Building an AI-Native Engineering Team: A Practical Guide to AI Agents

Introduction: AI Is No Longer Just an Autocompletion Tool

AI models are advancing at astonishing speed, expanding their capacity to handle complex, multi-step tasks.
Today’s leading systems can sustain continuous reasoning for hours.
METR (Aug 2025) data shows state‑of‑the‑art models can reason for 2 hours and 17 minutes at ~50% success rate — with this duration doubling every 7 months.
In contrast, just a few years ago, models managed ~30 seconds of thought, only enough for simple code completions.
Now, with extended reasoning chains, AI agents can participate across the entire Software Development Lifecycle (SDLC) — planning, design, development, testing, review, and deployment.
---
AI Evolution Timeline
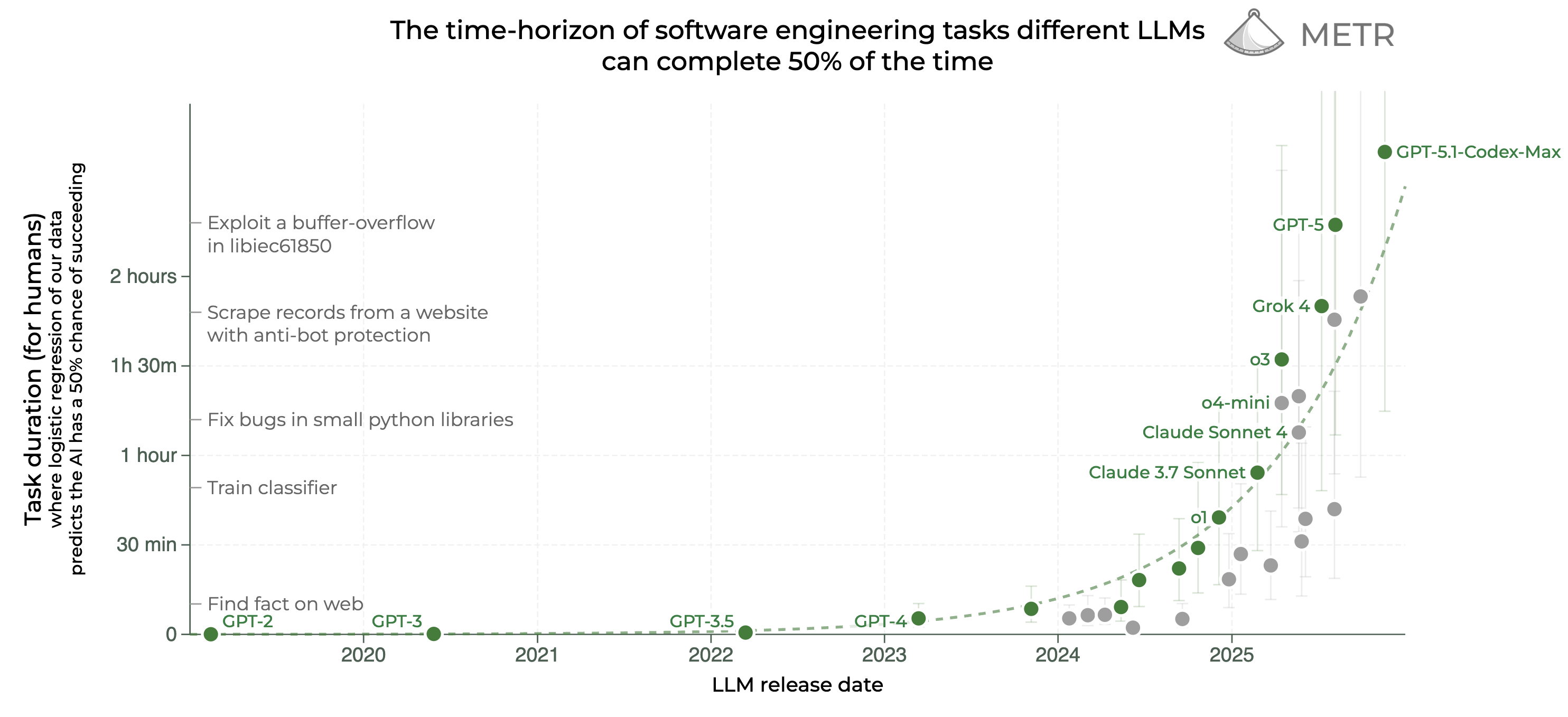
(Chart showing AI task-duration progression)
- 2020 – 2022 (GPT‑3/3.5): Quick facts lookup & minor bug fixes (seconds–minutes).
- 2023 – 2024 (GPT‑4 / Claude Sonnet): Handle more complex logic.
- 2025+ (o3, GPT‑5, Codex‑Max): Capable of exploiting vulnerabilities, bypassing anti‑scraping, and maintaining multi‑hour continuous work.
> Goal of This Guide: Equip engineering leaders with practical strategies to start building AI‑native teams today.
---
From “Autocompletion” to “Agents”
AI programming tools have transitioned through three major stages:
- Early: Predict next line or complete a small template.
- Mid: Role as chat-based pair-programmers inside IDEs.
- Now: AI Agents — generate full files, project architectures, transform design diagrams → code, debug multi-step problems, operate locally & in multi-agent cloud setups.
Four Core Upgrades:
- Unified Context — read code, configs, monitoring data without tool‑switching.
