Average Photograph Size Guide for Print and Digital Media
Learn the ideal photograph sizes for print and digital use, including common dimensions, resolutions, file formats, and compression best practices.
Understanding Photograph Size and Its Importance
The average photograph size plays a crucial role in both digital and print media. It refers to the physical or pixel dimensions of an image and determines how sharp or clear it appears on different platforms. Digitally, it’s expressed in pixels (width x height), while in print it’s measured in inches or centimeters. The ideal size varies depending on the purpose — such as a Facebook profile picture, a wedding album spread, or a billboard.
Whether you’re a photographer, designer, or social media manager, mastering photograph sizes ensures:
- High image quality without pixelation
- Correct aspect ratio for various layouts
- Faster website load times through optimized file sizes
- Professional presentation for both print and online use
A mismatch between photo resolution and the intended use can lead to disappointing visuals and wasted storage space.
---
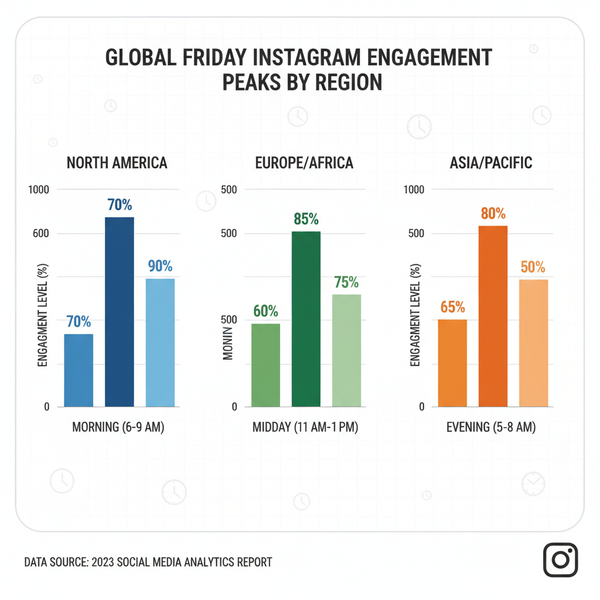
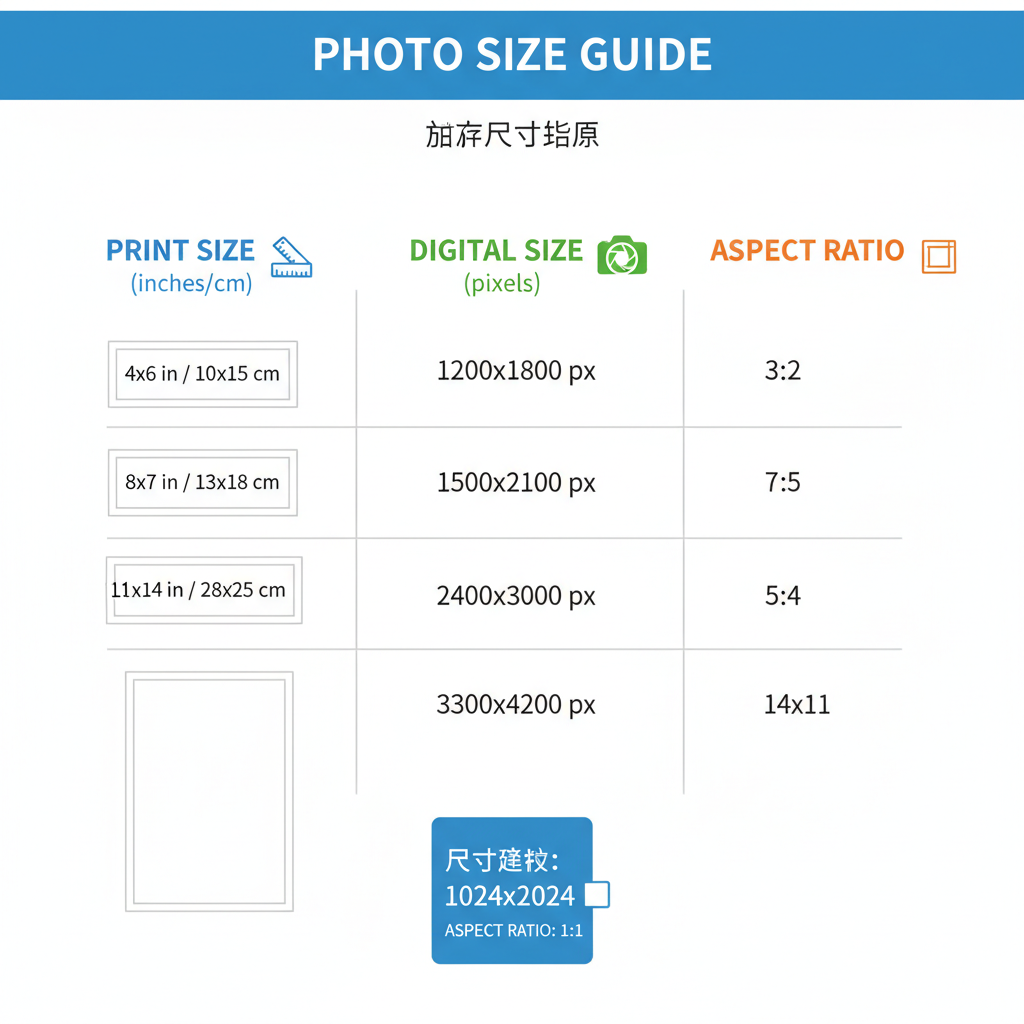
Common Photograph Dimensions for Print
When printing photographs, it's common to rely on industry-standard dimensions — many of which date back to film photography but remain widely used today.
Standard Print Sizes
