Agent Breakthrough! A Complete Guide to Core Agent Development Workflow

📑 Table of Contents
- Introduction to Agents
- Core Evolution and Core Modules of an Agent
- Building an Agent Using a Large Language Model (Developer’s Perspective)
- Evaluating Agents
---
🌟 From Workflow to Agentic AI
When data can think and code can make autonomous decisions, we move beyond workflows into Agentic AI. But how is a fully autonomous data analyst created?
After two years of deep exploration and iterative development, we’ve distilled the core elements of Agent creation — from planning, memory, tool orchestration to context engineering — step-by-step revealing how to build an intelligent entity that thinks and acts.
Whether you’re just curious, learning, or already building, this guide offers insights into architecture and practical implementation.
---
💡 Is a Fully Autonomous AI Data Analyst Possible?
Yes!
Our journey moved from:
- OlaChat (web-based chat)
- Coding Copilot
- Dola — our current Agentic AI data analyst
Dola — built by Tencent PCG Big Data Platform Department — lets users upload data tables and receive fully automated analysis in natural language.

---
📊 Dola’s Capabilities
- Fetch & process data
- Plan & execute complex data analyses:
- Anomaly attribution
- Profile comparison
- Stock/fund backtesting
- Housing price prediction
- Autonomously:
- Write SQL
- Correct SQL errors
- Query & visualize with Python
- Produce full reports
No coding — just conversation.
Example — Stock backtesting:
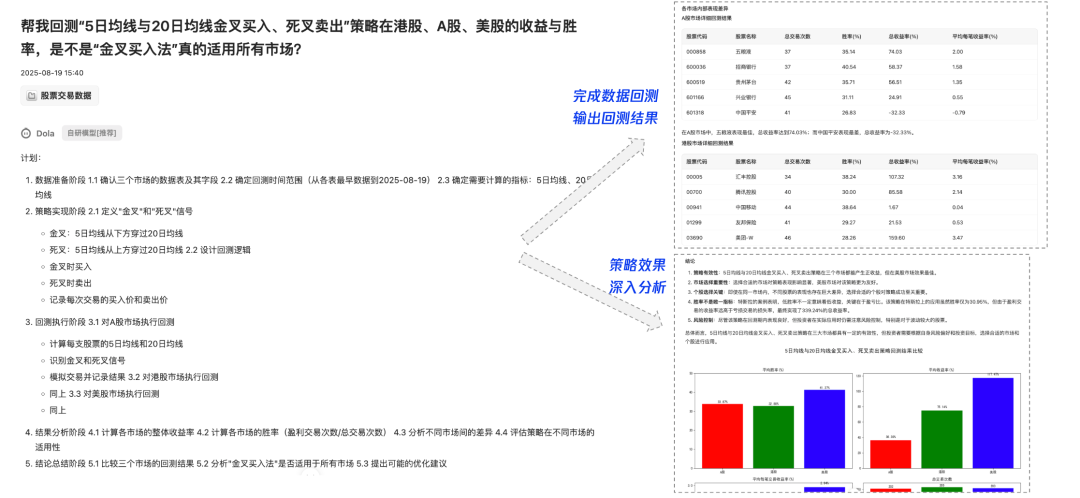
---
1️⃣ Introduction to Agents
1.1 What is an Agent?
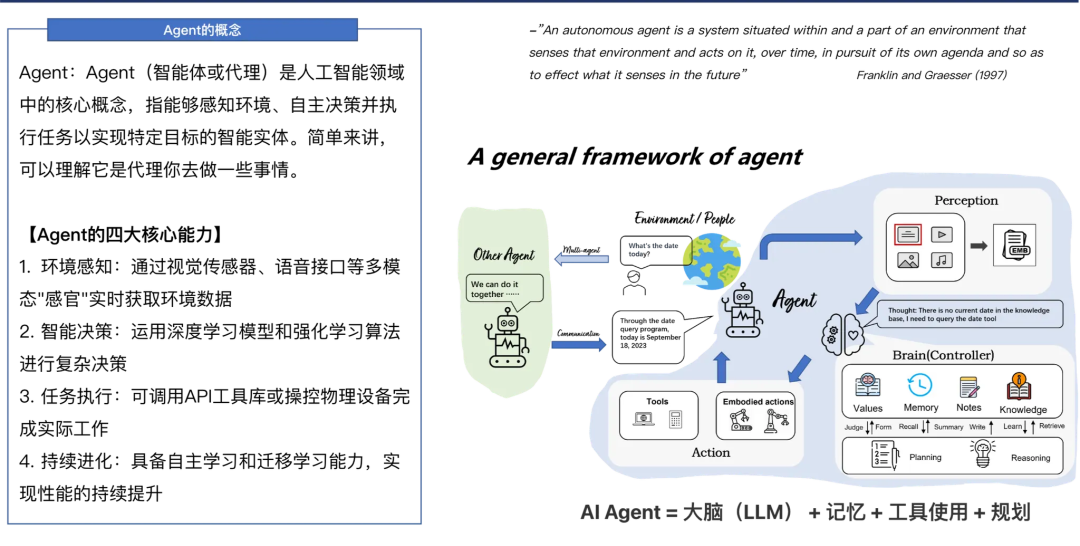
An Agent perceives its environment, makes autonomous decisions, and executes tasks to achieve goals.
Core Capabilities:
- Environmental Perception — Sensors & interfaces (visual, voice, etc.)
