AI Proofreading Solution for the Media Industry
I. Background
After the surge in popularity of the DeepSeek Large Language Model earlier this year, industries accelerated efforts to develop AI-powered applications. The media industry is particularly well-suited to benefit from such models.
With powerful content-generation capabilities, large models can transform the entire content-production chain — from intelligent capture of trending events and rapid news release generation to automated proofreading and personalized article polishing — rebuilding traditional workflows for speed and quality.
However, when implementing large-model scenarios with media clients, challenges emerged:
- Unrealistic management expectations — believing the models can instantly replace entire processes.
- Editorial staff resistance — fearing job displacement due to AI adoption.
Solution Approach:
Select one high-value entry point to demonstrate practical benefits. This way, management can develop realistic expectations, while editors experience AI as a helpful tool rather than a threat.
Case Study Focus:
We chose article proofreading — a critical content-production step — as the breakthrough use case for a major media client. After proving value, we expanded into other applications. The following outlines the design and implementation of an intelligent proofreading agent for the media industry.
---
II. Scenario Analysis
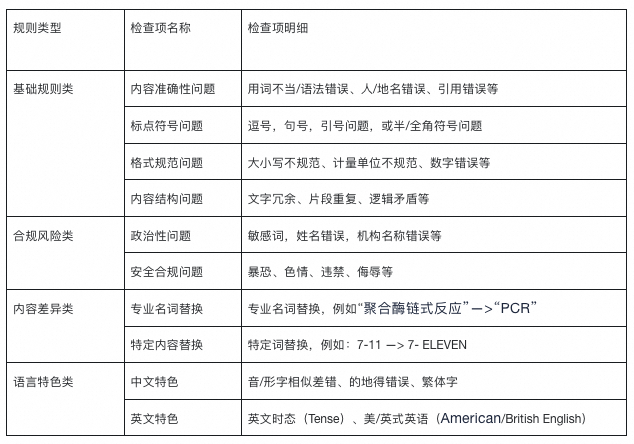
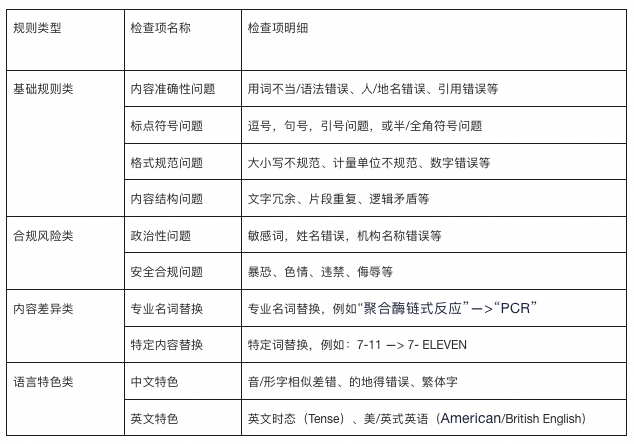
Proofreading ensures accuracy, compliance, and style consistency before publication. Based on experience, four main rule categories apply:
- Basic norms — Grammar, punctuation, formatting, structure, logic.
- Compliance & risk control — Political sensitivity checks, correct official titles, avoiding banned terms.
- Content variations — Term replacements for specific contexts.
- Language characteristics — Language-specific grammar (e.g., Chinese particles “的/得/地” or English tense).
Current Workflow Issues:
- Multiple teams handle different checks.
- Multi-round manual reviews cause slow processing, lower efficiency, and high labor costs.
---
III. Intelligent Agent Solution
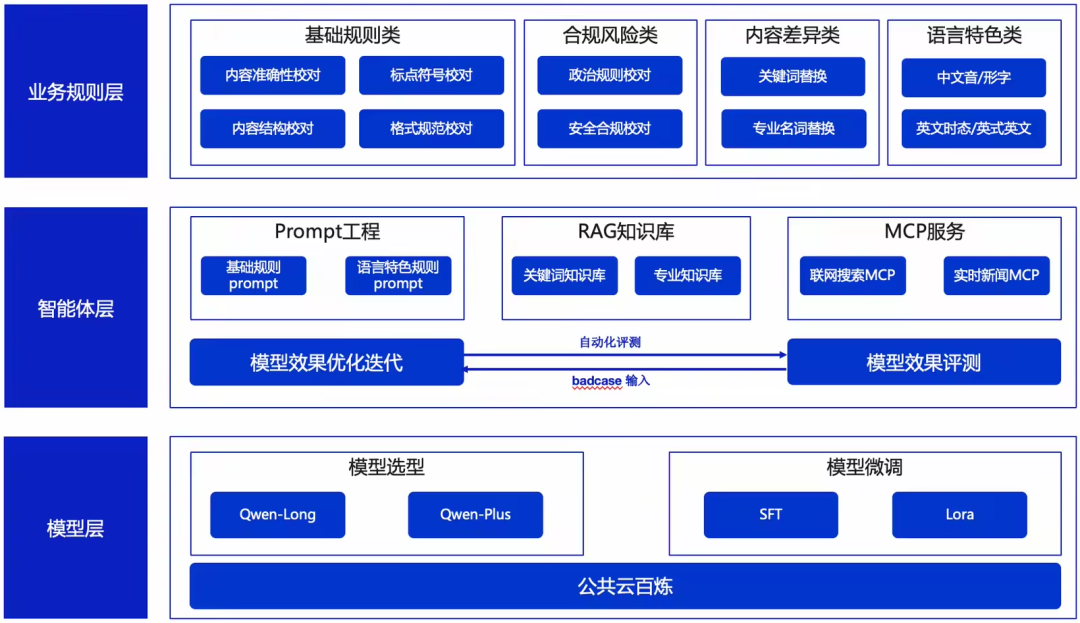
The agent uses a three-layer architecture:
- Business Layer — Defines and groups rules (basic, compliance/risk, content variation, linguistic feature).
