AliSQL Vector Technology Analysis (Part 1): Storage Format and Algorithm Implementation
# **AliSQL 8.0 Vector Index Deep Dive (Build 20251031)**
**_129th article of 2025_**
*(Estimated reading time: 15 minutes)*
---
## **01 — Background**
With the widespread adoption of **AI** and large-scale model applications, **high-dimensional vectors** have become a core representation for complex data like text, images, and speech. Demand for **vector storage and efficient retrieval** is growing rapidly in:
- **Recommendation systems**
- **Image search**
- **Natural language processing**
This trend raises new challenges for database technologies.
### Evolution of Vector Support in Databases
- **Specialized vector databases** have emerged to handle these needs.
- **Traditional RDBMSs** have started adding vector capabilities:
- **PostgreSQL** → `pgvector` plugin for efficient vector retrieval.
- **MySQL 9.0** → Introduced `VECTOR` type but limited calculations to *HeatWave* with **no general-purpose vector indexing**.
This gap forces enterprises to:
- Deploy **separate vector databases** OR
- **Migrate data** for high-dimensional computation.
---
### AliSQL’s Native Vector Solution
Built on **MySQL 8.0**, **AliSQL** offers:
- **Enterprise-grade vector data processing** out of the box.
- **Standard SQL interface** for vector matching + complex business logic.
- **HNSW algorithm-based vector indexes** for high-precision searches.
- **Cost-effective high-compatibility architecture** for rapid AI adoption.
This article focuses on **vector indexing**:
- **Storage formats**
- **Algorithm design**
> Helping readers **understand** and **practically use** these capabilities.
---
## **02 — Vector Usage Example**
AliSQL supports:
- Up to **16,383 dimensions** per vector.
- **Cosine similarity** (`COSINE`) & **Euclidean distance** (`EUCLIDEAN`) functions.
- **HNSW vector indexing** on full-dimension vector columns.
### **Example: Create Table, Insert Data, Search Vectors**
-- Create table with vector index
CREATE TABLE `t1` (
`id` INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
`animal` VARCHAR(10),
`vec` VECTOR(2) NOT NULL,
VECTOR INDEX `vi`(`vec`) m=6 distance=cosine
);
-- Insert data
INSERT INTO `t1`(`animal`, `vec`) VALUES
("Frog", VEC_FROMTEXT("[0.1, 0.2]")),
("Dog", VEC_FROMTEXT("[0.6, 0.7]")),
("Cat", VEC_FROMTEXT("[0.6, 0.6]"));
-- Perform vector search
SELECT `animal`,
VEC_DISTANCE(`vec`, VEC_FROMTEXT("[0.1, 0.1]")) AS `distance`
FROM t1
ORDER BY `distance`;
**Result:**
| animal | distance |
|--------|----------|
| Frog | 0.1000 |
| Cat | 0.5000 |
| Dog | 0.5657 |
---
### Real-World Applications
This capability enables:
- **Intelligent recommendations**
- **Semantic search**
- **Image similarity detection**
All **without** a separate vector database.
> For large AI-driven workloads and cross-platform content, tools like [AiToEarn官网](https://aitoearn.ai/) combine **technical backends** like AliSQL with **AI-assisted content generation**, **publishing**, and **monetization**.
Supported platforms: Douyin, Kwai, WeChat, Bilibili, Rednote (Xiaohongshu), Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, Threads, YouTube, Pinterest, X (Twitter).
---
### **Creating Vector Index on Existing Table**
ALTER TABLE `t1` MODIFY COLUMN `vec` VECTOR(2) NOT NULL;
-- Create vector index with default parameters
CREATE VECTOR INDEX vi ON t1(v);
---
## **03 — Detailed Explanation of Vector Indexes**
AliSQL prioritizes **HNSW** (Hierarchical Navigable Small World) as its **Approximate Nearest Neighbor (ANN)** algorithm.
