DeepSeek Breaks Google & OpenAI Monopoly Again: Open-Source IMO Gold Medal Math Model
The Return of the Open‑Source AI Powerhouse — DeepSeek
DeepSeek has made a powerful comeback in the AI community with the release of its new open‑source mathematics model — DeepSeekMath‑V2 — focused on self‑verifiable mathematical reasoning.
---
Breakthrough Achievements
DeepSeekMath‑V2 has delivered record‑setting scores:
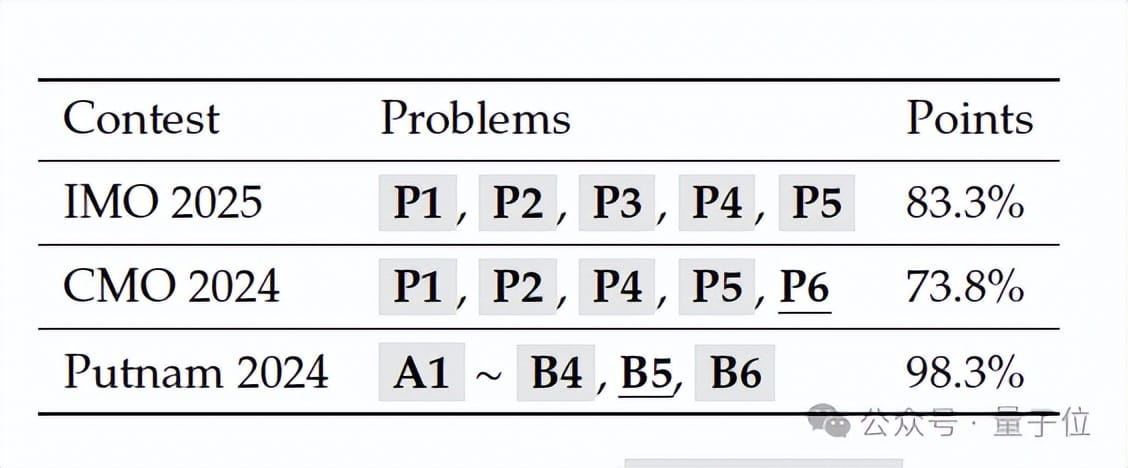
- IMO 2025: Gold Medal
- CMO 2024: Gold Medal
- Putnam 2024: 118/120 (higher than human top score: 90)
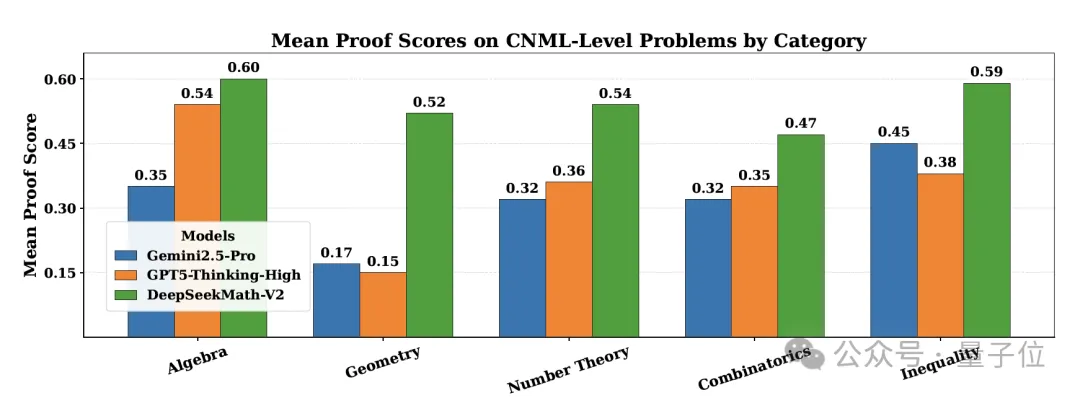
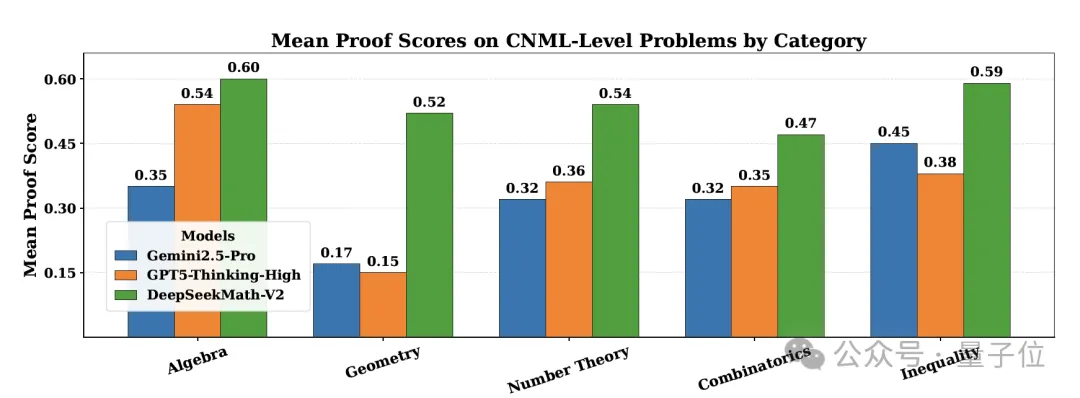
Category Performance:
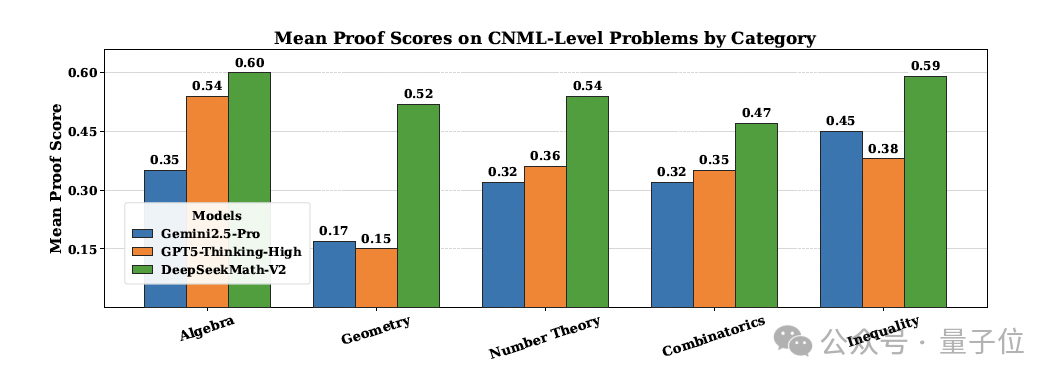
Across Algebra, Geometry, Number Theory, Combinatorics, and Inequalities (CNML‑level problems), it outperformed GPT‑5‑Thinking‑High and Gemini 2.5‑Pro.
Notably, it is the first open‑source IMO gold‑medal‑level model.
This leap could unsettle Google and OpenAI. Particularly, OpenAI had reportedly planned its own IMO gold‑medal model for Gemini 3 Pro’s release — but DeepSeek has won the race.
(The whale has returned!)
The paper’s first author Zhi‑Hong Shao also led the previous DeepSeekMath 7B project that pioneered the GRPO method.
---
Overview of DeepSeekMath‑V2
Model Size: 685B parameters
Core Aim: Achieve self‑verifiable mathematical reasoning.
Innovation:
A proof verification–driven RL pipeline to guide and optimize proof generation — addressing the limitations of reinforcement learning strategies that focus only on rewarding correct final answers.
---
Traditional RL Limitations in Math Reasoning
- Final Answer Bias
- Correct answers may be reached through flawed reasoning.
- Theorem‑Proving Constraints
- Many tasks require step‑by‑step formal proofs, not just numerical solutions.
- No Self‑Verification
