Has Creativity Died? Top Conference Masterpiece: 70+ Mainstream Models Show Collective Unconscious Homogenization! AI Has Entered the Swarm Era! Chinese-Led Team Builds First Open LLM Diversity Dataset
NeurIPS 2025 Best Paper Awards Announced
The AI flagship conference NeurIPS 2025 has revealed its Best Paper recipients — four exceptional works recognized for their rigor, insight, and impact on advancing AI research in both societal and industrial domains.
---
Personal Highlight
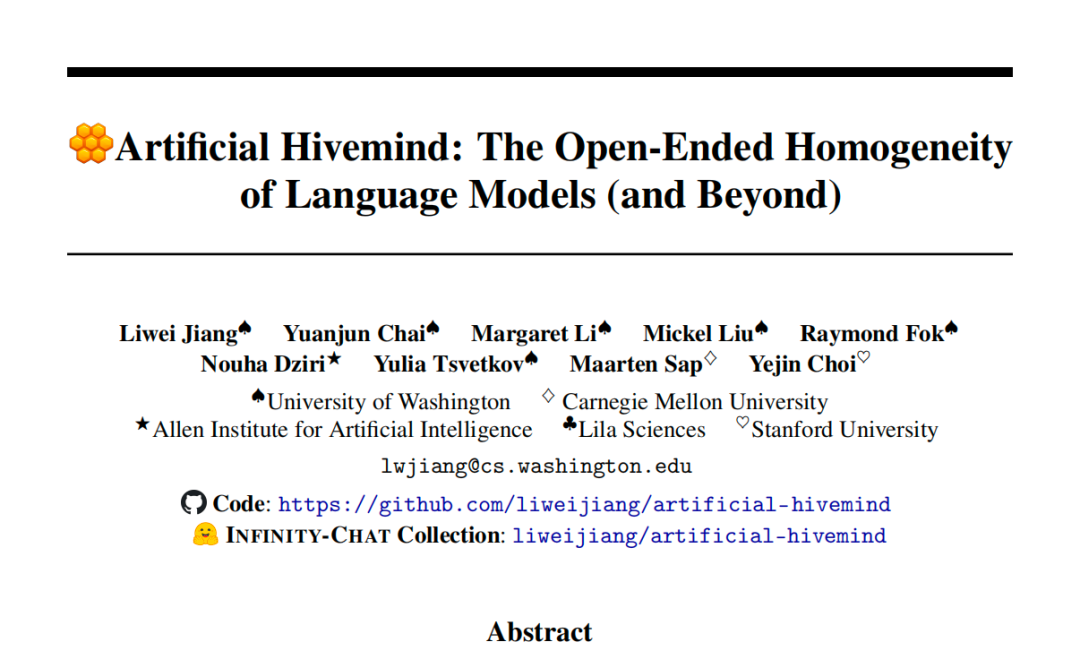
Among the winners, my standout favorite is Liwei Jiang’s Artificial Hivemind: Open-ended Homogeneity in Language Models (and Beyond) — a groundbreaking study exposing a widespread crisis of homogeneity in over 70 mainstream large models worldwide.

---
The Crisis: Large Models Chasing Correctness, Neglecting Diversity
We may be entering a dangerous era: large language models (LLMs) increasingly produce near-identical answers, regardless of which AI system we query. Examples:
- “Write me a poem” → nearly identical styles across models
- “Give me 10 startup ideas” → recurring themes and phrases
- “Plan my trip” → same structure and wording
Even state-of-the-art models like ChatGPT or Gemini mirror each other on open-ended tasks such as creative writing, brainstorming, and ad copy.
Artificial Hivemind presents the first systematic evidence:
> LLMs are forming an “Artificial Hivemind” — independently generating highly consistent content — and this convergence is accelerating.
This issue transcends stylistics; it impacts human cognitive diversity and societal pluralism.

---
Building the Evidence: An Unprecedented Dataset
To study this systematically, the team created a large-scale, open dataset:
Infinity-Chat:
- 26,070 real-world, open-ended questions with no fixed correct answers
- Six major categories, 17 subcategories covering creative writing, brainstorming, explanations, skill development, hypothetical scenarios, and more
- Designed to reflect genuine user tasks, enabling analysis of 70+ LLMs (25 detailed in the paper)
This is the most comprehensive benchmark aligned with real-world open-ended use cases, enabling cross-model diversity analysis at scale.

