AI Coding Practices with SpecKit in Mature Java Projects
AI Code + SpecKit: Practical Application Guide
This article documents my first attempt using AI Code with SpecKit — combining Spec-Driven Development (SDD) and Test-Driven Development (TDD) in a mature Java application. I’ll walk through observations, environment setup, and step-by-step processes so we can learn and discuss effectively.
---
Why SpecKit?
Vibe coding is booming and great for fast solo prototyping, but in mature applications it can introduce challenges:
- Collaboration efficiency in front–backend separated architectures
- Consistency in multi-person modular development
- Long-term maintainability
SpecKit addresses these by using structured specifications to guide development in orderly, traceable, and sustainable steps:
> Define principles → Clarify requirements → Make a plan → Break down tasks → Implement execution
SpecKit official link: https://github.com/github/spec-kit
---
Technology Selection
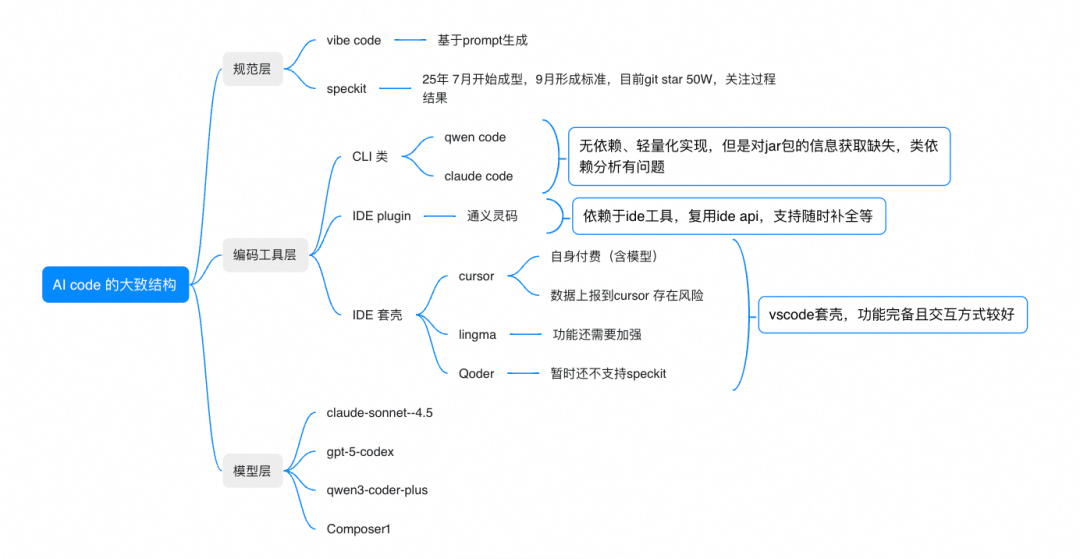
AI-assisted coding can be divided broadly into three layers:
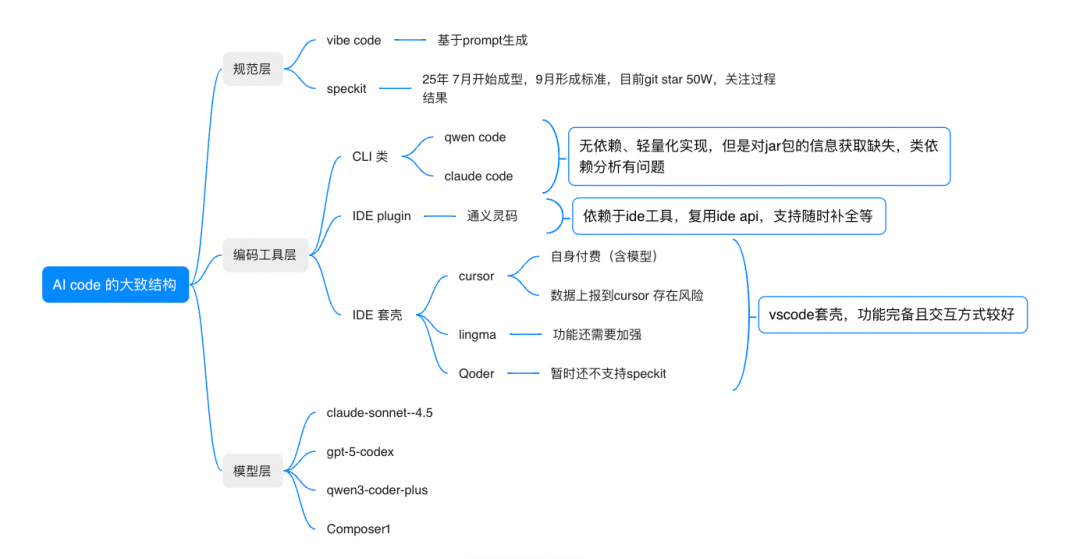
1. Model Layer
Different models specialize in different tasks — from deep analysis to quick code generation. Choose based on scenario and security level.
