All AI Gifts Already Have a Hidden Price Tag | Peking University’s Latest Paper Explained
AI Makes the World More Efficient — But More Monotonous in Thought
AI Future Compass — A frontline, plain-language column distilling highlights from top conferences and journals.
---
Generative AI: Promise vs. Reality
Generative AI is transforming industries and reshaping how humans write, think, and perceive.
After ChatGPT 3.5 launched, optimism surged: AI was expected to bring work equality.
- 2023 MIT Study (Science)
- Two economics PhDs provided empirical evidence that generative AI boosts productivity among lower-achieving workers, narrowing the gap with high performers.
> Science editors summarized: “Participants with weaker skills benefit most from ChatGPT…critical implications for future productivity inequality policies.”

But by 2025, evidence tells a different story.
A Harvard study — analyzing data from 62 million employees and 150 million recruitment records — found that AI reshapes the market with a “seniority bias”.
Seniority Bias in the AI Age
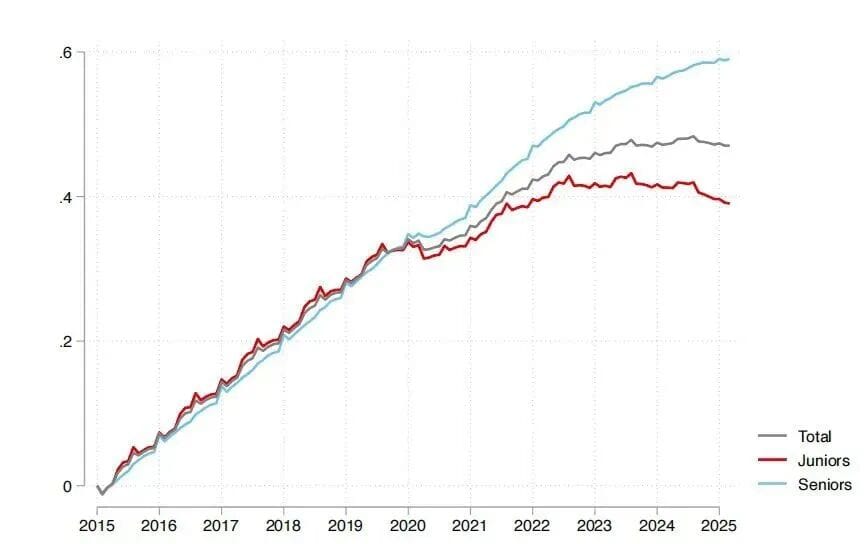
- 2015–2022: Junior and senior job growth aligned.
- 2023 onwards: Senior roles kept rising, junior roles declined.
- AI-heavy companies:
- Junior role headcount fell 7.7% in 6 quarters; senior roles stayed stable or grew.
- Driver: reduced hiring, not mass layoffs.
Instead of leveling opportunities, AI has intensified the Matthew Effect — strengthening the strong.
> Liang Jianzhang, Ctrip CEO: “AI will replace junior intellectual work, making life harder for young people as they begin careers, marry, and start families.”
---
Beyond Efficiency: What’s Happening to Human Creativity?
Key questions:
- Is AI’s efficiency boost truly enhancing personal capability?
- Or is it subtly unifying our thoughts?
- Does over-reliance on AI strengthen original thinking or diminish it?
Peking University’s Landmark Study
Professor Li Guiquan’s team published in Technology in Society (Q1, IF 12.5, ranked 2/271 in Social Science, Interdisciplinary).
Two-part study:
- Natural experiment — 410,000+ academic papers analyzed pre/post ChatGPT 3.5 release.
- Longitudinal lab experiment — Months-long tracking of participants’ cognitive abilities with/without AI.
---
01 — 410,000 Papers and the “Collective Unconscious”
> The most frightening thing is not noise, but everyone speaking in unison.
Methodology
- Data source: Web of Science core database — 21 disciplines.
- Sample: 17,000+ scholars; 419,344 authored papers before and after ChatGPT 3.5.
- Goal: Measure AI’s real impact on global knowledge production.
