BigQuery AI Functions: A New Chapter in the AI Era of SQL
Introduction
For decades, SQL has been the universal language for data analysis, especially for structured data.
Now, Large Language Models (LLMs) such as Gemini bring nuanced insights to unstructured data — text, images, and videos.
Historically, integrating LLMs into SQL workflows meant moving data, tuning prompts/parameters, and incurring high scaling costs — limiting adoption for many data practitioners.
---
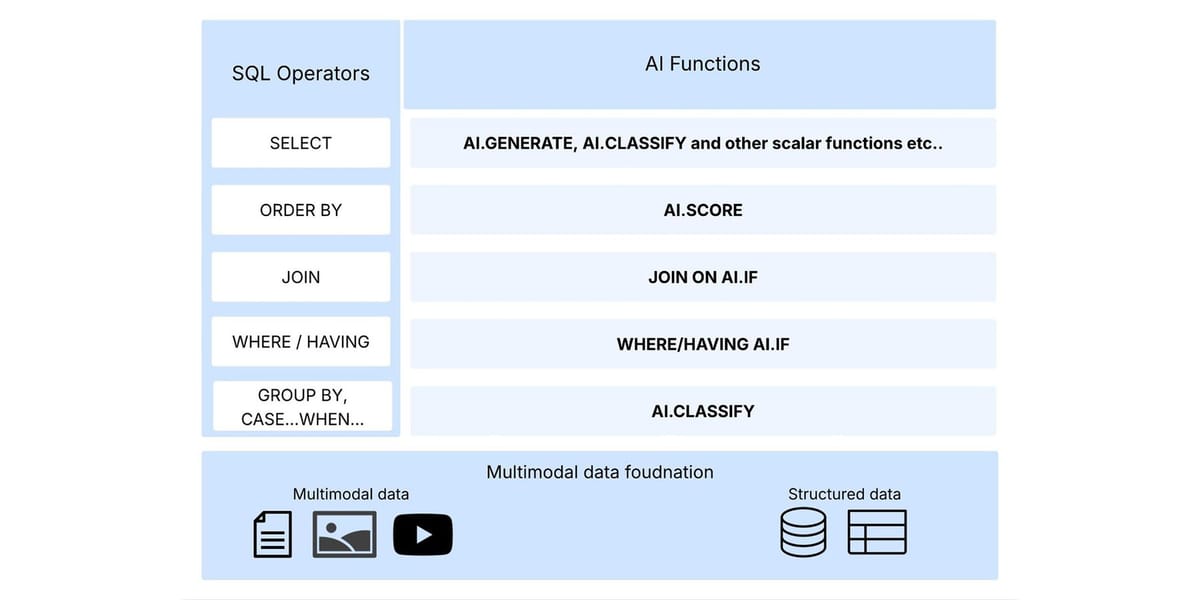
BigQuery-Managed AI Functions (Public Preview)
We’re excited to announce the public preview of BigQuery-managed AI functions — a set of SQL-native capabilities for the AI era.
Available functions:
- `AI.IF` – Semantic filtering and joining
- `AI.CLASSIFY` – Categorization of text or images
- `AI.SCORE` – Natural language ranking
Key advantages:
- Direct integration into SQL queries — no complex prompt engineering
- Optimized per use case — no manual model selection or parameter tuning
- Lower costs through intelligent prompt processing and query execution
---
What You Can Do
- Semantic filter/join:
- Use `AI.IF` in `WHERE` or `ON` clauses
- Categorize data:
- Use `AI.CLASSIFY` in `GROUP BY` clauses
- Rank by criteria:
- Use `AI.SCORE` in `ORDER BY` clauses
These functions make AI-powered workflows seamless for analysts and engineers.
---
Example Use Case: Content Creation and Publishing
Platforms like AiToEarn官网 complement BigQuery AI functions by combining:
- AI generation
- Analytics
- Multi-platform publishing
- (e.g., Douyin, Kwai, WeChat, Bilibili, Rednote/Xiaohongshu, Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, Threads, YouTube, Pinterest, X/Twitter)
This pairing lets users convert AI insights into shareable, monetizable content.
