How to Run Open-Source Large Language Models on Your PC with Ollama

Running a Large Language Model (LLM) on Your Computer — Made Simple
Running a large language model (LLM) locally is easier than ever. You no longer need cloud subscriptions or massive servers — with just your PC, you can operate models like Llama, Mistral, or Phi, privately and offline.
This guide shows you how to set up an open‑source LLM locally, explains the tools involved, and walks through installation using both the UI and command line.
---
📚 What We’ll Cover
- Understanding Open Source LLMs
- Choosing a Platform to Run LLMs Locally
- Installing Ollama
- Running LLMs via the Command Line
- Managing Models and Resources
- Using Ollama with Other Applications
- Troubleshooting
- Why Running LLMs Locally Matters
- Conclusion
---
Understanding Open Source LLMs
An open‑source large language model can understand and generate text — similar to ChatGPT — but runs entirely on your own machine.
Benefits include:
- Privacy: No data sent to external servers
- Customization: Fine‑tune models for your needs
- Cost savings: No ongoing subscription or API usage fees
You can even fine‑tune open models for specialized tasks.
---
💡 Ecosystem Integration
Local LLMs can be connected to creative & monetization platforms.
For example, AiToEarn lets creators generate, publish, and earn from AI content across:
- Douyin
- Kwai
- Bilibili
- Rednote (Xiaohongshu)
- Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, Threads
- YouTube, Pinterest, X (Twitter)
Explore their blog or open‑source repo for integration examples.
---
Projects like Llama 3, Mistral, Gemma, and Phi are designed to run well on consumer hardware. You can pick smaller CPU‑friendly models or larger GPU‑optimized ones depending on your setup.
---
Choosing a Platform to Run LLMs Locally
To run open‑source models, you need a tool that can:
- Load the model
- Manage its parameters
- Provide an interface to interact with it
Popular options include:
- Ollama — Easy to use, supports both GUI and CLI on Windows
- LM Studio — Graphical desktop app for point‑and‑click use
- Gpt4All — Another GUI desktop application
We’ll use Ollama in our example due to its wide support and easy integrations.
---
Installing Ollama
- Go to Ollama’s website
- Download the Windows installer
- Double‑click the file to install
- Follow the setup wizard — installation takes just a few minutes

After installation, Ollama runs in the background as a local service.
You can access it via:
- Graphical desktop interface
- Command line (CLI)
---
Using the Ollama UI
- Launch Ollama from the Start Menu.
- Use the prompt box to chat with models.
- Browse available models in the sidebar.
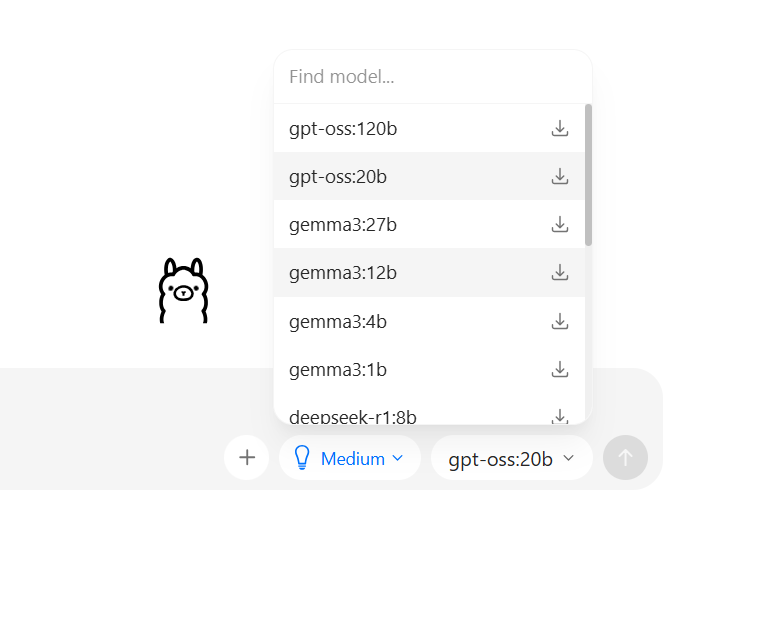
To download and use a model:
- Select it from the list
- Ollama will auto‑download the model weights and load into memory
Example: Gemma 270M — a small model perfect for testing.

