Connecting to Production: Cloudflare Workers Remote Binding Architecture Explained
# Cloudflare Remote Bindings: Local Development with Real Resources
**Remote bindings** link your locally running Worker code to **deployed resources** in your Cloudflare account — instead of simulated local resources.
Recently, Cloudflare announced that [remote bindings are now generally available](https://blog.cloudflare.com/cloudflare-developer-platform-keeps-getting-better-faster-and-more-powerful/#connect-to-production-services-and-resources-from-local-development-with-remote-bindings-now-ga).
With this feature, you can connect to **R2 buckets** and **D1 databases** while running Worker code locally — enabling testing against **real data and live services** without deploying at every iteration.
---
## Why Remote Bindings Matter
Remote bindings deliver:
- **Production parity** for local testing
- Faster iteration versus fully remote execution
- Access to collaborative or production datasets
- No compromise on local debugging improvements
---
## Workers Development History
### Early Approach: Remote Mode
Cloudflare’s original solution was `wrangler dev` in **remote mode**:
1. Deploy and preview your Worker on Cloudflare’s network for each change.
2. Live update previews as you develop.
Drawbacks:
- Complexity and maintenance overhead
- **Slower iteration speed** than true local execution
- Debugging instability
- Weak support for multi-worker scenarios
### New Approach: Fully Local with Remote Access
Since mid-2023, the default [`wrangler dev`](https://blog.cloudflare.com/wrangler3/) runs **fully locally**. Improvements include:
- [Wrangler](https://developers.cloudflare.com/workers/wrangler/) upgrades
- [Cloudflare Vite plugin](https://developers.cloudflare.com/workers/vite-plugin/)
- [@cloudflare/vitest-pool-workers](https://developers.cloudflare.com/workers/testing/vitest-integration/)
- [Miniflare](https://developers.cloudflare.com/workers/testing/miniflare/)
---
## Remote Bindings in Wrangler
You can still run remote mode via:
wrangler dev --remote
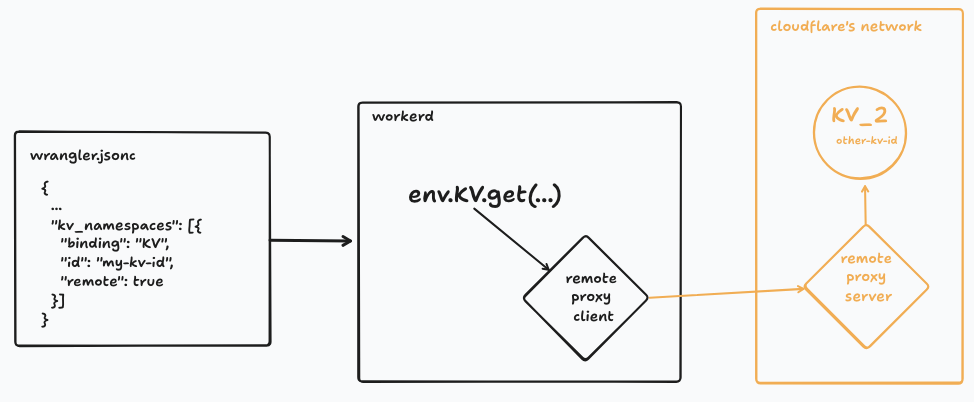
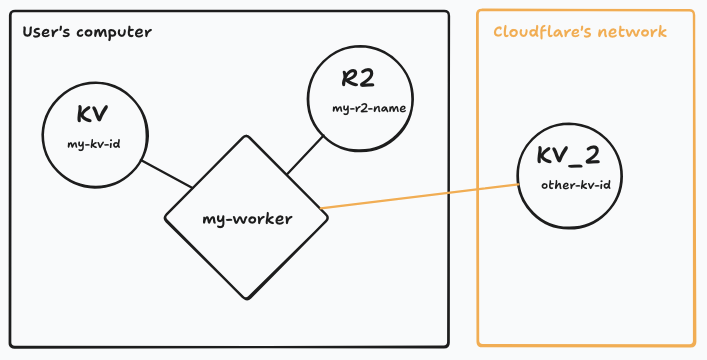
But now, as of **Wrangler v4.37.0**, you can **mix local and remote bindings per resource** by adding `"remote": true` to a binding in your config:
{
"name": "my-worker",
"compatibility_date": "2025-01-01",
"kv_namespaces": [{
"binding": "KV",
"id": "my-kv-id"
},{
"binding": "KV_2",
"id": "other-kv-id",
"remote": true
}],
"r2_buckets": [{
"bucket_name": "my-r2-name",
"binding": "R2"
}]
}
Benefits:
- No extra API keys or credentials — uses Wrangler’s built-in OAuth
- Flexibility to choose remote/local **per binding**
---
## How It Works in Production
Most Workers **bindings** boil down to a [service binding](https://developers.cloudflare.com/workers/runtime-apis/bindings/service-bindings/) — a network link between two Workers via HTTP or [JSRPC](https://blog.cloudflare.com/javascript-native-rpc/).