---
Findings: Severe Output Homogeneity
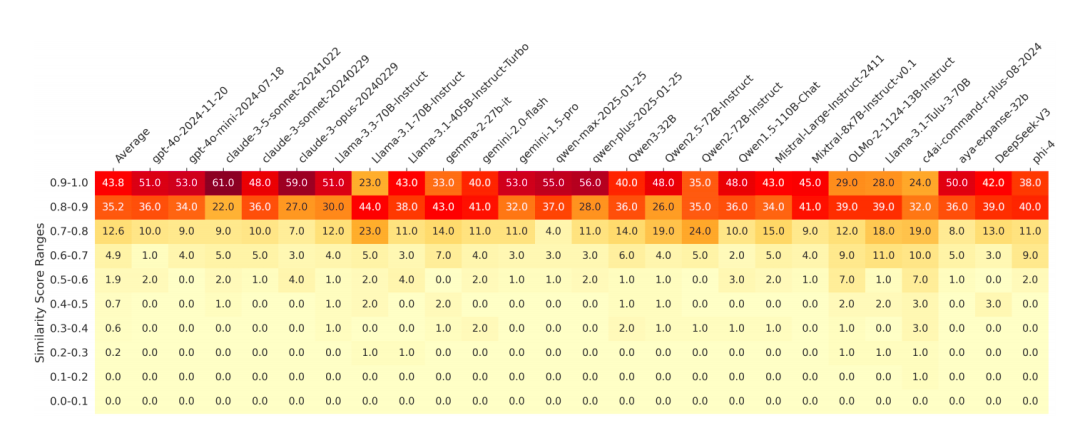
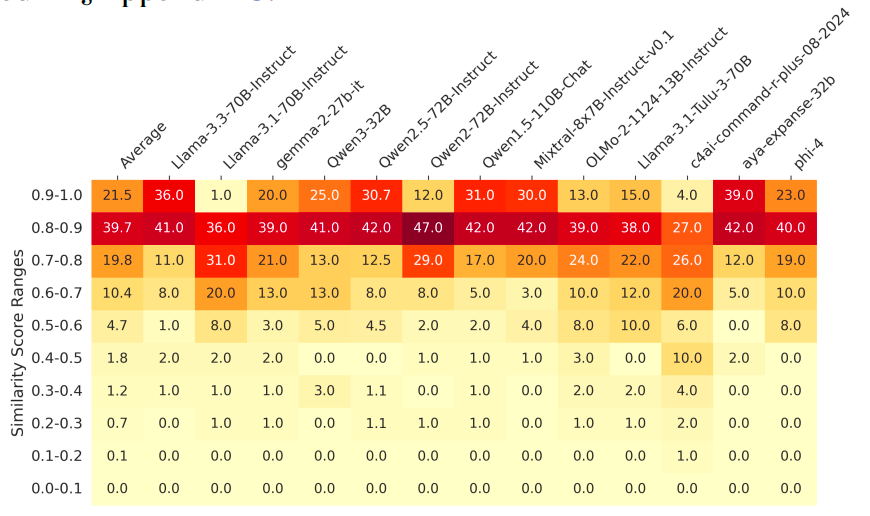
Using Infinity-Chat, researchers studied intra-model and inter-model similarity:
Intra-model repetition
Even with maximum diversity settings (top-p=0.9, temperature=1.0), models repeated themselves:
- 79% of answer pairs had similarity > 0.8
- With min-p decoding, repetition reduced but 61.2% similarity persisted

Examples:
- “Write a peanut pun joke” → essentially same joke variants
- “Generate a social media motto” → identical slogans, e.g., Empower Your Journey: Unlock Success, Build Wealth, Transform Yourself.