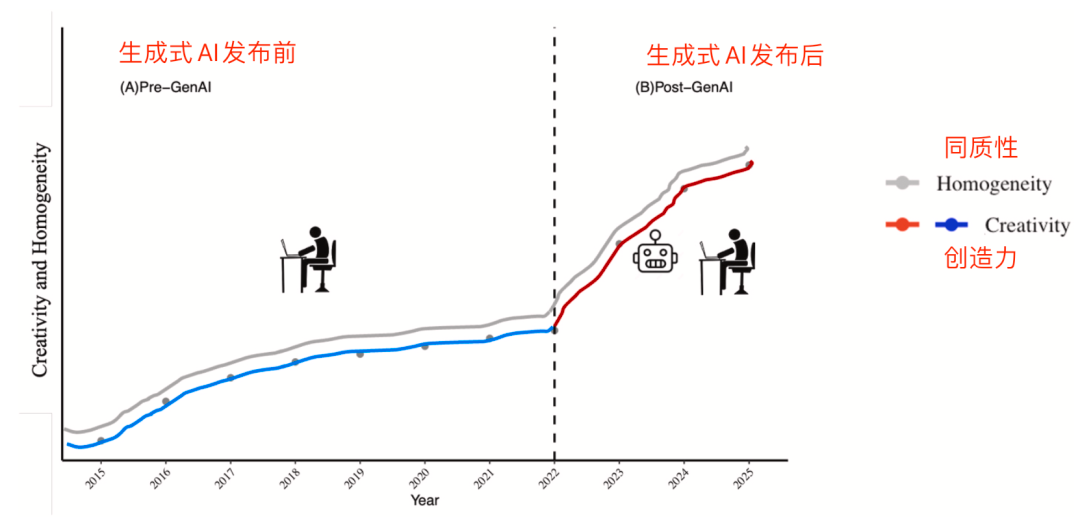
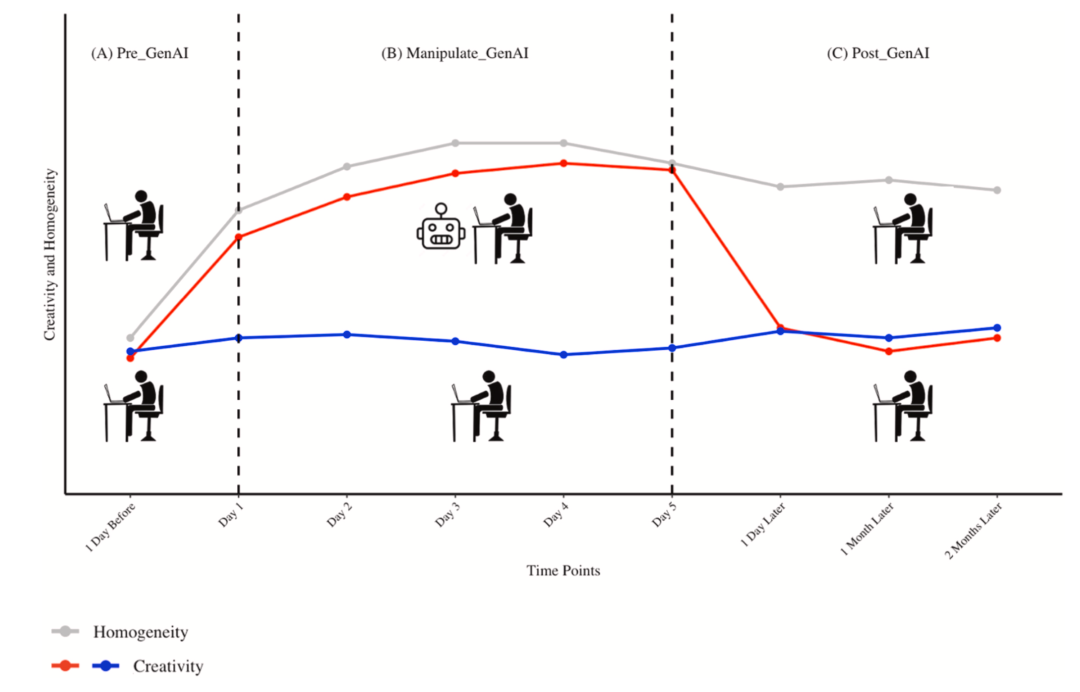
Changes in academic paper homogeneity and creativity pre/post AI.
---
Creativity vs. Homogeneity Pre/Post AI
Before 2022:
- Creativity (red/blue lines) and homogeneity (gray line) rose steadily.
After ChatGPT 3.5:
- Both slopes sharply increased.
- Conclusion: Faster and more homogeneous knowledge production.
Ensuring Causal Link
- Regression Discontinuity Design (RDD) pegged Dec 2022 release date as a natural breakpoint.
- Treatment vs. control: Access to AI quasi-randomly distributed via publication timings.
- Validated by statistical checks — no abnormal submission delays or rushes around breakpoint.
---
Measures
Creativity
- Quantity: Annual paper count per researcher.
- Quality: Journal quality (JCR Quartiles).
Homogeneity
- Content similarity: SBERT vectors + cosine similarity.
- Language style similarity: Character-level matching for repeated phrasing.
---
Findings
- Boost:
- +0.9 papers/year per researcher.
- +6% in average journal quality.
- Strongest in tech & physical sciences.
- Cost:
- +79% annual rise in language style similarity.
