From Completion to Agentic Edit: Trae’s Implementation and Evolution in Code Editing

Author
Editor|
Planning|AICon Global Artificial Intelligence Development and Application Conference
---
Introduction
When AI programming assistants enter the Agentic stage, they evolve from simple “completion tools” to true development partners—capable of self-planning, collaborating across files, and iterating based on feedback.
The Trae team followed a three-stage path:
Completion + Chat → Apply → Builder + Cue
Over time, they solved key challenges in precise file location, cross-file modification, and balancing efficiency, accuracy, and resource usage.
At the AICon Global Artificial Intelligence Development and Application Conference · Shenzhen Station, InfoQ interviewed Feng Xu, ByteDance/Trae Architect, who shared insights in his talk:
> "Practical Implementation of Trae Plugin in Agent Code Editing"
His analysis covered:
- Trade-offs between Apply and Search/Replace
- Cue’s intelligent completion
- Real-world implementations (e.g., Solar System Planets Page)
- Reusable engineering methodologies
---
The AICon Beijing Station, Dec 19–20, will focus on cutting-edge topics:
- Large model training & inference
- AI Agents
- New R&D paradigms
- Organizational transformation
Key question:
> How can we build a reliable, scalable, and commercial Agentic operating system so AI becomes a core driver of cost reduction, efficiency improvement, and growth breakthroughs?
📄 Detailed agenda: https://aicon.infoq.cn/202512/beijing/schedule
---
AI Programming Assistants: Challenges & Opportunities
Modern AI Agents can autonomously:
- Locate files
- Modify code
- Plan & execute development tasks
- Self-correct and iterate
Key challenges still remain:
- Insufficient precision in file location
- Difficulty in cross-file modification
---
Evolution of the TRAE Programming Assistant

Stage 1 — Completion + Chat
- Capabilities: Cursor-based code continuation
- Chat panel: Q&A code advice
- Limitation: Manual copy/paste required
Stage 2 — Check & Apply
- Innovation: Apply generated code blocks directly into files
- Autolocation: Model suggests target file for insertion
- Partial automation of editing tasks
Stage 3 — Builder + Cue (Current Stage)
- Cue:
- Intelligent, multi-line completions
- Predicts next cursor position
- Smart rewriting across files
- Builder:
- Understands project-level context
- Plans tasks
- Completes multi-file edits and iterations
---
From Code Completion to Agentic Edit
Code completion—powered by fill-in-the-middle techniques—was a strong core capability. But it was limited to the current cursor position.
Problem: Generated code still had to be copied manually.
Solution: Introduce the Apply mechanism.

---
Why Not Use Git Diff?
Two main issues hindered Diff format adoption:
- Model accuracy with syntax: Formatting errors break edit execution.
- Poor readability: Hard for users to verify correctness before applying.
---
Precision Merging Challenge
Since models output shorthand (only changed segments, with placeholders for unchanged sections), reinserting edits accurately into original files became non-trivial.
Solution: Train a specialized Apply model that:
- Receives original file + shorthand code block
- Outputs complete edited file
- Presents diffs for user approval
Model Requirements:
- Low latency
- Strong instruction following
- Long context support
---
Training Apply for Code Editing
Key training steps:
- Build shorthand datasets for different model habits (`existing code`, `.`, etc.)
- Cover diverse scenarios: adding comments, importing dependencies, deleting code, refactoring
- Include multiple programming languages
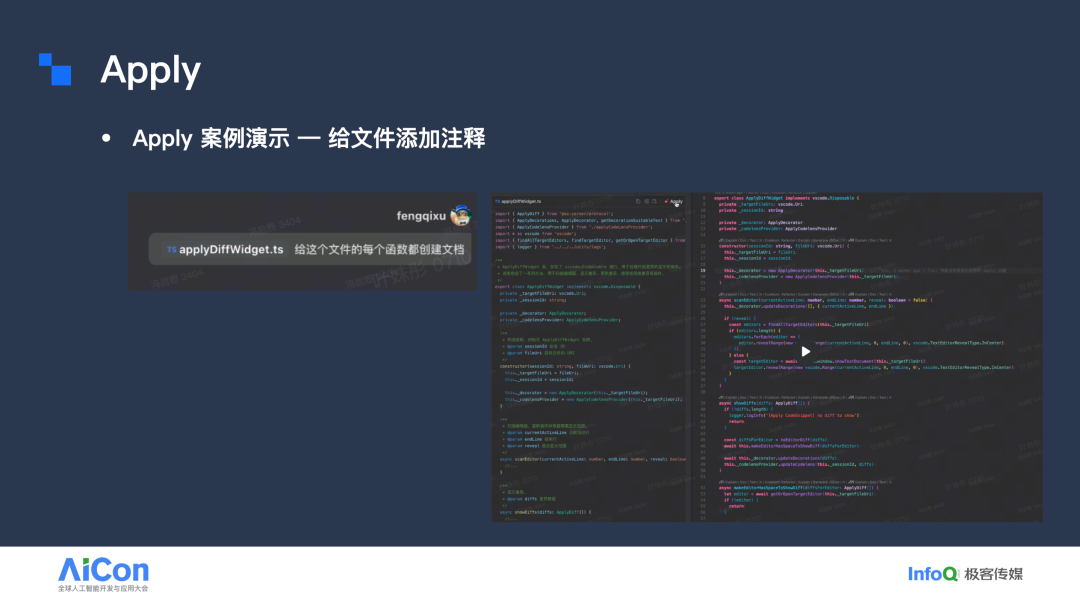
Example:
Instruction: "Add documentation for each function"
- Model generates shorthand doc comments
- Click Apply → File is updated with complete doc strings automatically
---
Apply Limitations
- Extra resource calls – Requires both Chat and Apply models
- Low efficiency – Small edits cause entire-file rewrites
- File length constraints – Context window limits can block edits
---
Cue: Smarter Code Completion
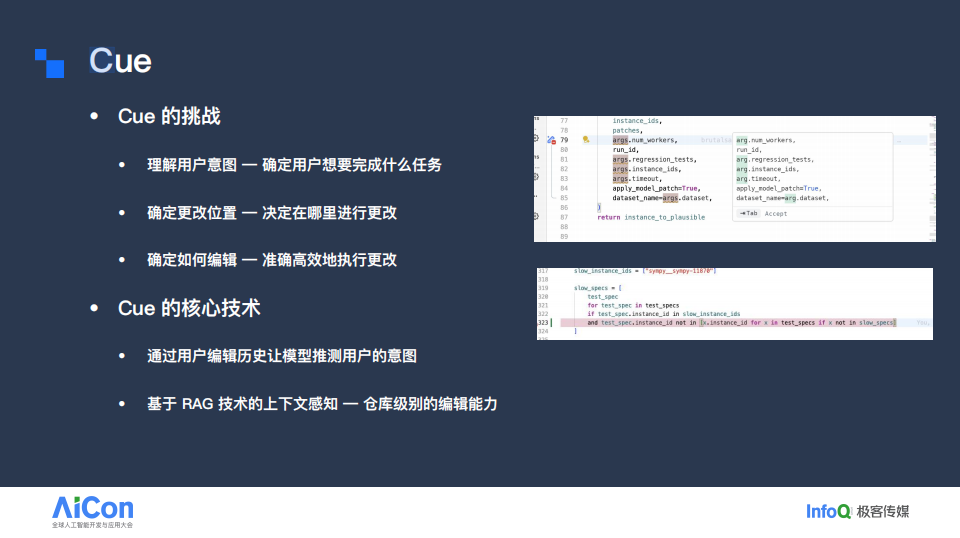
Cue features:
- Multi-point editing (insert, delete, replace)
- Cursor prediction (suggest imports after method creation)
- Cross-file edits using RAG for context awareness
---
Authentic Edit Era → Builder
Builder capabilities:
- Searches whole repository
- Chooses target files
- Makes coordinated edits across multiple files
Tools in Builder mode:
- Write to File
- Delete File
- Update File
---
The Limits of Apply in Agentic Scenarios
- High resource cost — multi-file edits multiply Chat + Apply calls
- Increased failure rate — two-stage process adds risk
- File length problems — impacts very long files

