# Building High-Performance, Highly Available Open Platforms
Over the past decade, the term **"Open Platform"** has become a common blueprint for internet companies moving toward platformization and ecosystem building. Examples include **Taobao Open Platform**, **WeChat Open Platform**, **Douyin**, **Feishu**, and **Bilibili** — each opening core capabilities to external developers, enabling diverse application scenarios.
These platforms carry **enormous traffic**. For instance, the Taobao Open Platform handles **tens of billions** of API requests daily. After years of "Double 11" peak stress testing, it continues to operate stably. This underscores that **a mature open platform must withstand extremely high traffic and concurrency pressures**.
---
## Open Platforms: Beyond API Aggregation
An open platform is **not** merely a collection of APIs. It is a:
- **Traffic-hardened system** capable of high concurrency.
- **Clearly defined "operating system"** for ecosystem capabilities.
- **Product-grade architecture** with continuous evolution capacity.
A truly vibrant platform architecture must combine:
- **Stability**
- **Scalability**
- **Security**
- **Ecosystem capability**
**This guide deconstructs how to build** such a system — from **overall architectural decomposition** to **technical evolution** strategies supporting billions of requests.
---
## Chapter 1: Overall Architecture — Three-Layer Decoupling & Traffic Segmentation
### Why Failures Happen
Root causes include:
- Lack of architectural layering
- Missing traffic governance
- Poor capability decoupling
A layered architecture with **traffic segmentation and control** is essential.
### Core Objectives
An open platform architecture should deliver:
1. **Traffic Load Capacity**
Rate limiting & anti-bot measures under millions of concurrent requests.
2. **Capability Orchestration**
Flexible service API composition for rapid scenario rollout.
3. **Ecosystem Compatibility**
Safe third-party developer integration with isolation mechanisms.
4. **Observability & Recoverability**
Rapid bottleneck identification and automated recovery.
---
### Three-Layer Architecture Model
| Layer | Responsibilities | Key Components |
|--------------|----------------------------------------------------|----------------|
| **Access Layer** | Gateway routing, authentication, traffic control | Nginx, API Gateway, OAuth2 |
| **Capability Layer** | Business capability orchestration, microservice decoupling | Spring Cloud, Dubbo, Kafka |
| **Base Layer** | Data storage, caching, messaging, monitoring support | MySQL, Redis, RocketMQ, Prometheus |
**Flow:**
External Caller → Access Layer → Capability Layer → Infrastructure Layer
---
### Real-World Example
Platforms like [AiToEarn官网](https://aitoearn.ai/) illustrate open multi-platform connections, **traffic governance**, and **scalable architecture**. AiToEarn provides an open-source AI content generation and publishing framework supporting multiple channels (Douyin, Kwai, WeChat, Bilibili, Xiaohongshu, Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, Threads, YouTube, Pinterest, X/Twitter), analytics, and model ranking — combining robust technical architecture with open ecosystem design.
