Evolution of Implementation Approaches for AI Search Front-End Typewriter Effects


---
## 📚 Table of Contents
1. Preface
2. Introduction
3. Early Implementation Plan
4. Increasing Requirement Complexity
5. Implementation with Modern Frameworks
6. Future Outlook
---
The **typewriter effect** is now a familiar yet powerful presentation technique in **front-end development**. Widely used on websites and apps, it offers **rich visual appeal** and a **distinctive interaction style**, enhancing content engagement.
This guide analyzes the **journey of evolving the typewriter effect** within AI-driven search response outputs — identifying **technical challenges, pros and cons**, and implementation improvements at each stage.
---
## ✏️ Quick Visual Summary
**Grasp the core ideas in 1 minute with these diagrams:**

---
## 01 — Preface
In conversational UIs backed by AI search, rendering text **word-by-word**—like an old-school typewriter—offers unique charm.
**Final Implementation Preview:**

---
## 02 — Introduction
**Scenario:**
AI-generated text is streamed from large models in segments, updating the interface incrementally — perfect for a typewriter effect.
**Benefits of the Typewriter Effect in AI Response UIs:**
- **Reduce waiting anxiety**
Shows incremental feedback instead of leaving the user idle.
- **Simulate natural dialogue**
Pauses and emphasis mimic human typing cadence.
- **Prevent information overload**
Moderates reading pace by chunking information.
- **Highlight real-time AI generation**
Reinforces perception of active computation vs. static answers.
---
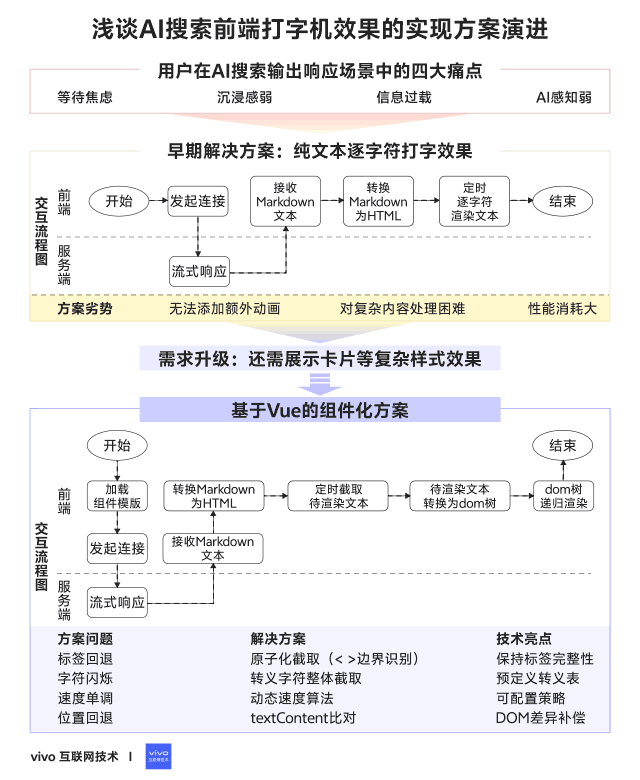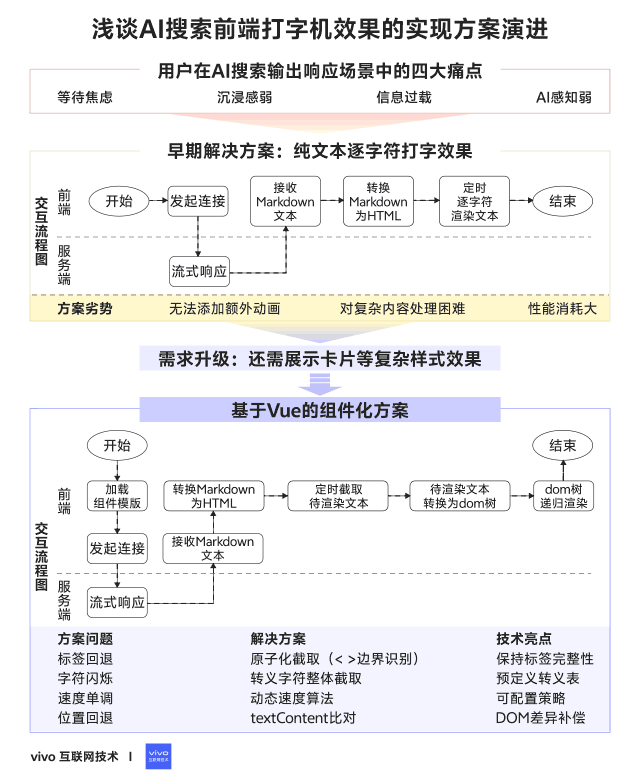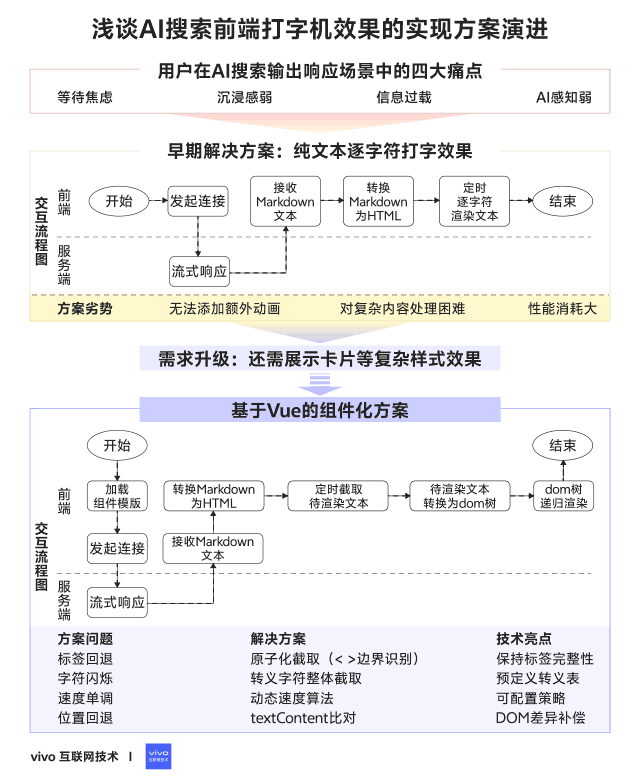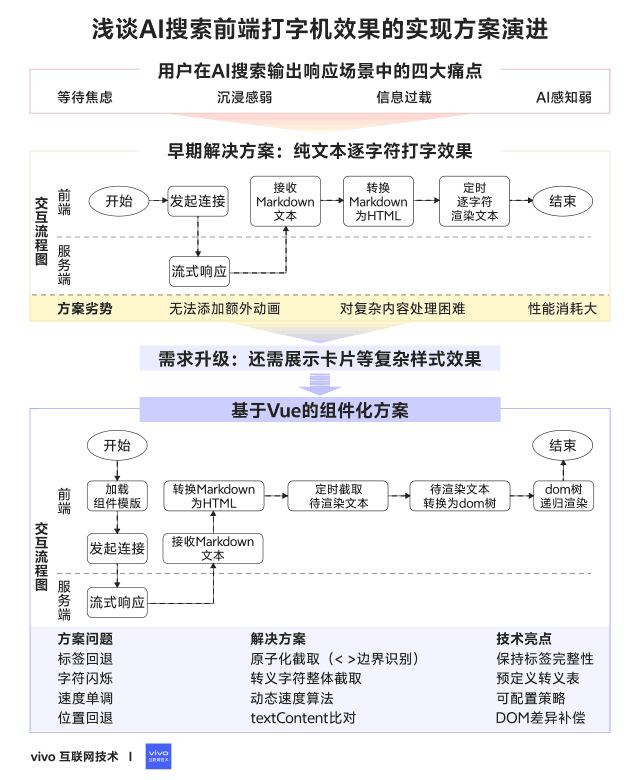
## 03 — Early Implementation Plan
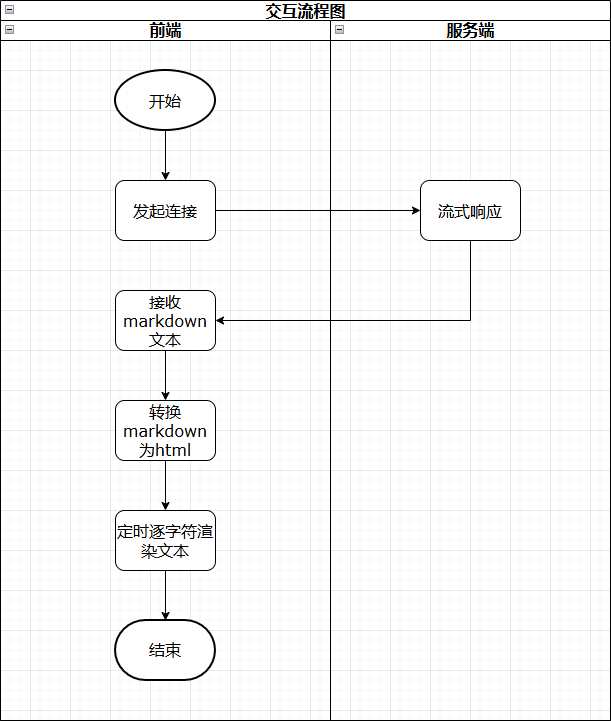
### Pure-text character-by-character typewriter effect
Initial design: stream user search-based output, append **one character at a time** to the page.
