AAAI 2026 Oral | UTS and PolyU Break the “One-Size-Fits-All” Mold: How Federated Recommendation Achieves Personalized Image-Text Fusion

Balancing Privacy & Personalization in Multimodal Recommendation Systems
In today’s move toward multimodal recommendation systems, the challenge is how to balance data privacy with personalized image–text understanding.
A research team led by Prof. Guodong Long (University of Technology Sydney), in collaboration with Prof. Qiang Yang and Prof. Chengqi Zhang (The Hong Kong Polytechnic University), has proposed a new framework — FedVLR — to address this challenge.
This work, tackling multimodal fusion heterogeneity in federated environments, has been accepted as an Oral Presentation at AAAI 2026, a leading AI conference.
---
The New Normal: Multimodal Meets Federated Learning
Modern recommendation systems often use images and text to assist decisions.
When combined with Federated Learning — where data stays local to preserve privacy — complexity increases.
The Dilemma in Current Approaches
- Privacy-first, feature-light: Skip multimodal processing and rely solely on ID-based features.
- One-size-fits-all fusion: Assume all users prefer image–text in the same way.
Reality check:
Preferences vary. For clothing, visuals matter; for electronics, textual specs dominate. Capturing these variations in a federated setting — without seeing individual data — is tough.
---
FedVLR: Rethinking Multimodal Fusion
The team’s key insight: Restructure the decision flow by letting the server handle heavy preprocessing while offloading personalized fusion decisions to lightweight client-side routing.

---
Pain Point: Multimodal in Data Silos
In centralized training, all interaction data is visible, so models can learn optimal fusion weights.
In federated learning, the server cannot see user behavior and must guess:
> For User A, is image more important than text?
Key Limitations
- Computational bottlenecks:
- Clients often can’t run large vision–language models like CLIP.
- No personalization:
- One global fusion rule ignores individual habits.
---
FedVLR Architecture: Server Prepares, Client Refines
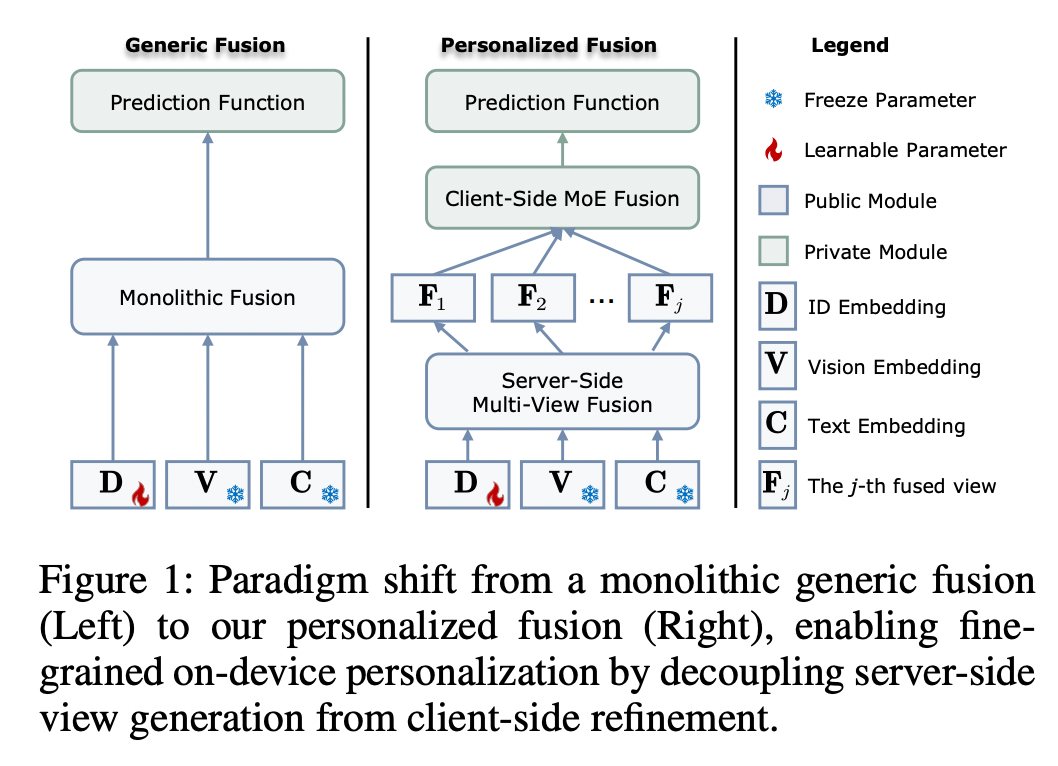
FedVLR decouples feature extraction from preference fusion via a two-layer mechanism:
Layer 1 — Server-Side “Multi-View Pre-fusion”
- Heavy computation locked to the server.