- Intelligent Decision-Making — Deep learning & reinforcement learning
- Task Execution — API calls, device control
- Continuous Evolution — Online learning & transfer learning
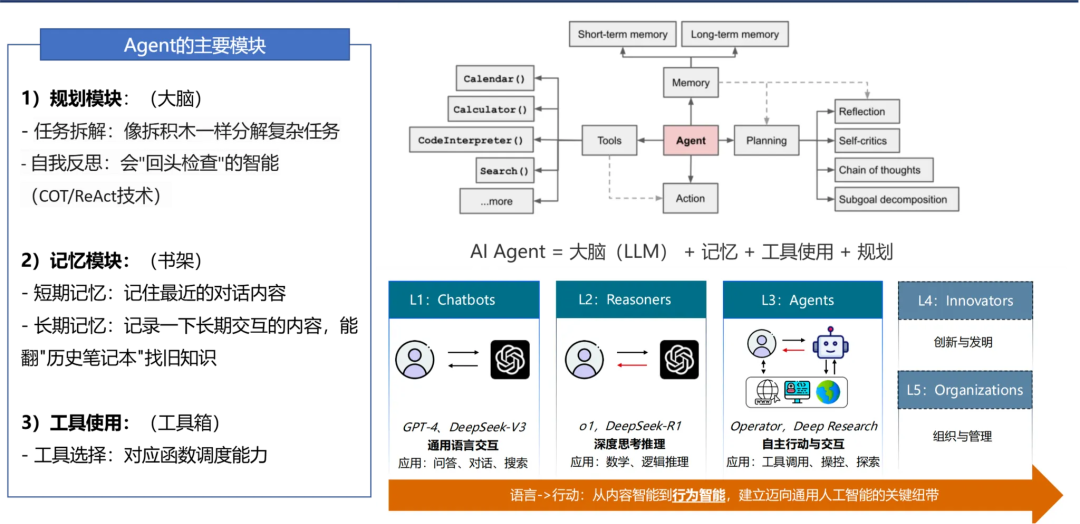
1.2 Basic Agent Framework
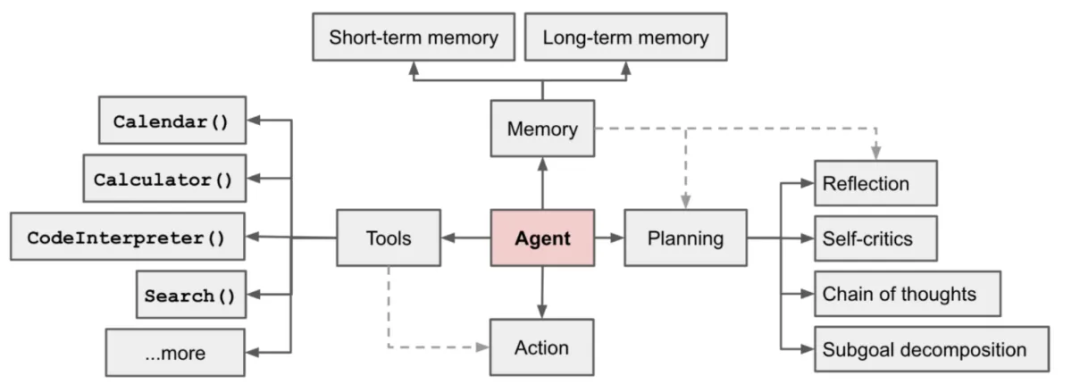
Includes:
- Planning
- Memory
- Tools & Execution (tool use)
- Brain — Large Language Model (LLM)
> AI Agent = Brain (LLM) + Memory + Tool Use + Planning
---
Ecosystem Note:
Platforms like AiToEarn官网 enable open-source AI content monetization and multi-channel publishing — demonstrating how Agents can integrate with production & monetization systems.