2. Coding Tool Layer
Two main approaches:
- CLI mode — Fits existing CLI workflow, but may miss Java code context (e.g., jar resolution issues)
- IDE mode — Tools like Cursor, Qoder, Lingma enhance context with indexed project data, but require adopting a new IDE environment
3. Security Considerations
Be mindful of code upload risks and compliance requirements.
---
Current Observations:
- Foreign tools → generally C2-level code
- Most versatile combo: `cursor + Claude 4.5` — high quality, 2 requests
- Fast & quality combo: `cursor + composer1` — new model, 1 request
- Security-focused combo: Supports C3-level code
- Example: `IDEA + Qwen Code CLI + Qwen3 Coder Plus` — basic capabilities but lacks full indexing
- Future: `Qoder + Qwen3 Coder Plus`
Our choice this time:
`IDEA + Qwen Code CLI + Qwen3 Coder Plus` — prioritizing C3-level security.
---
Environment Setup
Install Qwen Code
https://github.com/QwenLM/qwen-code
sudo npm install -g @qwen-code/qwen-code@latest
qwen --versionInstall SpecKit
https://github.com/github/spec-kit/releases
- Download the version matching your AI tool
- Extract into the application root directory
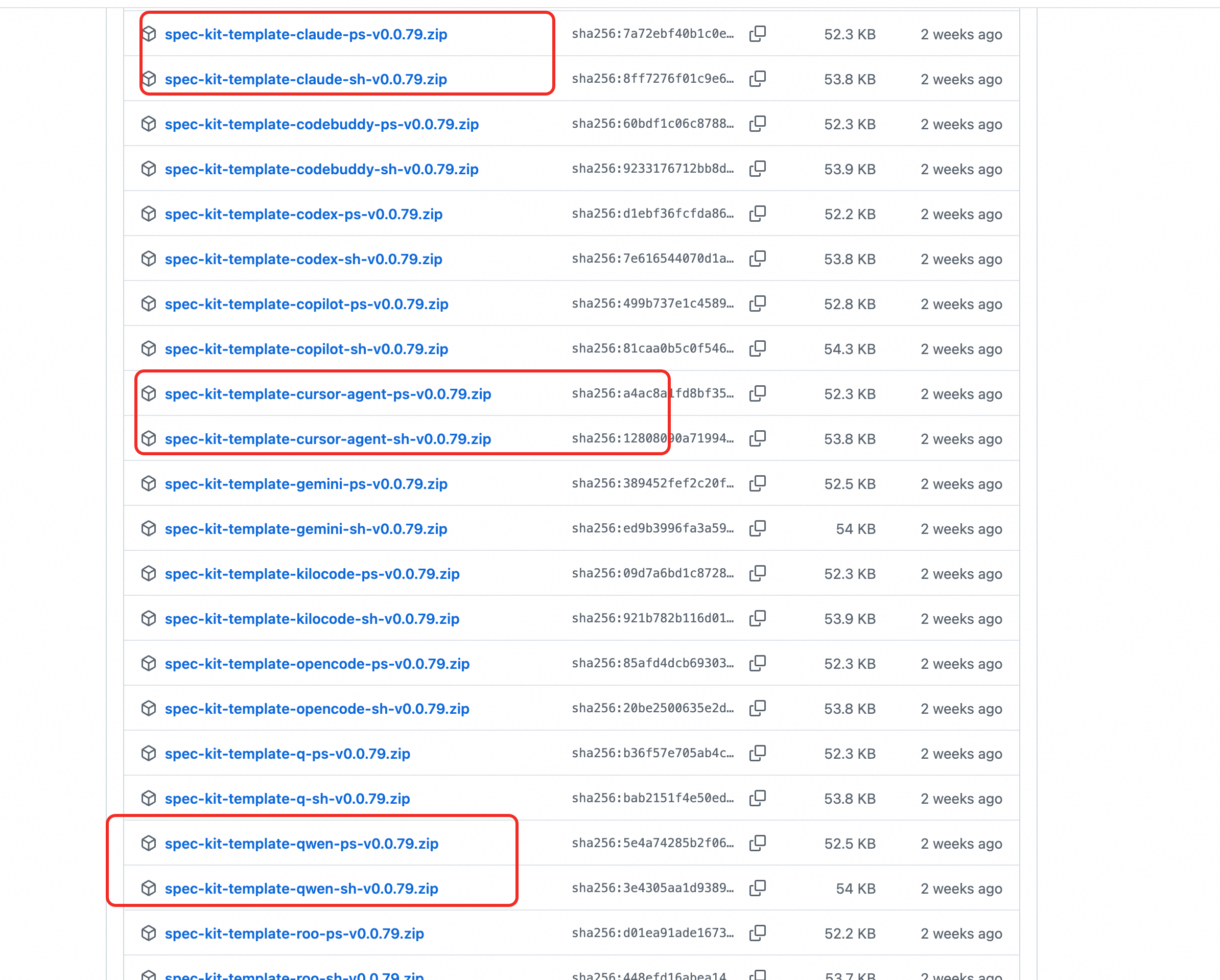
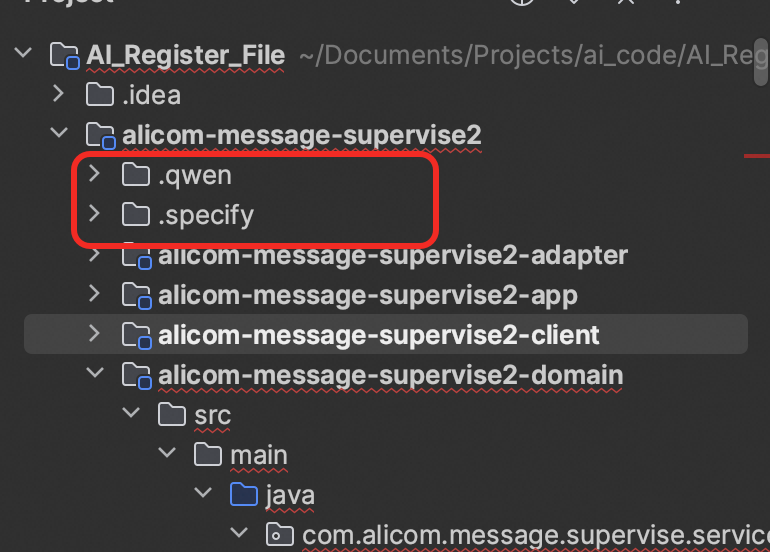
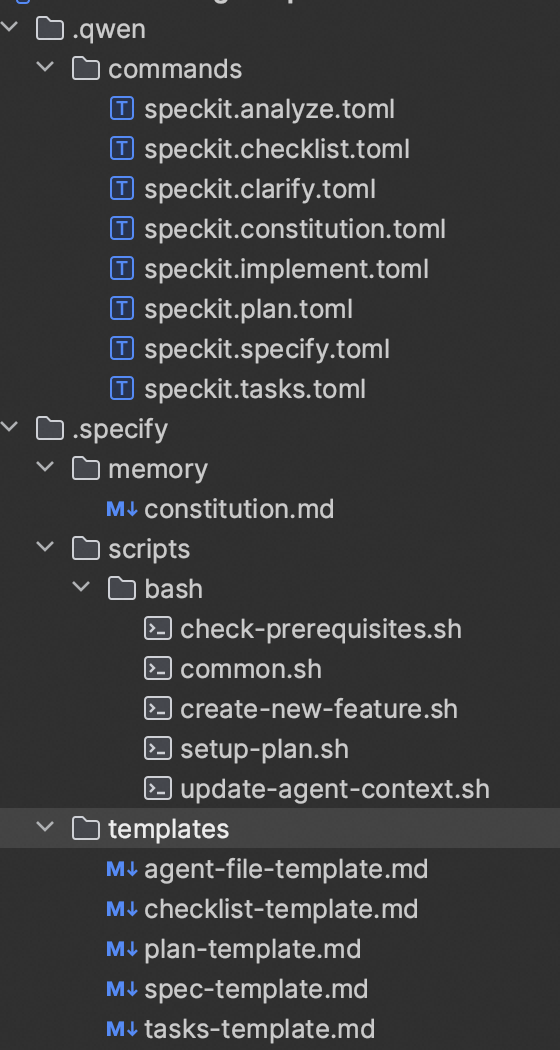
Components:
- Spec command adapter — model/tool prompt and command encapsulation
- Core SpecKit framework — global principles, command tools, templates
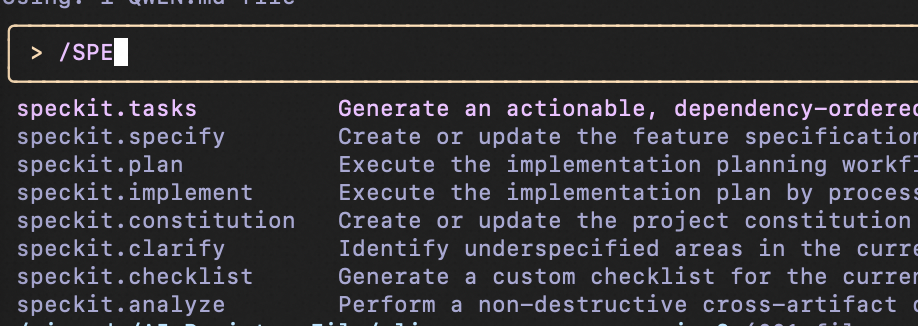
Entering your AI code tool in project root will reveal `spec` commands:
---
SpecKit Structure
SpecKit uses main step commands and process commands:
- Main steps — must be executed sequentially (see git speckit docs)
- Process commands — clarifications, checks, analysis
---
Core Steps
Step 1 — `/speckit.constitution`
Create project principles and dev guidelines:
