# Alibaba AI Codefuse Overview
This document describes how **CodeFuse**, Alibaba's enhanced AI programming system, enables **end-to-end automatic code generation** from natural language requirements—reshaping the software engineering paradigm.
---
## 1. Business Background
The AI-driven transformation of software engineering is shifting from **tool-assisted coding** to fully **requirement-driven development**.
**Vision at Ant Security & Intelligence Lab:**
In the near future, most repository code submissions will be auto-generated by CodeFuse.
This requires CodeFuse to evolve from:
- **Auto-completion and AI partner**
- To **AI Requirement Executor**
Delivering capabilities to:
- Parse natural language requirements
- Decompose tasks intelligently
- Search cross-repository files
- Generate code and related test cases
- Enforce security and compliance standards
---
## 2. Goals
1. **End-to-End Automation:** From business requirement → production-ready code.
2. **AI Contribution Target:** 60% AI-generated code in the large security domain.
3. **Security-by-Design:** Automate risk detection during requirement decomposition, enforcing rules such as:
- Queries must include `limit`
- Release functions must include hashing mechanisms
---
## 3. Main Challenges
### A. Complex Code Assets
- **Massive repositories:** 100K+ lines, legacy patches, multi-version support.
- **Technical debt:** Obsolete logic, dense architecture.
- **Intelligent parsing limits:** Difficulty understanding deep logic, cross-file dependencies, and hidden business rules.
### B. Complex Business Requirements
- **Decade-long domain knowledge:** Spread across code, documents, and workflows.
- **Surface-level AI understanding:** Current models fail to grasp deep semantics and relationships between files.
---
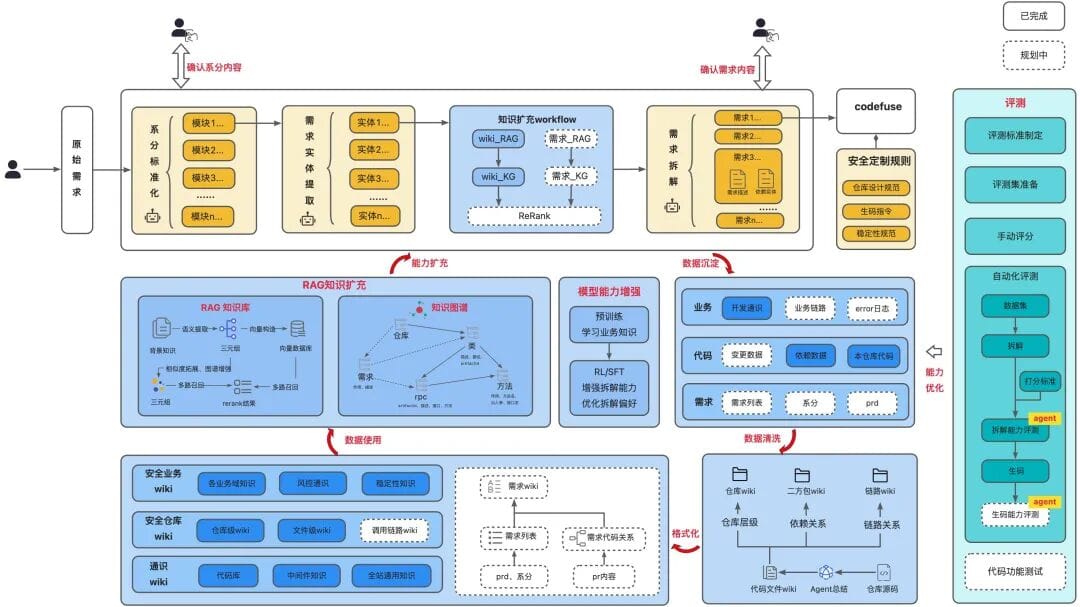
## 4. Construction Approach
### Overview
To tackle the above:
- **Standard AI coding workflow** from PRD → analysis → context enrichment → requirement breakdown → secure rules → incremental code generation.
- **Expanded model context** via multi-dimensional structured wikis and RAG + knowledge graph.
- **Continuous evaluation and optimization** of AI code generation quality.