---
1.3 Agent Classifications
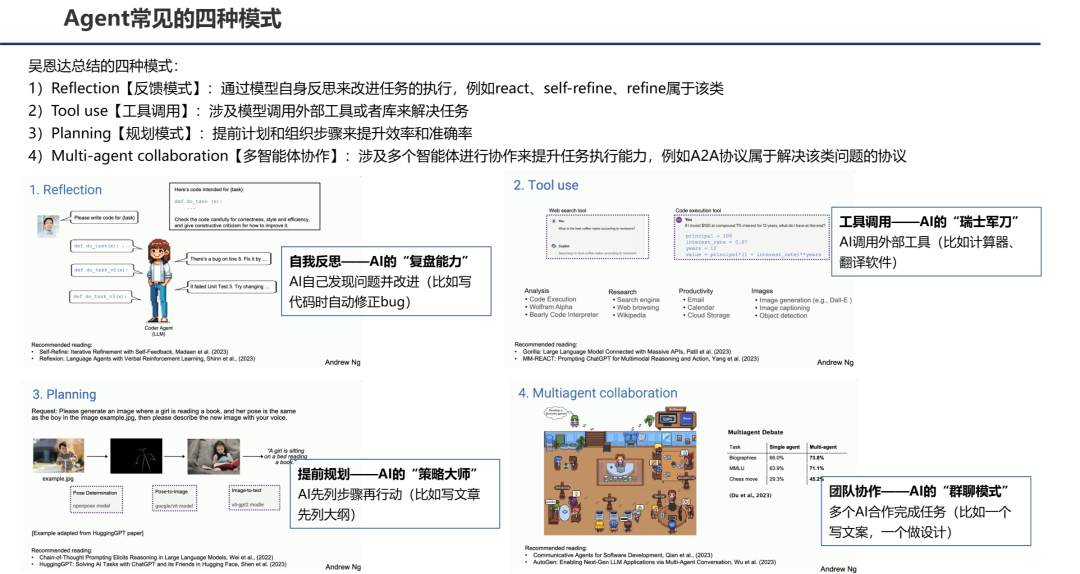
Types:
- Reflection Mode (ReAct, Self-Refine)
- Tool Use
- Planning Mode
- Multi-Agent Collaboration
---
Reflection Mode
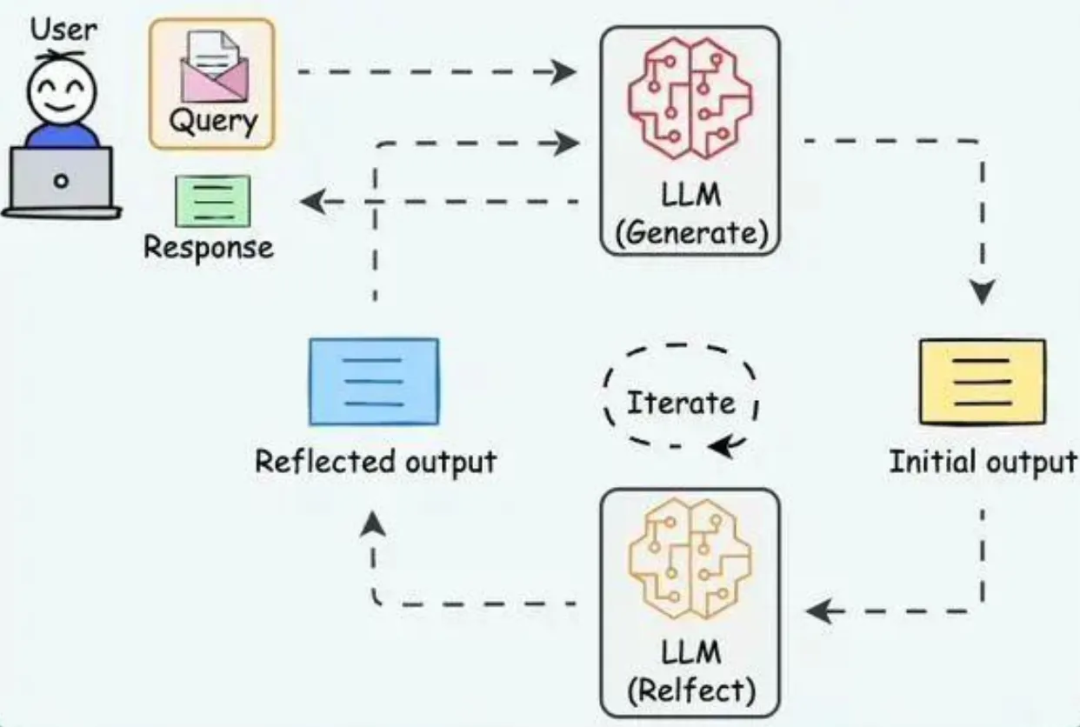
Continuous self-reflection after actions
Examples: ReAct, Self-Refine
---
Tool Use
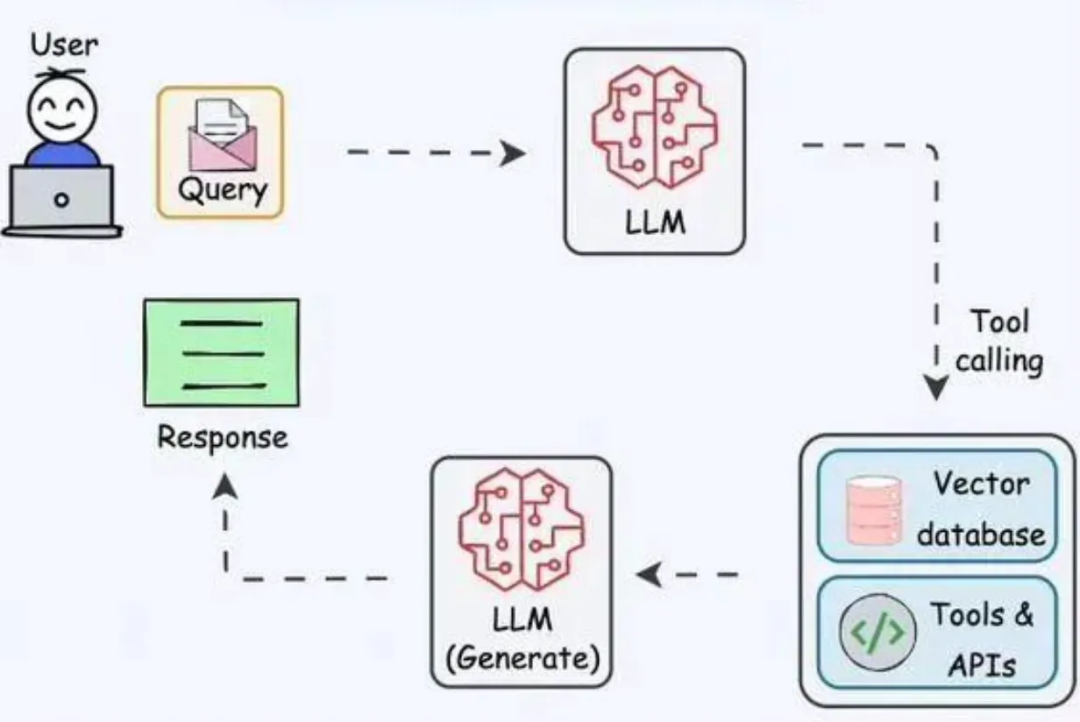
Integrating external APIs/tools to overcome LLM limitations.
---
Planning Mode
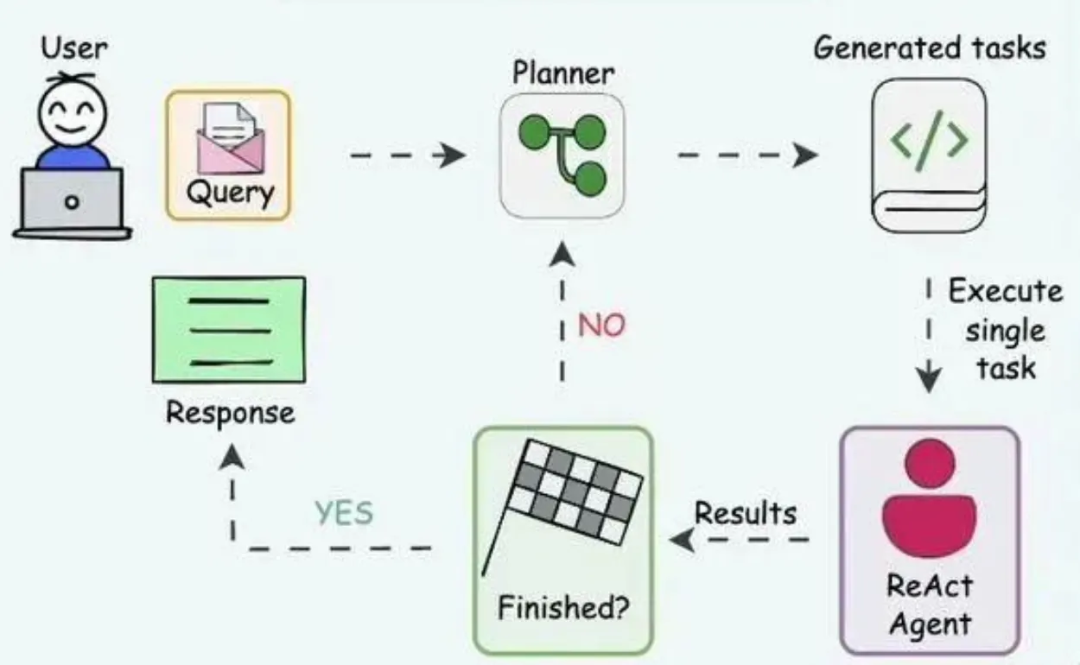
Hierarchical planning, step optimization for complex tasks.