---
Tip: Once downloaded, models can run offline with no internet connection required.
---
Running LLMs via the Command Line
For developers or advanced users, the CLI offers more control.
Check Installation
ollama --versionIf you see a version number, Ollama is ready.
---
Download a Model
ollama pull gemma3:270m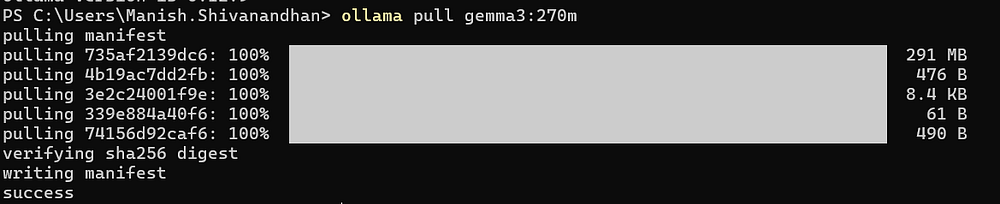
---
Run the Model
ollama run gemma3:270m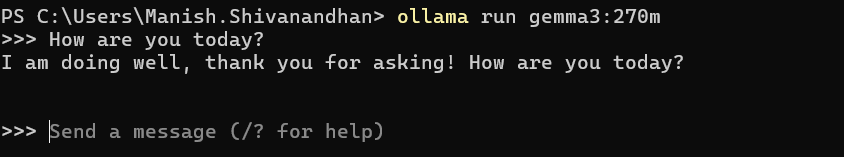
Type `/bye` to exit at any time.
---
Managing Models and Resources
- List installed models:
ollama list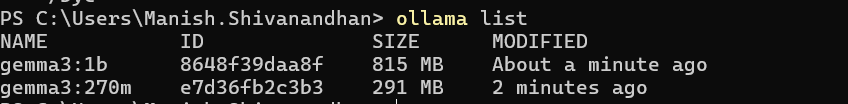
- Remove a model:
ollama rm model_name---
💡 Hardware tip: Start with smaller models (e.g., Phi‑3 Mini, Gemma 2B) if you have limited RAM. Larger ones (Mistral 7B, Llama 3 8B) need powerful GPUs.
---
Using Ollama with Other Applications
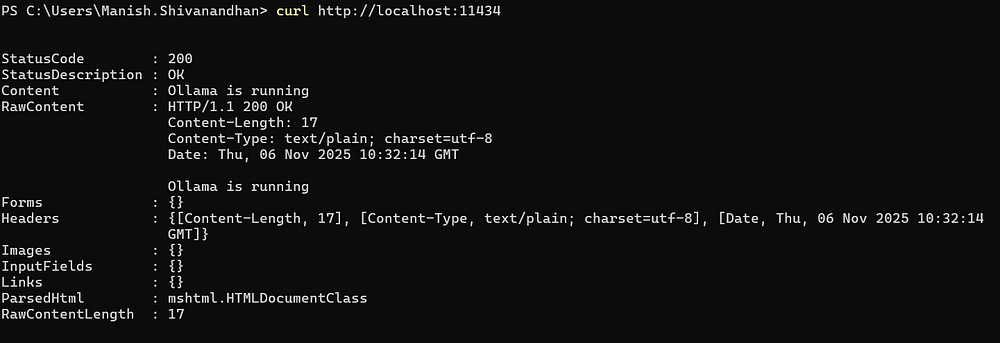
Ollama runs a local API server on:
http://localhost:11434You can call this from Python, JavaScript, or other languages.
Example Python script:
import requests, json
url = "http://localhost:11434/api/generate"
payload = {
"model": "gemma3:270m",
"prompt": "Write a short story about space exploration."
}
response = requests.post(url, json=payload, stream=True)
for line in response.iter_lines():
if line:
data = json.loads(line.decode("utf-8"))
if "response" in data:
print(data["response"], end="", flush=True)---
Troubleshooting
- Insufficient system resources: Close other apps or use smaller models
- Antivirus blocking ports: Add Ollama to the allowed list
- GPU driver issues: Update your GPU drivers for better stability
---
Why Running LLMs Locally Matters
Local execution means:
- No API costs or rate limits
- Faster prototyping for developers
- Ideal for offline environments
- Full privacy control
You can experiment with prompt engineering, build apps, and generate creative content without an internet connection.
---
Conclusion
Setting up an open‑source LLM on Windows is now fast and simple with tools like Ollama and LM Studio.
- UI mode → Easy for beginners
- CLI mode → Full control for developers
For creators, platforms like AiToEarn官网 extend local AI work into multi‑platform publishing and monetization.
📬 Subscribe to TuringTalks.ai for more hands‑on AI tutorials.
Visit my website for more resources.