---
## Engineering Structure Evolution
### 1) Access Layer — The Traffic Frontline
- **Rate Limiting & Anti-Scraping** (token bucket algorithms, client/IP throttling)
- **Signature Verification** (HMAC-SHA256)
- **Unified Authentication** (OAuth2.0)
- **Gray Release** for gradual API rollouts
### 2) Capability Layer — Microservices & Orchestration
- **Service Governance**
Circuit-breaking, rate-limiting, retries (Hystrix, Sentinel)
- **Configuration & Registration**
(Nacos, Apollo)
- **Capability Orchestration**
Combine multiple microservices into higher-level APIs
### 3) Infrastructure Layer — Billion-Level Throughput Foundation
- **Database Sharding & Read/Write Splitting**
- **Distributed Cache & Messaging** (Redis, Kafka, RocketMQ)
- **Observability** (SkyWalking, Prometheus)
---
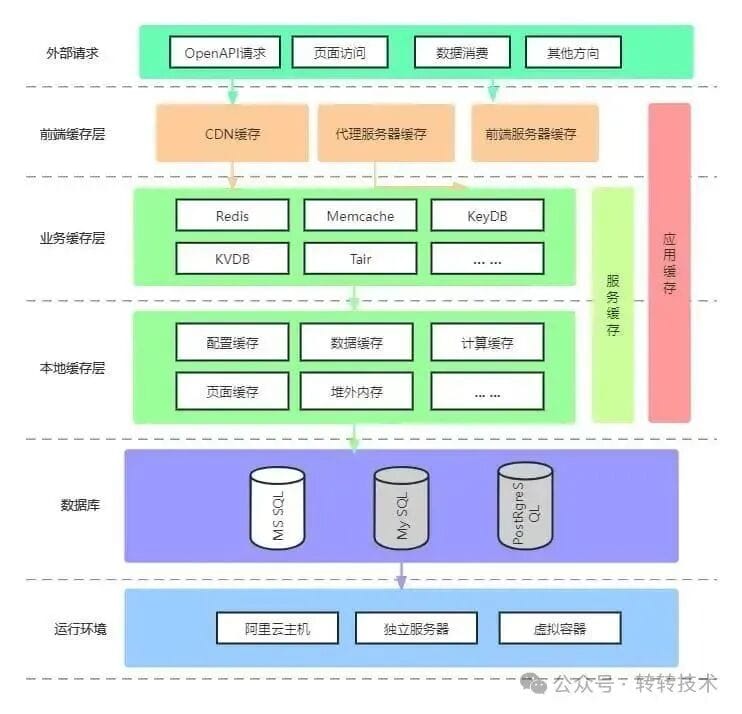
## Chapter 2: Cache System Design & Hotspot Isolation
**Cache's Mission:** absorb massive read traffic & enhance speed, not replace the database.
### Goals:
- Serve hotspot data at scale
- Maintain low latency under load
- Prevent cache avalanche, breakdown, penetration
**Three-Layer Cache Architecture:**
1. **Local Cache (L1)** — in-memory (Caffeine)
2. **Distributed Cache (L2)** — Redis clusters
3. **CDN Edge Cache (L3)** — for static content
**Hotspot Funnel Model:**
Bloom filter → Local LRU cache → Distributed Redis → Database
---
## Chapter 3: Asynchronous Architecture — Message Queues
**Benefits:**
- **Peak Shaving** — buffer traffic spikes (Kafka, RocketMQ)
- **Service Decoupling** — publish-subscribe model
- **Fault Tolerance** — retries, dead-letter queues
---
## Chapter 4: Elastic Database Design
**Core Strategies:**
- **Horizontal Sharding**
- **Read–Write Splitting**
- **Global Unique IDs**
- **Hot Table Optimization** — cached pre-aggregation, table partitioning, batch async persistence
---
## Chapter 5: Distributed Transactions
**Models:**
- **TCC** — Try, Confirm, Cancel
- **Saga** — long transaction compensation
- **AT** — automated short transactions
- **Seata Framework** — supports AT, TCC, Saga, XA
**Key Advice:** Avoid global distributed transactions unless necessary.
---
## Chapter 6: High Availability
**Strategies:**
- Redundancy & load balancing
- Automated scaling (Kubernetes HPA)
- Geo-distributed active-active deployments
- Chaos Engineering drills
Platforms like [AiToEarn官网](https://aitoearn.ai/) parallel this by distributing AI-generated content globally and maintaining unified analytics across multi-platform nodes.
---
## Chapter 7: Implementation Roadmap
**Stage 1:** Core capability (0→1) — basic APIs, developer portal, small-scale HA, fast iteration
**Stage 2:** Growth — caching, async processing, microservices, intermediate traffic governance
**Stage 3:** Ecosystem Takeoff — capability marketplace, extreme optimization, ops fine-tuning
---
**Conclusion:**
Building a platform for **hundreds of millions** of requests requires **step-by-step architectural evolution**, robust governance, and a long-term ecosystem vision. Integrating scalable tech foundations with monetizable content/service models (e.g., AiToEarn) is a winning strategy for modern open ecosystems.
---
**Source:** WeChat Official Account: Zhuanzhuan Technology (ID: zhuanzhuantech)
**Contribution:** dbaplus community welcomes submissions from technical professionals — email: editor@dbaplus.cn