Definition of Community Management for Brands and Its Benefi
Learn the meaning of community management, its online and offline strategies, key goals, roles, required skills, and how it benefits brand growth.

Introduction to Community Management in the Digital Era
In the fast-paced digital era, understanding the definition of community management is essential for brands looking to grow their presence and engage meaningfully with their audiences. Community management is the practice of building, nurturing, and sustaining a group of people connected by a shared interest, brand, or cause across both online and offline spaces. This article explores what community management means today, its goals, roles, skills, tools, benefits, and future trends, providing actionable insights for businesses aiming to thrive through authentic connections.

---
Definition of Community Management in the Digital Era
Community management refers to the process of building, growing, and nurturing an audience around a brand, cause, or shared interest. In today’s digital-first world, it involves creating meaningful interactions between a brand and its followers across online platforms. At its core, community management fosters trust, encourages dialogue, and transforms passive audiences into active brand advocates.
The definition of community management has evolved from physical forums or brand clubs into complex digital ecosystems. It is no longer limited to customer service or occasional engagement; it has become a strategic discipline that integrates content creation, audience analytics, and personal connection to shape long-term relationships.
---
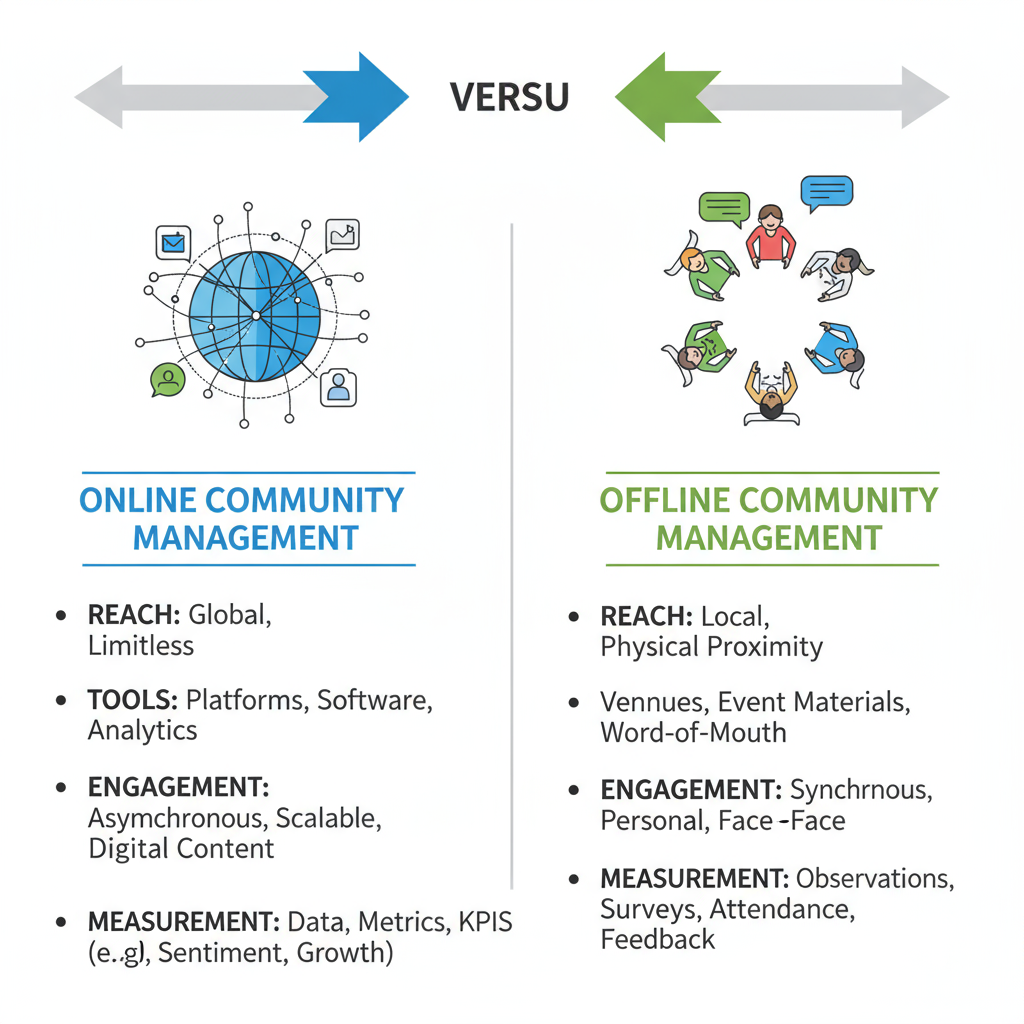
Difference Between Online and Offline Community Management
While both online and offline community management share the goal of building strong relationships, their environments, tools, and strategies differ significantly.
Online community management focuses on:
- Social media platforms (Facebook Groups, LinkedIn, etc.)