---
### 4.1 Construction Framework
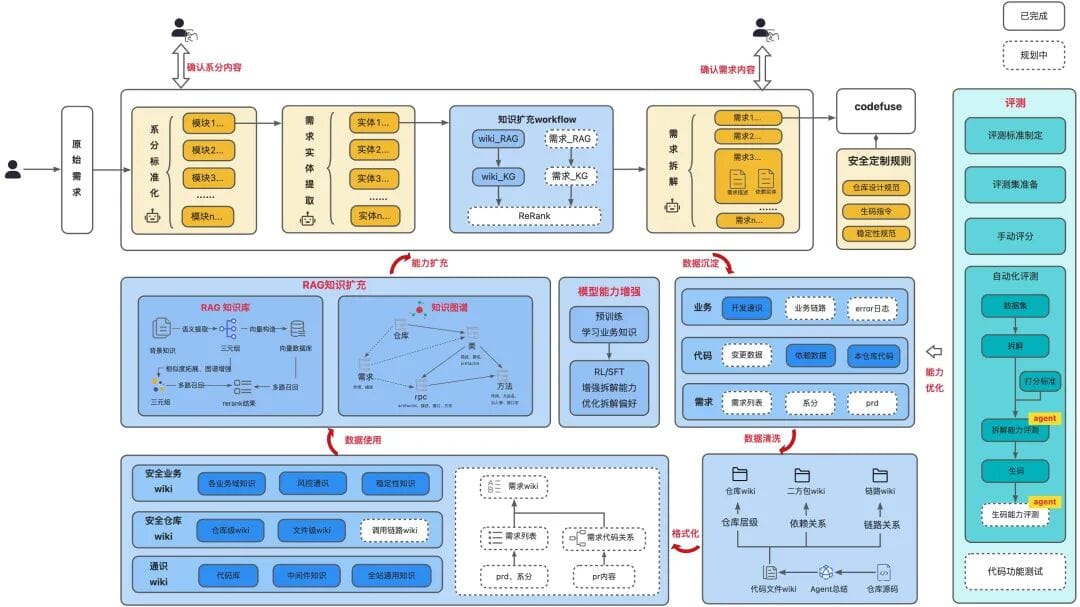
---
### 4.2 Expanding Business Knowledge
#### Wikis for Context Enrichment
- **Security Business Wiki:** Risk control, stability guidelines, "Three Weapons", circuit breakers.
- **Security Repository Wiki:** Repo/file/call-chain knowledge for precise code targeting.
- **General Knowledge Wiki:** Middleware and common dev specs.
- **Requirements Wiki:** PRD-linked domain semantics.
#### RAG-Based Retrieval
Challenges:
- **Low recall accuracy:** Use entity extraction, search tags, application-specific recall strategies.
- **High storage/retrieval costs:** Optimize query flow and prune irrelevant content.
#### Knowledge Graph Enhancement
- Index nodes as `file path + repository`
- Prune graph down from 1B→1M nodes, preserving essential semantic accuracy.
---
### 4.3 Model Capability Strengthening
- **Continuous pre-training** with domain corpora.
- **Reinforcement learning** on requirement decomposition.
- **Multi-dimensional rewards** via GRPO in `sllmworks` framework:
- Output format
- Number of tasks
- "Three-step change" adherence
- Robustness
- Task dependency correctness
Evaluation:
- Manual + automated checks
- Use subtasks for final code gen and other doc generation
---
#### Training Data Quality Management
**Current:**
Reverse-engineer PR → subtask list → requirement, apply filtering and agent verification.
**Issues:**
Semantic deviations, label granularity, distribution mismatch.
**Plan:**
1. Manually labeled "golden set"
2. Scenario categorization and difficulty layering
3. Deduplication
4. Curriculum learning
---
## 5. Standardized Workflow for End-to-End Code Generation
### 5.1 Automated System Analysis Document Generation
**Problems:**
- Inconsistent formats and missing logic.
- Absent non-functional requirements (availability, stability).
**Solutions:**
- Unified templates (business processes, state transitions, permissions).
- Agent-generated draft docs, developer review.
**Templates:**
- **Business Entities Table**
- **Domain Functions Table**
- **Application Services Table**
- **State Machine Table**
- **Interactions Table**
- **High Availability Table**
---
### 5.2 Requirements Subtask Decomposition
**Challenges:**
- Token overflow with large modules
- Need atomicity and clarity
**Solutions:**
- Break into single-responsibility subtasks
- Dependency ordering
- Balance simplicity and detail
---
### 5.3 Repository Code Generation Specification
**Approach:**
- Use model + CodeFuse repo indexing.
