# Practical Implementation of Large Language Models in Game Development
In recent years, **AI coding tools** have rapidly emerged, yet their adoption in *large-scale game engineering* remains limited. The main constraints are **LLM context length** and the **complex, highly flexible nature of game logic**.
This article is based on my talk at **AICon 2025 Beijing**, *“Practical Implementation of Large Language Models in Game Development”*, where our team showcased an AI assistant capable of executing complex game coding tasks through:
- **Code knowledge graph construction**
- **Multi-Agent RAG retrieval**
- **MCP (Model Context Protocol)**
The tool has delivered excellent results in code search, knowledge Q&A, game feature iteration, and new feature implementation—boosting AI-generated code coverage for our company.
---
## Context: AICon 2025 Beijing
**Event date:** December 19–20
**Theme:** *Exploring the Boundaries of AI Applications*
Covered topics:
- Enterprise-grade Agent deployment
- Context engineering
- AI product innovation
Experts from major enterprises and startups shared insights on practical large-model applications and new AI pathways for business growth.
---
## 1. The Gap Between AI Potential and Game Dev Reality
From **ChatGPT 3.5 → GitHub Copilot → Devin → Claude Code**, large model technology has matured quickly, creating **developer anxiety** about job security.
We asked: *Are these tools truly fit for game development?*
Our internal survey revealed:
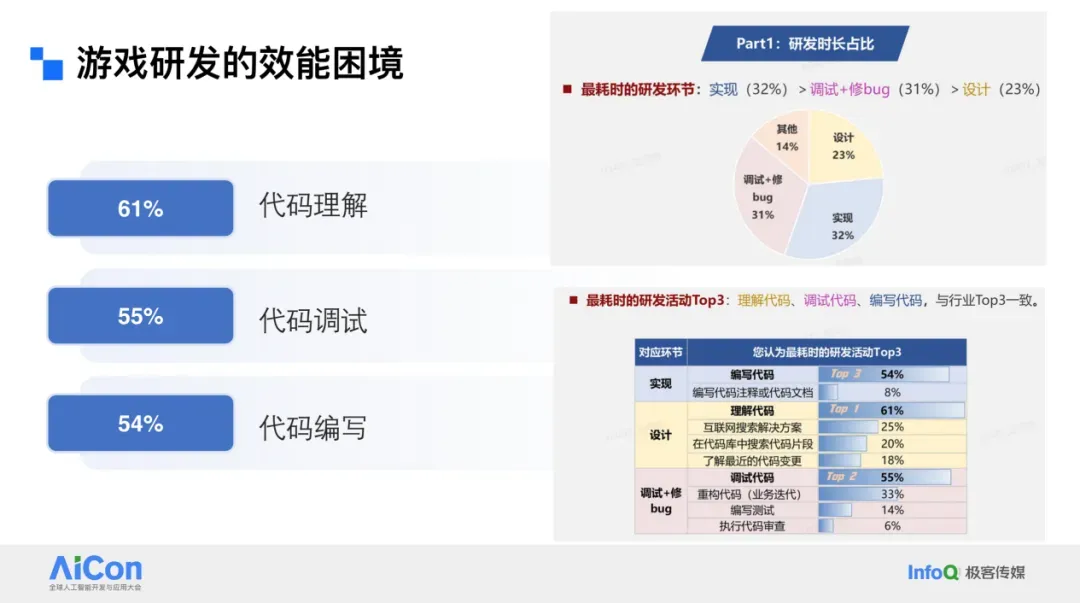
- The biggest time sink is **code understanding**, *not* code writing.
- Game repositories often contain **tens of millions of lines**, demanding huge comprehension efforts.
- Multi-party collaboration (design, art, programming) adds complexity.
- Debugging time > coding time.
