Baidu’s Big Data Cost Governance Practices
Introduction
This article presents cost governance practices for big data within Baidu MEG (Mobile Ecosystem Group), set against the backdrop of rapid business growth and the imperative to reduce costs and increase efficiency. It addresses:
- Key challenges currently faced
- Optimization strategies for computing and storage
- Governance achievements
- Future directions
The goal is to offer the industry actionable governance experience.
Total: 7,590 words | Estimated read time: 19 minutes
---
01 Background
With Baidu’s business expansion, offline data volumes — and the associated costs — are rising dramatically. Applying big data governance is critical to sustain growth while controlling expenditure.
We examined the situation from three perspectives:
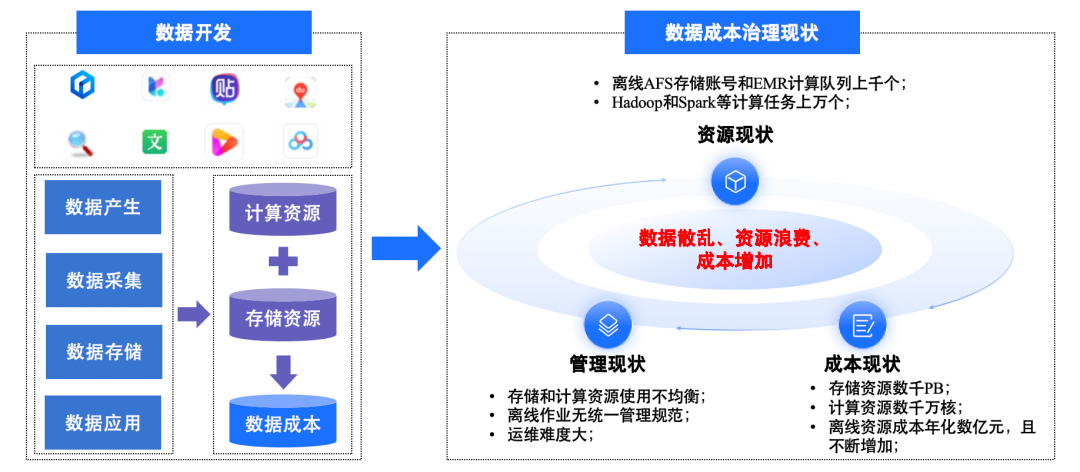
Resource Status
- Multiple offline business types across product lines
- Hundreds/thousands of AFS (Appendonly File Storage) accounts and EMR (E-MapReduce) queues
- No unified governance start plan or standard
Management Status
- Uneven resource utilization
- Inconsistent storage/computing queue management
- Lack of comprehensive procedures
- Inefficient computing tasks, challenging maintenance
Cost Status
- Tens of millions of offline computing cores
- Thousands of petabytes of storage
- Annual costs in the billions RMB
- Without optimization, costs will continue to climb
Summary
Key issues include:
- Data fragmentation
- Resource waste
- Escalating costs
Solution: Create unified governance standards and a big data resource management platform to deliver:
- Storage, computing, task, and cost views per product line
- Engine-level optimization for storage and computing
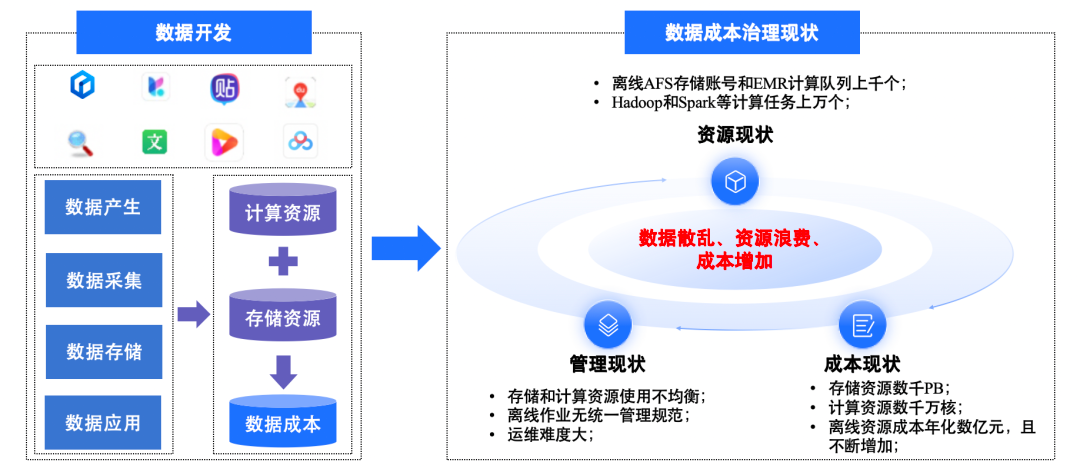
△ Current state of data cost governance
---
02 Data Cost Governance Practice Plan
2.1 Overall Governance Framework
We devised a framework comprising:
- Data asset health measurement
- Platform capabilities
- Engine empowerment
Focus: Computing + Storage governance for cost reduction and efficiency.