- Notable thematic convergence in physical sciences, arts, humanities.
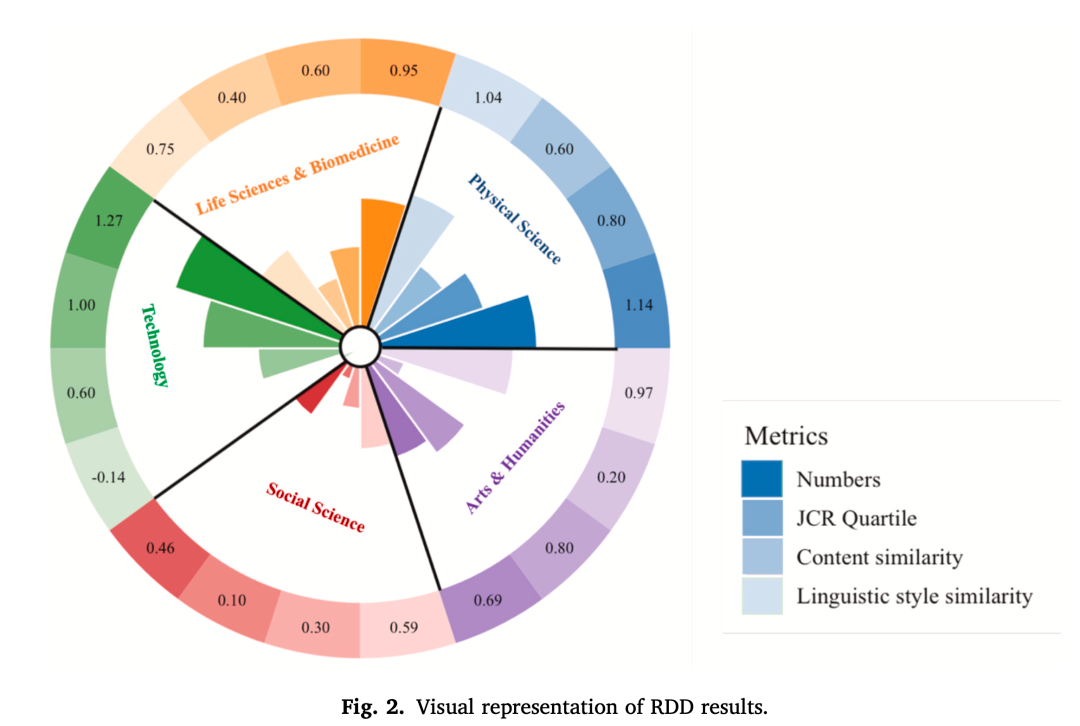
RDD results confirm efficiency gains coupled with uniformity.
Global output faces a “great trade-off” — higher efficiency, less diversity.
---
02 — AI’s Creativity Scars
> Once thought bows to habit, it loses the possibility of creation.
Small-scale studies echo macro trends:
- Cornell: AI assistants push expression toward Western paradigms.
- Santa Clara: AI use raises semantic similarity in ideas.
- MIT (EEG study): AI-assisted writing lowers brain activity vs. independent work.
Most research stops at immediate effects — few examine long-term impacts post-AI removal.
---
Peking University’s Longitudinal Experiment
Design:
61 university students randomly split into:
- AI Experimental Group: Used ChatGPT 4.
- Control Group: No AI use.
Stages:
- Day 1: Baseline creativity test (no AI).
- Days 2–6: Daily creativity tasks (AI vs. no AI).
- Days 7, 30, 60: Follow-up creativity tests (no AI).
---
Creativity Tests:
- Divergent thinking — Alternative Uses Task (AUT).
- Creative problem solving — e.g., “smart bike” features.
- Convergent thinking (RAT) — added in follow-up phase.
- Insight problem — Candle Problem.
Scoring:
Consensual Assessment Technique (CAT) with blinded expert raters — ICCs > 0.90.