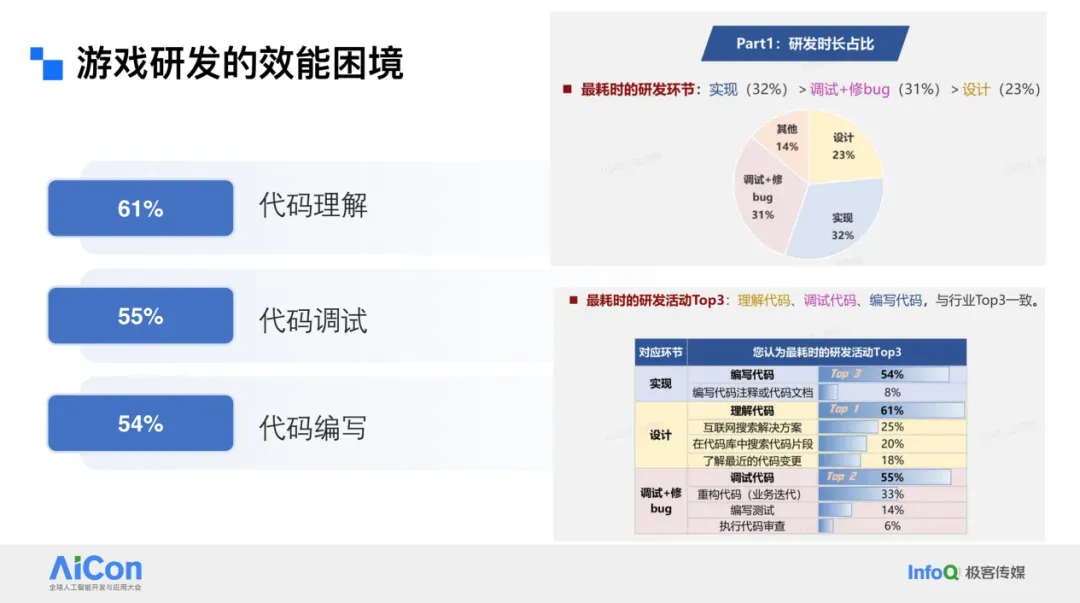
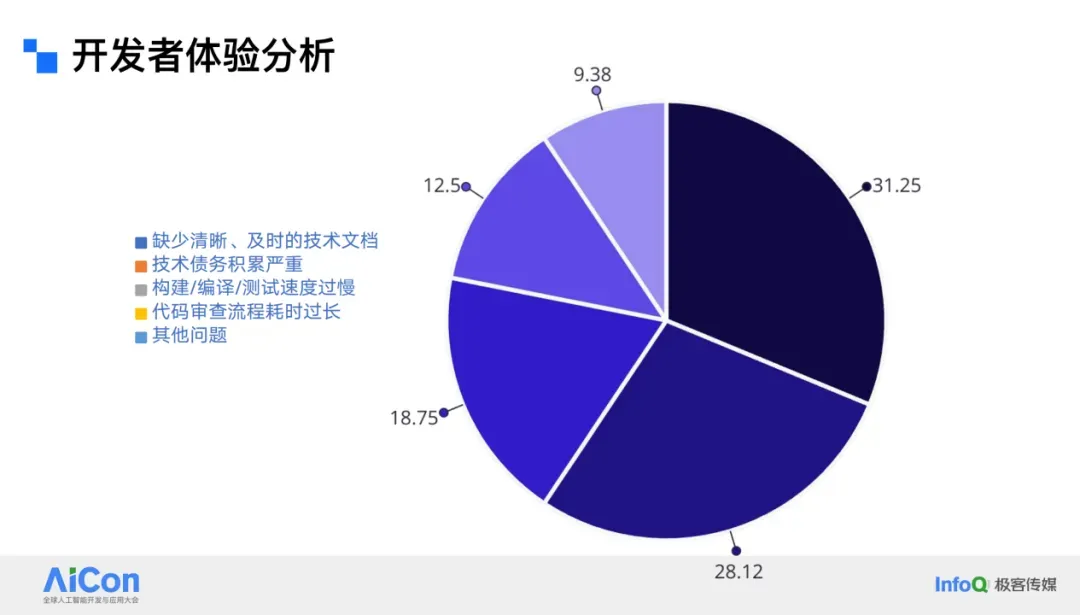
### Main Bottlenecks
1. **Incomplete technical documentation** (~30% impact) due to tight release cycles.
2. **Technical debt accumulation** (~28% impact) from repeated shortcuts under time pressure.
3. **Slow pipelines** (testing, compilation, and debugging more complex than web development).