---
Search/Replace Approach
Mechanism:
- Model specifies `old content` → Replace with `new content`
- Works for any file length
- No second model call
Challenges:
- Strict format adherence
- Accurate escaping (JSON)
- Long strings may hit context limits → requires chunking or arrays
---
Apply vs Search/Replace: When to Use
- Chat Mode: Prefer Apply (better UX)
- Builder Mode: Prefer Search/Replace (accuracy, efficiency)
---
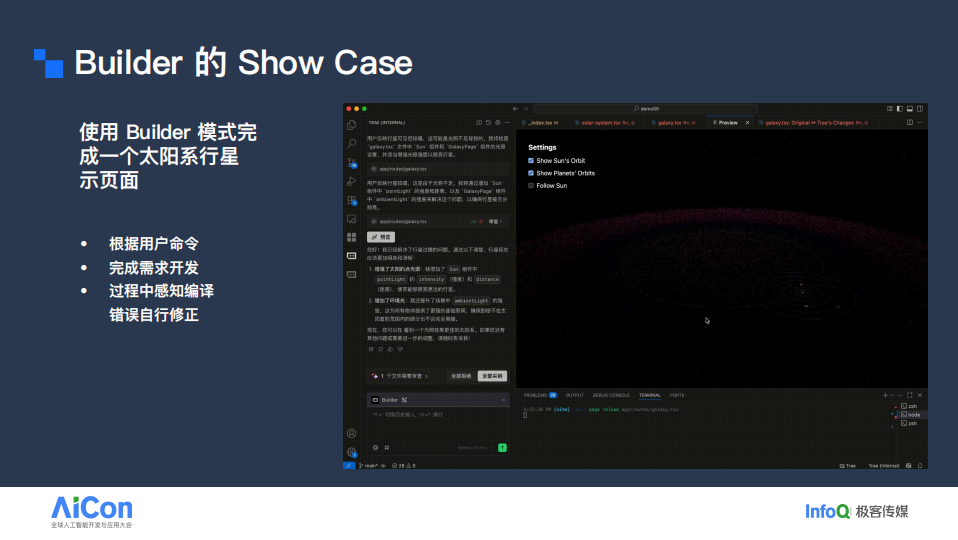
Builder Showcase Example
Case: Implementing a Solar System planetary orbit page
- Iterative feedback loop
- System refines display until fully complete
---
Summary and Outlook
Three development stages:
- Apply model — Targeted code edits
- Cue — Instant, intelligent completions
- Agentic Edit — Fully autonomous repository-wide edits
Future directions:
- Improve accuracy & efficiency
- Explore Multi-Agent frameworks
- Enhance planning & reasoning abilities
---
Cross-Domain AI Application — AiToEarn Insight
Open-source platforms like AiToEarn官网 extend these principles to multi-platform content creation & monetization.
Capabilities include:
- AI content generation
- Cross-platform publishing (Douyin, Bilibili, Facebook, YouTube, etc.)
- Analytics & AI model rankings (AI模型排名)
More info: AiToEarn博客
---
✅ Key Takeaway:
Whether for code editing tools like Trae or creative content pipelines like AiToEarn, the integration of automation, intelligent planning, and cross-file/context awareness is critical to achieving scalable, efficient, and monetizable AI workflows.



