Google Cloud C4 Cuts GPT OSS Total Cost of Ownership by 70% with Intel and Hugging Face
# Benchmarking GPT OSS on Google Cloud C4 VMs with Intel® Xeon® 6 (Granite Rapids)
Intel and Hugging Face partnered to demonstrate **real-world performance gains** from upgrading to **Google’s new C4 Virtual Machine (VM)**, powered by **Intel® Xeon® 6 processors (codenamed Granite Rapids – GNR)**.
They benchmarked the **OpenAI GPT OSS Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) Large Language Model** to measure text generation improvements.
**Key outcome:**
- **1.7× Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) gain** over earlier-generation Google C3 VM instances
- **1.4×–1.7× TPOT throughput/vCPU/dollar**
- **Lower hourly cost** compared to C3 VMs
---
## 1. Introduction
### What is GPT OSS?
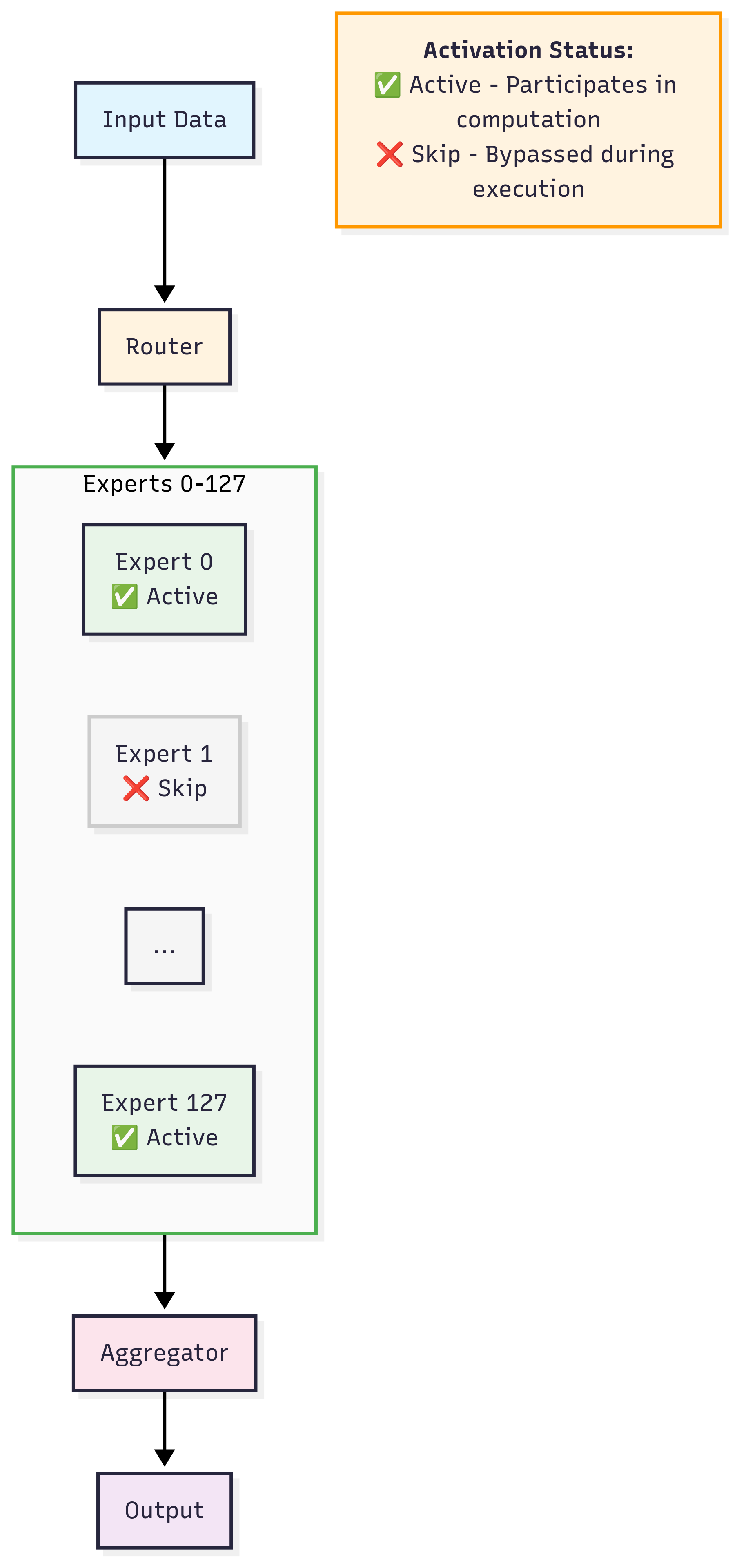
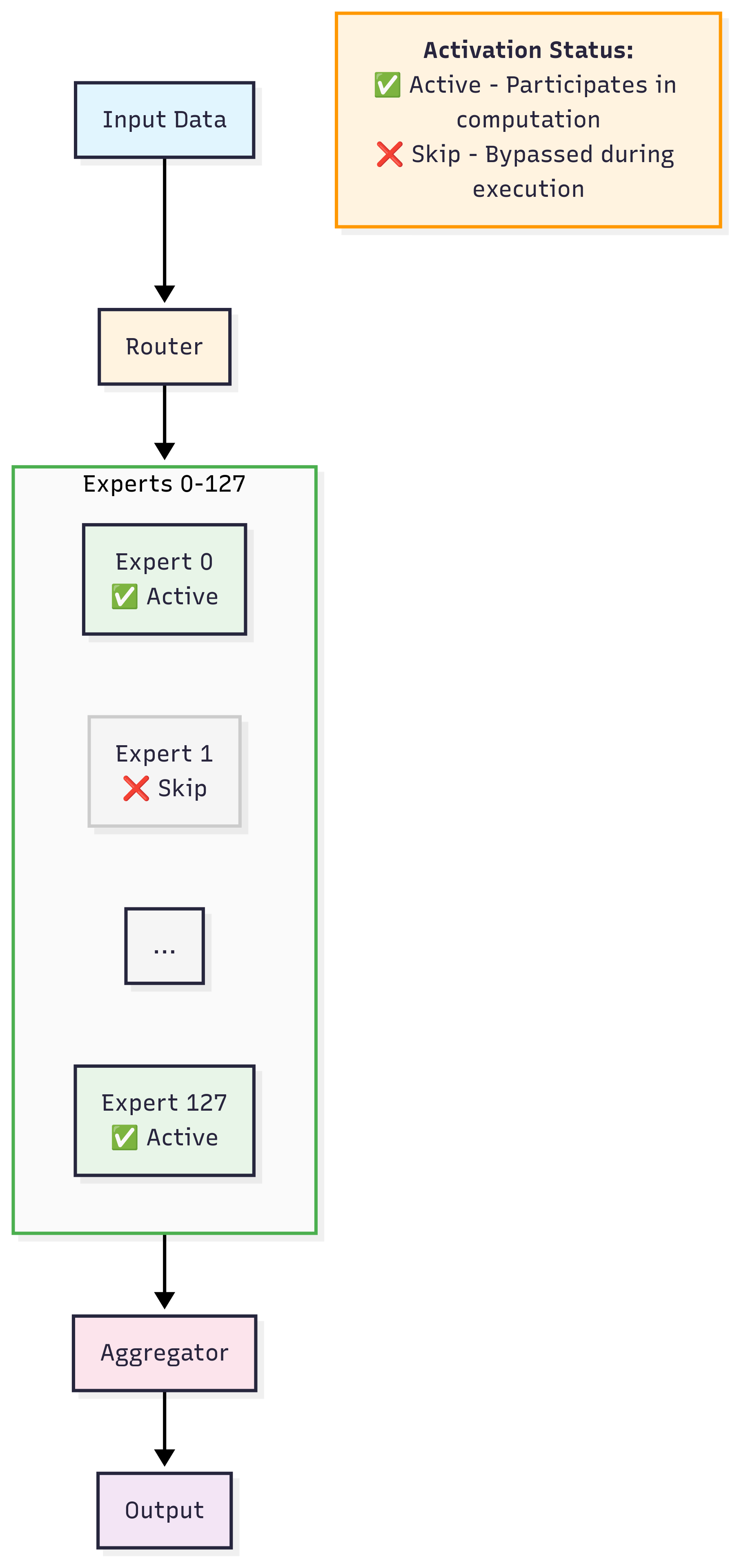
GPT OSS is an open-source **Mixture of Experts (MoE)** model from OpenAI.
