How Does a Carousel Work in Parks and Interactive Design
Explore how carousels operate in amusement parks and digital design, covering mechanical components, power systems, motion control, and safety elements.
Introduction to Carousels and Their Versatile Applications
Carousels, whether found in amusement parks or as dynamic web design components, are captivating rotating devices designed to engage audiences and present multiple items within a single, interactive frame. In the physical world, a carousel is a large circular platform with seats or sculptures — often horses or thematic figures — revolving around a central axis. In digital environments, the term refers to image sliders or content rotators in UI design, cycling through elements automatically or on user input. This article provides a detailed look at how does a carousel work, exploring both mechanical rides and digital implementations.
---
History and Evolution of Carousels
The first carousels emerged in 17th‑century Europe as cavalry training devices, gradually transforming into amusement rides by the 19th century with the advent of steam power. Decorative artistry and engineering advancements — particularly electric motor technology — refined the experience, creating smoother, safer rotations. In modern times, “carousel” also denotes digital sliders, marking an evolution from purely mechanical entertainment to versatile visual interfaces.
---
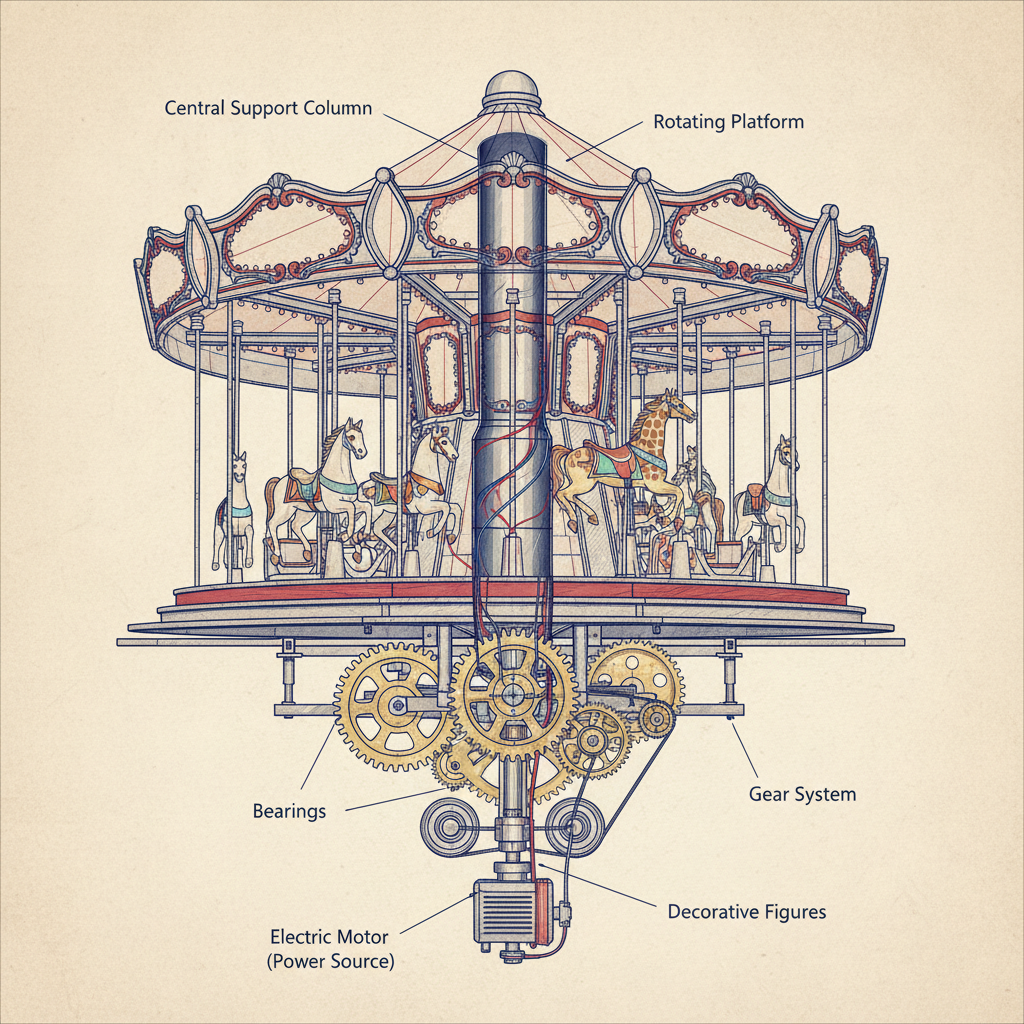
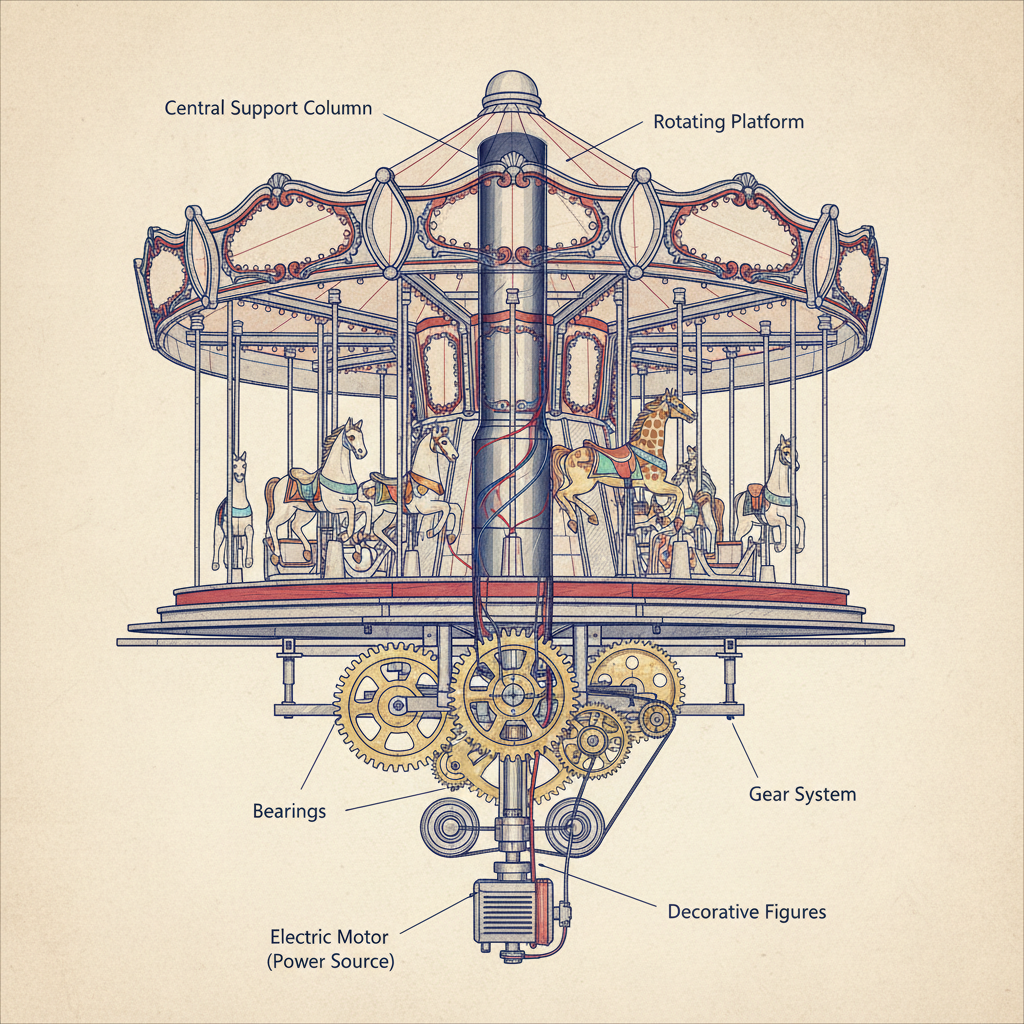
Mechanical Components of Traditional Amusement Park Carousels
Physical carousels operate through interconnected mechanical systems designed for synchronized, reliable motion.