---
Multi-Agent Collaboration
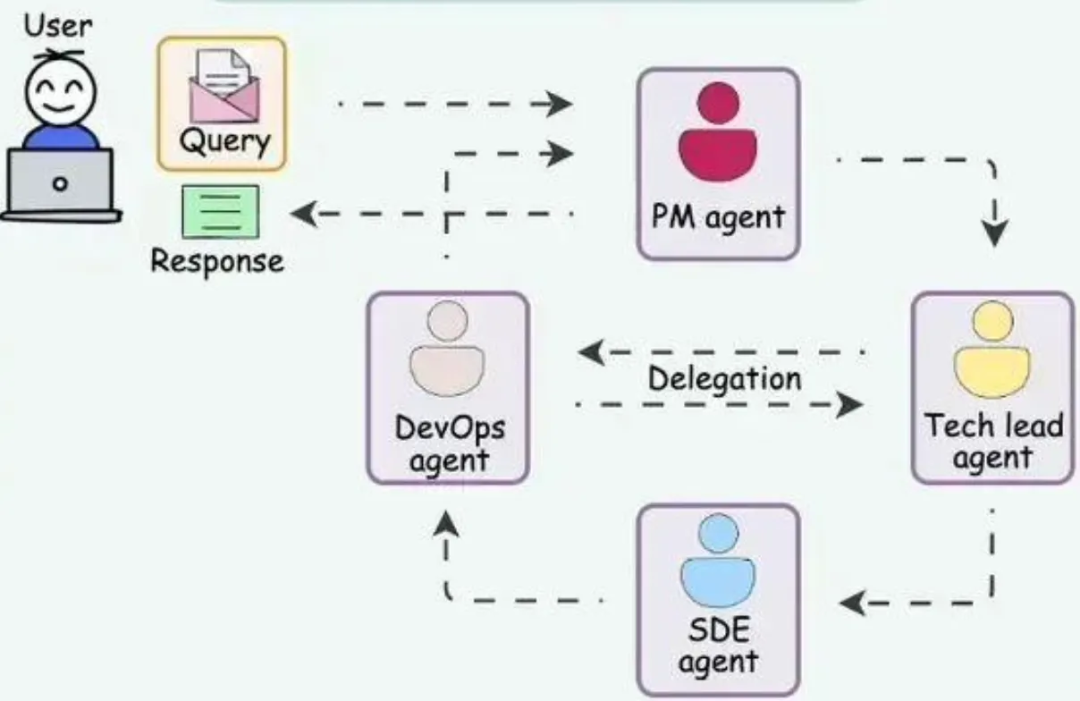
Multiple agents coordinate using frameworks like A2A, federated learning.
---
1.4 Agent Development Framework Evolution
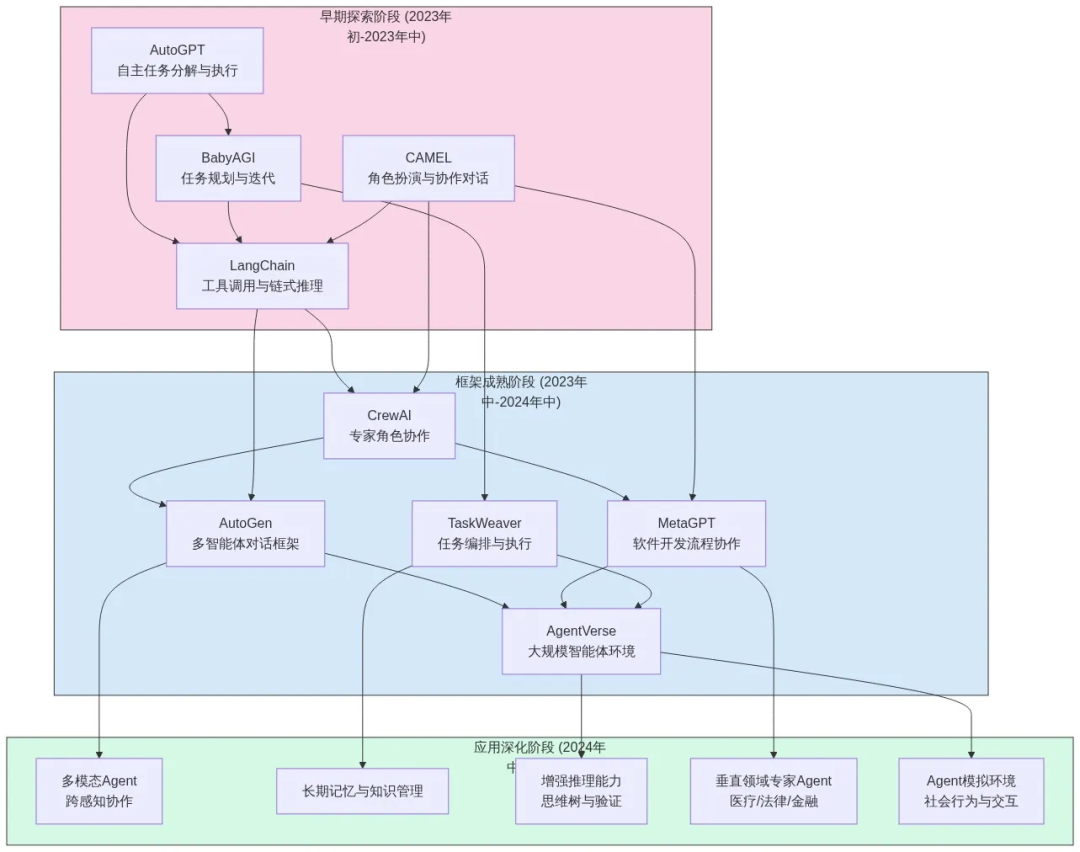
Stages:
- Early Exploration (2023) — Simple cooperation mechanisms
- Framework Maturation (2023–2024) — e.g., Microsoft AutoGen; scalability focus
- Application Deepening (2024–2025) — Specialized domain agents (finance, dev, content)
Framework comparison:
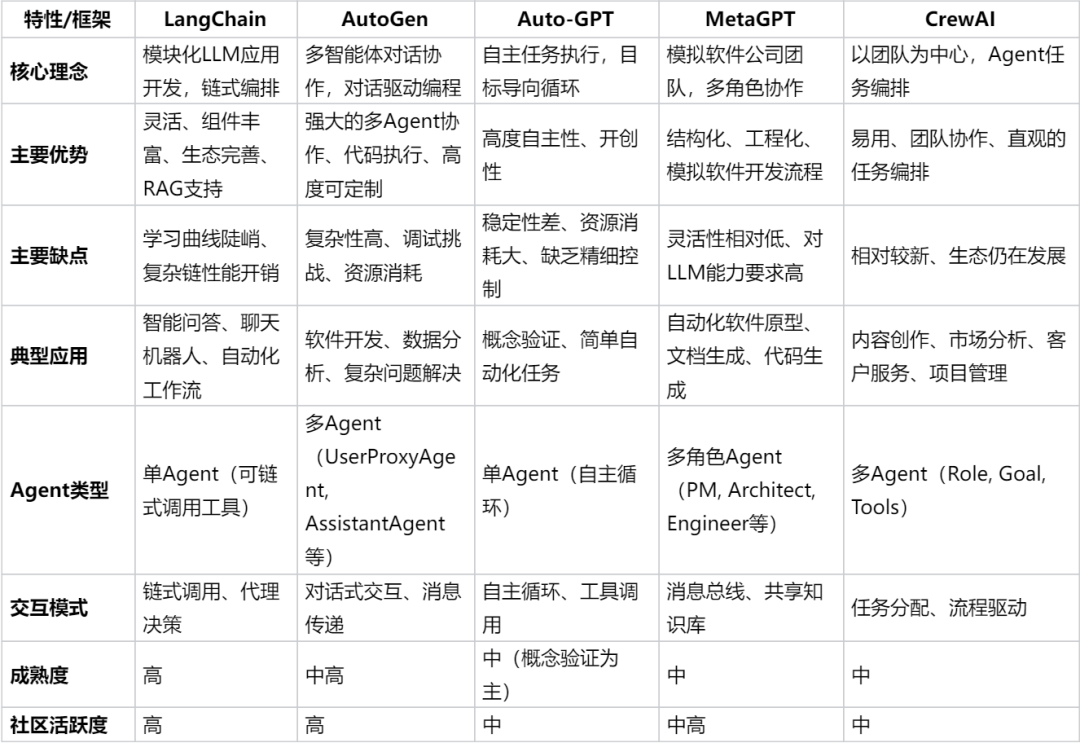
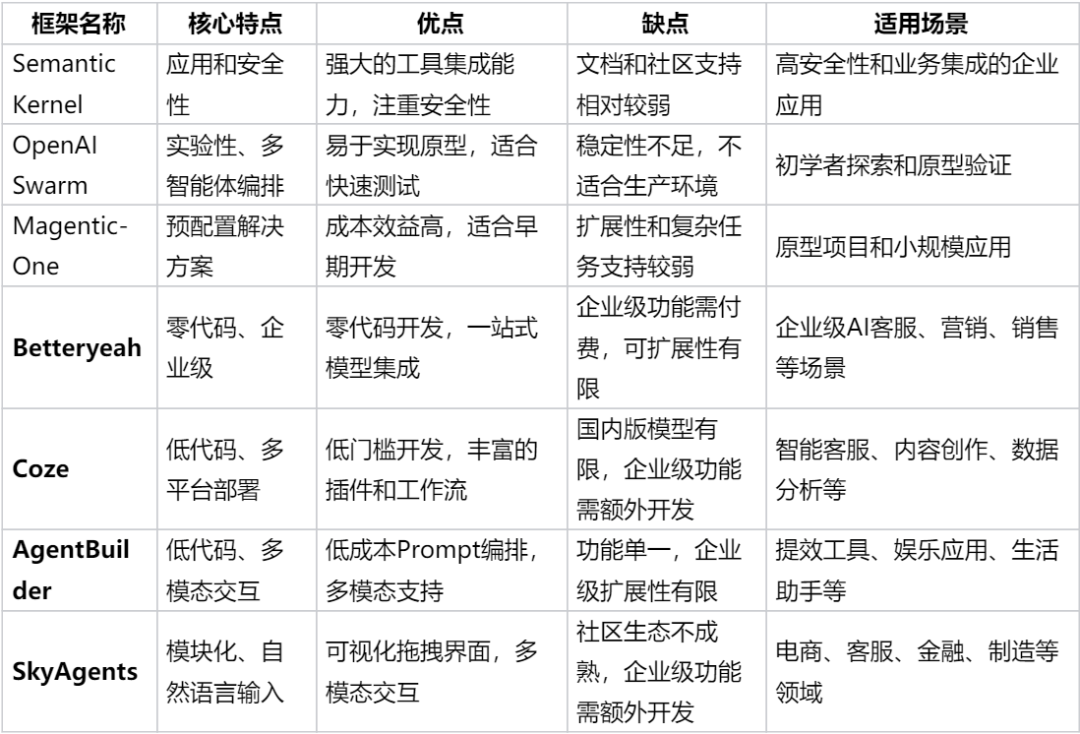
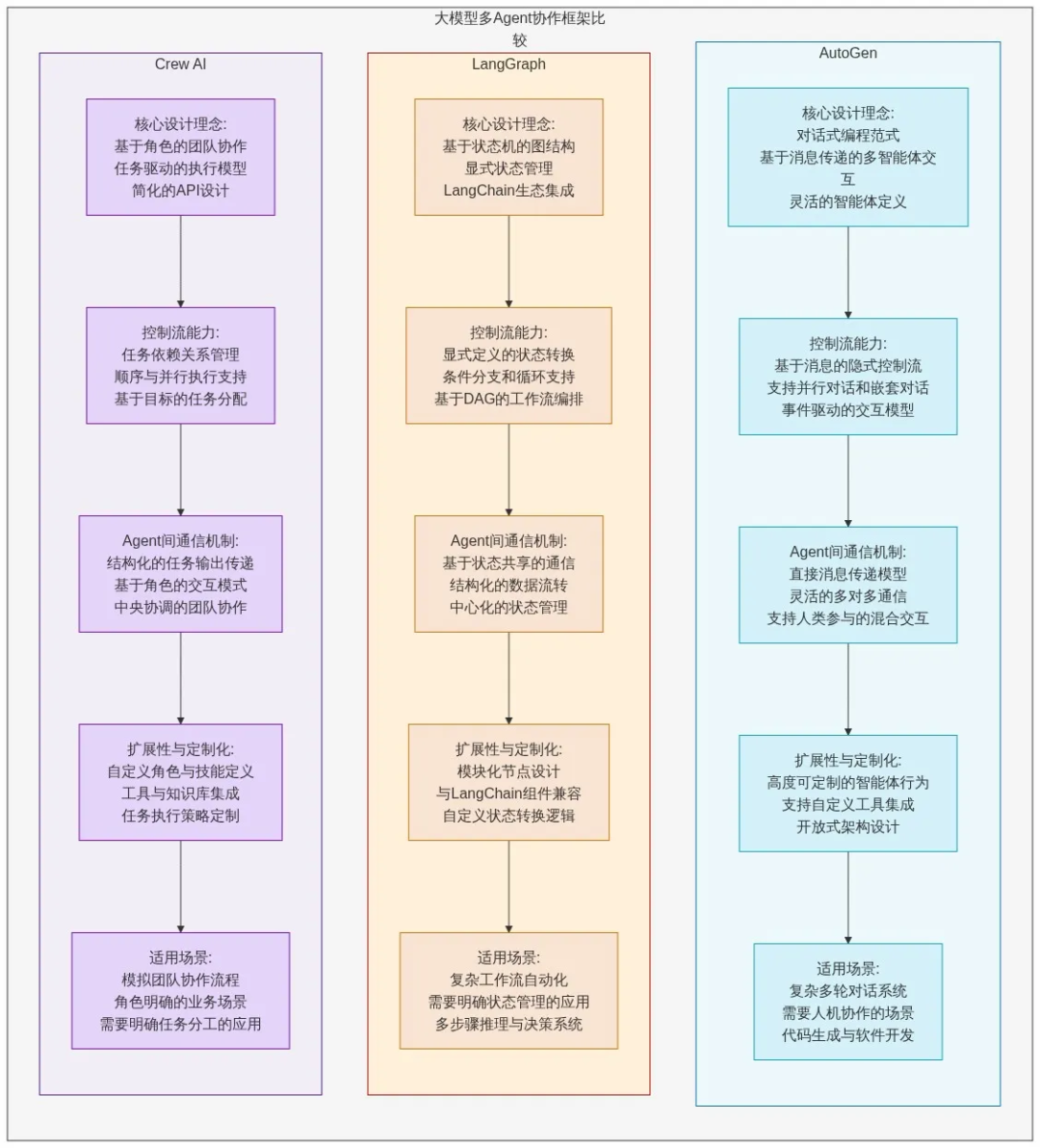