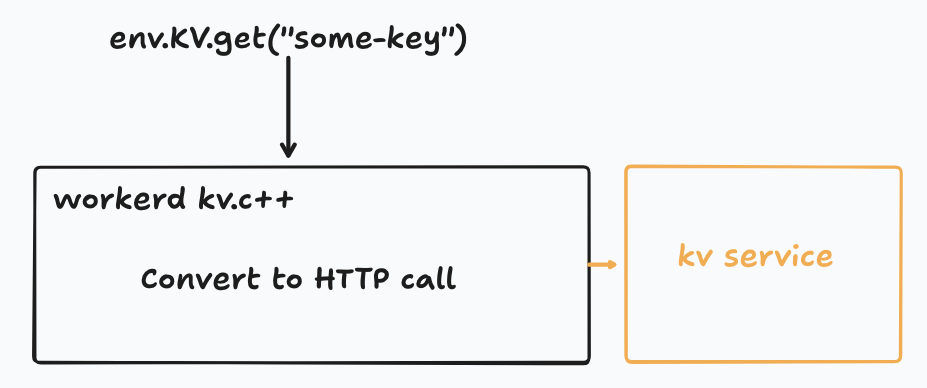
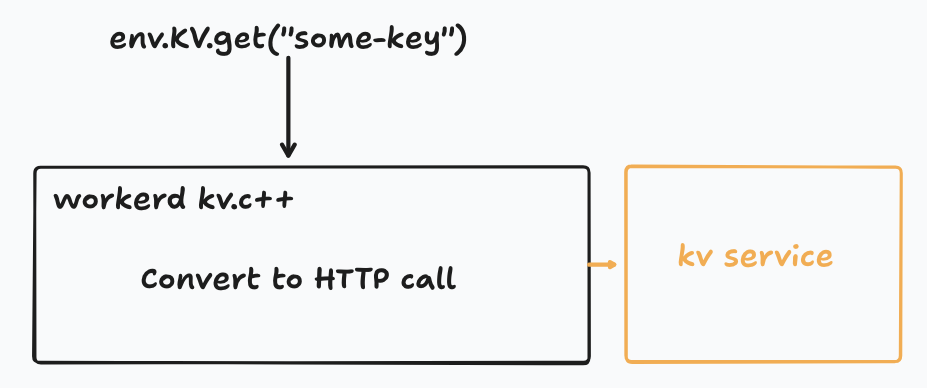
Example (KV binding flow):
1. Your Worker calls `env.KV.get("key")`
2. Workers runtime translates into HTTP request to the KV service Worker
3. Response returned over network
---
## How It Works Locally with Remote Bindings
Cloudflare’s local runtime ([workerd](https://github.com/cloudflare/workerd)) translates `env.KV.get()` into an HTTP request or JSRPC call **directly** to the remote service — bypassing the production runtime.
**Architecture:**
Hybrid setups are possible — some bindings local, some remote:
---
## Handling JSRPC Bindings
Bindings like [Images](https://developers.cloudflare.com/images/transform-images/transform-via-workers/) use JSRPC. Local remote binding support is powered by:
- [Cap’n Web](https://blog.cloudflare.com/capnweb-javascript-rpc-library/)
- WebSockets connection between `workerd` and remote runtime
This allows **JSRPC-backed** bindings to function remotely in local dev mode.
---
## Remote Bindings Beyond `wrangler dev`
To extend this to other tools:
- `wrangler` package exports utilities like `startRemoteProxySession`
- Built-in support for [Cloudflare Vite Plugin](https://developers.cloudflare.com/workers/vite-plugin/) and [`vitest-pool-workers`](https://developers.cloudflare.com/workers/testing/vitest-integration/)
Docs: [Remote Bindings Documentation](https://developers.cloudflare.com/workers/development-testing/#remote-bindings)
---
## How to Try It
1. Update to **Wrangler v4.37.0**
(or `@cloudflare/vite-plugin` v1.13.0, `@cloudflare/vitest-pool-workers` v0.9.0)
2. Use `wrangler dev` normally
3. Add `"remote": true` to any binding in your Wrangler config
---
## Related Context: AI Content Workflows
For developers creating **cross-platform AI-powered content pipelines**, **[AiToEarn](https://aitoearn.ai/)** offers an **open-source** global monetization framework:
- AI content generation
- Cross-platform publishing
- Analytics & [model ranking](https://rank.aitoearn.ai)
- Supports Douyin, Kwai, WeChat, Bilibili, Rednote, Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, Threads, YouTube, Pinterest, and X (Twitter)
Resources:
- [AiToEarn官网](https://aitoearn.ai/)
- [GitHub repository](https://github.com/yikart/AiToEarn)
- [Online docs](https://docs.aitoearn.ai/)
---
**Summary:**
Cloudflare remote bindings unify **local dev speed** with **production resource access**, enabling realistic testing without deployment overhead. Pair this with automation tools like AiToEarn for multi-channel AI publishing, and you have a powerful workflow for both backend apps and creative pipelines.