Core Components
- Central Mast: Structural axis for rotation.
- Platform: Rotating deck accommodating riders.
- Ride Figures: Ornamental horses, animals, or themed seats mounted to poles.
- Drive System: Transfers power to the platform.
- Gearing: Regulates speed and torque.
- Bearings: Support weight and minimize friction.
- Canopy & Decorative Elements: Shelter and enhance thematic appeal.
---
Rotating Platform Mechanism: Step-by-Step Operation
An amusement carousel’s rotation relies on the combined action of balanced structure, geared power transmission, and precise mechanical linkages:
- Motor Engagement: Activates rotational energy.
- Gear Transmission: Transfers motion to the platform via gears or chains.
- Central Shaft Rotation: Mast spins, supported by bearings.
- Deck Coupling: Platform moves in sync with shaft.
- Counterweight Balance: Distributes rider load evenly, easing motor strain.
This engineering allows all figures to move harmoniously, with some rides adding vertical oscillation for extra visual flair.
---
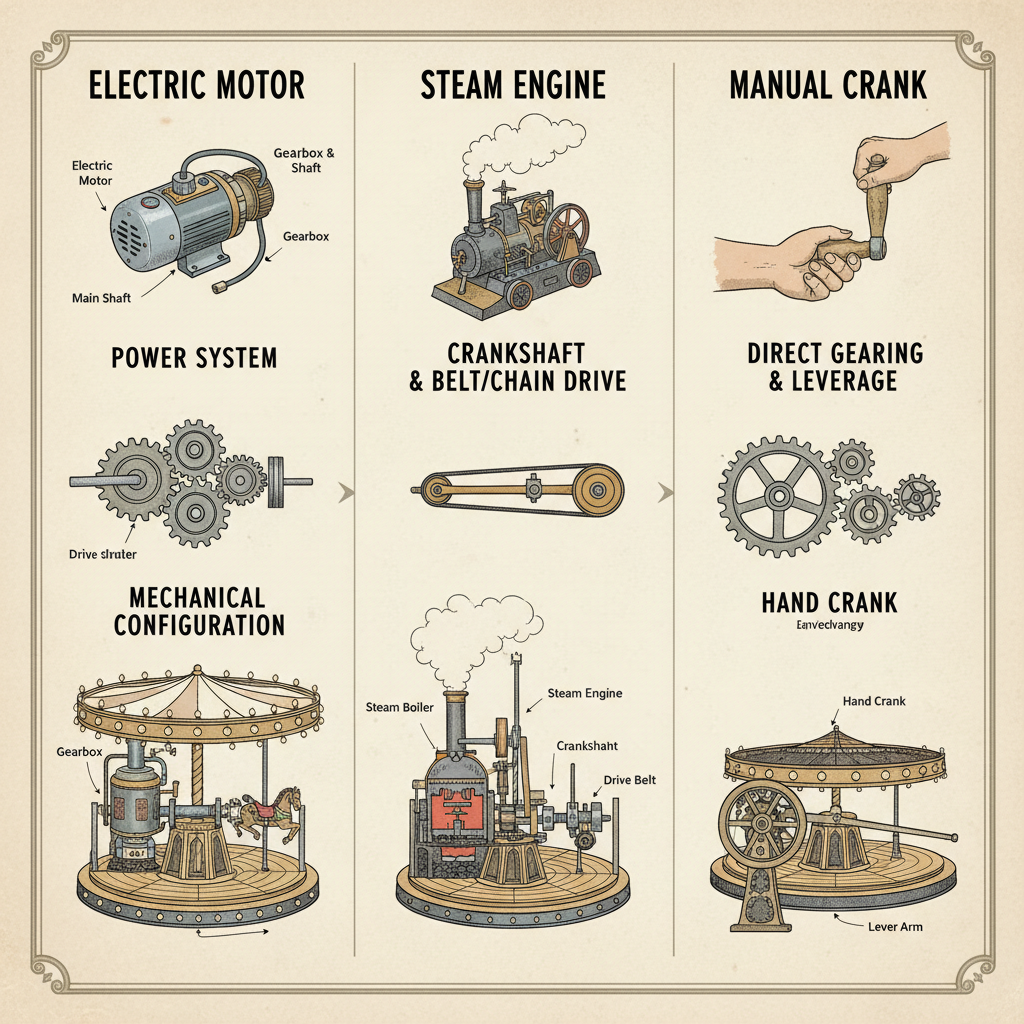
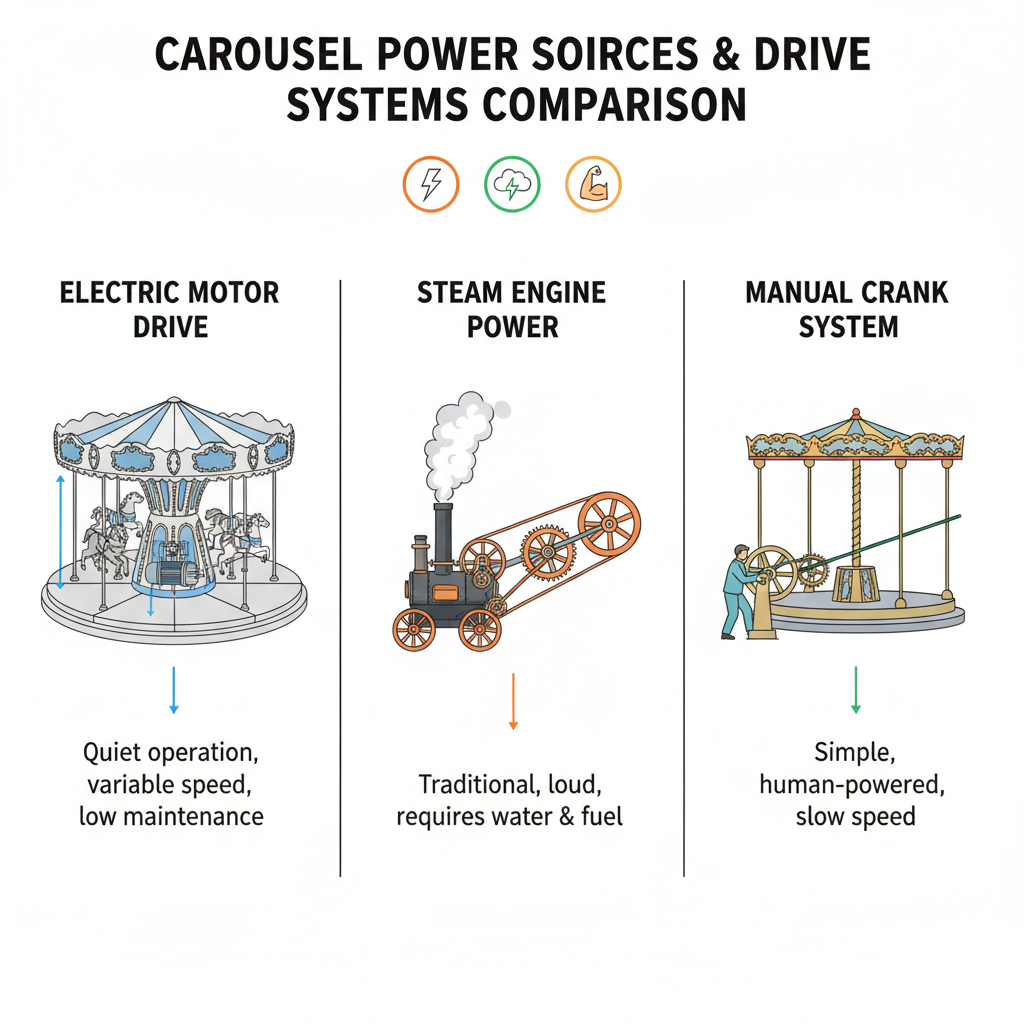
Diverse Power Sources and Drive Systems
Carousels can be powered by multiple systems:
- Electric Motors: Offer consistent, adjustable speeds for most modern installations.