- Pre-trained vision–language models generate multiple candidate fusion views:
- View A: Image-dominant
- View B: Text-dominant
- View C: Balanced
- These semi-finished dishes provide rich visual–text content understanding without burdening client devices.
Layer 2 — Client-Side “Personalized Refinement”
- Lightweight Mixture of Experts (MoE) router runs locally.
- Uses private interaction history to compute personalized weights.
- Processing stays on-device — preferences never leave the client.
---
Engineering Benefits: Plug-and-Play Personalization
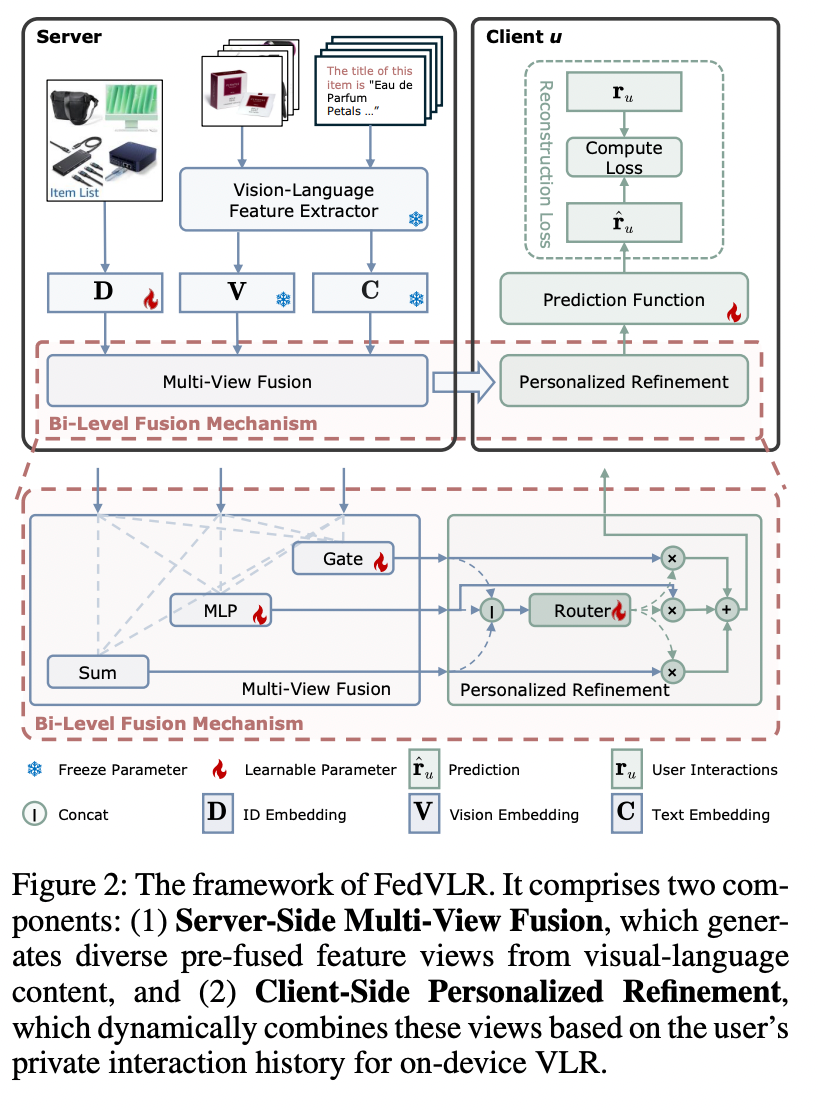
FedVLR is modular and easy to integrate into existing federated recommendation pipelines.