Here are some widely used print dimensions with their inch and centimeter equivalents:
| Print Size (inches) | Size (centimeters) | Common Use |
|---|---|---|
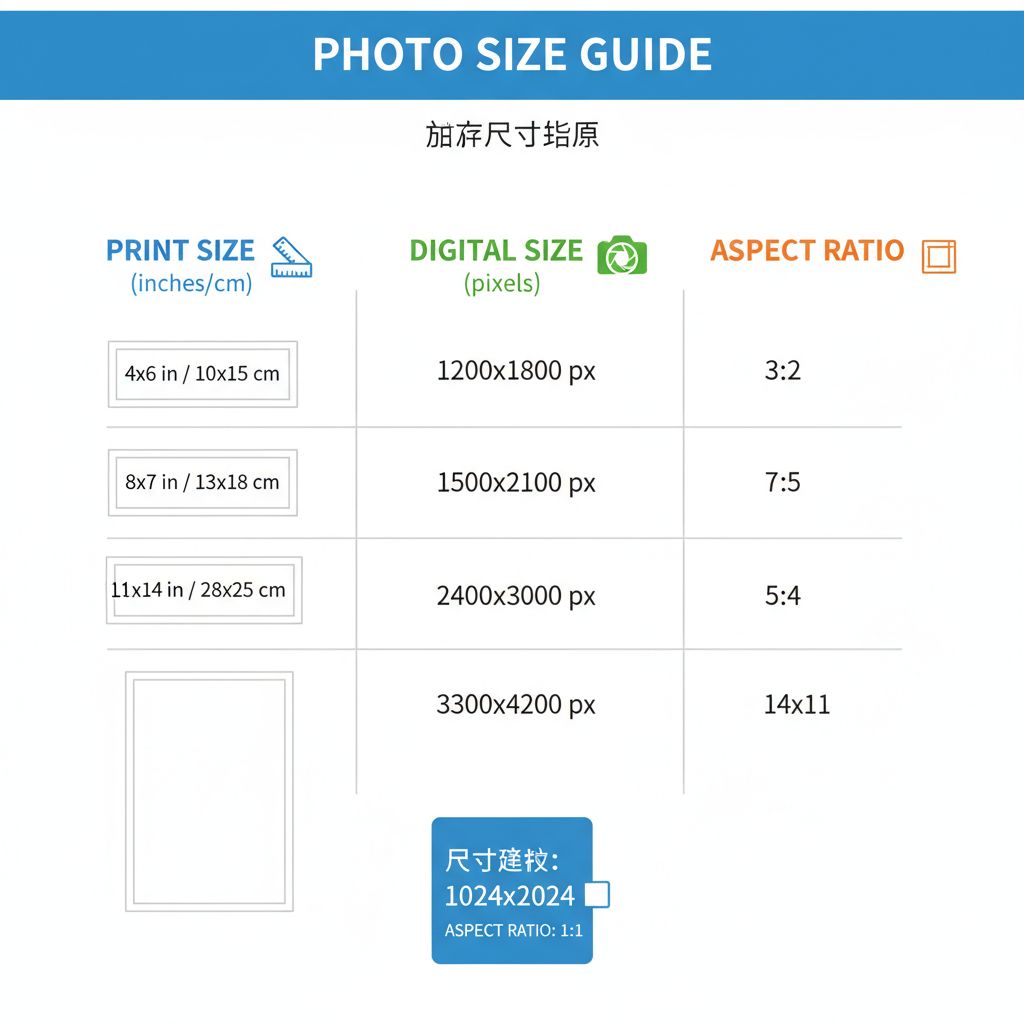
| 4 x 6 | 10.2 x 15.2 | Standard snapshot prints |
| 5 x 7 | 12.7 x 17.8 | Framed photos |
| 8 x 10 | 20.3 x 25.4 | Portrait / Studio prints |
| 11 x 14 | 27.9 x 35.6 | Posters / Wall art |
| 16 x 20 | 40.6 x 50.8 | Large format prints |
Tip: For top-quality printing, aim for 300 DPI (dots per inch) or higher. For instance, a 4 x 6 print should be at least 1200 x 1800 pixels.
---
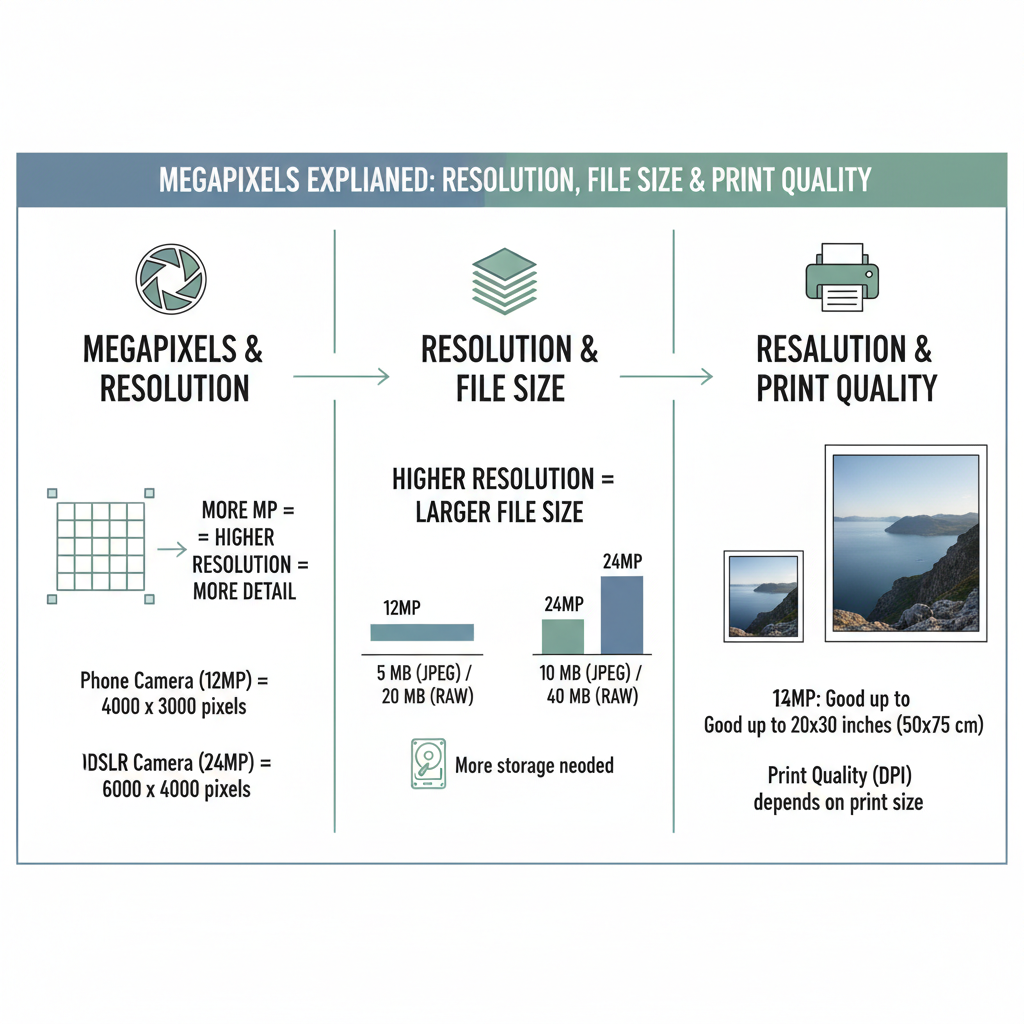
Average Digital Photograph Size in Pixels
Digital photo sizes are generally determined by the resolution capability of your device's camera sensor.