- Brand-owned forums and mobile apps
- Real-time engagement through live chat, comment moderation, and polls
Offline community management usually revolves around:
- In-person events like trade shows, meetups, or workshops
- Printed newsletters or physical monographs
- Telephone-based customer interaction
| Aspect | Online | Offline |
|---|---|---|
| Accessibility | Global, 24/7 | Local, time-bound |
| Scalability | High (viral potential) | Limited to capacity |
| Tools | Social platforms, automation, analytics | Event logistics, printed media |
| Data Collection | Instant and granular | Survey-based, slower |
---
Core Goals of Community Management
The following goals form the backbone of effective community management:
- Engagement – Encouraging two-way communication through posts, comments, and live sessions.
- Loyalty – Creating an environment where members remain active and emotionally invested.
- Feedback Loop – Gathering valuable insights to improve products or services.
- Brand Advocacy – Motivating members to promote the brand organically.
---
Key Roles and Responsibilities of a Community Manager
A community manager serves as both strategist and caretaker of the brand’s public space. Common responsibilities include:
- Content Curation: Sharing relevant articles, tips, and brand updates.
- Moderation: Ensuring that discussions remain constructive and on-topic.
- Crisis Handling: Addressing negative feedback with professionalism.
- Analytics: Monitoring engagement metrics and membership growth.
- Collaboration: Working with marketing, PR, and product teams for coordinated campaigns.
---
Essential Skills for Successful Community Management
The human element is central to community management. Skills include:
- Communication – Crafting clear, relatable messages.
- Empathy – Understanding the emotional context of members’ concerns.
- Conflict Resolution – Defusing heated discussions without alienating participants.
- Analytics Proficiency – Using data to refine engagement strategies.
- Adaptability – Staying agile amid shifting trends and audience behavior.
---
Platforms and Tools Commonly Used
Community managers leverage a blend of social networks, purpose-built tools, and analytics software. Popular choices include:
| Platform | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Facebook Groups | Private or public group discussions |
| Slack | Real-time collaboration and niche communities |
| Discord | Gaming or interest-based communities with voice/chat |
| HubSpot | CRM integration and customer engagement |
| Google Analytics | Traffic and behavior analysis |
---
Benefits for Businesses
Effective community management delivers tangible business outcomes:
- Stronger Retention: Members feel part of the brand’s story, reducing churn.
- Organic Reach: Word-of-mouth spreads via engaged advocates.
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: Faster, friendlier responses to concerns.
- Product Improvement: Direct user feedback shapes iterations.
- Competitive Edge: Differentiates the brand through authentic engagement.
---
Common Challenges and Pitfalls to Avoid
Managing a community isn’t without obstacles. Frequent pitfalls include:
- Neglecting Moderation: Allowing spam or abusive content to persist.
- Over-Automation: Losing the human touch in communication.
- Ignoring Feedback: Missing opportunities to fix issues.
- Inconsistent Activity: Sudden drops in engagement erode trust.
---
Case Studies of Successful Strategies
Case Study 1: Tech Startup Forum
A hardware startup launched a branded forum for early adopters. By appointing active community moderators and responding to queries within 24 hours, they reduced support tickets by 30%. Members began creating tutorials, boosting organic SEO presence.
Case Study 2: Lifestyle Brand Instagram Community
A lifestyle apparel company used Instagram Stories polls and Q&As to spark daily interaction. This strategy increased follower engagement rates by 120% over six months and improved repeat purchase rates.
---
Actionable Tips for Building and Sustaining an Engaged Community
Here are practical pointers you can implement now:
- Set Clear Guidelines: Define acceptable behavior and enforce rules consistently.
- Reward Contribution: Highlight active members through features or discounts.
- Blend Online and Offline Touchpoints: Offer meetups alongside virtual events.
- Leverage Analytics: Identify high-engagement content patterns.
- Foster Dialogue, Not Monologue: Ask open-ended questions and invite diverse input.
---
Future Trends in Community Management
Community management is set to evolve rapidly, driven by technology and user expectations. Watch for:
- AI Moderation: Automated yet context-sensitive filtering of content.
- Hyper-Personalization: Tailored experiences based on member profiles.
- Multi-Channel Integration: Unified communication across social, email, and apps.
- Virtual Reality Spaces: Immersive environments for interaction.
- Predictive Engagement: AI-driven insights to anticipate member needs.
---
Summary and Next Steps
The definition of community management extends far beyond basic moderation—it is a blend of strategy, empathy, and data-driven decision-making aimed at forming loyal, engaged communities. Successful brands understand the differences between online and offline practices, employ skilled community managers, and utilize the right tools to drive meaningful engagement.
To harness these benefits:
- Audit your current community engagement methods.
- Invest in training and tools for your community management team.
- Stay ahead of trends by adopting new technologies and focusing on personalized interactions.
Start building a vibrant, connected community today and transform your audience into lifelong brand advocates.