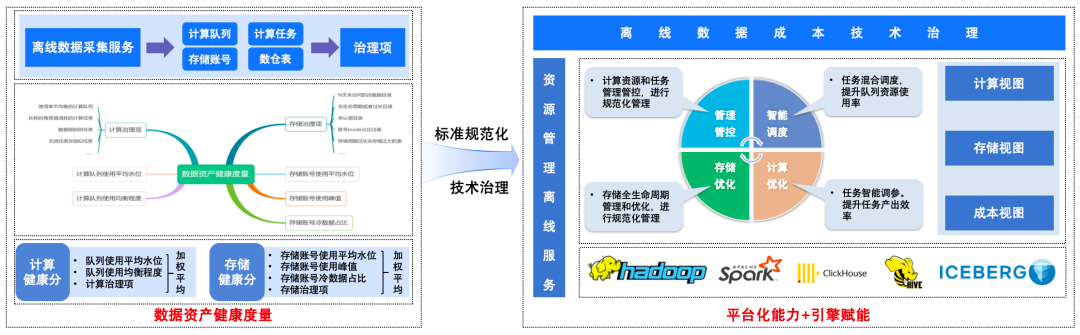
△ Overall framework for data cost governance
---
2.1.1 Data Asset Health Measurement
We introduced a unified health score metric to assess computing and storage resources.
Data Collection
From an offline data acquisition service, gathering:
- Computing queues
- Tasks
- Storage accounts
- Data tables
Governance Items
- Computing: Uneven utilization, long-running high-resource tasks, data skew, invalid tasks.
- Storage: Cold data (1/2/N years), anomalous lifecycles, low inode utilization, unclaimed directories.
Health Scores
- Computing Health = Weighted average of utilization, balance, governance items.
- Storage Health = Weighted combination of usage, peak, cold data ratio, governance factors.
Benefit: Consistent, standardized measurement guides governance across product lines.
---
2.1.2 Platform Capabilities
Our Big Data Resource Management Platform aggregates all offline computation and storage data into:
- Computation View: Queue usage, tasks, lifecycle management, optimization.
- Storage View: Account usage, directory cleanup, migration, cold data mining.
- Cost View: Unified visual of total offline resource costs.
---
2.1.3 Engine Empowerment
Many users lack tuning awareness for tasks. We leverage engine capabilities to:
- Computation: Machine learning-driven intelligent parameter tuning for optimal configurations.
- Storage: Analyze datasets for smart compression without impacting performance.
---
03 Computation & Storage Cost Optimization
3.1 Computation Governance
Three key optimizations:
3.1.1 Management Control
- Manage >1,000 EMR queues, >10,000 Hadoop/Spark tasks
- Apply 30+ real-time control policies, e.g.:
- Concurrency limits
- Basic parameter tuning
- Zombie task control
- Coverage: Millions of cores, 200,000+ daily control triggers.