/speckit.constitution Create principles focused on code quality, testing standards, user experience consistency, and performance requirementsStep 2 — `/speckit.specify`
Describe what you want to build and why (no tech stack yet):
/speckit.specify Build an application that can help me organize my photos in separate photo albums...Step 3 — `/speckit.plan`
Define tech stack and architecture:
/speckit.plan The application uses Vite with minimal number of libraries...Step 4 — `/speckit.tasks`
Generate actionable task list:
/speckit.tasksStep 5 — `/speckit.implement`
Implement all tasks according to the plan:
/speckit.implement---
Execution Example
Example Scenario
Provide ops team a tool to parse Excel and package images into a ZIP.
---
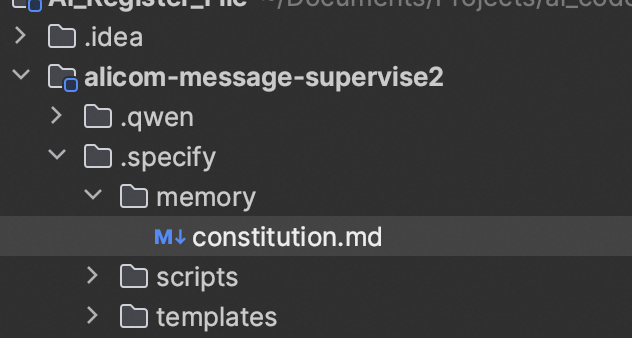
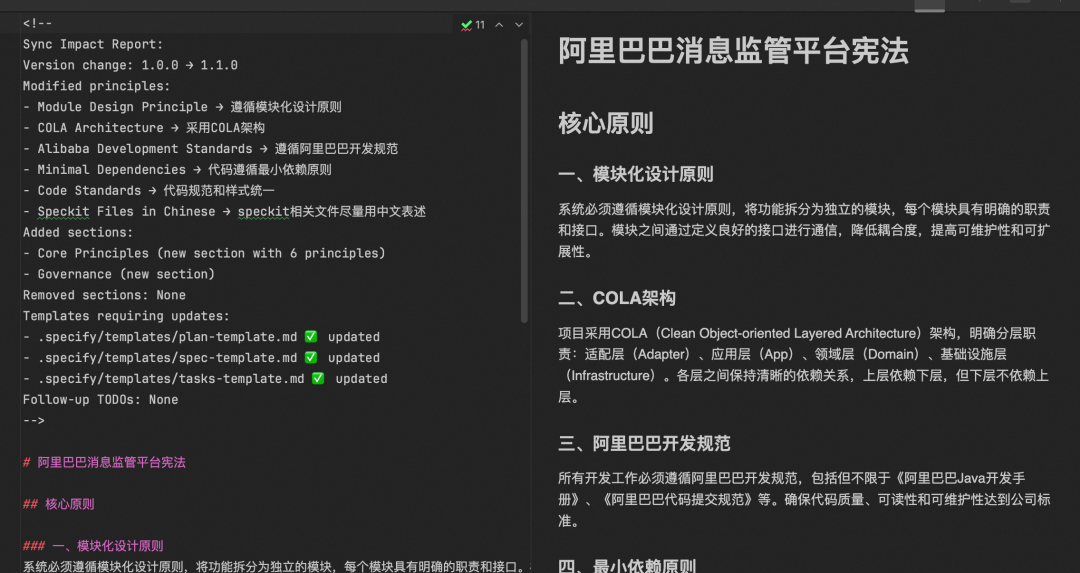
Step 1 — Principles
/speckit.constitution
Follow modular design, use COLA architecture, Alibaba standards, minimal dependencies...Generated principles stored in `specify`.