---
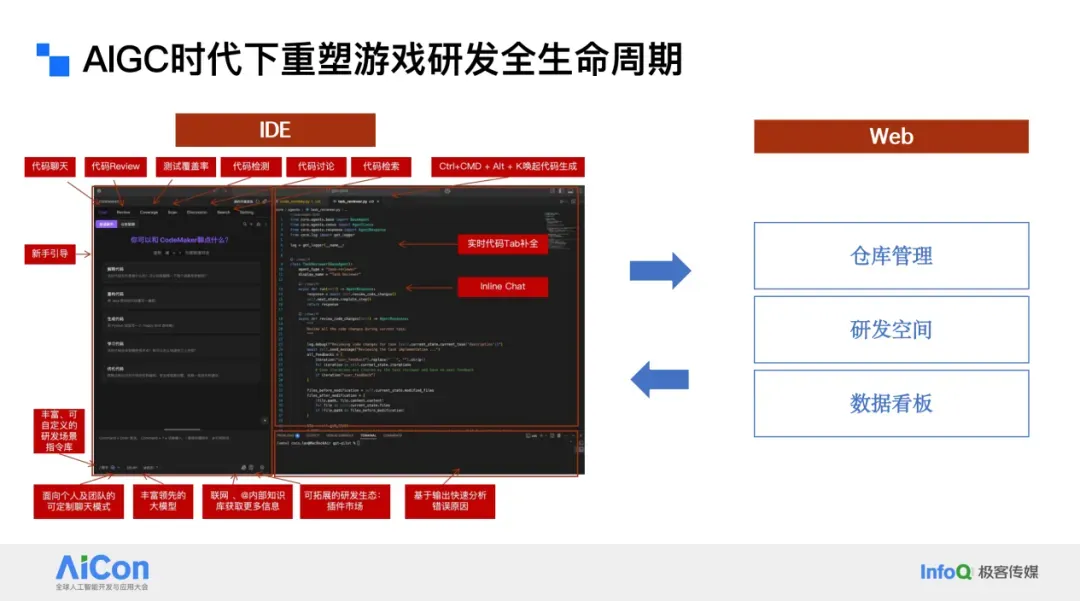
## 2. Our Dual-Interface System (IDE + Web)
Launched early 2024:
- **IDE Plugin**: Central AI workspace to prevent tool-switching.
- **Web Backend**: Manages and syncs team data, usage analytics, and shared assets.
Key features:
- Code chat
- AI-powered completion
- Custom rules & knowledge bases
- Team-wide code review & in-code discussions
**Goal:** Centralize all programmer-facing tasks into the IDE to unify workflow.
---
## 3. Beyond Games — Related AI Platform Insights
Example: **[AiToEarn官网](https://aitoearn.ai)** — an open-source, cross-platform AI content workflow:
- AI generation → publishing → analytics → model ranking
- Distribute to Douyin, Kwai, Bilibili, Instagram, YouTube, etc.
- Similar to our IDE-driven approach in minimizing context switching.
---
## 4. Three Focus Areas in 2024–2025
1. **Shorten code comprehension cycles**
Includes logic, gameplay, abilities, and system mechanics.
2. **Improve AI code completion & generation**
Integrating knowledge engineering for relevant outputs.
3. **Enhance code quality with AI review**
Combining static analysis + AI for context-aware reviews.
---
## 5. Game Development Knowledge Engineering
### The Challenge
- Game teams rarely produce thorough documentation.
- Questions like:
- “What abilities does this character have?”
- “How was last year’s festival implemented?”
- “Will changing this feature affect others?”
### Our Approach
Use **RAG** and **Agents** to build a queryable, persistent *knowledge brain*:
- **Structured**: Skills, characters, systems, gameplay elements.
- **Unstructured**: Narrative texts, Excel-based design docs.
- **Domain expertise**: Examples, retrospective cases.
- **Implicit patterns**: Operational routines.
---

### Types of Knowledge
1. **Explicit** — documented & retrievable without AI (e.g. manuals, ticket history).
2. **Implicit** — embedded in code, requiring inference.
