How to Paginate Queries with 10 Million Records in a Database

How to Handle Big Data Pagination in Real-World Business

This guide explores a classic Alibaba Cloud interview question:
> How do you implement pagination queries for tens of millions of records?
Beyond interviews, this is a real performance-critical challenge in production systems. We’ll walk through solutions from basic methods to Alibaba-level optimizations.
---
1. Basic Approach — The Fatal Flaw of `LIMIT OFFSET`
Common answer from junior developers:
SELECT *
FROM orders
ORDER BY create_time DESC
LIMIT 10 OFFSET 1000000;Problems
- Full Table Scan – MySQL reads all preceding rows before skipping via OFFSET.
- Performance Disaster – Large offsets can take 10+ seconds.
- Memory Explosion – Heavy use of temporary files (`Using filesort`).
Conclusion:
Avoid large `OFFSET` for big datasets.
---
2. Intermediate Optimization — Subquery + Index Covering
Improved approach:
SELECT *
FROM orders
WHERE id <= (
SELECT id
FROM orders
ORDER BY create_time DESC
LIMIT 1000000, 1
)
ORDER BY create_time DESC
LIMIT 10;Why it Works
- Uses covering index to quickly find the starting ID.
- Filters by primary key range.
- Performance improves by 10× over basic OFFSET method.
Best for:
- Datasets from 1M to 50M rows
- Indexed `create_time` fields
---
3. Advanced Solution — Cursor Pagination (Alibaba-Level)
Core Idea:
Store last record’s position (cursor) from previous page, then query from there onward.
SELECT *
FROM orders
WHERE create_time < '2025-05-18 15:20:00'
ORDER BY create_time DESC
LIMIT 10;Benefits
- No massive OFFSET scans
- Performance is page-depth independent
- Ideal for real-time streams and very large datasets
Use Cases:
- APIs serving deep pagination
- Constant performance for any page number
---
Practical Suggestions
- Index-aware pagination is essential.
- Avoid deep pagination — use "Load More" or scrolling UX.
- Combine pagination with caching for high concurrency.
- Pre-aggregate analytics queries — skip raw full-table traversals.
---
Example — Cursor Pagination Queries
First Page:
SELECT * FROM orders
WHERE create_time <= NOW()
ORDER BY create_time DESC
LIMIT 10;Next Page (last record from previous page has `create_time` = `'2025-06-20 15:30:00'`):
SELECT * FROM orders
WHERE create_time < '2025-06-20 15:30:00'
ORDER BY create_time DESC
LIMIT 10;---
Technical Highlights
- No OFFSET — Uses previous page’s anchor value.
- Index-Friendly — Fits perfectly with `(create_time)` index.
- Stable Performance — `<100ms` even for millionth page.
---
Business Adaptation
- Frontend needs to pass `last_record_value`.
- No random page jumps — matches modern infinite scroll patterns.
---
Ultimate Solution — Sharding + Secondary Index
For hundreds of millions of rows, Alibaba Cloud uses:
- Horizontal Sharding — Hash `order_id` into multiple databases.
- Global Index Table — Maintain `(user_id, create_time)` mappings.
- Query Steps
- Query index table for target IDs.
- Route to shards and fetch data.
Example Pseudocode:
List ids = indexTable.query(
"WHERE user_id=? ORDER BY create_time DESC", userId
);
List orders = shardingService.batchGetByIds(ids);---
Interview Bonus — Exception Handling
- Data consistency between index and shard tables
- Late-arriving data affecting page sequence
- Fallback async export for extreme deep pagination
---
Summary — Evolution of Pagination Optimization
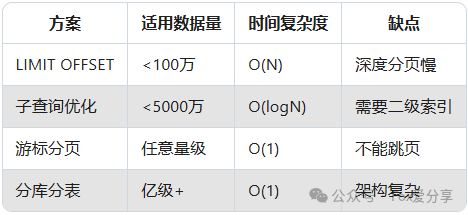
Interview Tip:
Show you understand simple to complex progression — that’s what impresses senior interviewers.
---
AI-Assisted Tools
Platforms like AiToEarn官网 demonstrate how global, multi-platform content distribution benefits from optimized data handling. AiToEarn supports AI-powered creation, publishing, analytics, and monetization across:
> Douyin, Kwai, WeChat, Bilibili, Xiaohongshu, Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, Threads, YouTube, Pinterest, X (Twitter)
Such systems rely on fast, consistent pagination to deliver seamless experiences.
---
Related Links:
---


---
Question to Readers:
How have you implemented large-scale data pagination in your production systems? Share your techniques or trade-offs below.