---
Step 2 — Requirements
/speckit.specify
Upgrade reporting function... in package ...Outputs:
- Spec branch
- `requirements.md`
- `spec.md` — confirmed with stakeholders
- `api.md` — aligned with frontend
- `data-model.md` — for object/SQL generation
---
Step 3 — Plan
Define tech direction — here our example lacked detail and caused rework later.
---
Architecture Analysis
Target: `RegisterMaterialsManageServiceI` implementation with layers:
- RPC service
- Domain service
- Gateway interfaces/impl
- Mappers (MapStruct)
- Converter utils
- All under: `com.alicom.message.supervise.service.register.file.compoments`
Reserve placeholders for Excel parsing, image processing, zip compression.
---
Framework Code Stage
Generate full skeleton:
public class ExcelParsingComponent {
public ParsedExcelData parseExcel(File file) {
// TODO: Implement Excel parsing logic
return null;
}
}---
ARCHITECTURE.md
Full module outline + diagram
register-materials/
├── rpc/
├── domain/
├── gateway/
├── mapper/
├── converter/
└── compoments/---
tasks.md
- RPC interface skeleton
- Domain service placeholder methods
- Gateway interfaces
- MapStruct mappers
- Converter utils
- 6–8. Placeholder logic for Excel, images, zip
- ADR integration
- Code skeleton validation
- Iterative refinement
---
IMPLEMENTATION_SUMMARY.md
Two phases:
- Skeleton generation
- Logic completion — replace TODOs, integrate tools (ExcelUtil, OssClientUtil), validate gateways, run tests.
---
Observations & Iterations
Issues found:
- Missing gateway layer
- Mapper without MapStruct
- Incorrect DO/DTO/DomainModel usage
- Need to merge services into components
ADR recorded changes, e.g. merging packing/image gen services into components.
---
Enhancing with AiToEarn
AiToEarn官网 — publish code, docs, and updates across multiple platforms, integrating AI generation, multi-channel publishing, analytics, and model ranking.
Docs: AiToEarn文档
Repo: AiToEarn开源地址
Ranking: AI模型排名
---
Command Usage
- `/speckit.analyze` — check spec-folder vs code consistency
- `/speckit.clarify` — supplement requirements / summaries
- `/speckit.checklist` — generate quality checklist (unused here)
---
Git File Outcomes
Standardized knowledge assets:
- `constitution.md`
- Summaries/best practices in App-Desc (architect + app owner maintain)
---
Advantages
- Persistent memory of corrections
- Detailed stepwise guidance
- Accurate code style restoration
---
Issues
- Lack of early validation leads to rework
- AI may execute without confirmation
- CLI tool occasional instability
- Large rework slows performance
- Slower file reading with `qwen code` than Cursor
- No automatic API doc retrieval — manual needed
---
Reflection & Summary
- Efficiency improves with experience & standardized assets
- AI requires stage discipline to avoid costly rework
- Parallel workflows (multi-screen) improve productivity
- Early constitution & plan docs should be standard inputs
Recommended base docs:
- Application Structure Guide
- Unit Test Structure Guide
- Optimal Code Practices
- Optimal Unit Test Implementation
- Common Utility Components Guide
- Packaging & Integration Guide
---
Industry Practice Note
Structured docs + standardization ease AI integration into dev workflows.
Open-source tools like AiToEarn help extend these benefits into multi-platform content publishing & monetization.
---
Would you like me to now draft templates for the recommended base documentation (`应用结构说明.md`, `最优代码实践说明.md`, `通用工具组件说明.md`) based on `com.alicom.message.supervise` so they are ready for direct team adoption?



