Altman Admits Google Threatens OpenAI, to Launch New Model "Shallotpeat

The Situation Has Changed
With Google’s Gemini 3 Pro and Nano Banana Pro shaking up the AI industry, former benchmark-setter OpenAI is starting to feel the heat.
This shift may have been anticipated by OpenAI’s CEO, Sam Altman.

Altman’s Internal Warning
According to an internal memo leaked by The Information, Altman admitted to staff last month:
> Google’s recent advances in AI may bring some temporary economic headwinds to our company.
> We know we have work to do, but we are catching up quickly.
At that point, OpenAI researchers already knew Google was developing a superior model — Gemini 3.
Altman’s statements served two purposes:
- Reassure the team in CEO-speak.
- Subtly acknowledge that OpenAI had begun falling behind Google.
From Leader to Challenger
The question is:
- How did OpenAI lose its clear lead?
- How did Google reinvent itself in only three years?
The origins may trace back to a party Sergey Brin attended, where an OpenAI staffer named “Dan” asked him:
> In the greatest transformative moment in computer science, what are you doing?
That moment sparked Brin’s shift from relaxed, book‑reading afternoons to hands‑on AI work.
OpenAI may have inadvertently awakened a sleeping giant.

Google’s Recent Pressure
Both Gemini 3 Pro and Nano Banana Pro have been met with glowing reviews.
- Gemini 3 Pro was jokingly dubbed “GPT‑5.1” by netizens due to its leap over the previous version, 2.5 Pro.
- OpenAI’s models are now being used as benchmarks for Google’s progress, a sign of growing competition.
In an unusual move, Altman publicly congratulated Google:
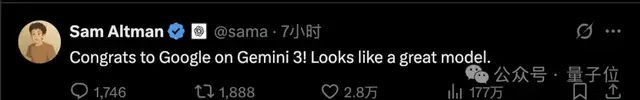
Yet the leaked memo shows he was far from relaxed:
> I expect the atmosphere out there will be rather unpleasant for a while.
Threats to Key Revenue Streams
Google’s Gemini 3 excels at:
- Automatic website generation
- Product design tasks
- Programming
Programming is one of OpenAI’s most important revenue streams. Losing ground here is a serious concern.