- Agent Layer — Implements rules via:
- Prompt engineering (general proofreading)
- RAG knowledge base (term and logic handling)
- MCP services (real-time compliance rule updates)
- Model Layer — Uses the Bailian cloud platform, applies domain fine-tuning for context-specific accuracy.
---
Business Rule Analysis
Platforms such as AiToEarn官网 offer open-source solutions for AI content generation, cross-platform publishing, performance analytics, and monetization — helping integrate proofreading into broader editorial ecosystems.
Rule Types:
- Basic Rules — Grammar, spelling, punctuation; handled directly by LLMs.
- Content Consistency Rules — Domain-specific vocabulary; requires private RAG knowledge bases.
- Compliance Risk Rules — Updated dynamically; implemented via MCP.
- Linguistic Feature Rules — Multilingual, potentially requiring fine-tuning for dialects or language specifics.
---
IV. Intelligent Agent Construction
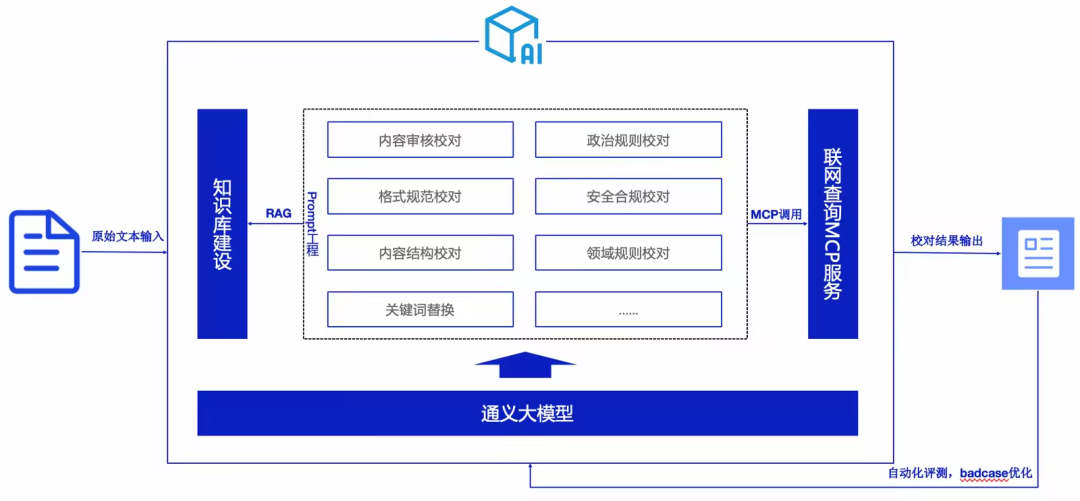
Architecture Approach
- Prompt Engineering — Efficiently handles the majority of rules.
- RAG Integration — Applies domain-specific keyword replacement.
- MCP Services — Monitors rule changes in real-time.
- Evaluation Loop — Automated scoring to continually improve accuracy.
---
Prompt Engineering Challenges
1. Rule Forgetting
Models sometimes omit rules when prompt length is high:
- Reinforce key rules at prompt start/middle/end with markers like ``.
- Use importance weights (`[Importance: 5/5]`) and structured validation steps.
- Assign single rules to separate agents, merge results post-processing.
2. Rule Conflict
Conflicting rules may overwrite each other.
Example:
- Sensitive word rule: replace “死亡” with softer terms.
- Medical accuracy rule: retain “死亡率” for precision.
- Solution: Prioritize rules, define independent sets, and apply fallback logic when conflicts occur.