An MoE uses multiple specialized “expert” sub-networks plus a *gating network* that decides which experts to run per input token.
**Advantages:**
- **Efficient scaling** of parameters without a linear increase in compute cost
- **Specialization** across data distributions
- **CPU inference viability** — only a small set of experts runs per token
---
### Intel & Hugging Face Optimization
Intel and Hugging Face added an execution optimization ([PR #40304](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/pull/40304)) that:
- Eliminates wasteful computation (experts no longer process all tokens)
- Processes only **assigned tokens per expert**
- Reduces FLOPs and improves performance efficiency
---
This type of framework-level improvement makes **cloud AI workloads** more cost-effective.
Creators and developers can leverage such gains in workflows via platforms like [AiToEarn官网](https://aitoearn.ai/), which support:
- AI-powered creation
- Global multi-platform publishing
- Monetization tracking
---
## 2. Benchmark Scope & Hardware
We benchmarked GPT OSS in **controlled/repeatable** text generation tests to separate:
1. Architectural differences between **C4 (Xeon 6 – GNR)** and **C3 (Xeon 4th Gen – SPR)**
2. Execution efficiency of **MoE inference**
**Focus metrics:**
- **Steady-state decoding latency** (per-token)
- **Throughput scaling** with larger batch sizes
- Fixed sequence length, static KV cache, **SDPA attention** ensured deterministic results
---
### Configuration Summary
- **Model:** [unsloth/gpt-oss-120b-BF16](https://huggingface.co/unsloth/gpt-oss-120b-BF16)
- **Precision:** bfloat16