While ChatGPT still leads Gemini in usage and revenue, the gap is shrinking.
---
Financial Pressures
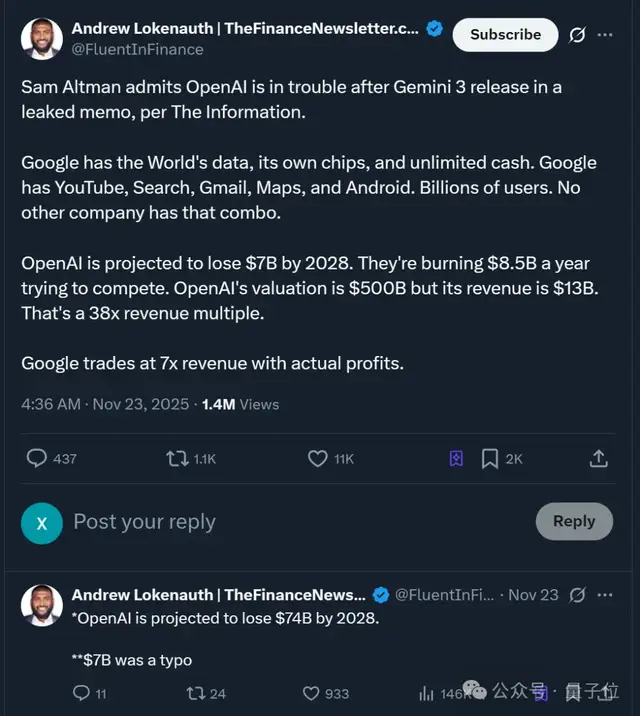
OpenAI’s growth is staggering:
- Revenue: From ~$0 in 2022 to an estimated $13 B in 2024.
- Costs: Over $100 B projected for pursuing human‑level AI, plus billions in server rentals.
Google, meanwhile:
- Market cap: $3.6 T
- Free cash flow: $70 B in the past year
- Cloud business: Profits partly boosted by renting servers to… OpenAI.
Simply put:
- OpenAI lacks a financial advantage.
- A portion of its spending to catch up flows back to Google via cloud service fees.
---
Morale Management
In his memo, Altman urged focus:
> We need to withstand short-term competitive pressure and stay focused… We have accumulated enough strength to endure the emergence of excellent models elsewhere.
Yet he admitted the burden:
> We have to do so many hard things at once — the best research lab, the best AI infrastructure company, the best AI platform/product company… this is our destiny.
Many observers note a weariness in his tone.
Public Perception
- Gemini 3 Pro launched
- OpenAI’s next move: adding a group chat feature to ChatGPT
- Online reactions: “trying to look busy without substance”
In effect, the offense–defense dynamic has reversed.
---
How Google Pulled Ahead
The Counterattack: Pretraining Success
OpenAI’s own memo identifies pretraining as the key:
> Google’s success in pretraining especially surprised many AI researchers…
Previously, OpenAI:
- Struggled to make gains during pretraining
- Focused on “reasoning models” that require more compute
By summer, while prepping GPT‑5, they discovered:
> Adjustments that worked for smaller models failed for larger ones.
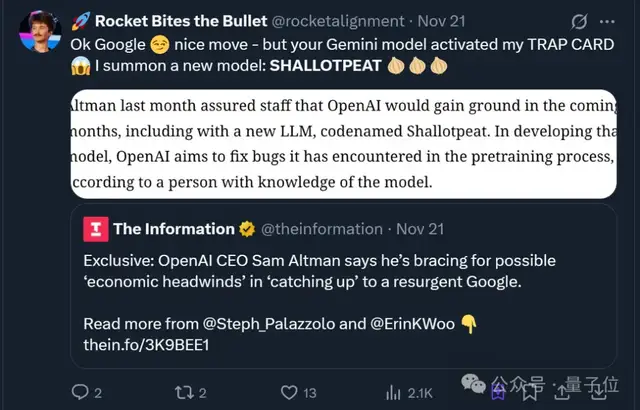
Next step: Release a new model, “Shallotpeat”, to fix pretraining challenges.
---
Industry-Wide Shift: Full‑Stack Competition
Google’s edge now comes from full‑stack control:
1. Infrastructure Layer
- Own TPUs + Google Cloud
- Control costs and strategy
- Even rents compute to rivals (including OpenAI)
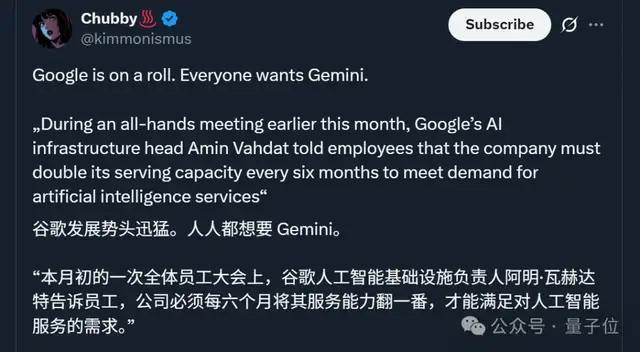
- Doubling service capacity every six months to meet AI demand
2. Products & Distribution Channels
- 2 B+ Android users
- Google Search and Workspace reach massive audiences
- Rapid AI integration into Search, YouTube, Android
3. The Virtuous Cycle
- Stronger models → Better products
- Better products → Faster user growth + richer data
- Richer data → More efficient pretraining → Stronger models
---
The Challenge for OpenAI
OpenAI now faces not just technical competition but a capital, compute, and distribution powerhouse.
The real drama is just beginning.
---
Parallel Trend: Tools for Independent Creators
As AI competition shifts toward full‑stack ecosystems, open‑source solutions help individuals participate at scale.
For example:
- AiToEarn官网 — an open‑source global AI content monetization platform
- AiToEarn开源地址 — connects AI generation tools, cross‑platform publishing, analytics, and model ranking
Creators can:
- Generate, publish, monetize content across multiple platforms
- Douyin, Kwai, WeChat, Bilibili, Rednote, Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, Threads, YouTube, Pinterest, X/Twitter
- Operate without massive infrastructure investment
These efforts show that AI’s reach is expanding beyond giants like OpenAI and Google to global creative communities.
---
Would you like me to create a summary infographic version of this rewritten article so your readers can quickly grasp key points visually? That could make the Google–OpenAI rivalry far more engaging.