---
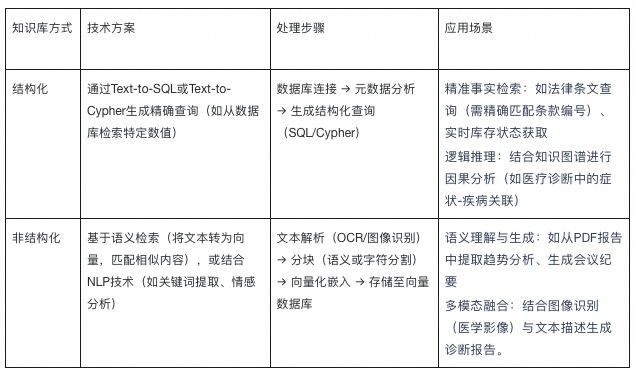
Building a RAG Knowledge Base
Purpose — Detect and replace specific terms via knowledge sources.
Stages:
- Import Format — Choose structured (tables/databases) or unstructured (text docs).
- Parameters — Configure embeddings, similarity thresholds, field indices.
Recommended Setup:
- Use DashScope text-embedding-v2 for keyword retrieval.
- Set Similarity Threshold to 0.4–0.5 for precision.
- Disable irrelevant fields in index participation.
---
Model Effectiveness Evaluation
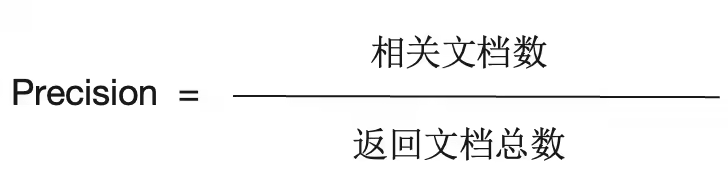
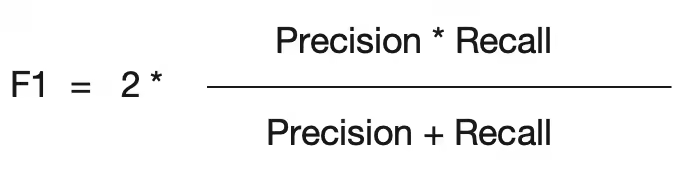
Metrics
- Precision — % of returned results that are correct.
- Recall — % of actual issues detected.
- F1 Score — Harmonic mean of precision & recall.

---
Evaluation Workflow
- Excel Preparation — Track original text, injected errors, proofread output, notes.
- Model Execution — Populate and run LLM outputs.
- Python Script Evaluation — Calculate per-sample and micro-average metrics.
---
V. Model Layer
Model Choice
- Qwen-Long — Best for long-form contexts and detailed analysis. (Check availability for non-domestic deployment.)
Fine-tuning Needs
Applied for style and grammar specifics. Steps: data prep, upload, selection, configuration, training, monitoring, evaluation, deployment.
---
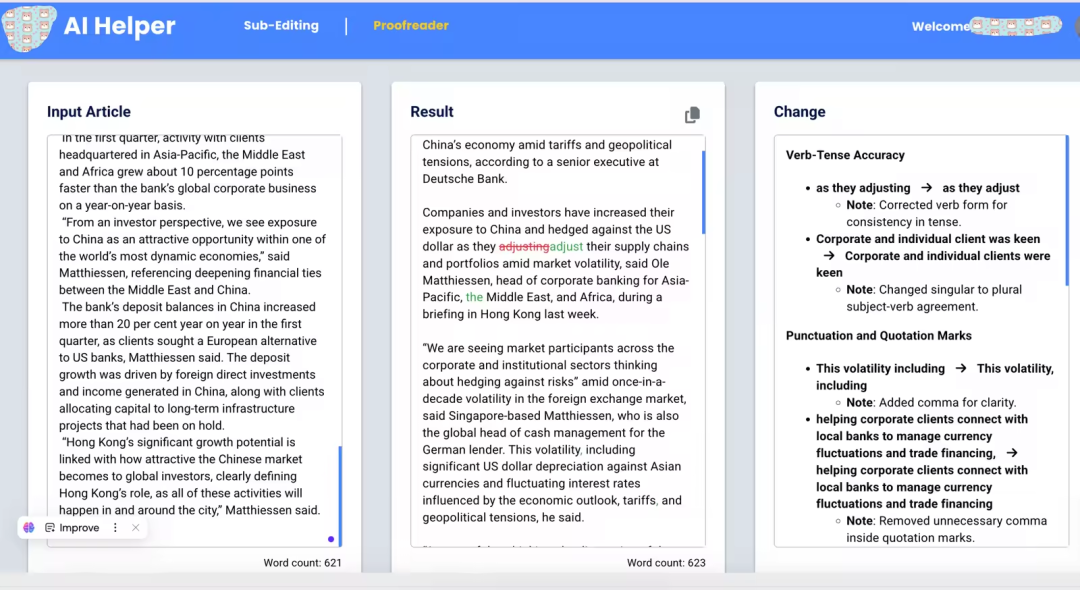
VI. Case Implementation — Media Client Agent
Proofreading Rules for English Media
- Tense consistency
- Punctuation norms
- British English spelling
- Sentence structure
- Style guide replacements
---
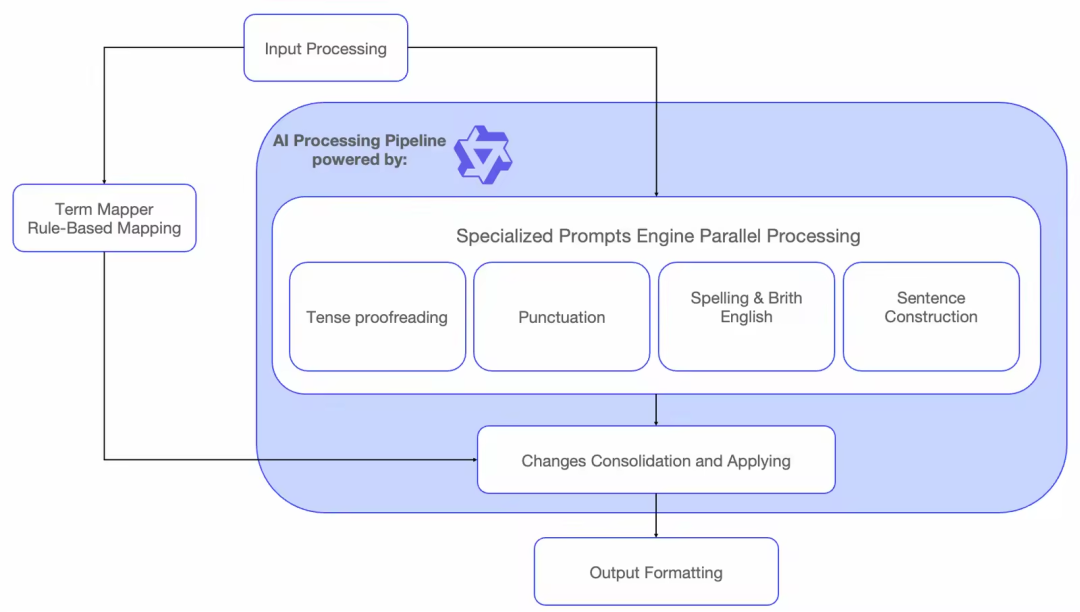
Intelligent Agent Objectives
- Base model: Qwen-Long via Bailian.
- Parallel execution to avoid bottlenecks, merging changes at the end.
---
Iterations & Optimizations
- 5 development rounds.
- Focused on improving RAG recall and prompt design.
- Eventually replaced RAG keyword replacement with string matching for higher accuracy.
---
VII. Special Language Optimizations
1. English Tense