Advantages:
- No heavy edge-side preprocessing
- Seamless integration into frameworks like FedAvg or FedNCF
- Zero extra communication overhead
- Strict privacy compliance
---
Real-World Parallels: Cloud Power + Local Customization
Platforms like AiToEarn官网 apply similar principles in content monetization — heavy cloud-based generation with lightweight local personalization.
By connecting generation, publishing, analytics, and rankings, they mirror FedVLR’s privacy–personalization synergy.
---
FedVLR in Action: Results & Validation
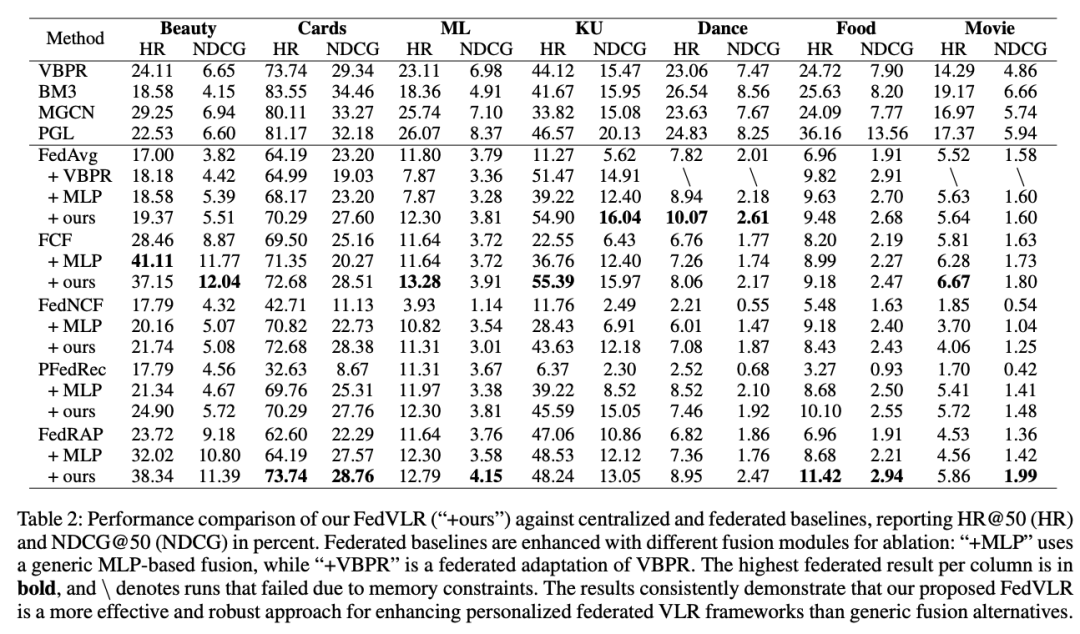
Experiments on Public E-commerce & Multimedia Datasets
Highlights:
- Consistent gains in NDCG and HR across baseline models.
- Cold-start boost in sparse data — personalized fusion helps utilize limited data effectively.
---
Broader Impact: A Paradigm for Federated Foundation Models
In an era of limited edge computing power and increasingly powerful cloud models, the challenge is:
- Benefit from cloud-scale knowledge
- Preserve local privacy
- Avoid expensive deployment costs
FedVLR offers a path:
> Cloud: General content understanding
> Edge: Private preference modeling
This reduces the thresholds for communication and computation — enabling use of complex multimodal and generative AI models in privacy-sensitive contexts.
---
Conclusion
FedVLR is more than a model; it’s a deployable enhancement framework for federated multimodal recommendation.
By smartly dividing work between server-side preprocessing and client-side personalization, it:
- Preserves privacy
- Improves recommendation accuracy
- Enables real-world deployments even on limited hardware
With its open-source release, the community can adapt and extend it to new applications — including AI-powered content creation platforms that demand both personalization and privacy.



