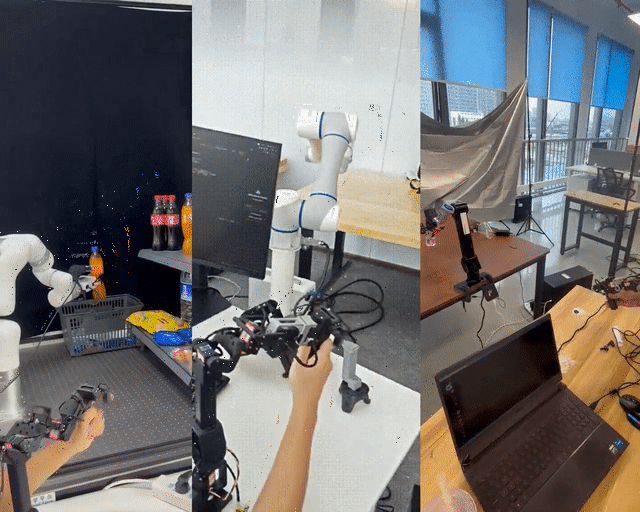
---
Why U-Arm? — Lower Cost, Higher Efficiency
Teleoperation Challenges
- Mainstream approach: Teleoperation is the key method for collecting robotic manipulation data.
- High cost barrier: Traditional isomorphic setups (e.g., ALOHA project) require two identical master-slave pairs, costing over USD 20,000.
- Limitations of low-cost options: VR systems, game controllers, and GELLO frameworks face singularity issues and require adaptation.
U-Arm’s Innovation
- Cost: Entire system under 400 RMB.
- Compatibility: Works with 95% of mainstream robotic arms.
- Flexibility: Master-slave arms no longer need identical geometry — joint order consistency and visual feedback ensure smooth operation.
---
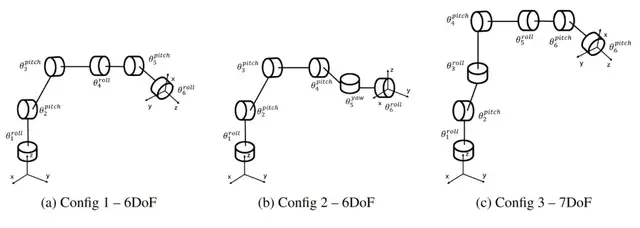
Hardware Design Principles
Master-Slave Compatibility
- Observation: Human visual feedback compensates for geometric differences.
- Design basis: Most 6-axis/7-axis arms have only three joint order types.
- Solution: Three mechanical configurations tailored for these topologies — enabling plug-and-play control.
---
Software Compatibility
- Uses a ROS-based control framework to decouple commands:
- Controllers packaged as ROS nodes.
- Subscribe to U-Arm’s joint angle topics.
- Forward to the slave arm’s interface.

---
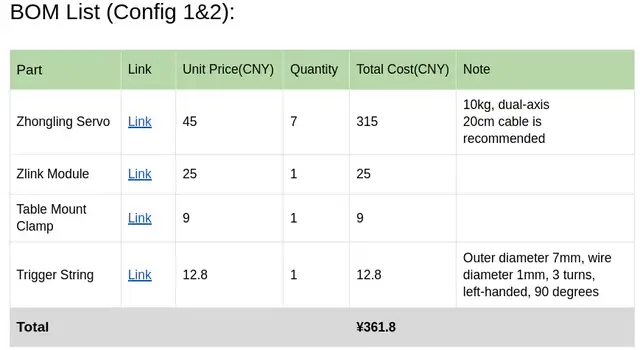
Cost Reduction in Servo and Control
- GELLO example: BOM USD 288.24, with > USD 250 on servos and control boards.
- U-Arm uses RMB 45 servos — total hardware cost < 400 RMB (excluding printing materials).
- Design prioritizes maintainability and lifespan.
---
Structural & Usability Optimizations
- Removed servo gearboxes, kept encoders only.
- Double-axis fixed joints → Smooth motion, no gravity drop near workspace limits.
- Adjustable servo horn screws for fine movement resistance control.