- Headlines: present tense for immediacy.
- Past events in past tense.
- Direct quotes keep original tense.
2. British English Localisation
- Spelling: color → colour, organize → organise, etc.
- Vocabulary: apartment → flat, elevator → lift.
- Grammar differences handled via prompts and fine-tuning.
---
VIII. RAG Limitations & Alternative Approach
Challenge: Low recall in long texts.
Solution: Replace with engineering-based string matching:
- Match keywords directly from KB.
- Append matches to prompt for model decision-making.
- Use API-based execution over Bailian for flexibility.
---
IX. Code Implementation Snippets
Workflow includes:
- Load & filter guidelines
- Batch concurrency via ThreadPoolExecutor
- Retry logic with max attempts
- Save outputs to Excel
(Code samples retained as in original for technical reference.)
---
X. Business Results
- 4-month delivery from planning to rollout.
- Positive client adoption, paving the way for additional AI applications: AI search, blogs, translation, avatars.
---
XI. Conclusion
Large models are reshaping the media landscape — their integration into editorial workflows demands precision, domain expertise, compliance awareness, and ongoing optimization.
Key Takeaway:
AI will not remove editorial roles overnight; instead, it will create new opportunities. Embracing AI’s efficiencies enables professionals to focus on higher-value tasks, emerging as leaders in a transformed industry.
---
Further Reading & Tools:
- AiToEarn官网 — Open-source AI content generation + monetization platform.
- Multi-platform publishing: Douyin, Kwai, WeChat, Bilibili, Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, Threads, YouTube, Pinterest, X (Twitter).
- Documentation | GitHub | AI模型排名
---
Would you like me to produce a flow diagram summarizing the Prompt Engineering → RAG/Keyword Matching → Model Execution → Evaluation Loop pipeline described above? That would make this document even quicker to grasp visually.