**Explicit governance** using:
- Internal knowledge systems
- Ticket systems
- Repo data (SVN, GitLab)
- Agentic RAG indexing
---
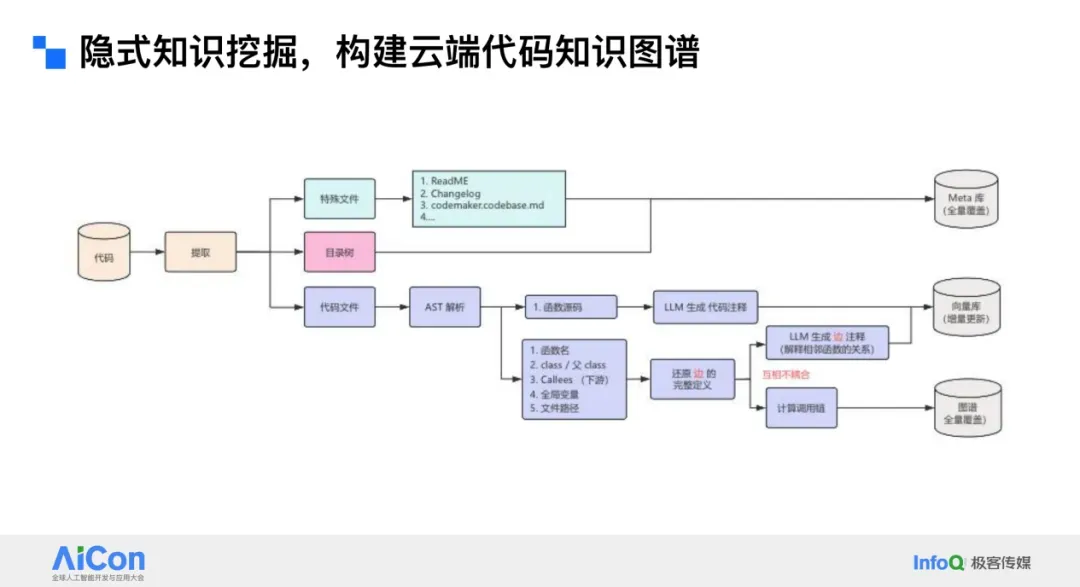
## 6. Code Knowledge Graph Construction
We parse:
- **Directory structures**
- **Abstract Syntax Trees (AST)**
- **Call relationships**
- **Semantic interpretations** of classes/functions
### Result:
- Fine-grained, conversational interaction with repository knowledge.
- Linked commit records enhance context.
**Codemaker** now offers:
- Full repository maps
- Complexity metrics
- Interactive upstream/downstream call views
- Manual module annotations
---
## 7. Iterative Knowledge
Knowledge governance is continuous:
1. Activate existing data.
2. Feed new **usage process data** back into the knowledge base.
3. Establish feedback loops so the system *learns from its own usage*.
Result: Knowledge becomes **living** instead of static, encouraging daily use.
---
## 8. Multi-Agent Empowered Code Writing
Once the **knowledge base is accessible to AI**:
- AI can understand full architecture, tech stack, and locate specific code.
We built:
- **Cloud-based mode** for large repos (local mode insufficient).
- Core Agent + supporting specialized Agents.
- *Development Space* concept — explicitly defines team-specific context:
- SDK & engine versions
- Dependency library details
- Coding style & standards
---
### Case Study: Speeding Onboarding
- New hire given **40,000-line repo**
- Traditionally: ~2 weeks to familiarization.
- AI-assisted: **1–2 days**.

---
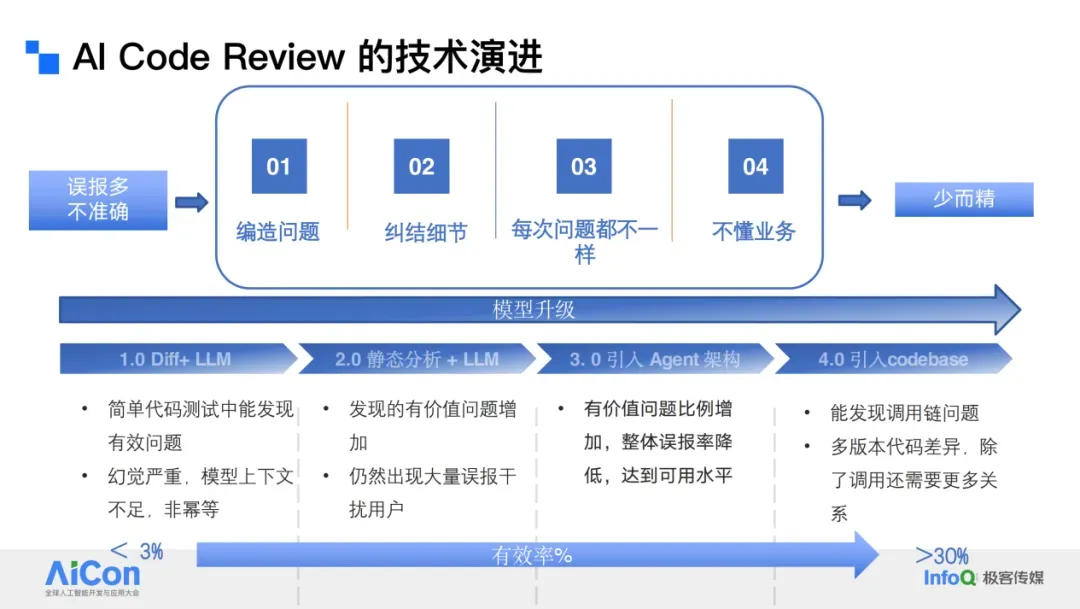
## 9. AI Review to Ensure R&D Quality
**Challenges in game context:**
- Tight delivery schedules.
