Best Buffer System Selection and Applications Guide
Learn how to choose the best buffer system for pH stability in labs, pharmaceuticals, food, and more with key factors, uses, and comparisons.
Introduction to Buffer Systems and Their Importance
Buffer systems are vital in science, engineering, medicine, and industry for maintaining a stable pH. This stability ensures chemical reactions, biological processes, and industrial operations run under optimal conditions. Whether in medical laboratories analyzing patient samples, pharmaceutical facilities stabilizing drug formulations, or environmental engineering projects, the best buffer system safeguards precision and consistency. Without an appropriate buffer, results can be inconsistent, costly, or unusable.
In many fields, the proper selection and handling of the best buffer system is the difference between reliable results and failed experiments.
---
What is a Buffer System and How it Works Chemically
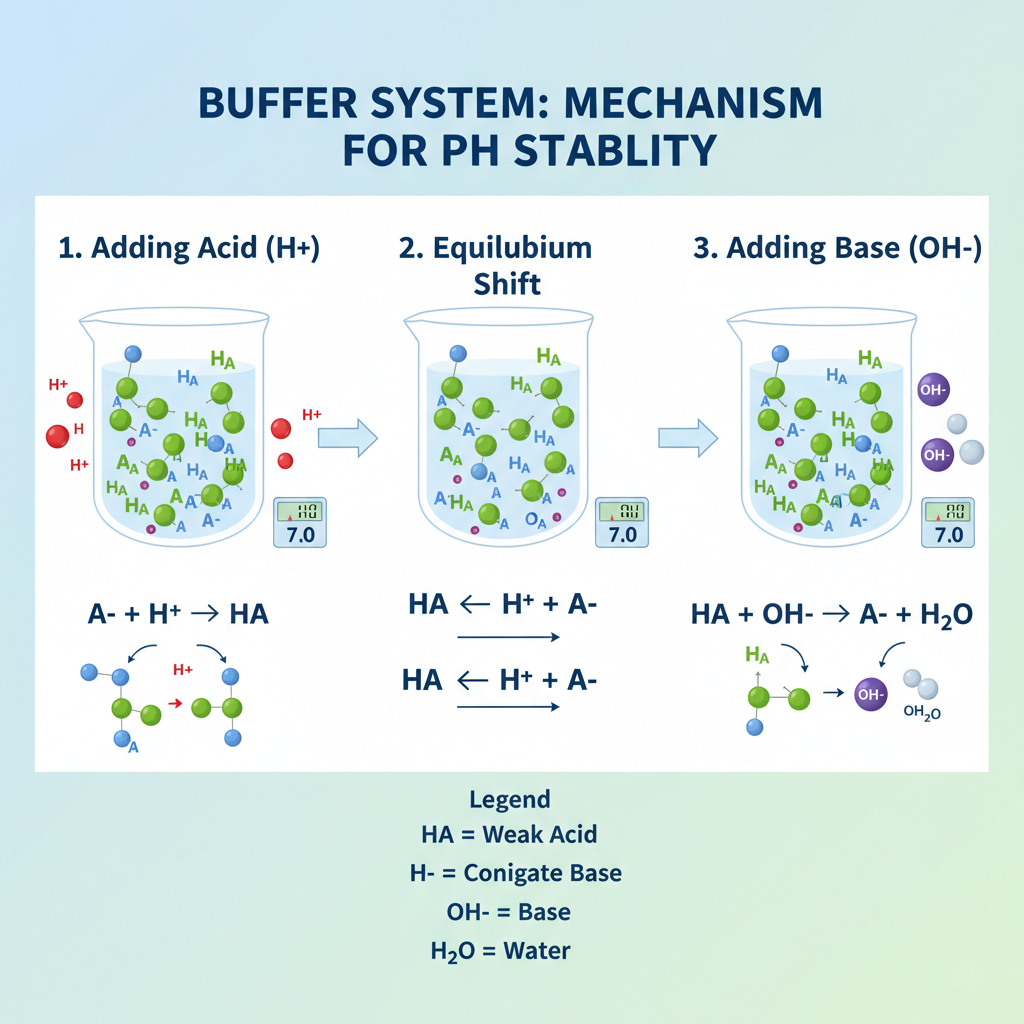
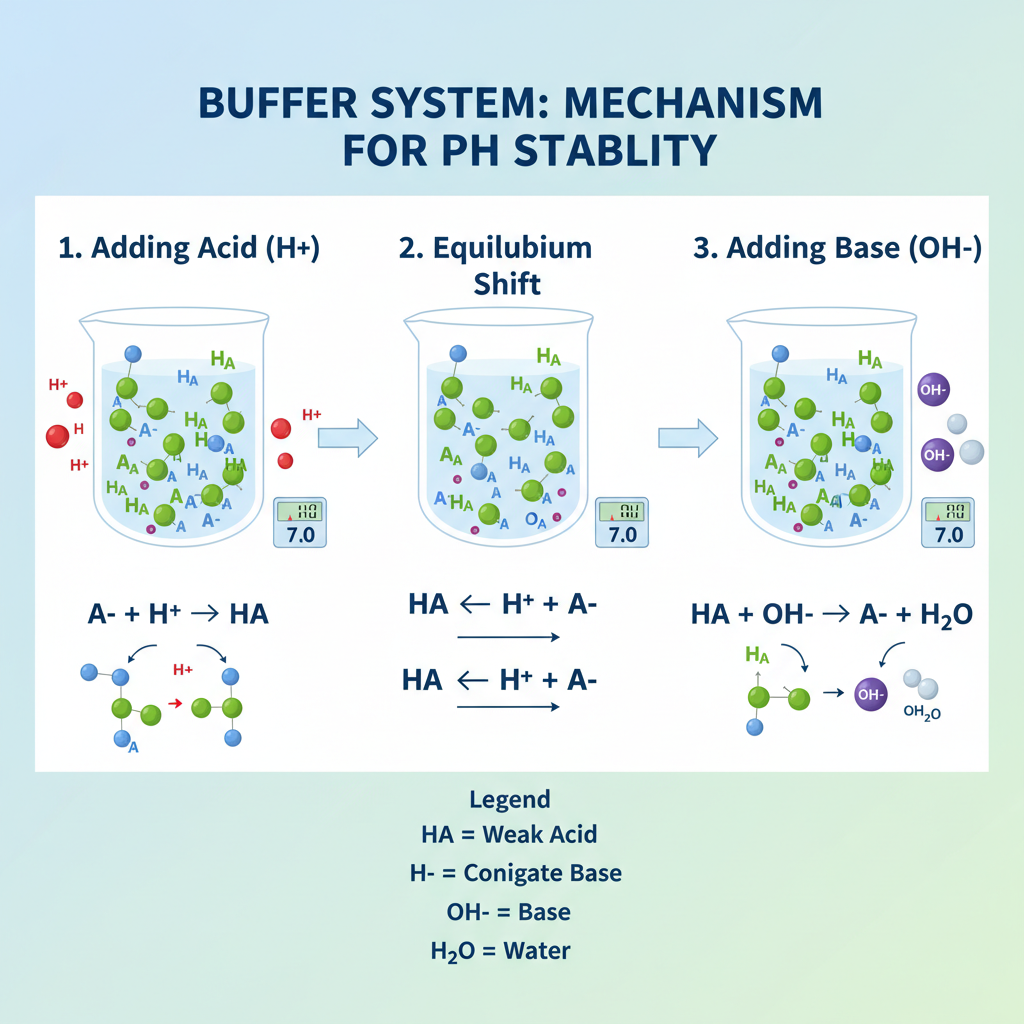
A buffer system is a solution that resists pH changes when small amounts of acids or bases are introduced. Typically, it consists of:
- A weak acid and its conjugate base
- Or a weak base and its conjugate acid
When an acid (H⁺) is added, the buffer’s conjugate base neutralizes it. Conversely, when a base (OH⁻) is added, the weak acid component neutralizes it. This buffering effect is explained by the Henderson–Hasselbalch equation:
pH = pKa + log([A⁻]/[HA])Where:
- pKa = acid dissociation constant
- [A⁻] = concentration of conjugate base
- [HA] = concentration of weak acid
By adjusting the ratio of acid to conjugate base, a buffer can be tailored to a precise pH range.
