Optimizing Buffering Images for Faster Web Performance
Learn how to optimize image buffering to boost site speed, enhance Core Web Vitals, and deliver a smooth visual experience for users worldwide.
Optimizing Buffering Images for Faster Web Performance
In today’s digital landscape, speed and responsiveness are essential for user engagement and SEO success. One critical aspect of web optimization is buffering images—the process of preloading graphical data so it’s ready to display without delay. High-resolution and image-heavy sites must pay special attention to buffering to achieve faster web performance, improve Core Web Vitals, and ensure a seamless visual experience for users.
---
What Is Buffering in the Context of Images?
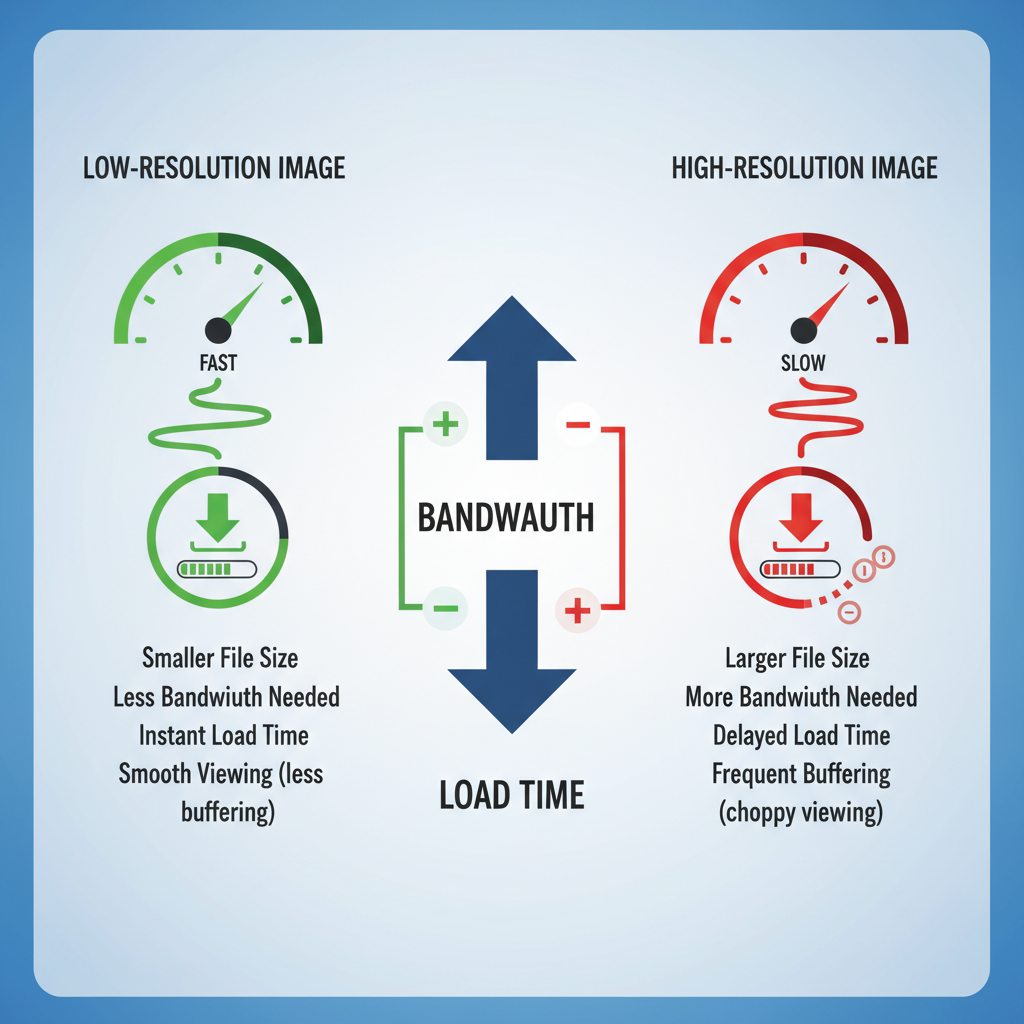
Buffering in web design refers to temporarily storing data in memory or cache for quick retrieval. For images, this means preloading files either on the client side (browser) or server side before they are needed on screen.