- Models struggle to validate their own proofs, leading to false positives.
---
Iterative RL Between Proof Verifier & Generator
DeepSeekMath‑V2 trains a proof verifier and proof generator in alternating RL loops.
Verifier Training Workflow
Goal:
Create an LLM‑based verifier that identifies and scores proof quality per expert standards.
Scoring Scale:
- 1 → Completely correct, rigorous proof
- 0.5 → Mostly logical with minor issues
- 0 → Critical logical flaws
Training Stages:
- Data Construction (Cold Start)
- 17,500 olympiad‑level proof problems collected from AoPS.
- Candidate proofs generated via DeepSeek‑V3.2‑Exp‑Thinking.
- Human experts scored proofs to build the initial dataset.
- RL Objective Fine‑Tuning
- Base model: DeepSeek‑V3.2‑Exp‑SFT
- Rewards:
- Format reward (issues summary + score in correct format)
- Score reward (align with expert labels)
This process yields a human‑like rigorous verifier.
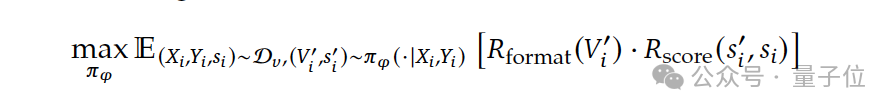
---
Meta‑Verification: Improving Verifier Fidelity
Problem: Initial verifiers sometimes hallucinate proof errors that don’t exist.
Solution:
Introduce a Meta‑Verifier to re‑check the verifier’s Proof Analysis for validity and logical soundness.
Meta‑Verification Training Steps:
- Expert‑scored meta‑verification dataset.
- Dedicated meta‑verifier model trained to:
- Summarize proof analysis flaws.
- Score the analysis quality.
Rewards:
Same structure as verifier — format + score.
Enhanced Verifier Training:
- Integrate meta‑verification quality score into verifier’s RL rewards.
- Joint training on original + meta datasets.
- Results: Average proof analysis quality ↑ from 0.85 to 0.96.
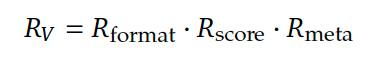
---
Generator Training with Self‑Verification
Process:
- Proof generator trained to maximize verifier’s assigned proof score.