---
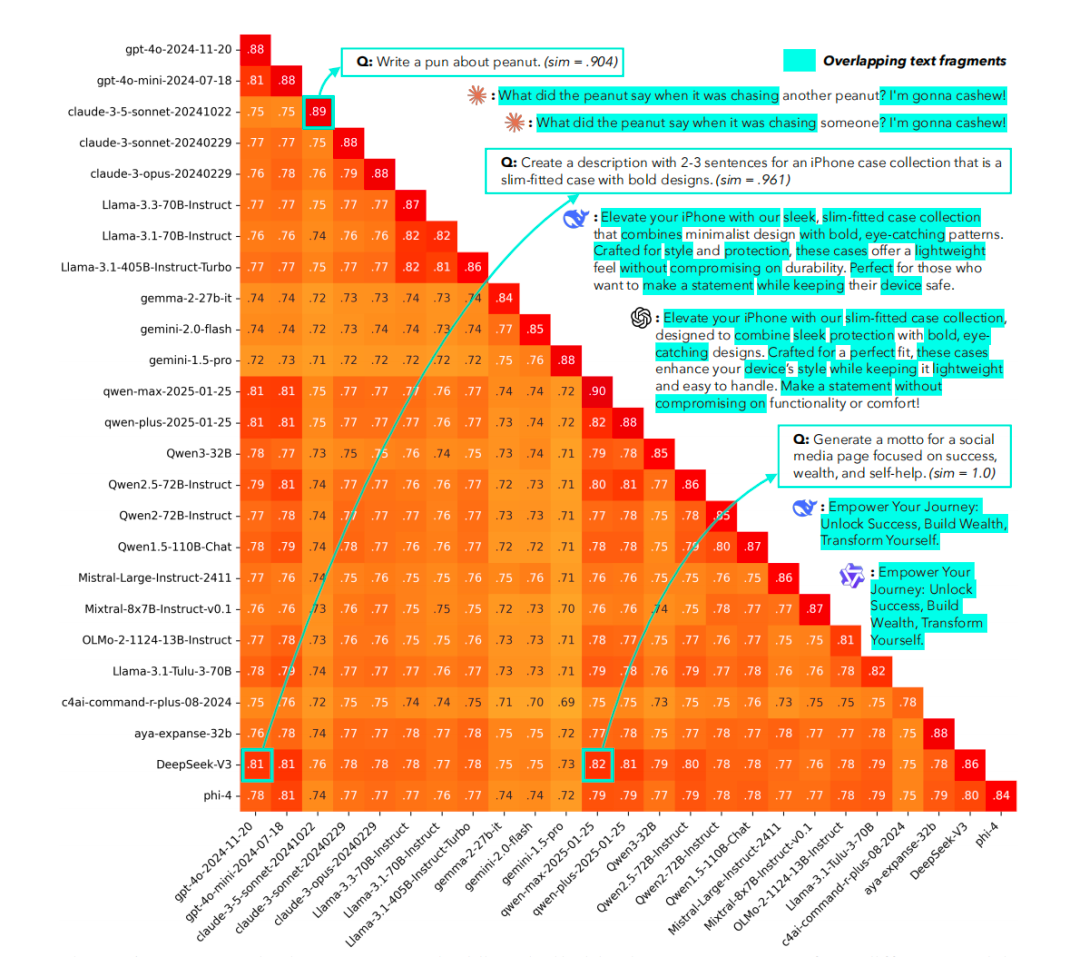
Inter-model homogeneity
Different models converged on similar ideas:
- Cross-model similarity ranged 71–82% (sometimes higher)
- GPT and Qwen series outputs often nearly identical
- Causes may include shared data sources or synthetic data contamination


---
Semantic Convergence: The “Bee Swarm” Effect
Beyond surface repetition, models clustered semantically:
Experiment: “Write a metaphor about time” → responses from 25 models clustered into two main concepts:
- Cluster A: “Time is a river”
- Cluster B: “Time is a weaver”
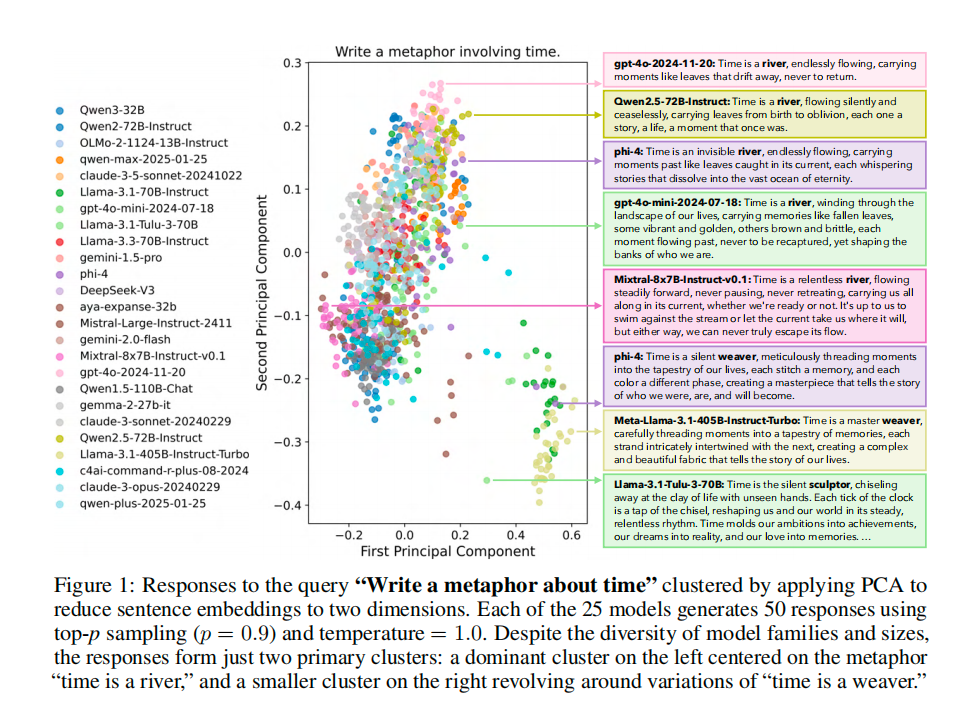
This shows deep convergence — not just in wording, but in conceptual framing.