When an image is effectively buffered, it appears instantly once called for display. Without buffering, the browser must fetch the file at render time, potentially causing noticeable delays and visual disruptions.
---
Why Buffering Matters
Buffering impacts two critical performance factors:
- User Experience: Reduced load times increase engagement and reduce bounce rates.
- Site Speed: Faster image rendering boosts SEO metrics, including Google’s Core Web Vitals.
Additional benefits of optimized buffering include:
- Smooth transitions in image-heavy galleries
- Snappy, interactive UI for apps
- Minimized “layout shift” and flickering during load
---
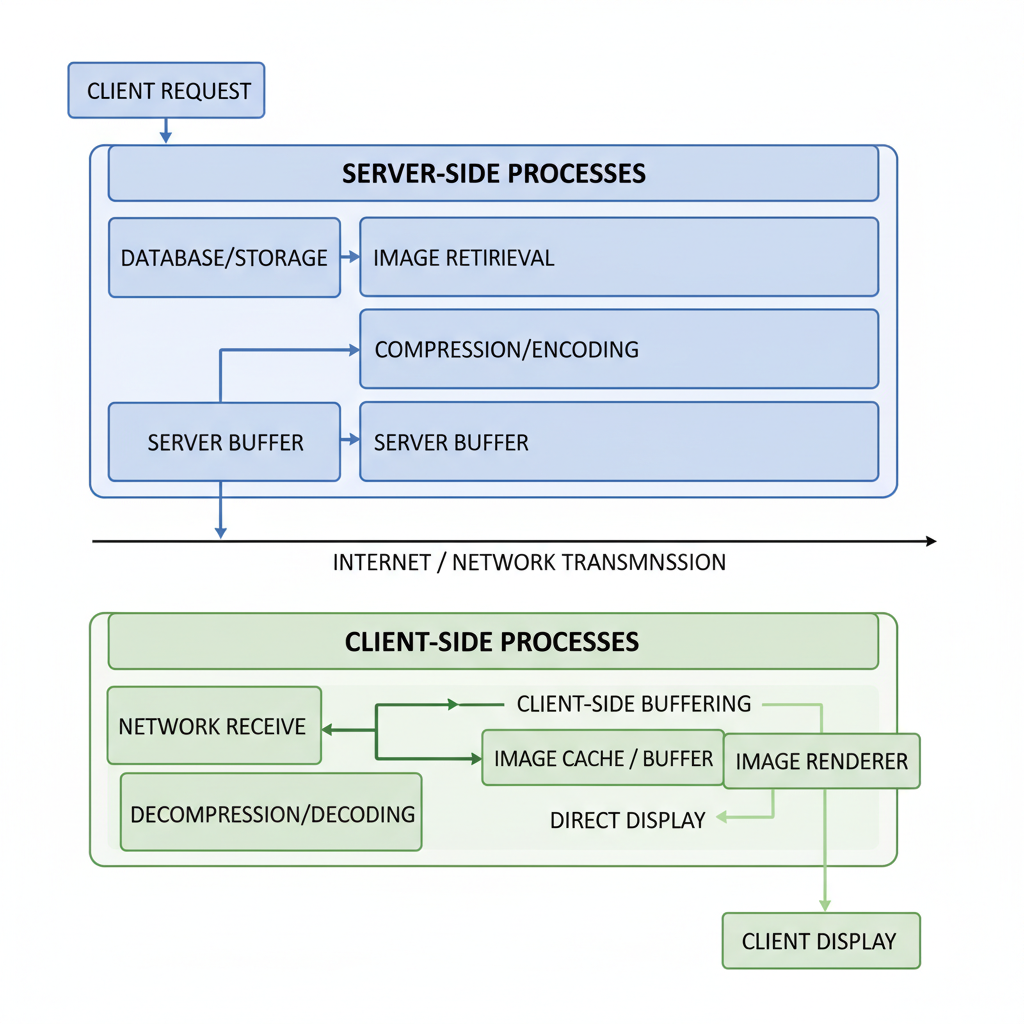
Client-side vs Server-side Image Buffering
Web developers can choose between two primary approaches to image buffering:
| Approach | Mechanism | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Client-side Buffering | Images preload in the browser’s memory | No extra server load, responsive UI for repeated views | Consumes client memory, limited by browser capabilities |
| Server-side Buffering | Images are processed and stored in cache on the server | Optimized delivery and compression, ideal for global traffic | Requires backend resources, may present scalability challenges |
The optimal choice depends on your website’s structure, target audience, and available resources.