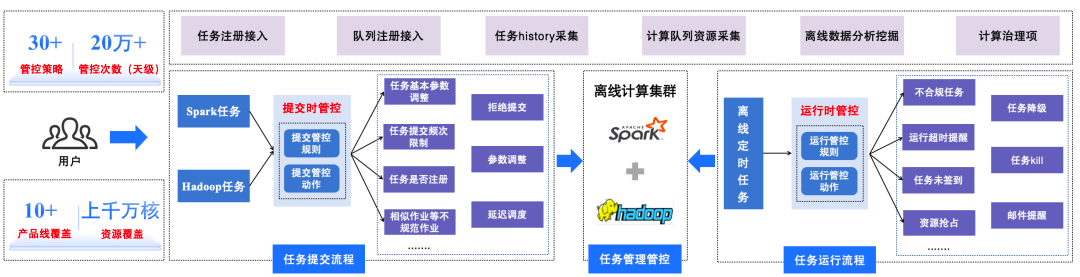
△ Task Management and Control Workflow
---
3.1.2 Hybrid Scheduling
Findings:
- Hadoop: High CPU, low memory
- Spark: Lower CPU, high memory
- Low average utilization with time-varying peaks
- Queue fragmentation
Solution:
Hadoop + Spark hybrid scheduling:
- Submission: Rank tasks by priority + time
- Scheduling: Apply strategy chains for optimal queue selection
- Execution: Balanced utilization, improved low-frequency queues
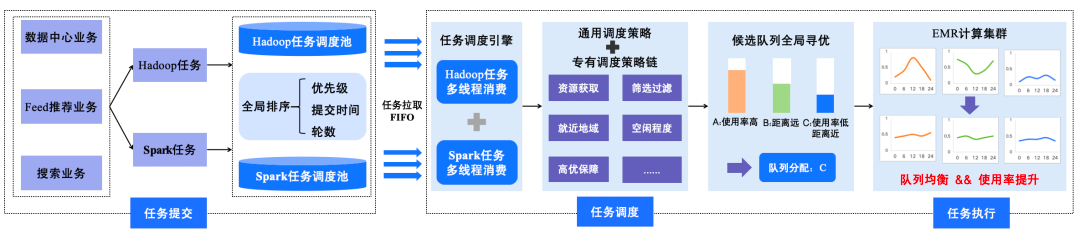
△ Task Hybrid Scheduling Workflow
---
3.1.3 Intelligent Parameter Tuning
Challenges:
- Poor configuration awareness → wasted resources
- Spark engine optimizers overlook routine job-specific info
Solution:
- Model-trained tuning for `spark.executor.instances`, `spark.executor.cores`, `spark.executor.memory`
- Iterative parameter recommendation & feedback cycles
- HBO (History Based Optimization):
- Joins/Aggregations tuning
- Shuffle partition adjustment
- Serialization optimization
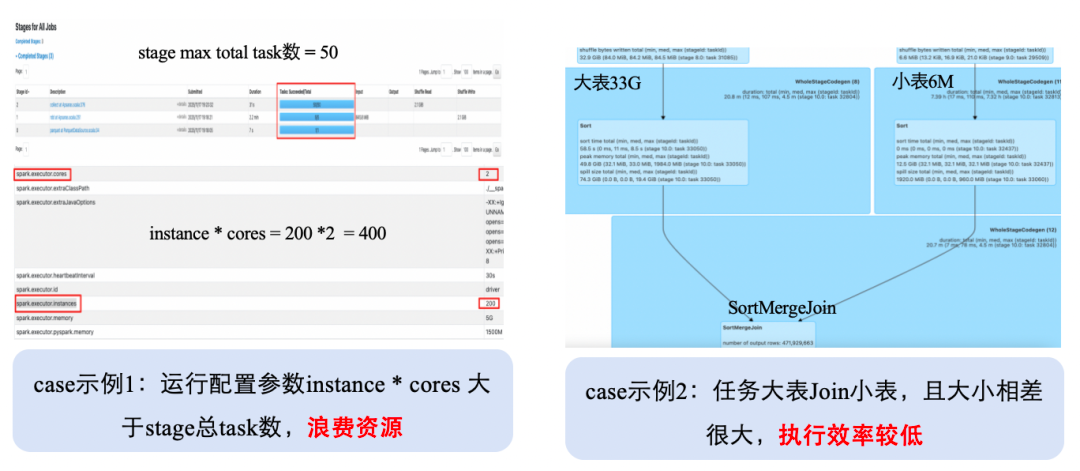
△ Task Parameter Configuration Case