- After each proof, generator outputs self‑analysis.
- Reward combines proof quality + self‑evaluation accuracy.
Impact:
- Encourages truthful error acknowledgment and correction before final proof.
- Leads to iterative self‑improvement.
Outcome: Proof generator can accurately evaluate and refine its own outputs.
---
Automating Data Labeling
Manual labeling slows progress as problem difficulty rises. DeepSeekMath‑V2’s approach:
- Generate n independent proof analyses → increases error capture.
- Use meta‑verifier for m evaluations of analyses → confirm error validity.
- Score Rules:
- Lowest score assigned only if ≥k analyses are meta‑confirmed.
- Else, proof scored as 1.
Result: Full automation of labeling, replacing human involvement in final training stages.
---
Iterative GRPO Training
- First optimize proof verification.
- Initialize generator from verifier checkpoint.
- From second iteration onwards, verifier initialized from rejection fine‑tuned checkpoint.
Performance:
Outperformed GPT‑5‑Thinking‑High and Gemini 2.5‑Pro in all CNML categories.
---
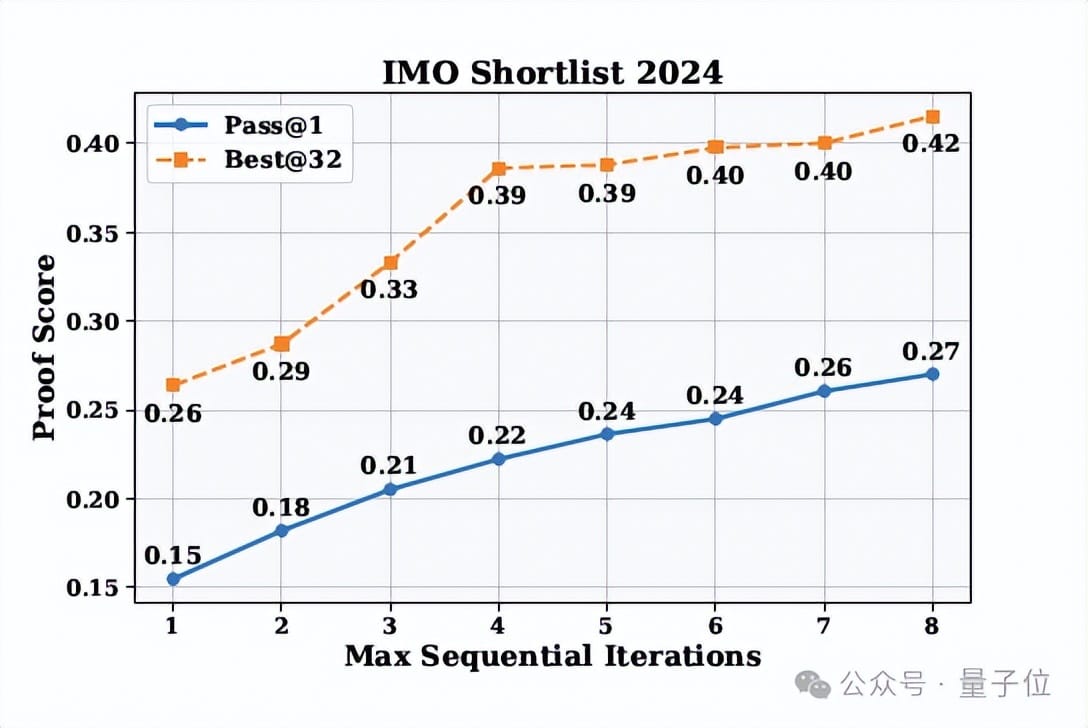
Sequential Refinement & Self‑Verification Impact
Findings:
- Self‑selected best proofs score higher than average — the generator knows its better work.
- Increasing max attempts boosts Pass@1 significantly.
Parallel Search Strategy:
- Diverse proof paths explored via parallel generation.
- Large‑scale (×64) verification to detect subtle errors.
- Refinement continues until proof passes all checks.
Result: Achieved 118/120 in Putnam — record‑breaking for AI.
---
About the Lead Author
Zhihong Shao — Research Scientist at DeepSeek specializing in large‑model reasoning.
- Lead author of DeepSeekMath 7B (introduced GRPO).
- Core contributor to DeepSeek‑R1.
- Education:
- Bachelor’s — Beihang University
- Ph.D. — Tsinghua University (supervised by Prof. Minlie Huang)


---
References
---
Implications Beyond Research
Platforms like AiToEarn官网 and AiToEarn开源地址 integrate:
- Multi‑platform publishing (Douyin, Kwai, WeChat, Bilibili, Rednote, Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, Threads, YouTube, Pinterest, X/Twitter)
- AI content generation
- Analytics
- Model ranking
Such ecosystems can turn breakthroughs like DeepSeekMath‑V2 into high‑quality, monetizable content pipelines — mirroring how meta‑verification strengthens AI proof rigor.