---
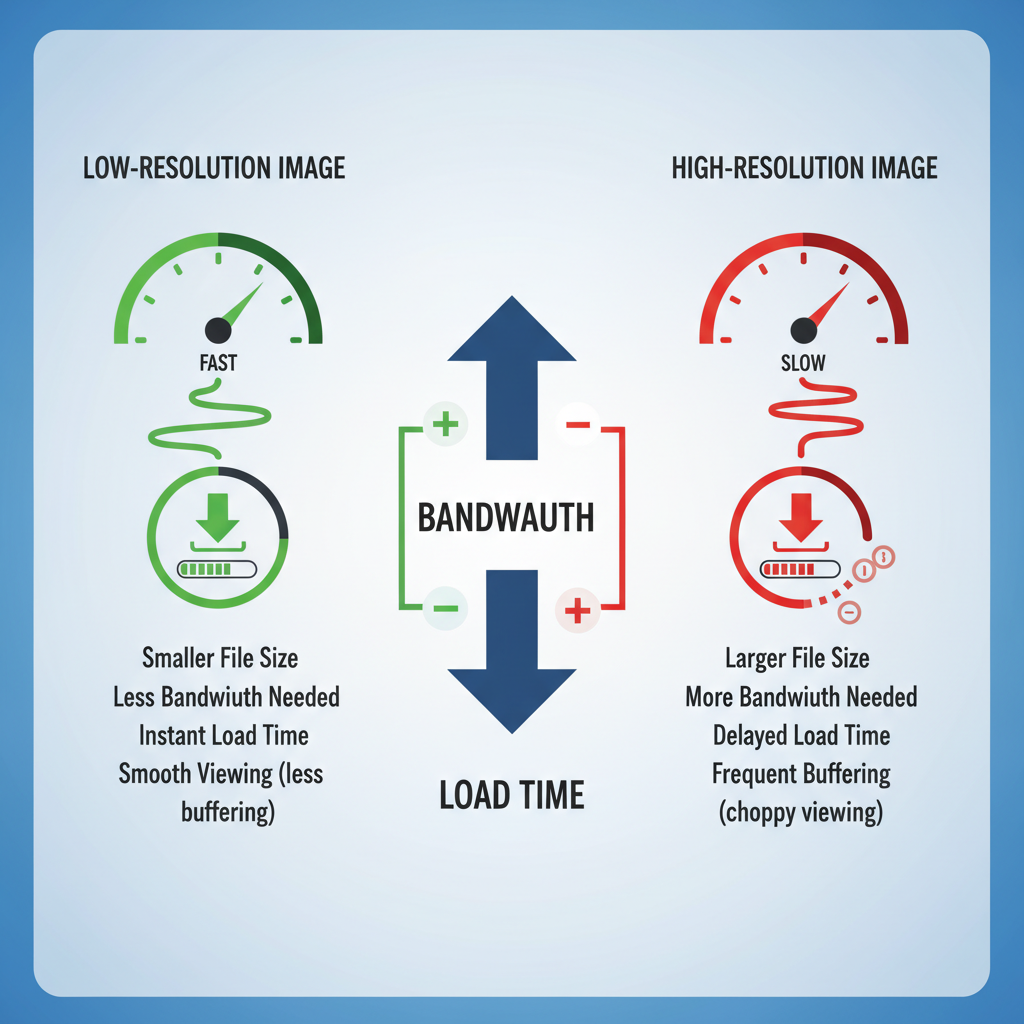
Common Challenges with High-Resolution Image Buffering
Large, detailed images can significantly affect buffering performance. Key challenges include:
- File Size: Bigger files increase download and buffering latency.
