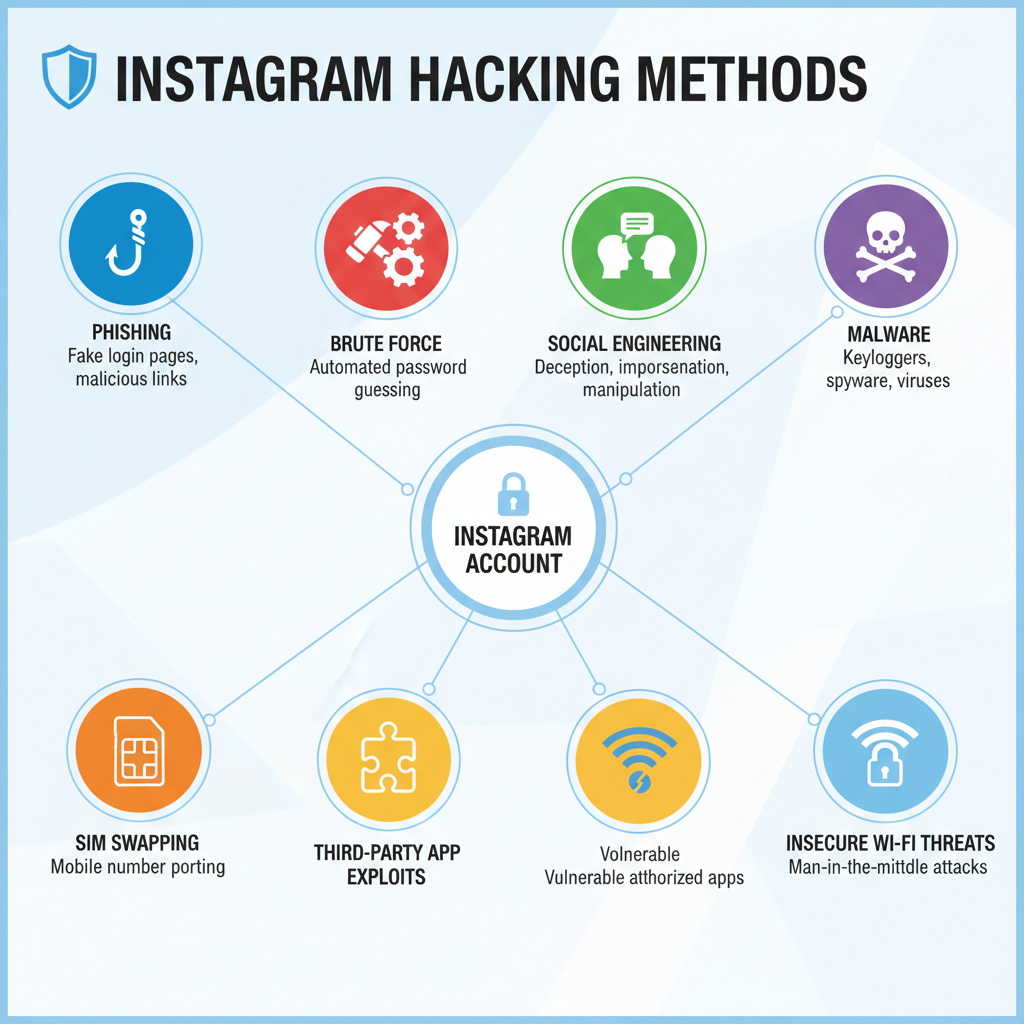
How Do People Hack Instagram Accounts and Stay Safe
Learn common Instagram hacking methods like phishing, brute force, and social engineering, plus practical tips to secure and recover your account.

Introduction to Instagram Hacking Trends and Risks
Instagram remains one of the most used and influential social media platforms across the globe, making it a prime target for cybercriminal activities. Understanding how people hack Instagram accounts is vital for maintaining your security in today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape. By recognizing attack patterns and risk factors, you can better safeguard your profile, data, and online reputation.
Hackers deploy a diverse arsenal of techniques — from phishing and brute force attacks to social engineering and malware deployment. These malicious activities can lead to identity theft, financial loss, and lasting reputational harm.

This comprehensive guide explains the most common hacking tactics directed at Instagram, illustrates how to spot them early, and details the steps you can take to secure and recover your account effectively.
---
Common Hacking Methods Targeting Instagram
Instagram account breaches can occur through multiple, often overlapping, techniques. Here are some of the most frequent methods attackers use:
- Phishing schemes — Fake login portals crafted to steal your credentials.
- Brute force / credential stuffing — Automated guessing or using leaked passwords.