---
2️⃣ Core Evolution & Modules
Workflow vs Agent
- Workflow: Pre-defined task steps
- Agent: Autonomously defines & explores tasks
---
2.1 Planning Module
- Task Decomposition — CoT
- Reflection & Refinement — ReAct loop:
- Thought
- Action
- Observation
- Answer
Frameworks: Planner + Executor
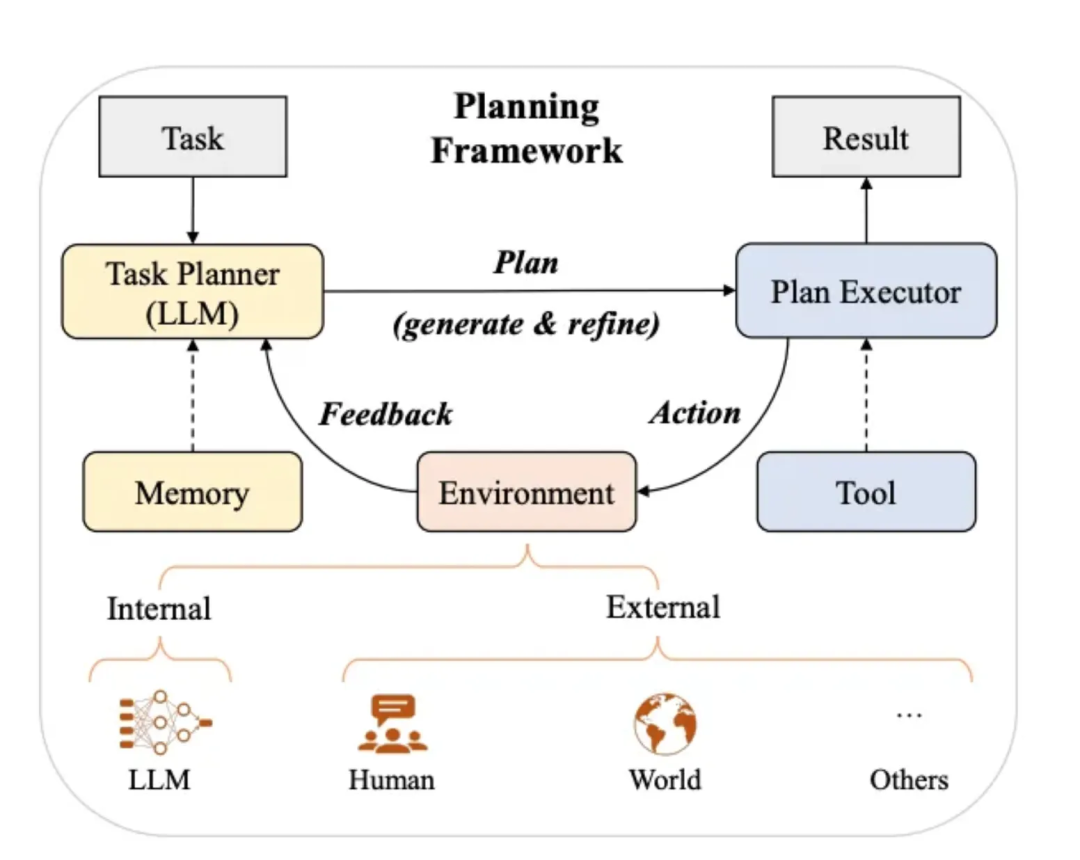
---
2.2 Memory Systems
Purpose: Overcome LLM context window limits
Layers:
- STM — current context
- MTM — topic segments & popularity
- LTM — user profiles, stored via vector DB/RAG
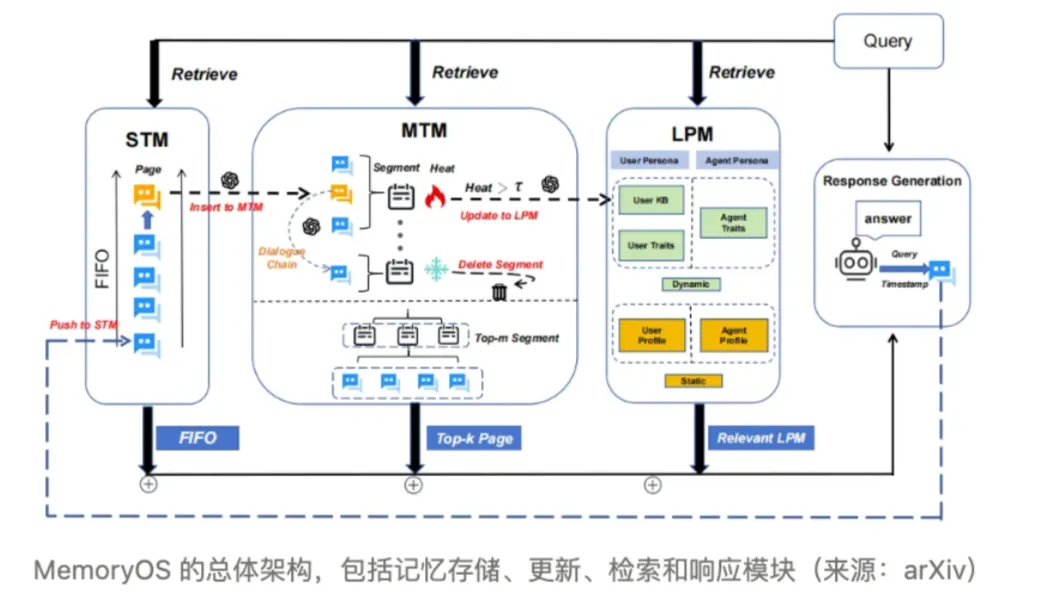
---
2.3 Tool / Function Scheduling