### Architecture Highlights:
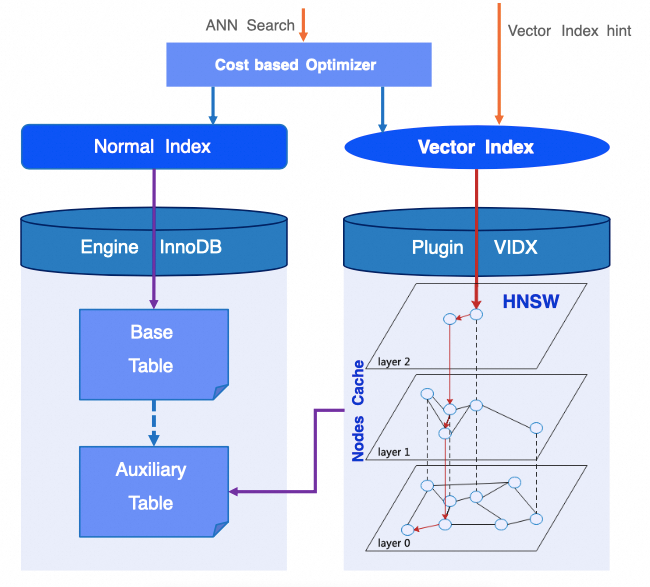
1. ANN query chooses an appropriate index after **cost estimation**.
2. Full HNSW graph stored in **auxiliary table** → persisted on disk.
3. **Nodes Cache** maintained in memory via vector index plugin → higher speed.
**Diagram:**
---
### **3.1 — HNSW Algorithm Overview**
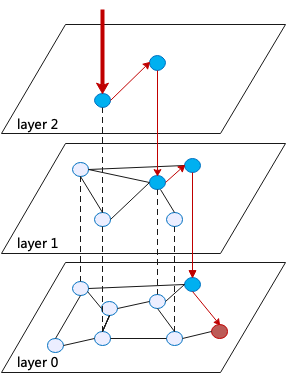
#### Design Principles:
- **Multi-layer graph** → top layers for *fast jumps*, bottom layer for *precise search*.
- **Nearest neighbor connections** per layer.
**Diagram:**
---
#### Nearest Neighbor Search (Single Layer)
**Steps:**
1. Input: target node `q`, number `ef`, candidate set `C`, result set `W`.
2. From `C`, pick closest node `c` → explore neighbors `e`.
3. If `e` is:
- Not visited
- Closer to `q`
→ add to `C` and `W`.
4. Stop when closest in `C` is farther than farthest in `W`.
5. Output: first `ef` nearest nodes in `W`.
---
#### Insert Algorithm (`Insert`)
**Parameters:**
- `M` → max neighbors per layer.
- `L` → max layer index.
**Process:**
1. Determine insertion layer `l` for node `q`.
2. From layer `L` down to `l+1` → greedy search (`ef = 1`) to find entry point.
3. From `l` down to `0` → full search (`ef = M`, `ef = 2M` for layer `0`), insert, connect neighbors.
4. Shrink neighbor list if it exceeds `M`/`2M`.
---
#### KNN Search Algorithm
1. **Fast jump**: Layers `L` → `1` → greedy search (`ef = 1`).
2. **Precise search**: Layer `0` → retrieve `K` nearest neighbors.