---
Common Applications of Buffer Systems
Buffers are indispensable across industries and research fields:
- Laboratories – For enzymatic assays, nucleic acid stability, and protein purification
- Pharmaceuticals – Stabilizing injectable solutions, oral medications, and topical formulations
- Food Industry – Controlling acidity, enhancing flavor, and extending shelf-life
- Aquariums – Maintaining stable water chemistry for aquatic organisms
- Agriculture – Regulating nutrient availability and soil pH
Choosing the best buffer system for each application ensures accuracy, product quality, and regulatory compliance.
---
Key Factors in Choosing the Best Buffer System
When selecting your buffer, evaluate:
- Target pH Range – Choose buffers where pKa ≈ target pH for maximum effectiveness
- Ionic Strength – Critical for biological systems; influences macromolecule stability
- Temperature Stability – Avoid buffers with large pH shifts across your working temperature range
- Chemical Compatibility – Prevent interference with detection assays or reactions
- Cost & Availability – Readily accessible components simplify workflow
- Safety – Consider toxicity when working with living systems or pharmaceuticals
---
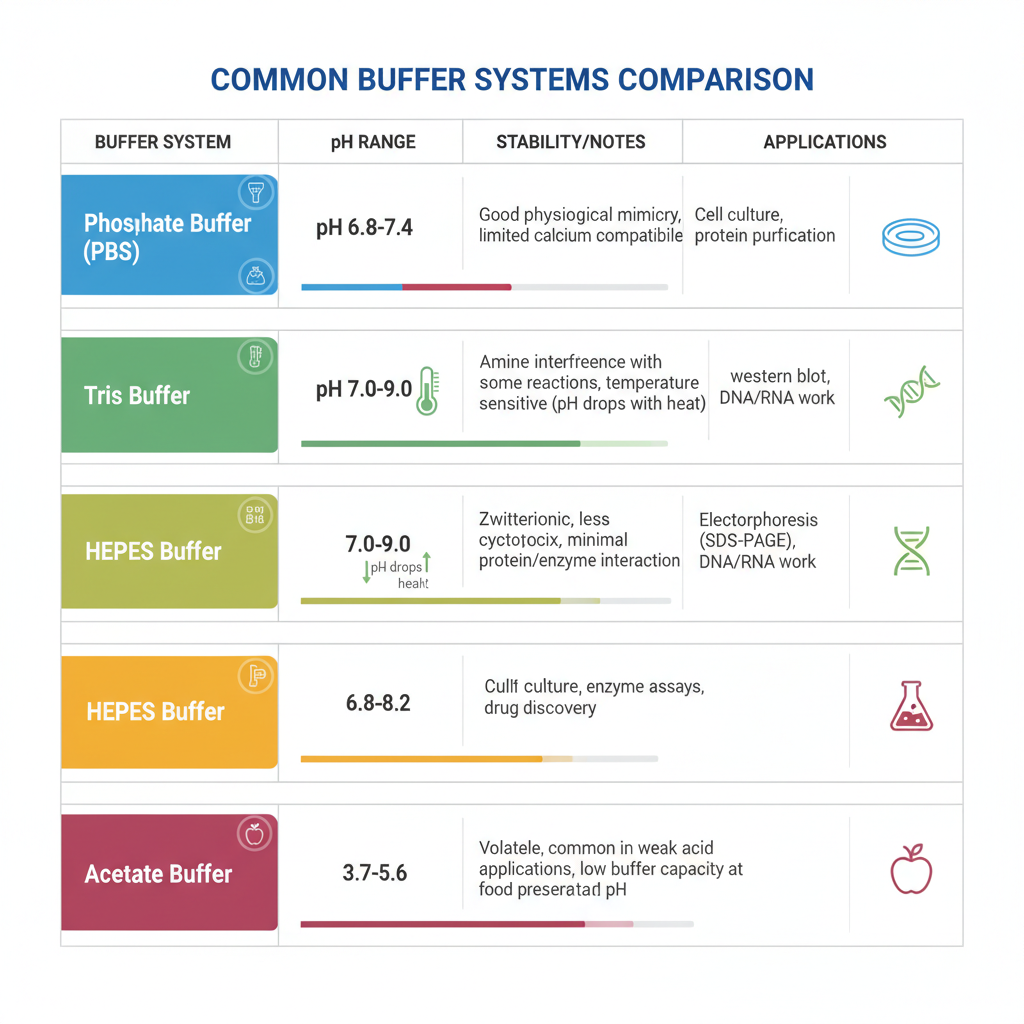
Comparison of Popular Buffer Systems
| Buffer System | pKa at 25°C | Effective pH Range | Main Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phosphate Buffer | 7.2 | 6.5–7.5 | Cell culture, molecular biology, biochemical assays |
| Tris Buffer | 8.1 | 7.0–9.0 | Protein work, electrophoresis, nucleic acid analysis |