- Create `.project_rule` for each repo (DAL→Repository→Service→Controller layers).
---
### 5.4 Layered Code Generation
**Reasons for MVC layer-by-layer:**
1. Maintain module dependency order.
2. Avoid token limits and context loss.
**Solutions:**
- Separate workflows per layer
- Unified naming conventions and quality rules
---
### 5.5 Automated Review of Outputs
**Problems:**
- High risk trusting raw AI outputs without review.
**Solutions:**
- Custom prompts for summarizing:
- Structural changes
- Coverage scope
- Stability measures
- Implementation plans
---
## 6. Evaluation & Knowledge Base Updates
### Dynamic Data Updates
- Sync with evolving repos/requirements
- Process data from requirement breakdown
- Expand KB and KG with precise recall data
### Capability Evaluation Metrics
- **Recall Rate, Accuracy Rate**
- **Model Breakdown Scores:** Format, dependency, robustness
- **End-to-End AI Coding:** Business types, scenarios, requirement types, complexity
---
## 7. Construction Progress
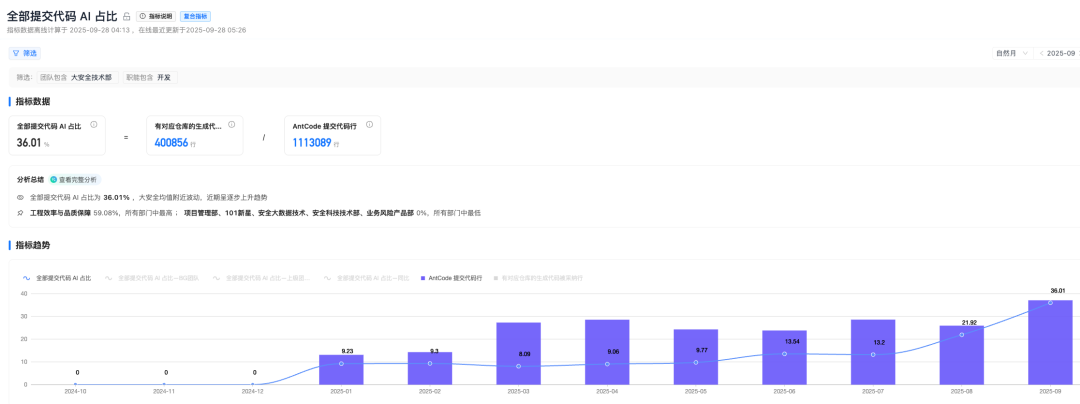
### AIcoding Adoption
- **CodeFuse user AI-submitted code:** 43.25%
- **Overall AI-submitted code:** 36.01%

### Production Practice Cases
#### Case Processing Platform
- **20K lines generated**, full workflow.
#### Intelligent UI Assistant
- **3K+ lines**, >70% adoption.
#### One-Click Secondary Package Integration
- Auto circuit breaker integration in risk control system.
---
## 8. Next Steps
### Challenges
- Lacking unified technical risk control standards
- New risks arising alongside governance
- Insufficient historical data at design and breakdown stages
### Proposed Solutions
- Shift risk detection to requirements/design stage
- Optimize coding standards
- Continuous data collection and evaluation
---
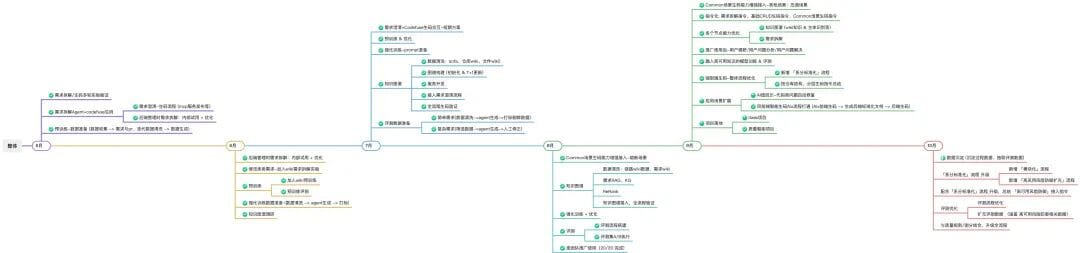
## 9. Continuous Capability Enhancement
**Capability R&D Planning:**
---
**Acknowledgments:**
Thanks to the CodeFuse, GRT, and GeaMaker teams for their support in capability expansion and Q&A guidance.
---