---
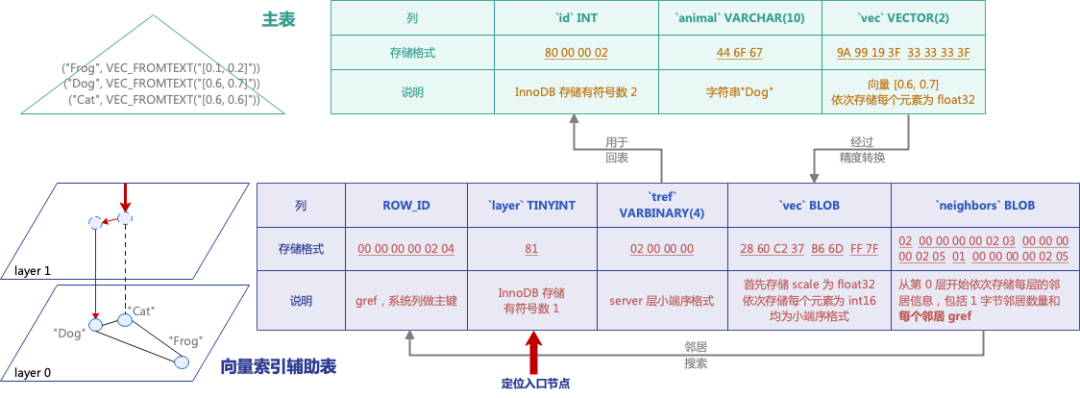
### **3.2 — Vector Index Storage Format**
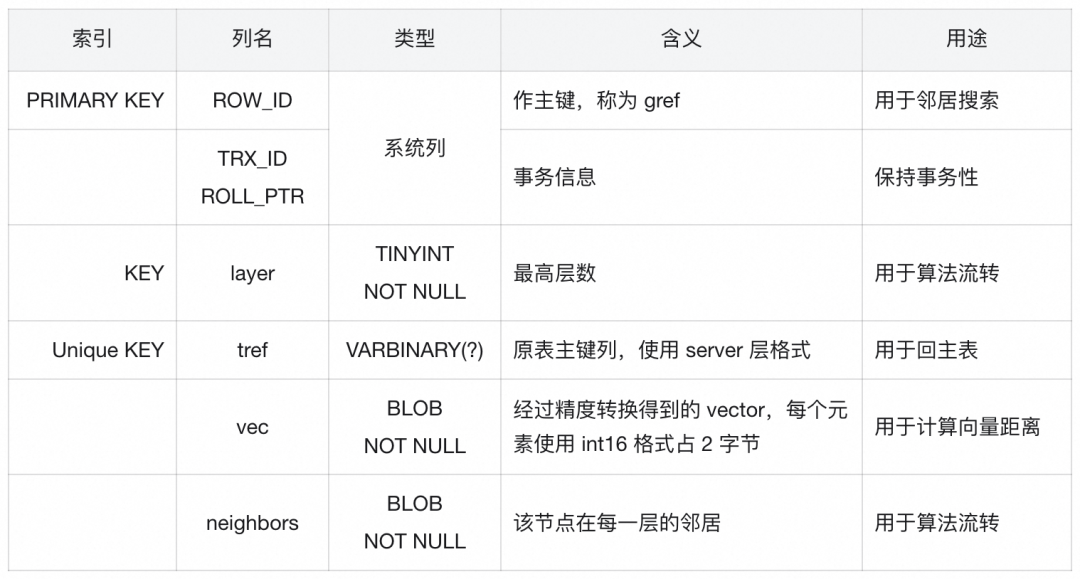
**Auxiliary Table Fields:**
1. **`gref`** → graph ref PK (InnoDB `ROW_ID`).
2. **`layer`** → indexed for quick entry point location.
3. **`tref`** → PK of source table in **little-endian**.
4. **`vec`** → stored as `int16` + scaling factor (`float32`).
5. **`neighbors`** → count (1 byte) + list of `gref`s.