| Citrate Buffer | 3.1, 4.7, 5.4 | 3.0–6.2 | Food industry, pharmaceuticals, antigen retrieval |
| Acetate Buffer | 4.76 | 3.6–5.6 | Microbiology, enzyme reactions, food preservation |
---
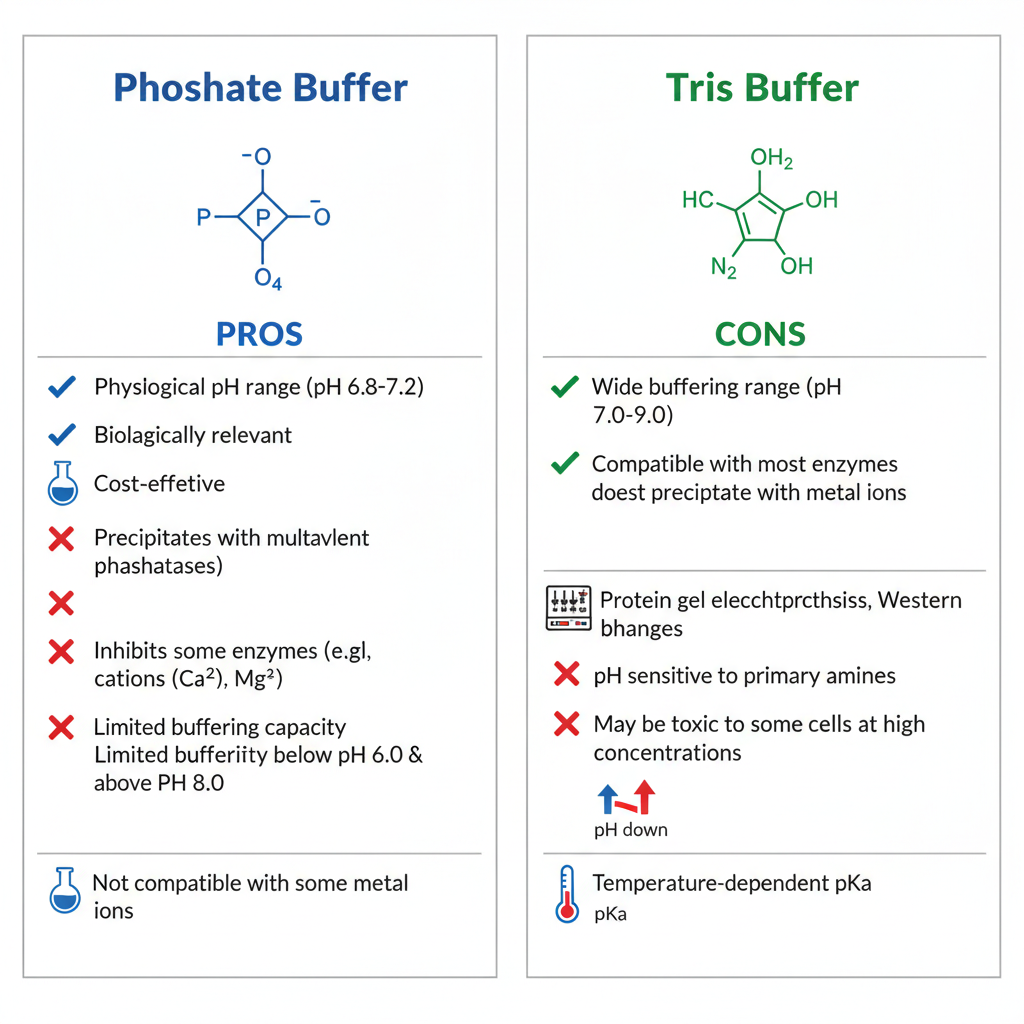
Pros and Cons of Each Buffer Type
Phosphate Buffer
Pros:
- Strong buffering near neutral pH
- Broad biological compatibility
- Non-toxic in most applications
Cons:
- Precipitates with divalent cations (Ca²⁺, Mg²⁺)
- Possible enzyme inhibition
Tris Buffer
Pros:
- Ideal for slightly alkaline conditions
- Stable at room temperature
Cons:
- Temperature-dependent pH variations
- May interact with aldehyde fixatives
Citrate Buffer
Pros:
- Strong buffering in acidic ranges
- Metal-chelating capability
Cons:
- Removes essential metal cofactors in enzymes
- Limited for processes needing those metals
Acetate Buffer
Pros:
- Inexpensive and easy to prepare
- Useful in microbiological work
Cons:
- Narrow pH range
- Volatile at high temperatures
---
Guidelines for Preparing and Maintaining a Buffer System
To ensure a consistent best buffer system:
- Apply Henderson–Hasselbalch equation to determine component concentrations
- Dissolve components in distilled water for purity
- Adjust pH with strong acids or bases carefully
- Account for temperature using a compensated pH meter
- Sterilize appropriately — filter for heat-sensitive buffers
- Store correctly away from light and extreme temperatures
- Label storage containers with all relevant information
Regular inspections help prevent microbial contamination or precipitation.