- Structured Tool Execution — call compilers/test runners, output verifiable results.
- Persistent Project Memory — retain design decisions & constraints over long tasks.
- Evaluation Loops — run tests & performance checks automatically.
---
AI in Modern Engineering Workflows
Cross-team coordination is key when integrating AI agents.
Platforms like AiToEarn官网 offer open-source tools for:
- AI-assisted content generation
- Multi-platform publishing (Douyin, Kwai, WeChat, Bilibili, Rednote, Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, Threads, YouTube, Pinterest, X)
- Analytics
- AI model rankings (AI模型排名)
These capabilities complement AI-native development pipelines, optimizing both technical output and knowledge dissemination.
---
> OpenAI Case Study:
> - Weeks‑long dev cycles compressed into days
> - Documentation, test cases, legacy code clean‑up → fully delegated to Codex
> - Human ownership remains for complex & novel challenges; engineers focus on architecture and systems thinking.
---
SDLC Phases with AI Agents
---
Phase 1: Planning
Traditional Pain Point: Time-consuming manual code digging for feasibility estimates.
AI Assist:
- Integrate AI into ticketing systems.
- Auto-review requirements vs. codebase.
- Instantly flag services, dependencies, ambiguities.
Engineer Role:
- Delegate: Feasibility analysis, dependency mapping.
- Review: Accuracy of findings & timing estimates.
- Own: Strategic priorities & trade‑offs.
Checklist:
- Processes needing code/requirements cross‑checking.
- Start with auto‑tag & dedupe tickets.
- Scale to AI-driven task breakdowns.
---
Phase 2: Design
Traditional Pain Point: Sluggish scaffolding, design-to-code translation, mismatched implementations.
AI Assist:
- Generate boilerplate, structures, apply guidelines.
- Accept natural language/UI descriptions.
- Transform design files into compliant code.
Engineer Role:
- Delegate: Scaffolding, design conversion, styling.
- Review: Compliance & accessibility.
- Own: UX patterns, architecture.
Checklist:
- Use multi-modal AI.
- Link design tools via MCP.
- Build design→code workflows.
---
Phase 3: Build
Traditional Pain Point: “Code archaeology,” repetitive conventions in large repos.
AI Assist:
- Produce end-to-end features from requirements.
- Create data models, APIs, UI, tests, docs.
- Auto-fix build errors & propagate changes.
Engineer Role:
- Delegate: CRUD logic, wiring, test scaffolds.
- Review: Security, performance, subtle logic.
- Own: Abstract layers, cross-domain designs.
Checklist:
- Well-defined tasks first.
- AI to draft a `PLAN.md`.
- Maintain `AGENTS.md` for test/code checks.
---
Phase 4: Test
Pain Point: Test writing/maintenance drags under deadlines.
AI Assist:
- Suggest test cases.
- Detect overlooked edge cases.
- Auto-update tests on code changes.
Engineer Role:
- Delegate: Initial test code from specs.
- Review: Guard against “fake tests.”
- Own: Coverage strategy & adversarial insight.
Checklist:
- Include “write tests” as an AI stage.
- Force tests to fail pre‑build (`red light`).
- Encode standards in `AGENTS.md`.
---
Phase 5: Review
Pain Point: Code reviews time-heavy & inconsistent.
AI Assist:
- First-pass PR reviews.
- Understand logic/data flow.
- Detect real issues vs. verbose noise.
Engineer Role:
- Delegate: Draft reviews & iterate.
- Review: Architecture/design compliance.
- Own: Final merge approvals.
Checklist:
- Maintain “gold standard” review examples.
- Use review-tuned models.
- Track feedback to improve AI accuracy.
---
Phase 6: Document
Pain Point: Outdated docs due to manual upkeep.
AI Assist:
- Summarize code functionality.
- Generate architecture diagrams (Mermaid format).
- Auto-update docs at build/release time.
Engineer Role:
- Delegate: Summaries, APIs, dependencies.
- Review: Core service docs/public APIs.
- Own: Structure, templates, compliance & branding.
---
Phase 7: Deploy & Maintain
Pain Point: Context-switching between logs, metrics, code in high-pressure incidents.
AI Assist:
- Access logs via MCP.
- Trace root cause with logs + code + Git history.
- Pinpoint offending commits.
Engineer Role:
- Delegate: Log parsing, anomaly detection, patch drafts.
- Review: Validate diagnosis & fixes.
- Own: Critical/ sensitive decisions.
Checklist:
- Link AI to logging/deployment tools.
- Prepare incident analysis prompt templates.
- Run simulated drills.
---
Conclusion
AI agents transform engineering by automating multi-step grunt work, enabling engineers to focus on design, architecture, and strategy.
Engineers are upgraded, not replaced.
You remain accountable for vision and quality, while AI becomes a tireless partner in the SDLC.
Next Steps:
- Start small with guarded workflows.
- Set clear delegation/review boundaries.
- Scale as trust & accuracy grow.
---
Cross‑Platform AI Strategy
Open-source ecosystems like AiToEarn官网 extend beyond engineering:
- Generate AI content
- Publish simultaneously to major platforms
- Analyze performance
- Leverage AI rankings (AI模型排名)
Shared Philosophy: Let AI handle repetitive processes while humans guide strategy and enforce quality.