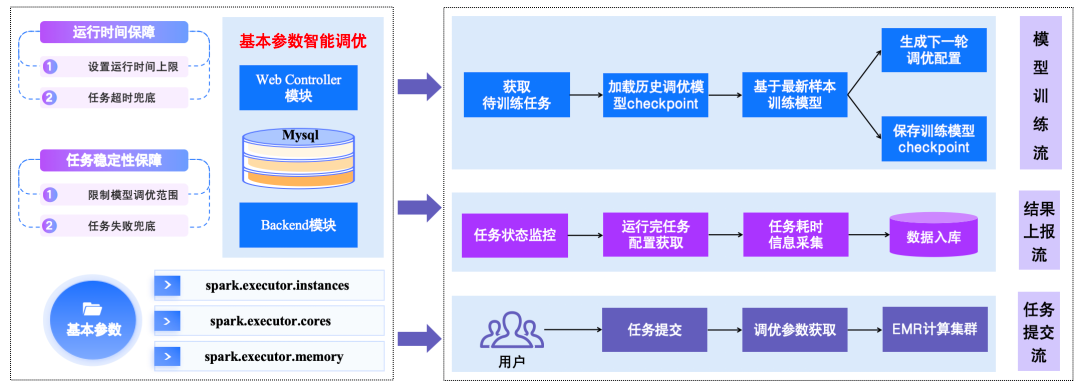
△ Basic Parameter Intelligent Tuning Flow
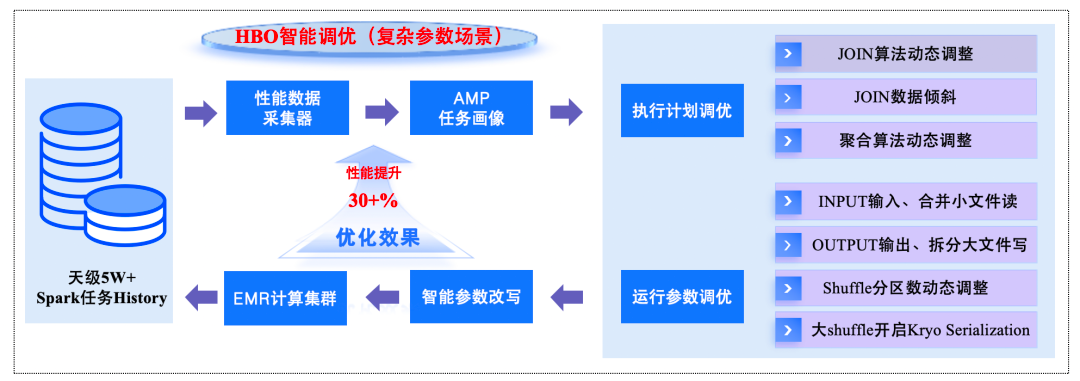
△ HBO Intelligent Tuning Flow
---
3.2 Storage Governance
Current Issues:
- Numerous unassigned accounts without quotas
- Data growth with redundant historical data
- Weak security controls
---
3.2.1 Lifecycle Management
Five layers:
- Access Layer: Standards for usage, quota, cold data handling
- Service Layer: Cold data detection, cost analysis
- Storage Layer: Ownership metadata in MySQL, usage in Table system
- Execution Layer: Daily cleanup, compression, monitoring
- User Layer: Dashboards, APIs, governance tools
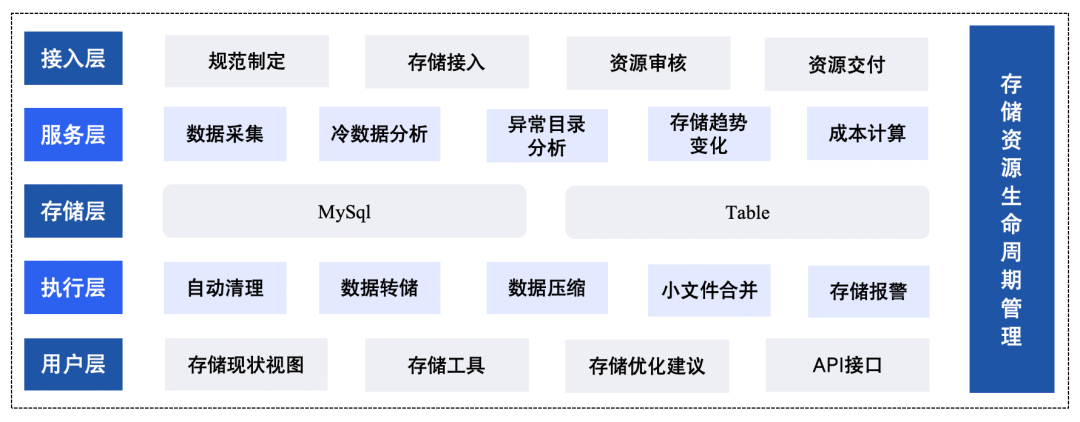
△ Storage Lifecycle Management Process
---
3.2.2 Basic Governance
- Parse quota + cold data
- Monitor trends, detect anomalies
- User-configured cleanup/compression/monitoring
- Scheduled execution via backend services
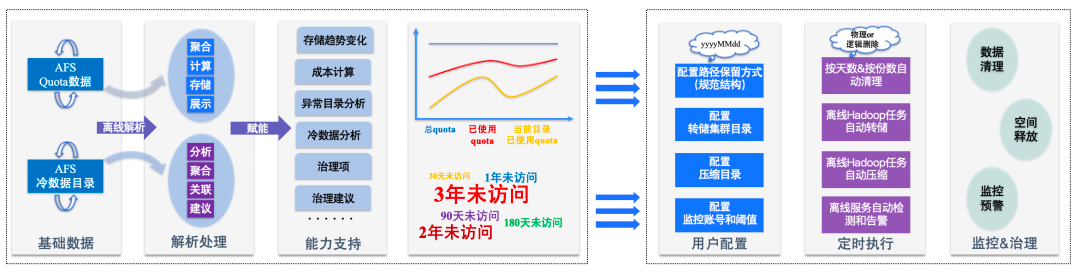
△ AFS Storage Basic Governance Process
---
3.2.3 Intelligent Compression