---
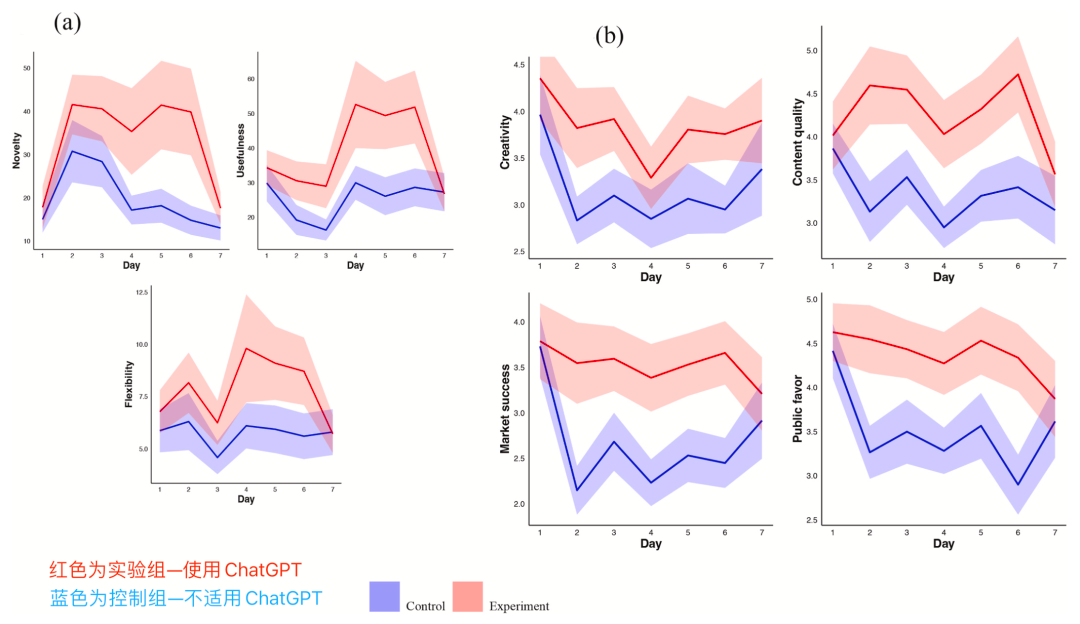
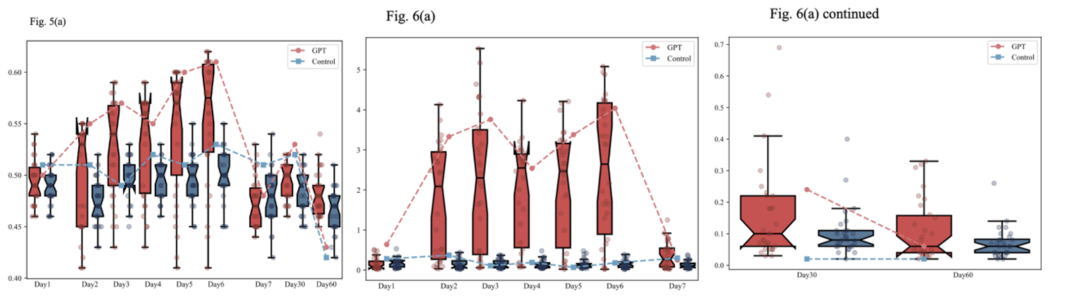
Results:
- Creativity boost: Short-lived. Disappeared once AI removed.
- By Day 60, AI group scored worse in convergent thinking.
- Homogenization: Persistent. Higher similarity still evident 2 months later.
Conclusion: AI can leave a lasting “creative scar” — long-term convergence in thinking and expression.
---
03 — If the World Runs Out of New Ideas
> It was the best of times, it was the worst of times.
- AI’s anchoring effect fixes thinking to initial AI outputs.
- Collective convergence accelerates with generative AI.
> Jensen Huang (CNN, July 2025): “If the world runs out of new ideas, AI’s productivity gains will turn into unemployment.”

Risk: Without fresh ideas, AI performs repetitive tasks instantly — eliminating jobs.
---
04 — Keeping Your Thinking Sharp in the AI Era
> AI reduces workload, but we need deep-thinking systems...and dialectical thinking. — Jensen Huang
Practical Steps:
- Use AI as a “thought sparring partner”
- Brainstorm multiple angles, challenge AI outputs, own final decisions.
- Deliberately introduce “cognitive friction”
- Argue with AI’s answers, find gaps, question assumptions.
- Schedule “no-AI time”
- Create with only pen & paper or a blank document to exercise independent thinking.
---
References
- Noy, S., & Zhang, W. (2023). Experimental evidence on the productivity effects of generative artificial intelligence. Science, 381(6654), 187–192.
- Zhou, Y., Liu, Q., Huang, J., & Li, G. (2025). Creative scar without generative AI… Technology in Society, 103087.
- Lichtinger, G., & Hosseini Maasoum, S. M. (2025). Generative AI as Seniority-Biased… SSRN.
- Kosmyna, N., et al. (2025). Your brain on ChatGPT… arXiv:2506.08872.
- CNN Interview with Jensen Huang (2025).
---
Recommended Reading

Stanford on theory of mind in LLMs

AI is building its own economy — are humans ready?
Chinese chipmaker declares “war” on US giant
---
---
In Summary:
AI’s power lies in efficiency — but risks lie in homogenization. With conscious strategies, creators can harness AI while safeguarding originality.
Open-source platforms like AiToEarn官网 — enabling multi-platform publishing, analytics, and AI model ranking — offer infrastructure to keep creativity sharp and productive in the AI era.