---
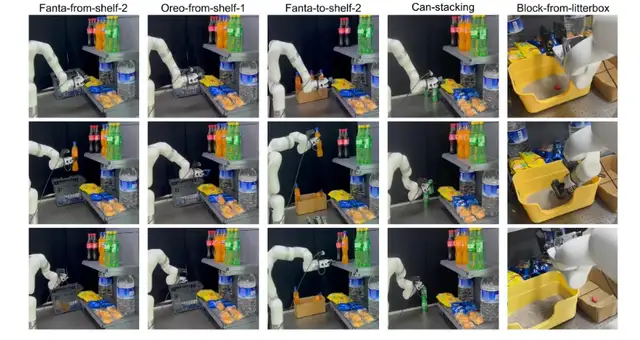
Performance Testing
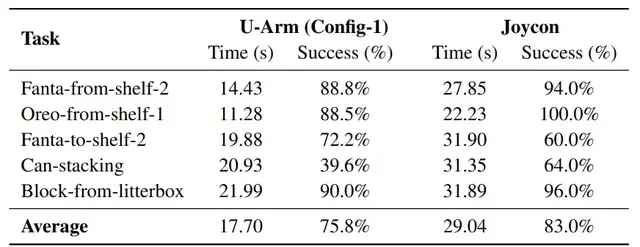
Test Tasks
- Pick Fanta from second-tier shelf → carton
- Pick cookies from first-tier shelf
- Sort products from carton → shelf
- Stack cans
- Pick strawberries from litter box
Comparison target: Game controller teleoperation (similar cost)
---
Test Results
- Average task time reduced by 39% vs. game controller.
- Gains due to redundant DOF control for faster sweeping motions.
- Slight drop in precision for tasks like can stacking — game controller provided more stability in fine movements.
- Trade-off considered acceptable for data collection speed.
---
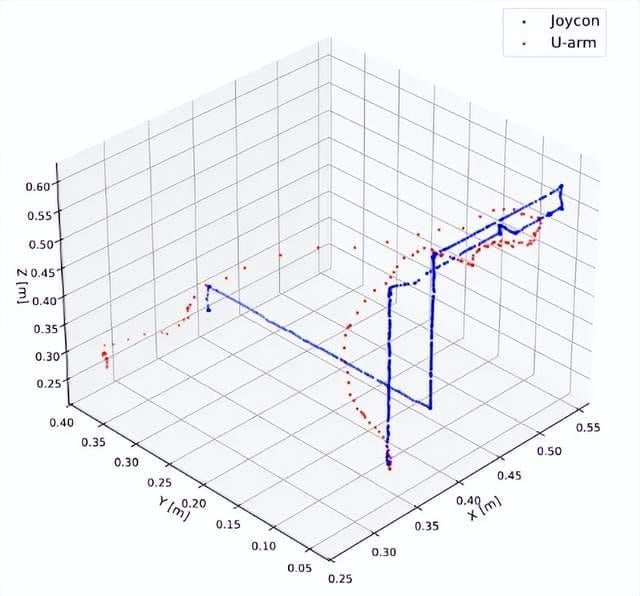
Data Quality Advantages
- Natural motion trajectories closer to real human operation.
- More consistent distribution when training models with mixed datasets — aiding convergence.
---
Open-Source Resources
All resources are publicly available including:
- Hardware files: STL, STEP
- Software routines
- Assembly guides
- SAPIEN simulation test routines
- Datasets for XArm6 — continuously updated on Hugging Face
Links:
- GitHub: github.com/MINT-SJTU/LeRobot-Anything-U-Arm
- Technical Report: arxiv.org/abs/2509.02437
- Hugging Face datasets: https://huggingface.co/MINT-SJTU
---
Enhancing Global Collaboration with AiToEarn
For robotics developers and dataset creators, AiToEarn官网 offers:
- Cross-platform publishing to Douyin, Kwai, WeChat, Bilibili, Xiaohongshu, Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, Threads, YouTube, Pinterest, X (Twitter)
- Analytics, AI model rankings, and monetization tools
- Seamless integration with robotics & AI projects to document experiments and reach global audiences
---
U-Arm marks a step toward affordable, high-quality teleoperation systems for robotics research and AI training — empowering both hobbyists and professional teams to collect diverse, life-like manipulation data at scale.