- Bandwidth Limitations: Slow mobile or rural connections struggle with large buffers.
- Browser Memory Limits: Most browsers have set allocations for image data.
- Rendering Bottlenecks: Complex file formats or graphics can slow the render pipeline.
---
Best Practices for Optimizing Image Buffering
Following proven optimization methods can greatly reduce buffering time:
- Choose Efficient Formats
- Use modern formats like WebP or AVIF instead of JPEG/PNG when possible.
- Apply Compression
- Tools such as ImageOptim or TinyPNG reduce size without noticeable quality loss.
- Lazy Loading
- Add `loading="lazy"` so off-screen images buffer only when they approach the viewport.
- Responsive Images
- Serve device-appropriate sizes using `` and `srcset`.
- Preload Critical Files
- Use `` for hero images or banners that must appear instantly.
---
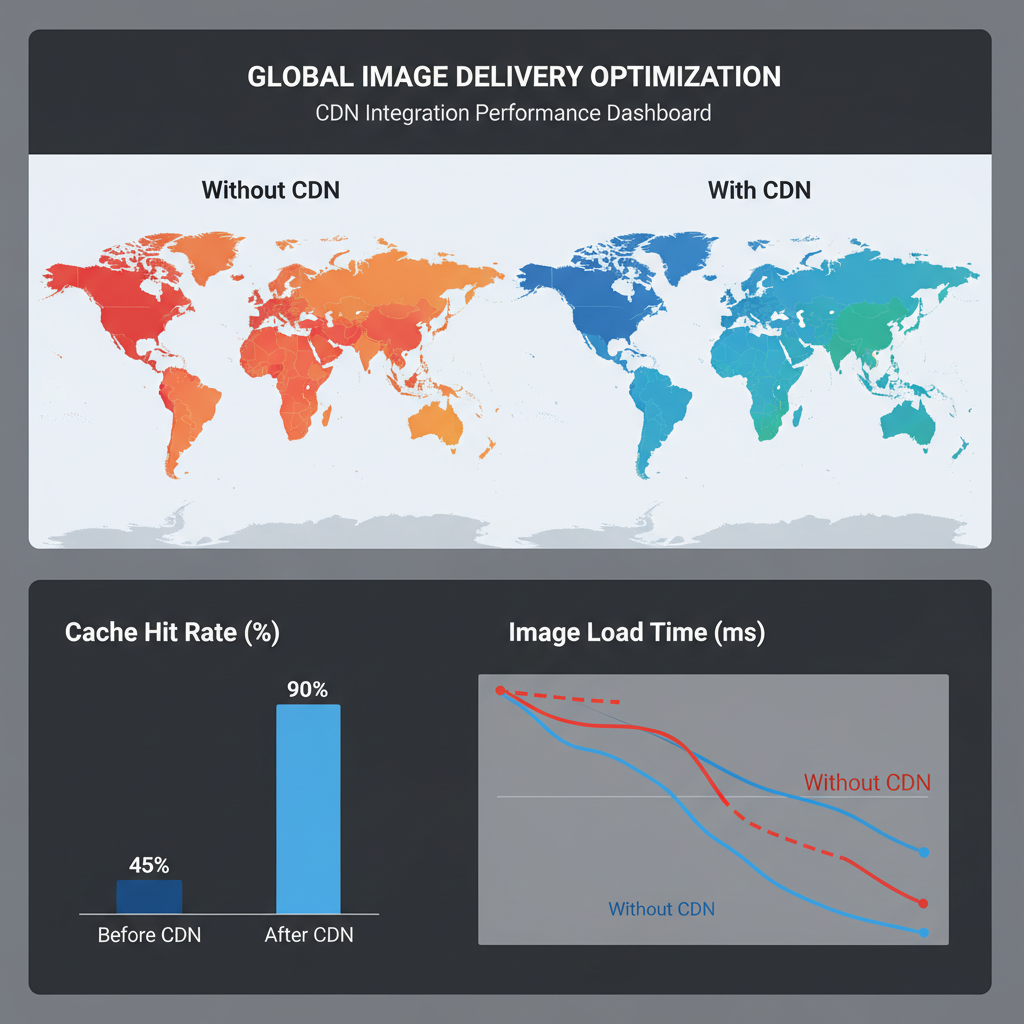
Using CDNs to Improve Buffering Times Globally
A Content Delivery Network (CDN) speeds up image delivery by caching assets on servers worldwide. When a user requests a file, it’s served from the nearest node.
Advantages of CDN buffering:
- Lower latency for global visitors
- Reduced load on your origin server
- Intelligent caching strategies
- Straightforward integration with most CMS platforms
Top CDN providers include Cloudflare, Akamai, Amazon CloudFront, and Fastly.
---
Browser Cache Strategies to Reduce Repeated Buffering
Caching lets the browser reuse images already downloaded, avoiding repeated buffering. Implementing effective cache-control headers is key:
Cache-Control: max-age=31536000, immutable
ETag: "abc123"Suggestions:
- Long-Term Cache for static assets
- ETag Validation for conditional refreshing
- Versioned Filenames to prevent stale content from persisting
---
How to Implement Progressive Image Loading
Progressive loading quickly shows a low-res preview, while a high-res file buffers in the background.
Example HTML:
Supporting JavaScript:
document.addEventListener("DOMContentLoaded", function() {