---
Safety Considerations and Handling Practices
Follow these protocols for all buffer handling:
- Wear PPE: gloves, goggles, lab coat
- Avoid inhalation and ingestion
- Use caution when handling acids and bases
- Dispose of chemical waste responsibly
- Prevent incompatibility reactions (e.g., phosphate + calcium-rich media)
---
Troubleshooting Common Buffer Issues
pH Drift
Cause: CO₂ absorption, evaporation, temperature fluctuation
Solution: Seal containers, maintain constant temperature, prepare fresh buffers
Contamination
Cause: Microbial growth
Solution: Work sterile, refrigerate, or add allowed preservatives
Precipitation
Cause: Incompatible ions or oversaturation
Solution: Switch buffers or adjust concentrations; filter solutions
---
Conclusion and Recommendations
Selecting the best buffer system depends on pH requirements, chemical compatibility, and application-specific factors:
- Neutral pH biochemical assays → Phosphate buffer offers stability and compatibility, but watch for ionic precipitation
- Alkaline protein work → Tris buffer excels if temperature is carefully managed
- Acidic or chelating needs → Citrate buffer is versatile for food and pharmaceuticals
- Microbial acidic media → Acetate buffer remains cost-effective and easy to prepare
By carefully matching your buffer to your experimental needs and adhering to preparation best practices, you enhance reproducibility, safety, and efficiency. For consistently reliable outcomes, invest time in selecting and maintaining the best buffer system for your laboratory or industrial process.