Common Camera/Phone Resolutions
Most modern smartphones and digital cameras capture between 12 MP and 48 MP:
- 12 MP: ~4000 x 3000 pixels
- 24 MP: ~6000 x 4000 pixels
- 48 MP: ~8000 x 6000 pixels
For online publishing, smaller images are more practical — for example, 1200 x 800 pixels is often enough for a blog post feature image.
---
How Megapixels Affect Image Resolution and File Size
One megapixel (MP) equals one million pixels. More megapixels mean:
- Higher resolution and detail
- Larger file sizes that require more storage
- More flexibility for cropping without losing sharpness
Example:
- 12 MP (~4000 x 3000 px): ~3–5 MB as JPEG
- 48 MP (~8000 x 6000 px): ~15–25 MB as JPEG, larger in RAW
---
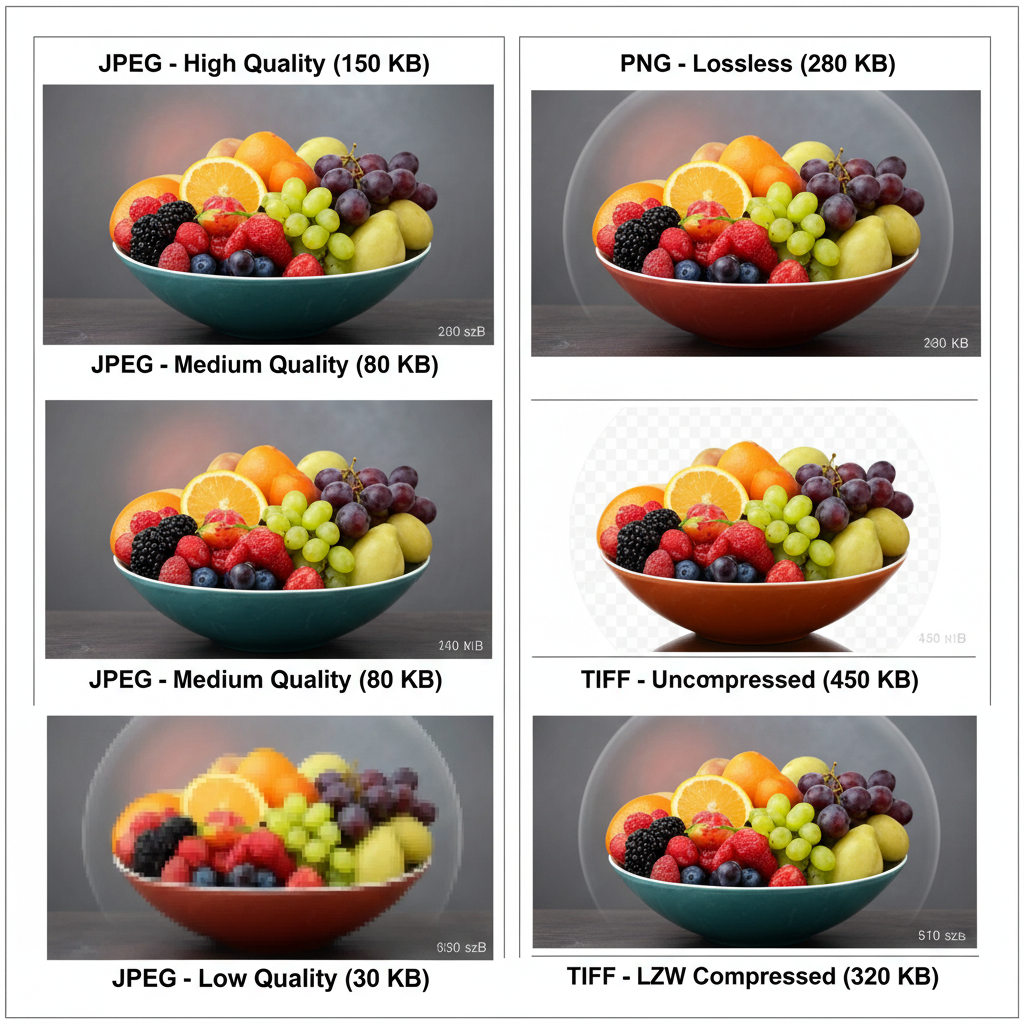
File Formats and Their Average Sizes
Your chosen file format also affects the image’s file size:
| File Format | Description | Average Size (12 MP) | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| JPEG | Compressed, lossy format | 3–5 MB | Web, general photography |
| PNG | Lossless compression with transparency | 5–10 MB | Graphics, screenshots |
| RAW | Uncompressed sensor data | 20–30 MB+ | Professional editing |
Note: RAW files offer superior editing flexibility but require significant storage space.
---
The Impact of Compression and Quality Settings
Compression is used to shrink file sizes by removing data — but overdoing it can degrade visuals:
- Low compression / high quality → Better detail, larger files
- Medium compression → Balanced file size and quality for web use
- High compression / low quality → Noticeable artifacts, smaller files
Tools like Adobe Lightroom, TinyPNG, and Squoosh can help compress without major quality loss.
---
Choosing the Right Size for Different Purposes
The average photograph size you choose should match your intended platform:
- Social Media
- Instagram feed: 1080 x 1080 px (square) / 1080 x 1350 px (portrait)
- Facebook cover: 820 x 312 px
