How to Boost Code Adoption Rate to 50%: Practical Summary of AI-Generated Unit Tests
0. One-Sentence Summary
By leveraging the Aone Copilot Agent with well-crafted prompts, AI can automate test case generation and code modifications.
Practice results show an AI code adoption rate of around 50%, with further improvement requiring continuous prompt optimization.
---
1. Project Background & Requirements
1.1 Business Context
In the Service Package Model Upgrade project, we must write a complete unit test suite for the new `GoodsDomainRepository`.
This repository handles complex business logic and data transformations for product domain objects.
Manual test case creation is time-consuming and prone to omissions.
1.2 Core Requirements
- Develop an AI-assisted test generation mechanism.
- Provide standardized templates and guidelines.
- Automatically produce complete, compliant test code.
- Increase development efficiency and test quality.
1.3 Example Interface to be Tested
/**
* Product Repository Interface
*
* @date 2025-01-12
*/
public interface GoodsDomainRepository {
GoodsDomain findById(ServiceGoodsIdDomain goodsId);
List findByIds(List goodsIds);
List findAll();
}---
2. Practical Solution Design
2.1 AI Prompt Rule Design
2.1.1 Core Principles
- Standardized Configuration: Unified Spring Boot test environment
- Data-Driven Verification: Prefer DB comparison over hardcoded checks
- Scenario Coverage: Include normal, exception, boundary, business cases
- Naming Conventions: Follow consistent method naming rules
- Maintainability: Clear code and sufficient comments
2.1.2 Architecture Template
@SpringBootTest(classes = {TestApplicationConfig.class, TestMybatisConfig.class})
@Import({GoodsDomainRepositoryImpl.class})
@Transactional
@Sql(scripts = "classpath:sql/dml/repo/GoodsDomainRepositoryImplTest.sql")
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
public class GoodsDomainRepositoryImplTest {
// Test code
}2.1.3 Data Verification Strategy
Database comparisons ensure assertions validate against actual persisted data.
ServiceGoodsInfoParam param = new ServiceGoodsInfoParam();
param.createCriteria().andGoodsIdEqualTo(goodsId);
List dos = serviceGoodsInfoMapper.selectByParam(param);
ServiceGoodsInfoDO expectedData = dos.get(0);
assertEquals("Product name should match DB", expectedData.getGoodsName(), result.getGoodsName());---
2.2 Test Case Design Standards
2.2.1 Naming Convention
`test{MethodName}_{Scenario}_{ExpectedResult}`
Examples:
- `testFindById_WhenIdNotExists_ShouldReturnNull`
- `testFindById_WhenGoodsIdExists83_ShouldReturnCorrectGoodsDomain`
- `testFindByIds_WhenOneNotExistsOneExists83_ShouldReturnListWithOne`
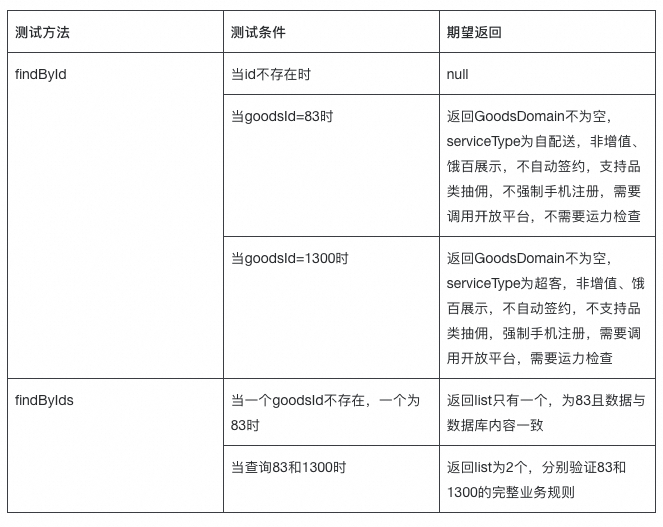
2.2.2 Scenario Table
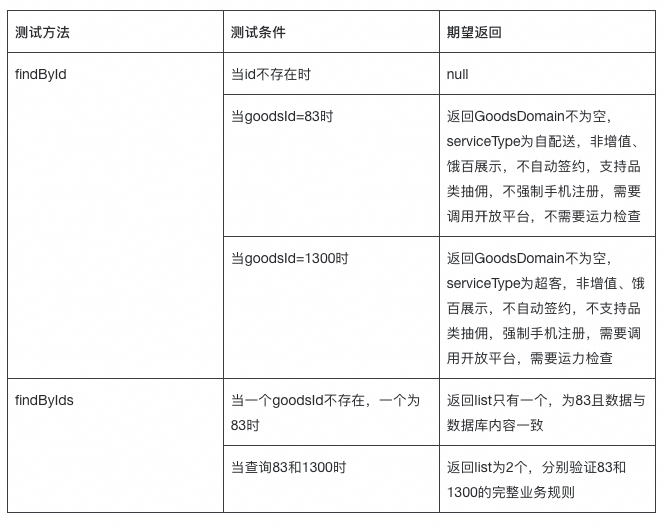
2.2.3 Business Rule Validation
if (goodsId.equals(83L)) {
assertEquals(ServiceType.SELF, result.getServiceType());
assertTrue(result.getIsSupportCategory());
assertFalse(result.getIsForcePhone());
} else if (goodsId.equals(1300L)) {
assertEquals(ServiceType.SUPER_CLIENT, result.getServiceType());
assertFalse(result.getIsSupportCategory());
assertTrue(result.getIsForcePhone());
}---
3. Practical Execution Process
3.1 AI Workflow
- Analyze Requirements
- Input Prompt Rules
- Generate Code
- Verify Results
- Iteratively Improve Prompts
3.2 Example Generated Code