- Data Warehouse Tables: Sort optimization, ZSTD compression, page size/level tuning
- Non-DW Tables: Hot/warm/cold classification, format optimization, scheduled compression
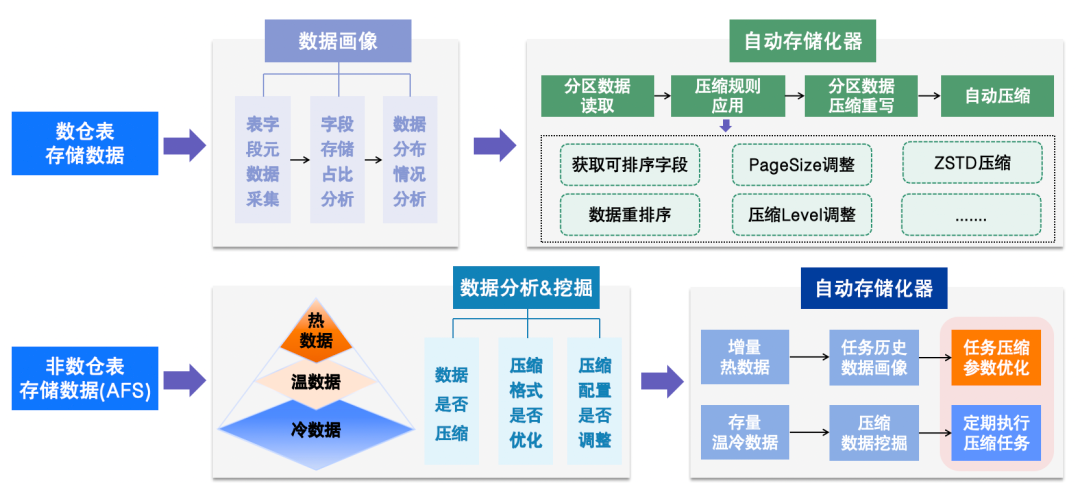
△ Intelligent Compression Process
---
Governance Achievements
Data Development & Cost Optimization
- Efficiency: Resource delivery from weeks → daily cycles
- Computing Cost: +30% EMR core utilization → tens of millions RMB saved annually
- Storage Efficiency: Managed thousands of accounts, cleaned unused data
- Storage Cost: +20% utilization → hundreds of PB freed
Governance Assets
- Standardized development processes
- Resource usage & cost dashboards
- Task lifecycle overviews
- Detailed governance item dashboards
---
Future Plans
We will:
- Continue refining standardized, intelligent governance
- Integrate lessons into processes and standards
- Explore AI-powered automation for broader applications
Data-heavy enterprises can benefit from similar AI + governance frameworks for both technical and creative workflows, ensuring efficiency, traceability, and sustainable growth.