- **Input length:** 1024 tokens (left-padded)
- **Output length:** 1024 tokens
- **Batch sizes tested:** 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64
- **Features:**
- Static KV cache
- SDPA attention backend
- **Metric:** Throughput in total generated tokens/sec
---
### Hardware Specs
| Instance | Architecture | vCPUs |
|----------|-----------------------------------------|-------|
| **C3** | 4th Gen Intel® Xeon® (SPR) | 172 |
| **C4** | Intel® Xeon® 6 (Granite Rapids – GNR) | 144 |
---
## 3. Creating the VMs
### 3.1 C3 VM Setup
1. Go to [Google Cloud Console](https://console.cloud.google.com/)
2. Create a VM → choose **C3**, machine type: `c3-standard-176`
3. Set **CPU platform** and enable **all-core turbo**
[](https://huggingface.co/datasets/Intel/blog/resolve/main/gpt-oss-on-intel-xeon/spr.png)
4. Configure OS & Storage:
[](https://huggingface.co/datasets/Intel/blog/resolve/main/gpt-oss-on-intel-xeon/spr-os.png)
5. Leave other settings default and click **Create**
---
### 3.2 C4 VM Setup
1. Go to [Google Cloud Console](https://console.cloud.google.com/)
2. Create a VM → choose **C4**, machine type: `c4-standard-144`
3. Set **CPU platform** and enable **all-core turbo**
[](https://huggingface.co/datasets/Intel/blog/resolve/main/gpt-oss-on-intel-xeon/gnr.png)
4. Configure OS & Storage same as C3
5. Click **Create**
---
## 4. Environment Setup
SSH into the VM and install Docker, then:
git clone https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git
cd transformers/
git checkout 26b65fb5168f324277b85c558ef8209bfceae1fe
cd docker/transformers-intel-cpu/
sudo docker build . -t