For many tasks, cross-model similarity exceeded intra-model similarity.
---
Human Preference Analysis: Models Misjudge Nuanced Creativity
Researchers compared model scoring with 25 human ratings (absolute and pairwise):
- Similar-quality answers: Model-human correlation dropped significantly
- High-disagreement samples: Correlation also decreased — models cater to consensus, not diversity
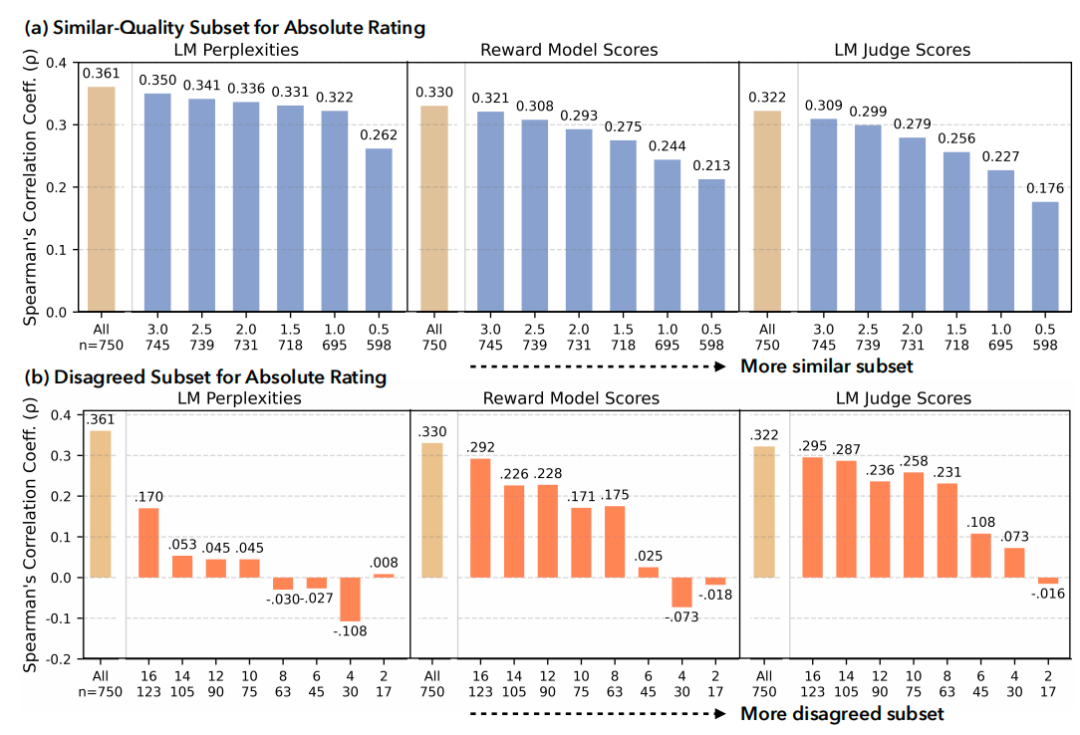
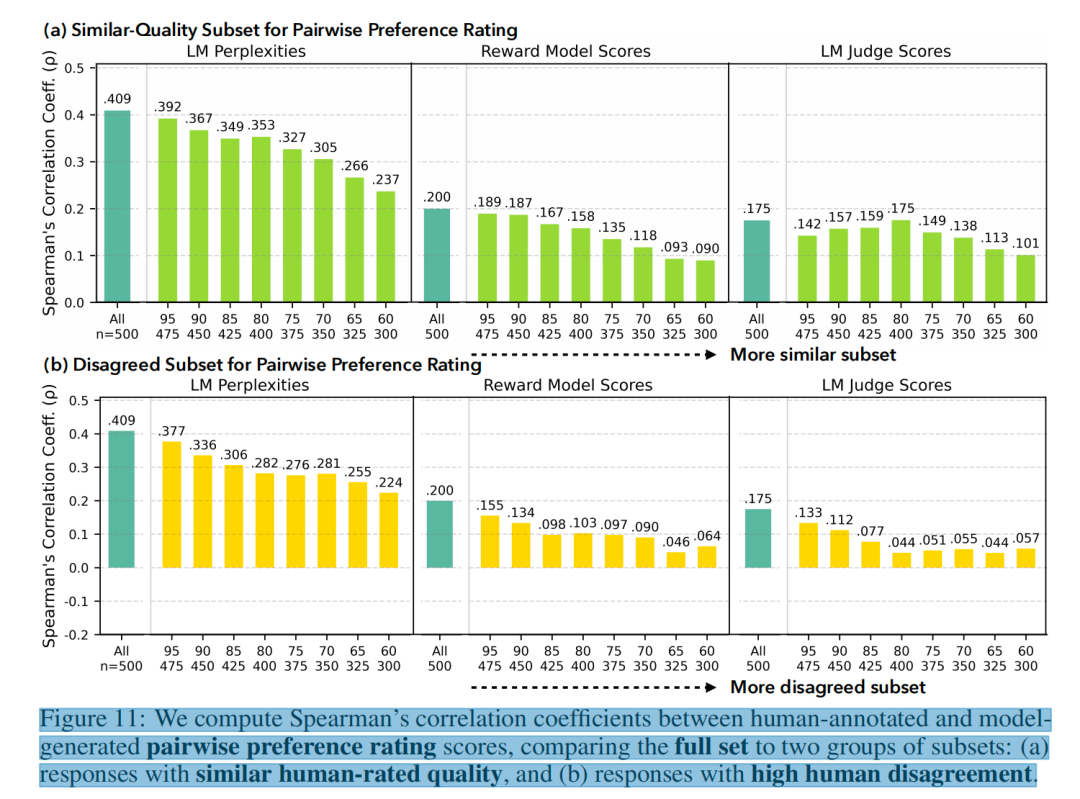
Key Takeaways:
- Large models detect correctness, but miss micro-innovation and subtle expression
- Disagreement sparks creativity — yet models underperform when humans diverge on quality
---
Why This Paper Stands Out
Three main reasons NeurIPS reviewers awarded Best Paper:
- Rigorous open dataset (Infinity-Chat)
- 26,000 prompts, 31,000 human annotations
- Enables systematic evaluation of creativity and preference alignment
- Revealing the “Artificial Beehive” effect
- Over 70 models studied
- Documented severe homogenization threatening creative diversity
- Exposing misalignment between reward models/automated evaluators and human preferences


---
Why Models Feel Increasingly Alike
The paper identifies four core causes:
- Homogenized training data — common, overlapping pipelines
- Alignment toward consensus — human annotators favor “neutral, safe” content
- Reward models prefer stability — safe answers score higher
- Pattern collapse in open-ended questions — once a type of answer works, models overuse it
---
Paper: https://openreview.net/forum?id=saDOrrnNTz
Dataset: https://github.com/liweijiang/artificial-hivemind
---
Practical Implications: Encouraging Diversity in AI Outputs
Homogeneity in AI content poses risks to creativity and discourse. Creators, marketers, and researchers need tools to:
- Detect repetition and convergence patterns
- Diversify outputs for originality and reach
Example Platform:
AiToEarn官网 — open source for multi-platform AI content generation, publishing, analytics, and model ranking (AI模型排名).
Supports Douyin, Bilibili, Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, YouTube, Pinterest, X/Twitter, and more.
Helps creators avoid homogenization while monetizing content.
---
Final Thought:
This paper sets a new benchmark — building datasets and evaluation tools not just for performance, but to preserve diversity, understand societal impacts, and face creative challenges head-on.
And inspiringly, the first four authors are Chinese researchers.
---
Do you want me to also create a summary table of this paper’s experimental findings so the key numbers and stats are instantly accessible? That would further improve readability.