- Social engineering — Manipulating victims through trust and deception.
- Malware / keyloggers — Malicious software capturing keystrokes and data.
- SIM swapping — Hijacking your phone number to bypass two-factor authentication.
- Exploiting third-party apps — Insecure applications exposing Instagram data.
- Public Wi-Fi interception — Stealing data via unsecured networks.
---
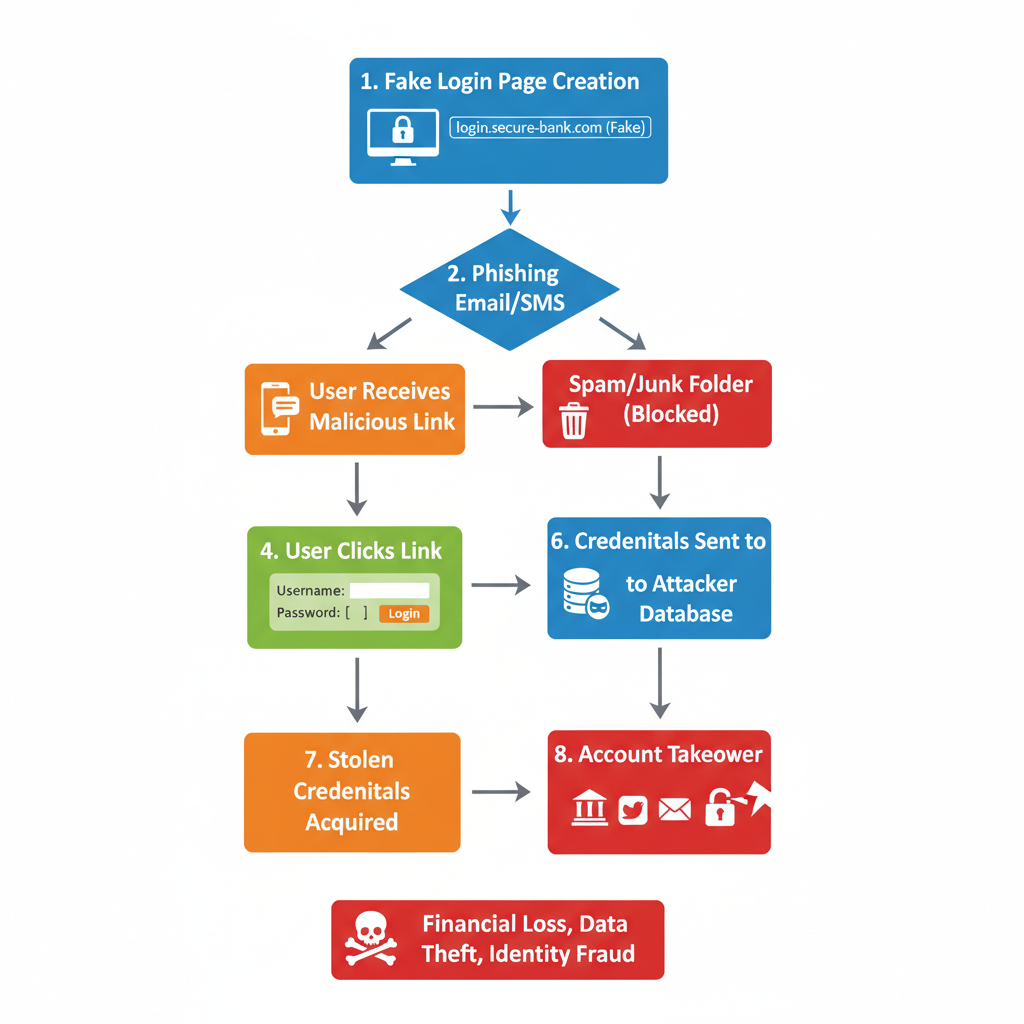
Phishing Attacks: Fake Login Pages and Email Scams
Phishing is one of the most widely used tactics for hacking Instagram accounts. Attackers build fake login pages resembling the official Instagram interface, tricking users into entering their usernames and passwords.
Common phishing scenarios include:
- Email spoofing — Emails purporting to be from Instagram, urging urgent action like "Account Verification" or "Security Alert".
- In-DM phishing — Direct messages containing suspicious links that lead to fake login pages.
- Clone websites — Replicas of Instagram’s platform hosted on unauthorized domains.
Pro Tip: Always verify URLs carefully. Legitimate Instagram links begin with https://www.instagram.com/.
---
Brute Force and Credential Stuffing Attacks
Brute force attacks employ automated bots that systematically try various password combinations until they succeed. Credential stuffing leverages stolen username-password pairs from other breaches to access your Instagram account.