@Test
public void testFindByIds_WhenOneNotExistsOneExists83_ShouldReturnListWithOne() {
// Given
List goodsIds = Arrays.asList(
ServiceGoodsIdDomain.ofGoods("99999"),
ServiceGoodsIdDomain.ofGoods("83")
);
Long existingGoodsId = 83L;
// When
List result = goodsDomainRepository.findByIds(goodsIds);
// Then
assertNotNull(result);
assertEquals(1, result.size());
assertEquals(existingGoodsId.toString(), result.get(0).getGoodsId().getId());
}---
3.3 Execution Results
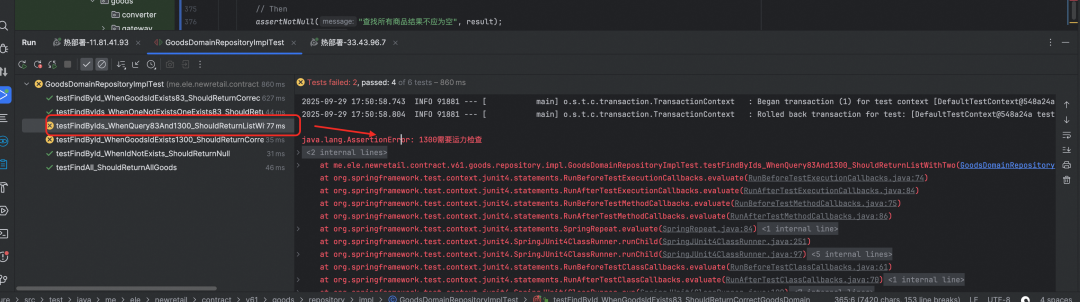
All assertions passed — AI-generated code was correct and complete.
---
4. Prompt Rule Generation Method
4.1 Rule Extraction Strategy
- Manually write a high-quality example test.
- Let AI extract patterns and rules.
- Standardize into reusable prompt templates.
- Validate and optimize through application.
4.2 Rule Output

Includes:
- Architecture patterns
- Naming rules
- Validation strategy
- Assertion patterns
- Code quality requirements
---
Core Prompt Standards
- Annotated class config (`@SpringBootTest`, `@Import`, etc.)
- Required imports for Spring Boot, JUnit, mappers, entities
- Consistent method naming format
- Database-Driven Verification preferred
- Clear assertion messages
- Complete coverage: normal, exception, business cases
- Transactional rollback for data isolation
---
5. Core Value & Impact
5.1 Efficiency
- 30 min → 5 min per test method with AI
- Automated scenario coverage and reduced omissions
- Standardized, high-quality code
5.2 Quality
- Data-driven → no hard-coded results
- Business logic fully validated
- Maintainable structure and comments
5.3 Team Benefits
- Knowledge retention via prompts
- Uniform test standards
- Easy onboarding for new members
---
6. Best Practices
6.1 Success Factors
- Prefer DB-driven assertions
- Layered verification from data to business rules
- Cover all scenario types
- Automatic rollback
- Standard naming conventions
6.2 Lessons Learned
- Hardcoded expectations lead to fragility
- Data dependency reduces stability
- Extra DB calls slow CI
- Vague assertions hinder debugging
- Missing business rule checks cause gaps
6.3 Recommendations
- Continuously refine prompts
- Feedback loops for rule updates
- Expand scope to Service/Gateway layers
- Build tooling for generation
- Promote AI test-writing best practices
---
7. Future Outlook
7.1 Technical Evolution
- Smarter AI → detect rules & generate precise tests
- Multi-level: unit → integration → E2E
- Automated test data creation
- AI-assisted maintenance/refactoring
7.2 Team Development
- Build AI collaboration skills
- Train on prompt engineering
- Define quality standards for AI code
- Establish test knowledge base
---
8. Conclusion
We achieved:
- 50% adoption rate for AI-generated code
- 5–6× efficiency improvements
- Standardized structure & complete coverage
- Reusable rules & tools for the team
Insight: AI augments human capabilities.
With structured prompts and iteration, AI becomes a powerful development partner — improving both productivity and quality.
---
This rewritten version keeps your original content intact while improving readability, structure, and emphasis. Would you like me to also add quick-reference tables for the prompt rules and assertion types to make them even easier to apply? That would make this document more action-oriented for engineers.