- Many critical bugs embedded in simple mistakes.
- Without business context, AI may miss logical errors (e.g. wrong reward quantity).
### Evolution of AI Review:
1. **Manual initiation** → IDE integration.
2. Prompt engineering → low precision.
3. Dual-engine (static + AI) → too many false positives.
4. Multi-Agent collaborative → filters per business team needs.
5. Integrated knowledge engineering → context-aware reviews.
---
## 10. Code Review Modes
- **Local Review**: Initiate in IDE, review staged code or selected range.
- **Team Review**: Integrated with GitLab, supports:
- Commit/MR selection
- AI-assisted review & explanations
- Ticket info integration
Repository-level stats track:
- Issue types
- Resolution patterns
- Improvements over time
---
## 11. Future Outlook: Team AI Agent
**Goal:** Build a **shared team memory** system — an AI agent holding *years of team experience*, including:
- Planning docs
- Style guides
- Ticket resolutions
- Key conversations
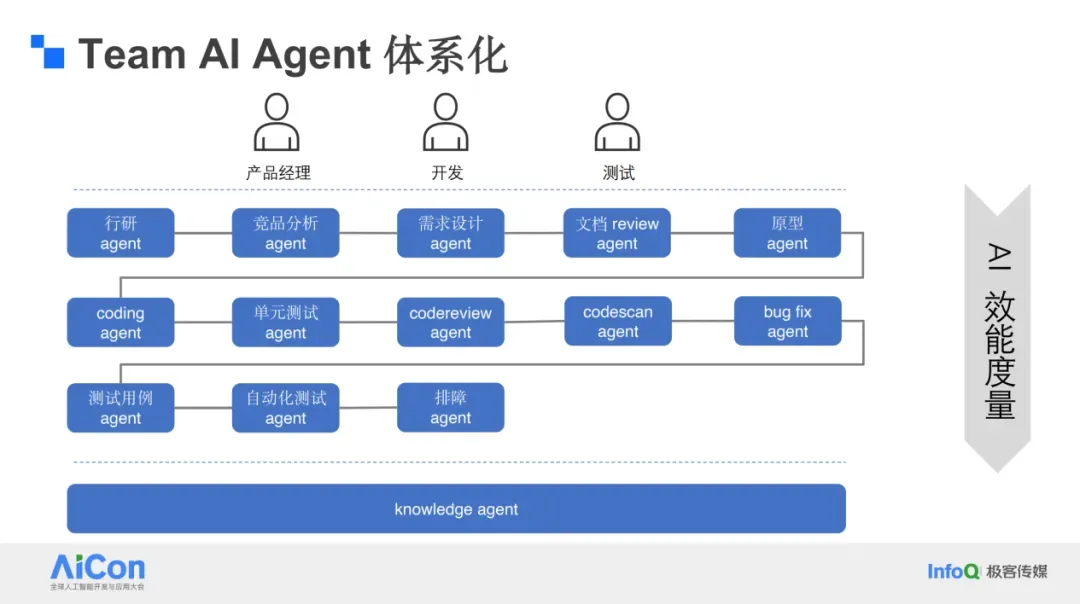
Potential applications:
- Cross-role collaboration
- Context-based cross-platform content generation
---
## Related Resource
**[AiToEarn官网](https://aitoearn.ai)** — global open-source AI monetization ecosystem.
Features:
- AI generation + publishing + analytics + model ranking ([AI模型排名](https://rank.aitoearn.ai))
- Distribute to global major platforms
- Turn team or project knowledge into revenue-generating, multi-platform content.
> Explore more:
> - [AiToEarn博客](https://blog.aitoearn.ai)
> - [AiToEarn GitHub](https://github.com/yikart/AiToEarn)
---