Attackers commonly succeed when:
- Passwords are weak or common (e.g., 'password123').
- The same password is reused across multiple services.
- Login systems lack rate-limiting safeguards.
| Attack Type | Method | Risk Level |
|---|---|---|
| Brute Force | Automated, repeated password guessing | High |
| Credential Stuffing | Using breached login credentials from other sites | High |
---
Social Engineering: Direct Messages and Impersonation
Social engineering preys on human psychology rather than technical security flaws. Attackers impersonate trusted contacts, popular influencers, or legitimate brands to coax victims into revealing confidential information.
Common scenarios include:
- Urgent pleas — “I’m locked out; please send me your password.”
- Collaboration offers — Fake brand deals directing you to external login pages.
- Prize notifications — “You’ve won a giveaway; log in here to claim your prize.”
Because these attacks rely on voluntary disclosure under false pretenses, they are particularly dangerous and harder to detect.
---
Malware and Keyloggers Targeting Instagram Users
Malware is capable of harvesting passwords, tracking activity, and enabling attackers to log in from their devices without detection.
Typical infection methods:
- Downloading pirated or cracked software.
- Opening email attachments from unknown senders.
- Installing unauthorized mobile apps from non-official sources.
Keyloggers, a specific type of malware, silently record every keystroke you make, capturing Instagram credentials in real time.
---
SIM Swapping to Bypass Two-Factor Authentication
SIM swapping involves breaching telecom security by convincing or bribing staff to transfer your phone number to an attacker’s SIM card. Once successful, this allows interception of SMS-based authentication codes.
Preventive measures:
- Use app-based 2FA like Google Authenticator rather than SMS.
- Set a dedicated SIM PIN through your mobile carrier.
- Limit public exposure of sensitive personal details such as phone numbers and birthdates.
---
Exploiting Third-Party Apps and Insecure Wi-Fi Connections
Third-party apps often request access to Instagram accounts for services like post scheduling, analytics, or photo editing. If such apps lack robust data protection measures, your credentials could be at risk.
Similarly, public Wi-Fi networks without encryption can expose your login information and session data to attackers.
Best practices:
- Authorize only applications from reputable sources.
- Always use a VPN when connecting via public Wi-Fi.
---
Signs Your Instagram Account May Have Been Compromised
Early detection drastically improves recovery chances. Warning signs include:
- Being logged out unexpectedly on all devices.
- Posts or messages you didn’t create appearing on your account.
- Unapproved changes to profile details.
- Receiving 2FA codes you didn’t request.
---
Step-by-Step Guide to Securing Your Instagram Account
Proactive steps to reinforce your account’s defenses:
- Change Your Password — Ensure it’s strong, complex, and unique.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) — Opt for app-based 2FA over SMS.
- Check Login Activity — Navigate to “Settings > Security > Login Activity” in Instagram.
- Audit App Permissions — Remove unused or suspicious third-party applications.
- Secure Your Email — Strengthen the account linked to Instagram for password resets.
- Update Devices Routinely — Apply software and OS updates promptly.
---
How to Recover a Hacked Instagram Account
If your account is compromised:
- Try a Password Reset — Use the “Forgot password?” option on the login screen.
- Review Emails From Instagram — Look for alerts or password change notifications.
- Use the ‘My Account Is Hacked’ Form — Available via Instagram’s Help Center.
- Provide Identity Verification — Instagram may request government-issued ID.
Immediate response is crucial for limiting damage and restoring account control.
---
Legal Consequences of Instagram Hacking and Reporting Suspicious Activity
Hacking an Instagram account is a criminal offense under cybercrime laws globally. Legal consequences can include:
- Significant fines.
- Prison sentences.
- Permanent bans from online platforms.
Report any phishing links or suspicious activities via Instagram’s built-in reporting features to help protect the community.
---
Ongoing Habits to Maintain Account Security
Building a long-term defense requires:
- Keeping operating systems, browsers, and apps up to date.
- Changing passwords regularly.
- Avoiding links from unknown sources.
- Enabling biometric security on devices.
- Maintaining secure backups of important account data.
---
Conclusion: Being Proactive Prevents Most Compromises
Understanding how people hack Instagram accounts empowers you to protect your digital presence more effectively. While attackers continually adapt their methods, consistent application of security best practices — such as strong authentication, mindful app permissions, and vigilant monitoring — will stop most threats before they cause harm.
Your Instagram profile often represents a significant part of your personal and professional identity. Treat its security as a priority, and act today to stay ahead of potential compromises.
Protect your account now — review your Instagram security settings and implement these strategies before a breach occurs.