**Precision Conversion Formula:**int16 = round( float32 / scale )
Where:scale = max_abs_value / 32767
**Example for `[0.6, 0.7]`:**
- Max abs value = `0.7`
- Scale = `0.7 / 32767` = `2.13629555e-05`
- Quantized vector: `[28086, 32767]`
- Storage: `[scale][dims]` in little-endian
**Diagram:**
---
### Real-World Context
For multi-platform AI applications, coupling **vector search engines** like AliSQL’s with platforms like [AiToEarn官网](https://aitoearn.ai/) allows:
- Seamless AI content creation
- Cross-platform publishing
- Data analytics
- Monetization pipelines
---
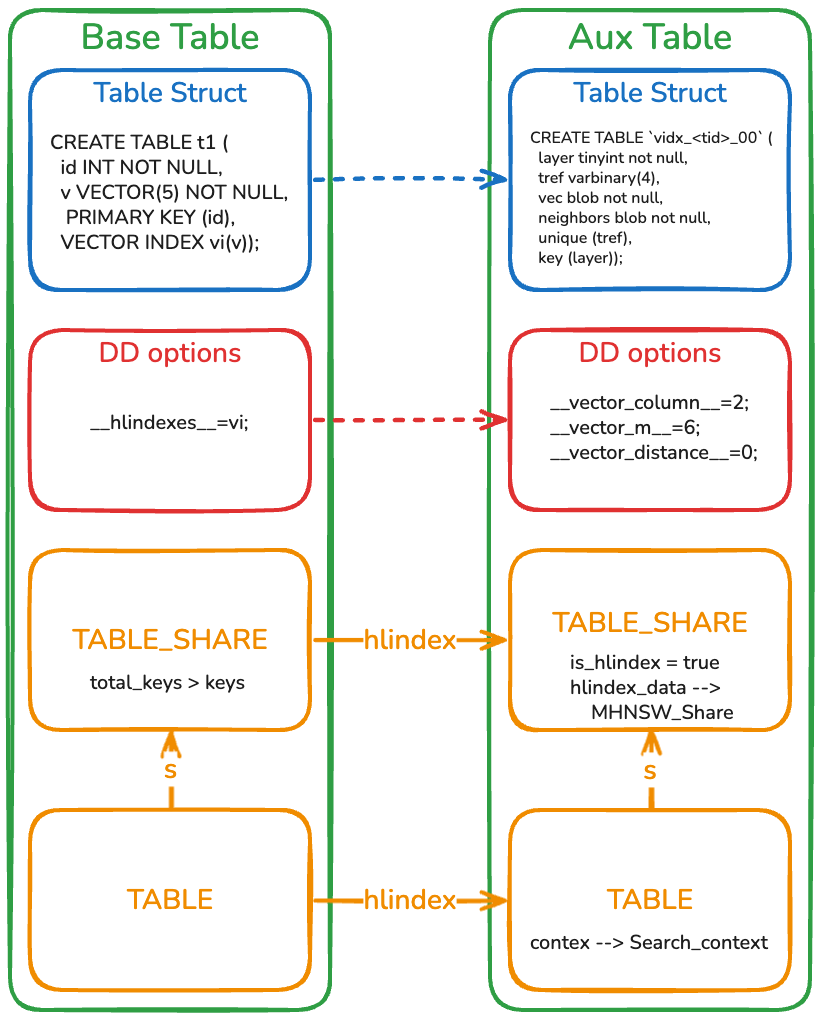
### **3.3 — DD Adaptation & DDL Atomicity**
#### Key Points:
- Auxiliary table name format: `vidx__00`.
- Invisible to user; tied to primary table via **DD** entries.
- Shared **Nodes Cache** & context objects for search results.
- Changes to both tables in same transaction → guarantees:
- **Atomicity**
- **Crash Safe**
**Diagram:**
---
## **Summary**
AliSQL’s vector indexing integrates:
- **HNSW ANN algorithm**
- **Compact vector storage via int16 quantization**
- **Full DD adaptation for metadata consistency**
- **Atomic DDL operations**
This fills a long-standing gap in MySQL ecosystem’s vector processing.
---
### **Next in Series**
**Part II: Node Cache and Concurrency Control**
- How **Nodes Cache** boosts query performance.
- How **concurrency control** ensures production-grade stability.
> Meanwhile, explore [AiToEarn官网](https://aitoearn.ai/) for **technical content publishing and monetization across major platforms**, backed by AI analytics like [AI模型排名](https://rank.aitoearn.ai).
---