- Hydraulic Systems: Facilitate smooth, powerful motion, ideal for large designs.
- Steam Engines: Historic technology now preserved in heritage rides.
Regardless of the source, energy flows into the drive system, enabling platform rotation.
---
Precision Through Gearing, Bearings, and Motion Control
High-quality gearing and bearings promote both safety and comfort.
Gearing
- Adjusts motor output speed.
- Distributes torque evenly.
Bearings
- Reduce friction.
- Support axial and radial loads.
Motion Control
- Combines mechanical and electronic systems for accuracy.
- PLCs enable programmable speed settings and operational sequences.
---
Safety Features and Rider Restraints
Safety remains paramount in carousel operation:
- Lap Bars or Belts: Secure seating.
- Anti-slip Flooring: Prevents falls during embark/disembark.
- Emergency Stop Mechanisms: Instant ride halting capability.
- Speed Limits: Regulate safe motion levels.
- Routine Inspections: Verify mechanical and electrical integrity.
---
Modern Interactive Enhancements
Contemporary carousels often integrate multimedia and dynamic effects:
- LED Lighting: Programmable for events or themes.
- Sound Systems: Synchronized music to enhance atmosphere.
- Animated Figures: Additional vertical or nodding motion.
- Seasonal Decorations: Thematic updates for holidays or special occasions.
---
Carousels in Web Design and User Interfaces
In digital design, carousels cycle through content such as images, products, or text — either automatically or under user control.
Common Types
- Image Sliders: Rotate photos at set intervals.
- Content Rotators: Swap varied media types seamlessly.
- Interactive Carousels: Enable navigation via clicks, swipes, or taps.
---
Coding Fundamentals for Digital Carousels
HTML, CSS, and JavaScript form the backbone of most web carousels.
Slide 1
Slide 2
Slide 3
.carousel {
display: flex;
overflow: hidden;
width: 100%;
}
.slide {
flex: 0 0 100%;
transition: transform 0.5s ease;
}let currentSlide = 0;
const slides = document.querySelectorAll('.slide');
function showSlide(index) {
const offset = index * -100;
slides.forEach(slide => {
slide.style.transform = `translateX(${offset}%)`;
});
}
setInterval(() => {
currentSlide = (currentSlide + 1) % slides.length;
showSlide(currentSlide);
}, 3000);---
Physical vs. Digital Carousels: Benefits and Purposes
| Aspect | Physical Carousels | Digital Carousels |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Entertainment ride | Display multiple content items in a compact space |
| Power Source | Electric, hydraulic, or vintage steam | Web browser execution via client-side scripts |
| Maintenance | Mechanical servicing, safety checks | Code updates, bug fixes |
| Audience | Park visitors | Website users |
| Interactivity | Passive (ride), visual/audio enhancements | Active (click, swipe), animations |
---
Maintenance Best Practices and Troubleshooting
Physical Carousels
- Lubricate gears & bearings regularly.
- Examine structures for cracks or rust.
- Check electrical wiring and connections.
- Test emergency systems frequently.
Digital Carousels
- Review mobile responsiveness.
- Debug scripts via browser console.
- Optimize assets for fast loading.
- Ensure accessibility with alternate navigation.
---
Examples of Innovative Carousel Implementations
- Theme Park Seasonal Overhauls: Holiday-themed paint and decoration.
- AR Integration: Augmented visuals aligning physical motion with digital overlays.
- E-commerce Product Sliders: Responsive showcases for product collections.
- Museum Displays: Rotating platforms to highlight artifacts.
---
Conclusion and Next Steps
Exploring how does a carousel work reveals fascinating parallels between physical rides and digital interfaces. Mechanical carousels combine precision engineering, safety systems, and artistic design to deliver memorable experiences. Digital carousels leverage code and responsive design to engage users and present information efficiently. Whether spinning under a canopy of lights or cycling through content on a webpage, carousels remain an enduring, versatile tool for captivating audiences.
Interested in building your own dynamic showcase or learning more about carousel mechanics? Start experimenting with both physical models and digital code to see which best suits your project goals.