Transform natural language into executable tool/API calls.
Benefits: Real-time data, external actions
Risks: Wrong params, hallucinated APIs, privacy issues
---
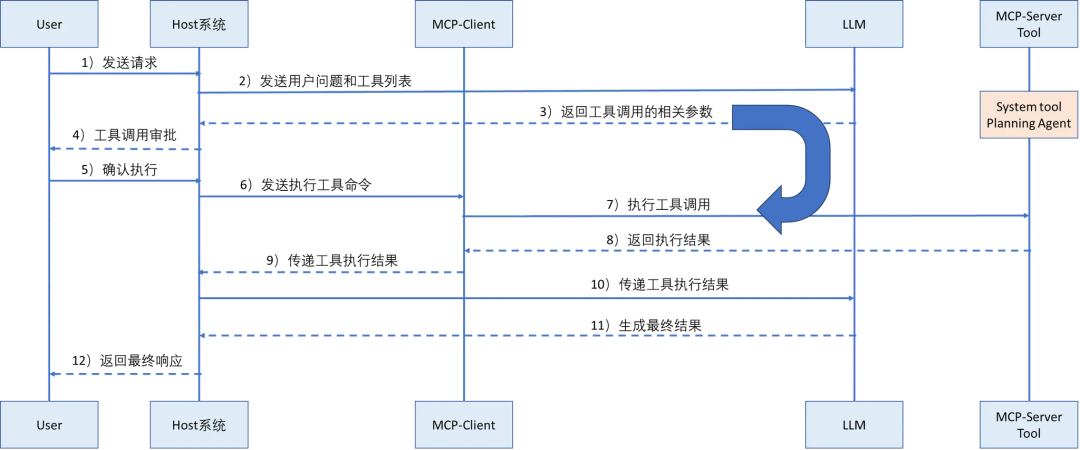
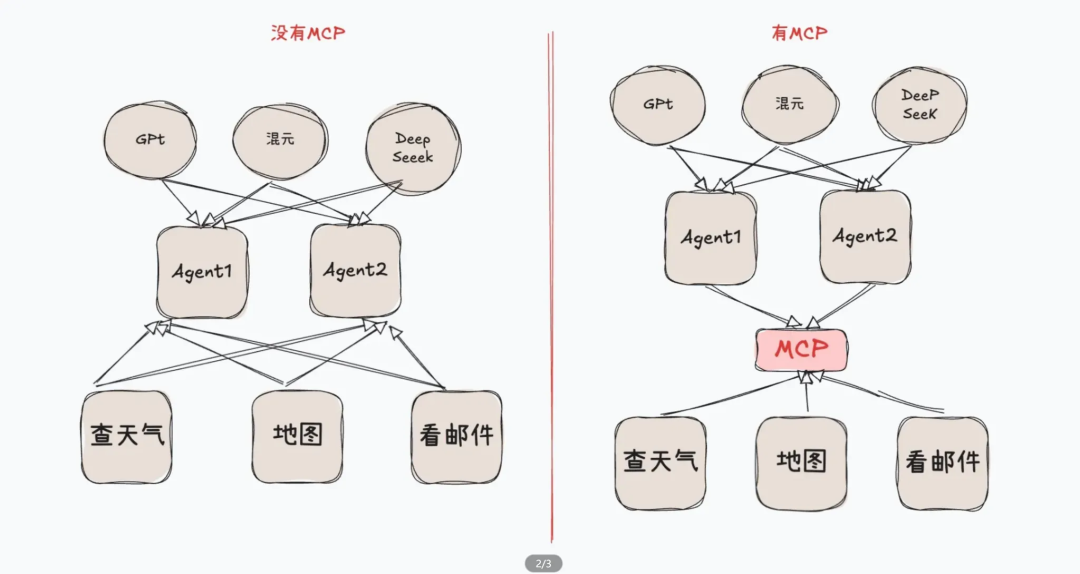
2.4 MCP Protocol
Host ↔ Client ↔ Server (tools/resources/prompts)
Advantages: Standardized integration, dynamic expansion
Cons: Logging difficulty, instability, performance cost
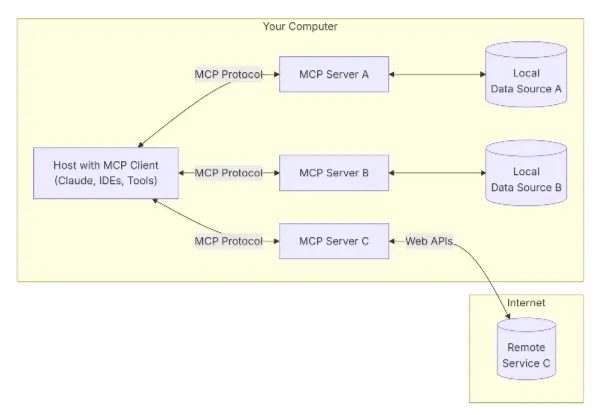
---
3️⃣ Building an Agent (Developer Perspective)
3.1 Factors Affecting Performance
- Framework choice (single vs multi-agent)
- Context engineering quality
---
3.2 Context Engineering — 13 Key Practices
- KV-Cache optimization
- Dynamic action constraints
- File system as extended context
- Attention steering via goal restatement
- Retain errors for learning
- Avoid few-shot trap
- Prompt consistency in terminology
- Dynamic prompts
- Tool capability boundaries
- Feedback granularity control
- Balance long/short-term memory
- Golden ratio of human intervention
- Multi-agent competitive validation
---
3.3 Memory System Implementation
Use STM + MTM + LTM layering to maintain context continuity & personalization.