document.querySelectorAll('img.progressive').forEach((img) => {
const highRes = new Image();
highRes.src = img.getAttribute('data-src');
highRes.onload = function() {
img.src = this.src;
};
});
});Benefits:
- Immediate content visibility
- Bandwidth efficiency for slower connections
- Enhanced visual appeal on image-heavy pages
---
Measuring Buffering Performance
Monitoring load speed lets you measure buffering improvements:
- Chrome DevTools → Network Panel: Check waterfall charts for image loads.
- Lighthouse Reports: Highlight optimization opportunities.
- WebPageTest: Simulate CDN and compression impact.
- GTmetrix: Test from multiple global locations.
---
Troubleshooting Slow Buffering
If image loading remains sluggish:
- Test Network Conditions using ping and speed tools.
- Profile Server Response times to find bottlenecks.
- Reduce File Sizes with scaling and compression.
- Optimize Render Threads by minimizing blocking scripts/styles.
- Review CDN Configurations for correct caching and edge delivery.
---
Future Trends in Image Buffering
Emerging developments shaping image buffering include:
- Adaptive Image Streaming: Adjust resolution based on network quality.
- AI-based Compression: Device-aware automated optimization.
- HTTP/3 + QUIC Adoption: Lower latency protocols for image transfer.
- Edge AI Processing: Real-time resizing and format conversion at the network edge.
These advancements aim to make even media-rich websites load nearly instantly.
---
Summary & Next Steps
By combining compression, lazy loading, responsive formats, CDN delivery, and smart caching, you can turn image buffering from a common bottleneck into a competitive advantage. Faster buffering enhances site speed, boosts SEO, and keeps users engaged.
Take action today—evaluate your current image buffering strategy, implement these best practices, and measure results using real-world performance tools to ensure your site delivers the fastest, most seamless visual experience possible.