---
Function Deep Dive
AI.IF — Semantic Filtering & Joining
Purpose: Filter or join data based on conditions written in natural language.
Use cases:
- Detect negative customer reviews
- Find images with certain attributes
- Extract relevant document content
Optimization: BigQuery evaluates non-AI filters first to reduce LLM calls.
Example — Semantic Filtering:
SELECT title, body
FROM bigquery-public-data.bbc_news.fulltext
WHERE AI.IF(("The news is related to Google, news: ", body),
connection_id => "us.test_connection")
AND category = "tech" -- Non-AI filter evaluated firstExample — Semantic Join for Entity Resolution:
WITH product_catalog_A AS (
SELECT "Veridia AquaSource Hydrating Shampoo" AS product
UNION ALL
SELECT "Veridia Full-Lift Volumizing Shampoo"
),
product_catalog_B AS (
SELECT "Veridia Shampoo, AquaSource Hydration" AS product
)
SELECT *
FROM product_catalog_A a
JOIN product_catalog_B b
ON AI.IF((a.product, " is the same product as ", b.product),
connection_id => "us.test_connection")---
AI.CLASSIFY — Data Classification
Purpose: Categorize text or images into user-specified labels.
Use cases:
- Route support tickets by topic
- Classify images by style
- Categorize articles by subject
Example — Content Categorization:
SELECT
AI.CLASSIFY(
body,
categories => ['tech', 'sport', 'business', 'politics', 'entertainment'],
connection_id => 'us.test_connection') AS category,
COUNT(*) num_articles
FROM bigquery-public-data.bbc_news.fulltext
GROUP BY category;---
AI.SCORE — Semantic Ranking
Purpose: Rank rows using natural language criteria.
Automated benefit:
BigQuery refines prompts into a structured scoring rubric for higher quality results.
Example — Ranking Top Positive Reviews:
SELECT
review,
AI.SCORE(("From 1 to 10, rate how much does the reviewer like the movie :", review),
connection_id => 'us.test_connection') AS ai_rating,
reviewer_rating AS human_rating
FROM bigquery-public-data.imdb.reviews
WHERE title = 'Movie'
ORDER BY ai_rating DESC
LIMIT 10;---
Built-In Optimizations
BigQuery-managed AI functions include:
- Prompt Optimization
- Transforms prompts for Gemini to boost quality and consistency
- Improves cache hit rates
- Query Plan Optimization
- Reduces LLM calls by reordering filters and joins
- Model Endpoint & Parameter Tuning
- Improves quality and consistency across executions
---
Getting Started
These functions complement general-purpose Gemini inference functions like `AI.GENERATE`.
Early Access: Sign up here
Documentation:
- Overview
- Python usage in notebook
- and API reference
For feedback: bqml-feedback@google.com
---
Choosing the Right Function
- Use Managed AI Functions (`AI.IF`, `AI.CLASSIFY`, `AI.SCORE`) when:
- You want optimized cost + quality
- You don’t need custom model selection
- Use `AI.GENERATE` when:
- You require custom prompts or additional control
- You want to choose from a range of LLMs
---
Complementary Tools for Publishing
If you want to build scalable AI-powered workflows and publish across platforms:
- Try AiToEarn官网 — open-source AI content monetization platform
- Integrates AI generation, multi-platform publishing, analytics, and AI model ranking (AI模型排名)
- Supports Douyin, Kwai, WeChat, Bilibili, Rednote/Xiaohongshu, Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, Threads, YouTube, Pinterest, X/Twitter
---
Would you like me to create a side-by-side visual cheat sheet showing when to use each BigQuery AI function (`AI.IF`, `AI.CLASSIFY`, `AI.SCORE`, `AI.GENERATE`) so it’s quick to decide in real workflows? That could make this even easier to use.