---
### 3.1 Detailed Steps
**Implementation Flow:**
1. **Cache incoming Markdown** from server streams.
2. **Append** new content to cached field.
3. **Convert Markdown to HTML** using `marked`.
4. **Render incrementally** with timed updates.
**Sample Code:**let fullText = 'test text'; // Full HTML
let index = 0; // Current index
let timer = window.setInterval(() => {
++index;
$dom.innerHTML = fullText.substring(0, index);
}, 40);
---
### 3.2 Why `innerHTML` over `appendChild`?
**Reason:** streamed Markdown often arrives incomplete — combining chunks accurately is easier with `innerHTML`.
Example:First: ** This is a
Later: title **
Final HTML:This is a title
---
### 3.3 Summary
**Pros:**
- Easy to implement
- Zero extra dependencies
**Cons:**
- Hard to add animated cursors
- Poor control over complex layouts
- Each update re-creates DOM → high performance cost
---
## 04 — Increasing Requirement Complexity
**New needs:**
- Interleave text with complex UI cards (apps, stocks, movies, etc.)
- Configurable & interactive layouts
**Challenge:** original approach is too rigid for heterogeneous, dynamic content.
---
## 05 — Implementation with Modern Frameworks
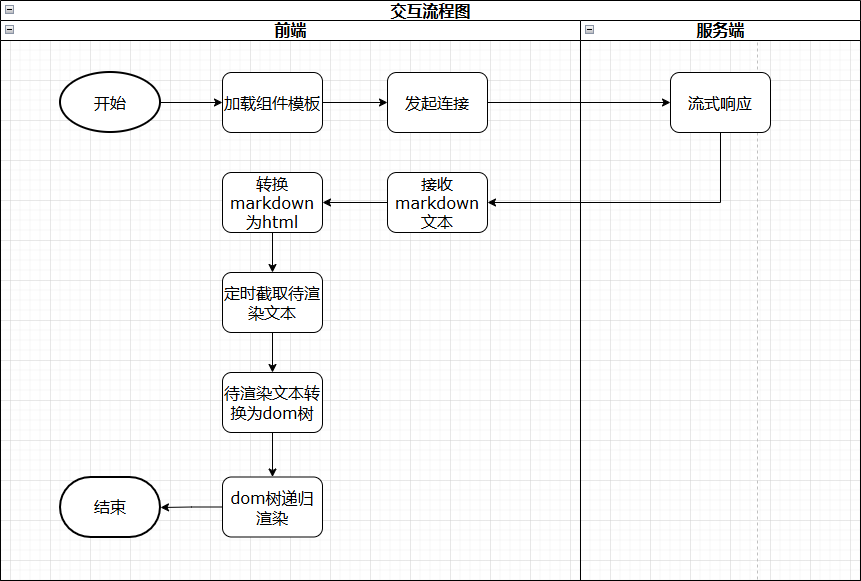
**Approach:** Vue Virtual DOM with Singleton Pattern
- **Singleton pattern:** only update existing nodes for consistency and performance.