- Twitter header: 1500 x 500 px
- Web
- Blog feature image: 1200 x 800 px
- Website banner: 1920 x 1080 px
- Thumbnail: 150 x 150 px
- Small print: 4 x 6 in at 300 DPI → 1200 x 1800 px
- Poster: 24 x 36 in at 150 DPI → 3600 x 5400 px
---
Tips for Resizing Without Losing Quality
Follow these steps for consistent results:
- Start with a high-resolution original
- Downscale rather than upscale
- Use bicubic or Lanczos resampling in editing software
- Keep an archive of the original files
Free tools like GIMP, Paint.NET, Canva, and Pixlr make resizing straightforward.
---
Storage Considerations for High-Resolution Photographs
Storing high-res photos requires careful planning:
- External hard drives for affordable backups
- NAS systems for team access
- Cloud storage (Google Drive, Dropbox, OneDrive) for anywhere access
Storage estimation:
- 1,000 JPEGs (~5 MB each) = ~5 GB
- 1,000 RAW files (~25 MB each) = ~25 GB
---
Average Photograph Size Quick Reference
| Use Case | Recommended Size | Resolution / Pixels | Approx. File Size |
|---|---|---|---|
| Social Media (Instagram) | Portrait / Square | 1080 x 1350 / 1080 x 1080 | 500 KB – 1.5 MB (JPEG) |
| Blog Feature | Landscape | 1200 x 800 | 1–2 MB (JPEG) |
| Standard Print (4x6) | Photo Print | 1200 x 1800 | 2–4 MB (JPEG) |
| Poster (24x36) | Large Print | 3600 x 5400 | 6–15 MB (JPEG at 150 DPI) |
| RAW Photo (12 MP) | Professional Editing | 4000 x 3000 | 20–30 MB |
---
Summary
Choosing the right average photograph size ensures that your images look crisp and load efficiently, whether you’re posting on social media, designing a website, or preparing prints. By understanding dimensions, resolution, formats, and compression, you can strike the ideal balance between image quality and file size.
Next step: Evaluate where your photos will be used, determine the needed resolution, and adjust your shooting or export settings accordingly for professional results every time.