sudo docker run -it --rm --privileged \
-v /home/:/workspace \
/bin/bash
---
### Inside the container:
1. **Install Transformers exact version**pip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git@26b65fb5168f324277b85c558ef8209bfceae1fe
2. **Install PyTorch CPU build**pip install torch==2.8.0 torchvision torchaudio --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu
---
## 5. Benchmark Procedure
For each **batch size**:
1. Create fixed-length left-padded input (1024 tokens)
2. Warm-up run
3. Set `max_new_tokens=1024`, measure **total latency**
4. **Throughput formula**:
\[
\text{Throughput} = \frac{\text{OutputTokens} \times \text{BatchSize}}{\text{TotalLatency}}
\]
Run:numactl -l python benchmark.py
---
### Example Benchmark Scriptimport os
import time
import torch
from datasets import load_dataset
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
INPUT_TOKENS = 1024
OUTPUT_TOKENS = 1024
def get_inputs(tokenizer, batch_size):
dataset = load_dataset("ola13/small-the_pile", split="train")
tokenizer.padding_side = "left"
selected_texts = []
for sample in dataset:
input_ids = tokenizer(sample["text"], return_tensors="pt").input_ids
if len(selected_texts) == 0 and input_ids.shape[-1] >= INPUT_TOKENS:
selected_texts.append(sample["text"])
elif len(selected_texts) > 0:
selected_texts.append(sample["text"])
if len(selected_texts) == batch_size:
break
return tokenizer(
selected_texts,
max_length=INPUT_TOKENS,
padding="max_length",
truncation=True,
return_tensors="pt"
)
def run_generate(model, inputs, generation_config):
inputs["generation_config"] = generation_config
model.generate(**inputs) # warm up