- **Vue benefits:** diff-based updates, reusable components, flexible layouts.
---
### 5.1 Design Concept
Define extensible HTML-tag-based format for server data.
Example:**Process:**
1. Parse tag + attributes.
2. Map to Vue component template.
3. Fetch and render item data.
---
### 5.2 Detailed Implementation
Auto-register Vue components:private init() {
let fileList = require.context('@/components/common/box', true, /\.vue$/);
fileList.keys().forEach((filePath) => {
let tagName = filePath.substring(filePath.lastIndexOf('/') + 1, filePath.lastIndexOf('.'));
this.widgetMap[tagName] = fileList(filePath).default;
});
}
Use **debounce** when converting Markdown to HTML to avoid stutter.
Filter irrelevant tags via **ultrahtml** parsing.
---
#### Recursive Rendering:let children = this.dom['children'] || [];
let renderChildren = children.map((child, index) => {
return h(CommonDisplay, { props: { dom: child, displayCursor: this.displayCursor, lastLine: this.lastLine && index === children.length - 1 } });
});
// Handle text nodes
if (this.dom['type'] === TEXT_NODE) return this.renderTextNode({ h, element: this.dom });
// Handle custom component tags
if (this.$factory.hasTag(tagName)) {
let widget = this.$factory.getWidget(tagName);
return h(widget, { props: { displayCursor: this.displayCursor, lastLine: this.lastLine, ...attributes } });
}
// Native HTML tags
return h(tagName, { attrs: this.dom['attributes'] }, renderChildren);
---
### 5.3 Common Issues & Fixes
1. **Character rollback with HTML tags**
- **Fix:** treat tags as atomic; render whole tag in one step. if (curChar === '<') {
let lastGtIndex = this.rawHtml.indexOf('>', this.curIndex);
if (lastGtIndex > -1) { this.curIndex = lastGtIndex + 1; return false; }
}
2. **Escaped character flash (`"`)**
- **Fix:** intercept entire escape sequence. if (curChar === '&') {
let match = this.config['writer']['escapeArr'].find(item => this.rawHtml.indexOf(item, this.curIndex) === this.curIndex);
if (match) { this.curIndex += match.length; return false; }
}
3. **Fixed typing speed**
- **Fix:** dynamic speed adjustment based on chars left. privatespeedFn({curSpeed, curIndex, totalLength}) {
let left = totalLength - curIndex;
let match = this.config['writer']['strategy'].find(item => (!item.min || item.min < left) && (!item.max || item.max >= left));
let speed = this.config['writer']['initSpeed'] - match.w * (left - (match.min || 0)) + match.b;
return this.config['writer']['smoothParam'] curSpeed + (1 - this.config['writer']['smoothParam']) speed;
}
4. **Cursor jumping backward**
- **Fix:** detect HTML change, adjust pointer until current text length ≥ previous. if (this.isHtmlChanged()) {
let domRange = document.createRange();
let prevFrag = domRange.createContextualFragment(this.prevRenderHtml);
let prevLen = prevFrag.textContent.length;
let diffNum = 1;
do {
this.curIndex += diffNum;
let curFrag = domRange.createContextualFragment(this.rawHtml.substring(0, this.curIndex));
let curLen = curFrag.textContent.length;
diffNum = prevLen - curLen;
if (diffNum <= 0) break;
} while (this.curIndex < this.rawHtml.length);
}
---
### 5.4 Summary
**Benefits of modern framework approach:**
- Efficient diff-based rendering
- Flexible embedded content
- Easier styling & animations
---
## 06 — Future Outlook
The journey from **simple string printing** to **Vue-powered dynamic interactive typing** demonstrates how front-end innovation evolves alongside AI.
**Key Takeaways:**
- Incremental improvements solve real UX issues.
- Flexible architectures unlock rich interactivity.
- Open-source ecosystems (e.g., AiToEarn) allow cross-platform content delivery and monetization.
By **learning, iterating, and experimenting**, we can craft richer, smoother user experiences — whether for conversational AI or any dynamic content interface.
---
**Explore AiToEarn:**
- [官网](https://aitoearn.ai/)
- [博客](https://blog.aitoearn.ai)
- [开源地址](https://github.com/yikart/AiToEarn)