---
3.4 Function Call Architecture
Workflow:
- User request
- Prompt composition
- Tool decision (LLM)
- Security approval
- Execution
- Result integration
- Final response
---
3.5 MCP Protocol Architecture
Adds resource management to function call workflow
Includes security checks, standardized execution & result formatting.
---
3.6 Multi-Agent Applications
Enhancement to context engineering — not covered in depth, see Anthropic case study.
---
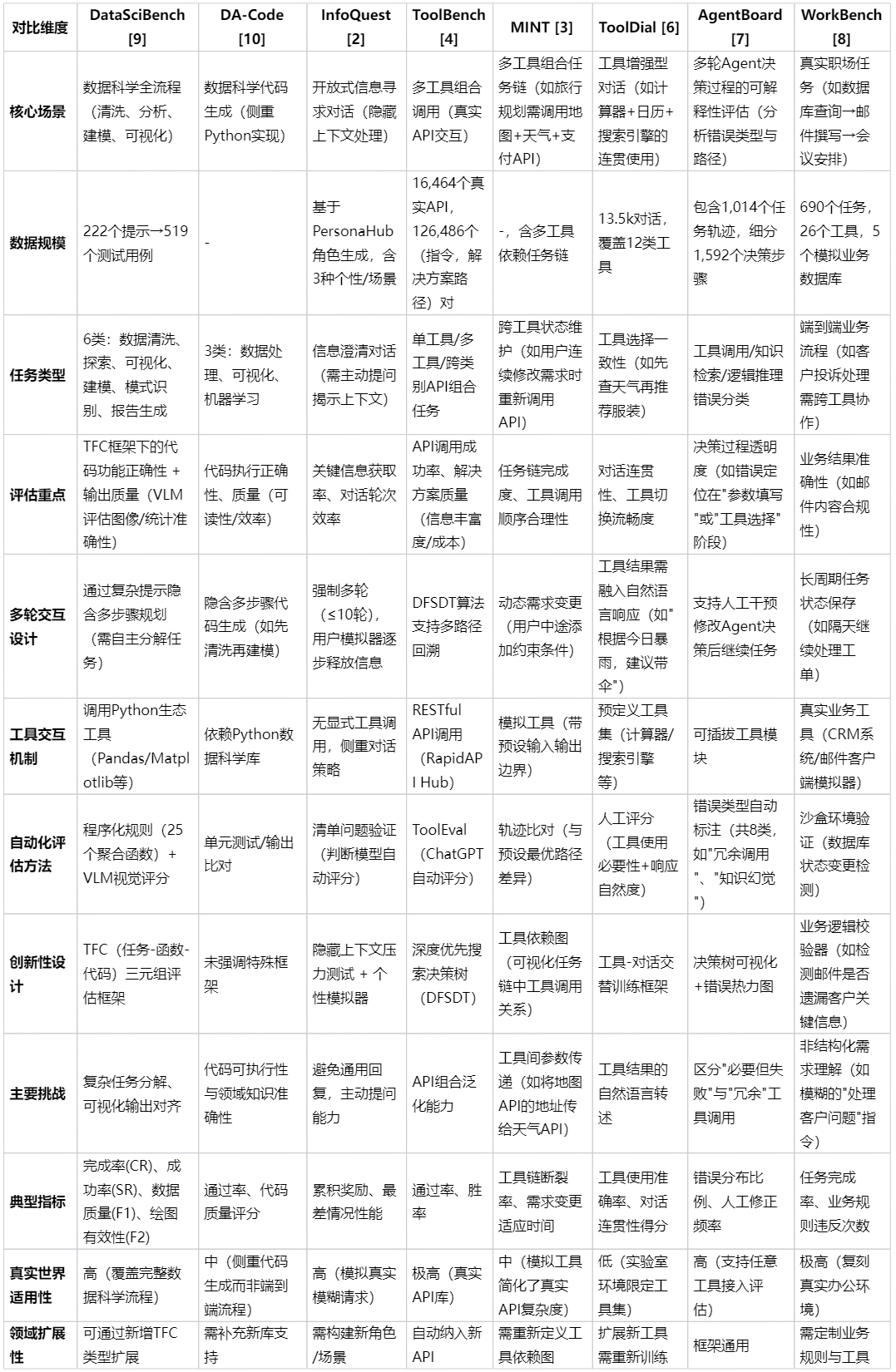
4️⃣ Evaluating Agents
No unified standard yet — common benchmarks:
- AgentBench
- InfoQuest
- MINT
- ToolBench
- GTA
- ToolDial
- AgentBoard
- WorkBench
- DataSciBench
---
🔗 References
See full list at article bottom — includes frameworks like LangChain, AutoGen, MetaGPT, CrewAI etc., and key surveys on Context Engineering & Planning.
---
Tip: If you plan to integrate your agent outputs into multi-platform publishing workflows, open-source platforms like AiToEarn官网 can help bridge AI generation with monetization — combining LLM agents with analytics & cross-channel publishing.