pre = time.time()
model.generate(**inputs)
latency = (time.time() - pre)
return latency
---
## 6. Results
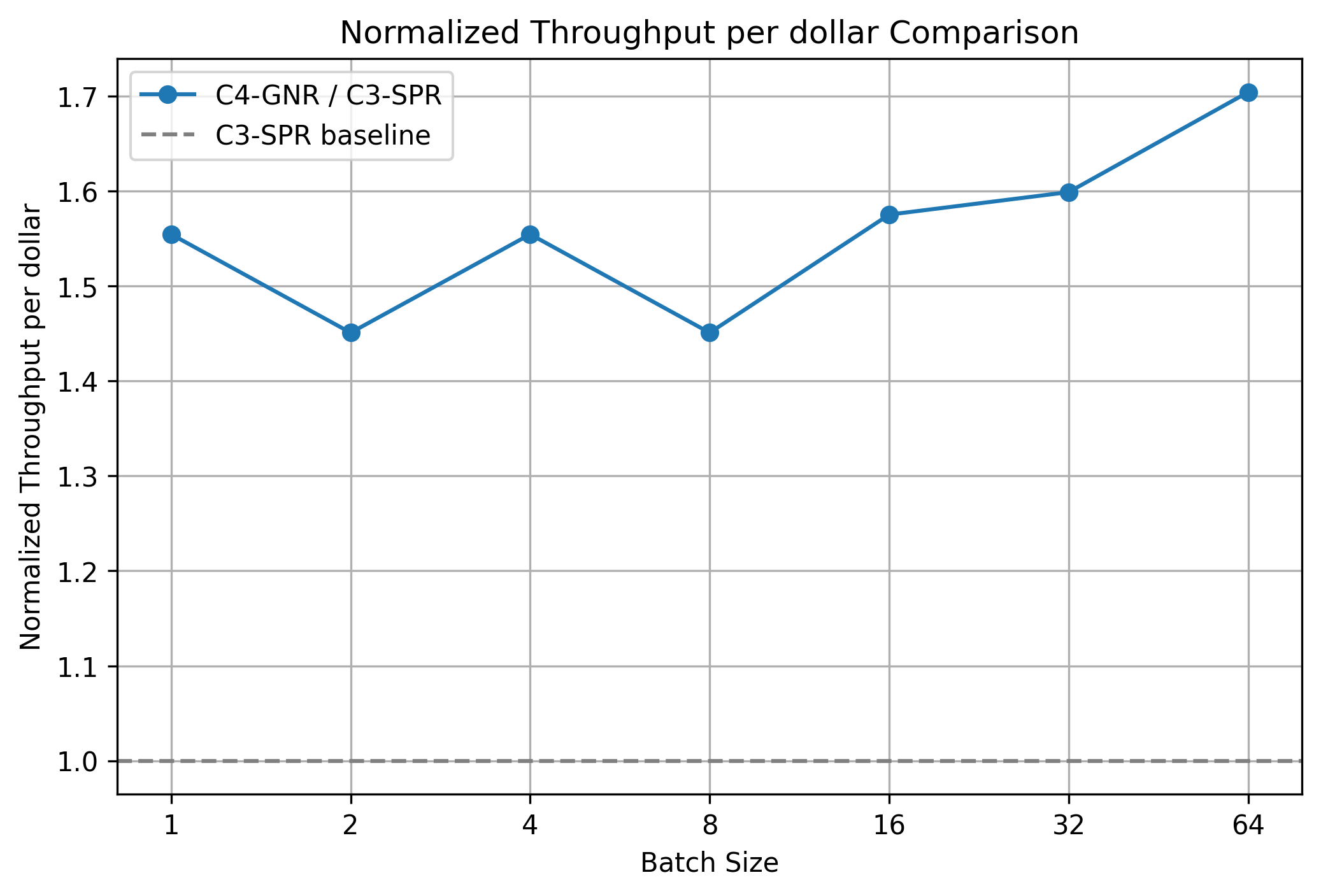
### 6.1 Normalized Throughput per vCPU
C4 (Xeon 6) shows **1.4×–1.7×** throughput/vCPU over C3.
Formula:Normalized Throughput = Throughput / vCPU_Count
Normalized comparison:normalized_throughput_per_vCPU =
(throughput_C4 / vCPUs_C4)
———————————————
(throughput_C3 / vCPUs_C3)
\[
\frac{\text{Throughput}_\mathrm{C4} / \text{vCPUs}_\mathrm{C4}}
{\text{Throughput}_\mathrm{C3} / \text{vCPUs}_\mathrm{C3}}
\]
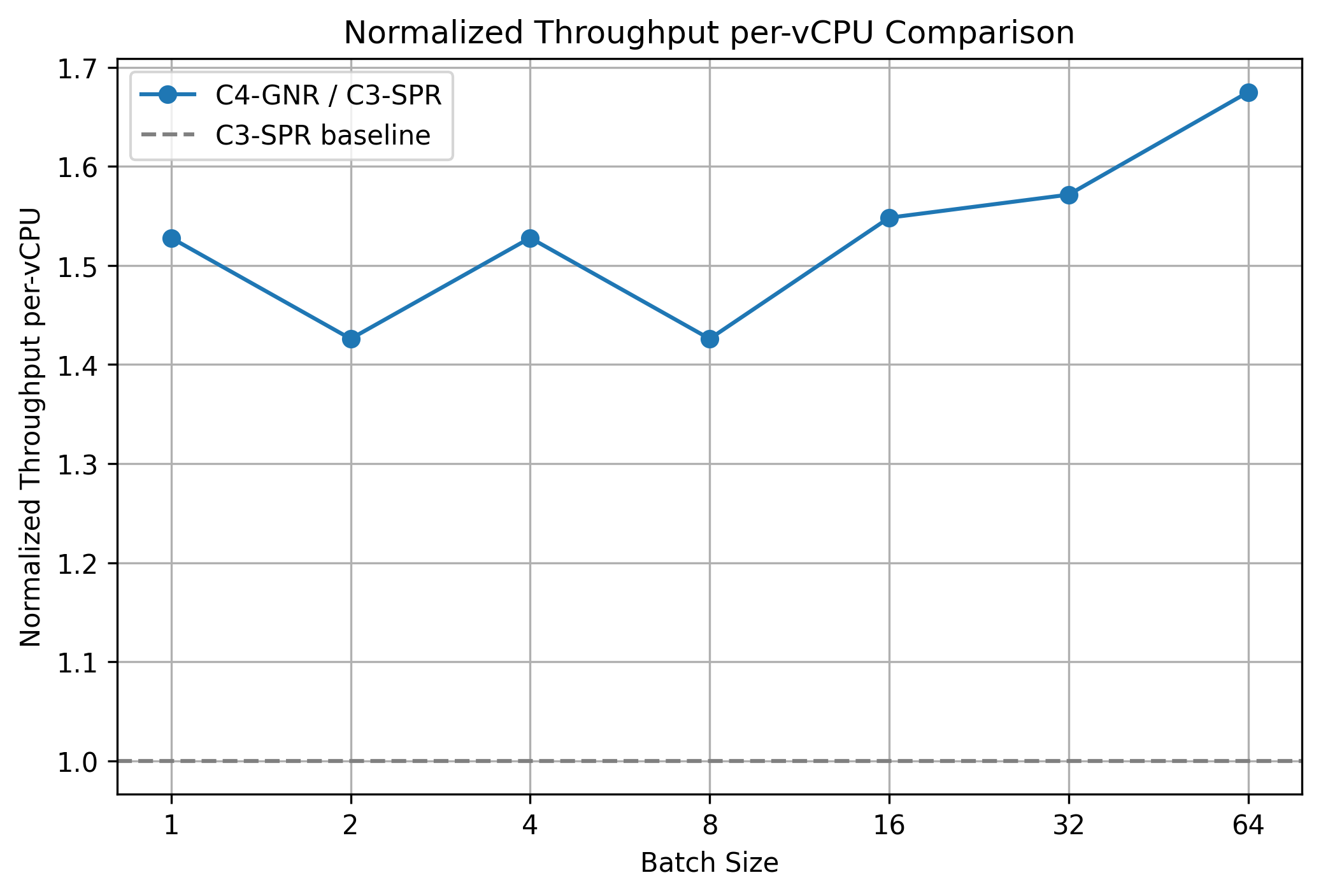
---
### 6.2 Cost & TCO Impact
At batch size 64:
- **C4 delivers 1.7× per-vCPU throughput** vs. C3
- Equal per-vCPU pricing ⇒ **1.7× TCO advantage** for C4
**Cost equation:**TCO_C3 / TCO_C4 ≈ 1.7
---
## 7. Conclusion
**Google Cloud C4 VMs + Intel® Xeon® 6 (GNR)**:
- Higher throughput
- Lower latency
- Better cost efficiency for large-scale MoE inference
With Intel & Hugging Face optimizations, GPT OSS MoE models can achieve **high efficiency on modern general-purpose CPUs**.
Creators and enterprises can integrate this compute efficiency into **global AI content workflows** via [AiToEarn](https://aitoearn.ai)—an open-source monetization platform enabling:
- AI content generation
- Multi-platform publishing (Douyin, Kwai, WeChat, Bilibili, Xiaohongshu, Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, Threads, YouTube, Pinterest, X/Twitter)
- Analytics and model ranking ([AI模型排名](https://rank.aitoearn.ai))
This bridges **high-performance AI inference** with **scalable monetization** opportunities.