Images of Dimensions Explained for Design, Web, and Math
Explore image dimensions across math, design, and digital media, and learn how to measure, interpret, and optimize them for clarity and performance.
Understanding "Images of Dimensions"
The phrase images of dimensions is relevant across multiple fields—from mathematics to photography, design, and digital media. Broadly, it describes the way we perceive, calculate, and represent the size, shape, and scale of subjects—whether as geometric shapes, photographs, blueprints, or 3D renderings.
In mathematics, "image" represents the set of outputs (points) a function produces, while "dimensions" indicate the number of coordinates necessary to define a point in space. In design and photography, image dimensions often mean the actual width and height of a file, measured in pixels or physical units. In physics, dimensions refer to measurable extents like length, width, height, and sometimes even time.
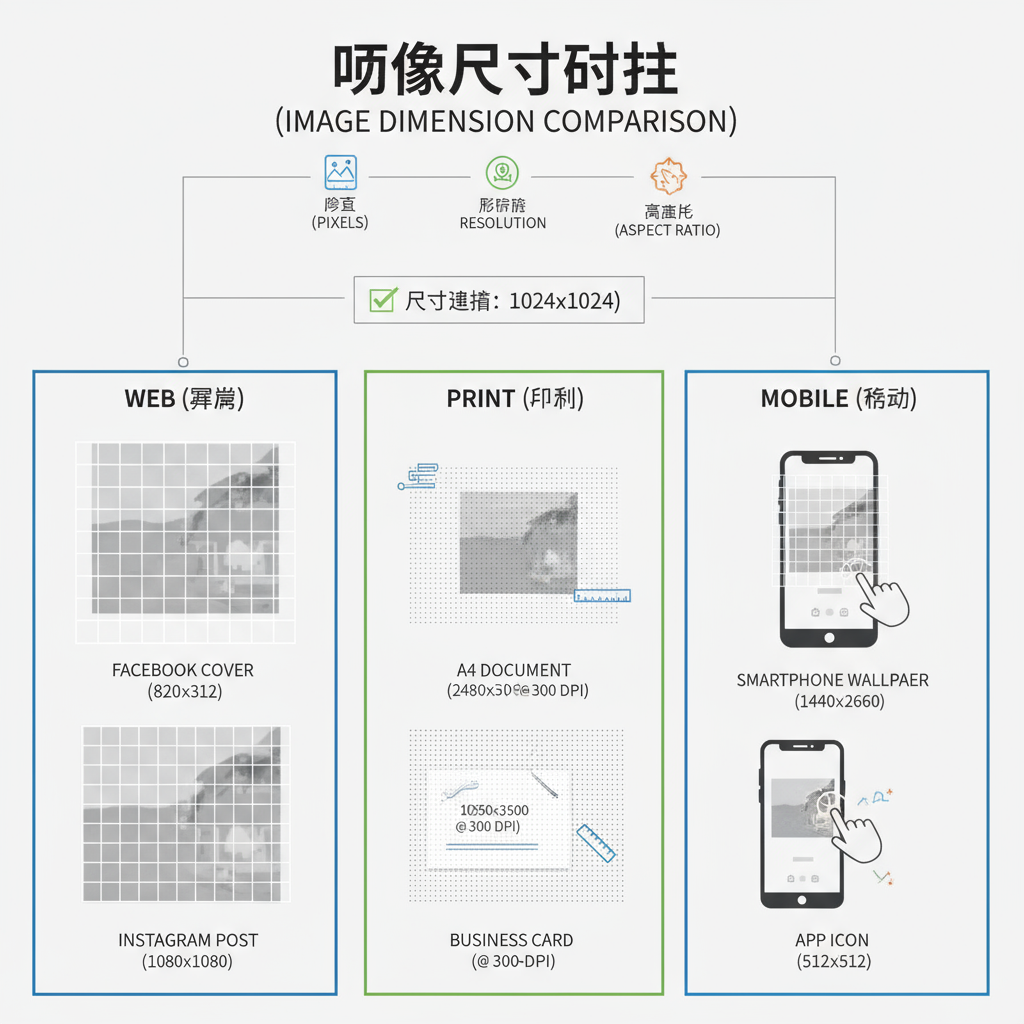
To truly understand the concept, it helps to examine these contexts individually and see how they interconnect for both theory and application.
---
Image Dimensions in Digital Media
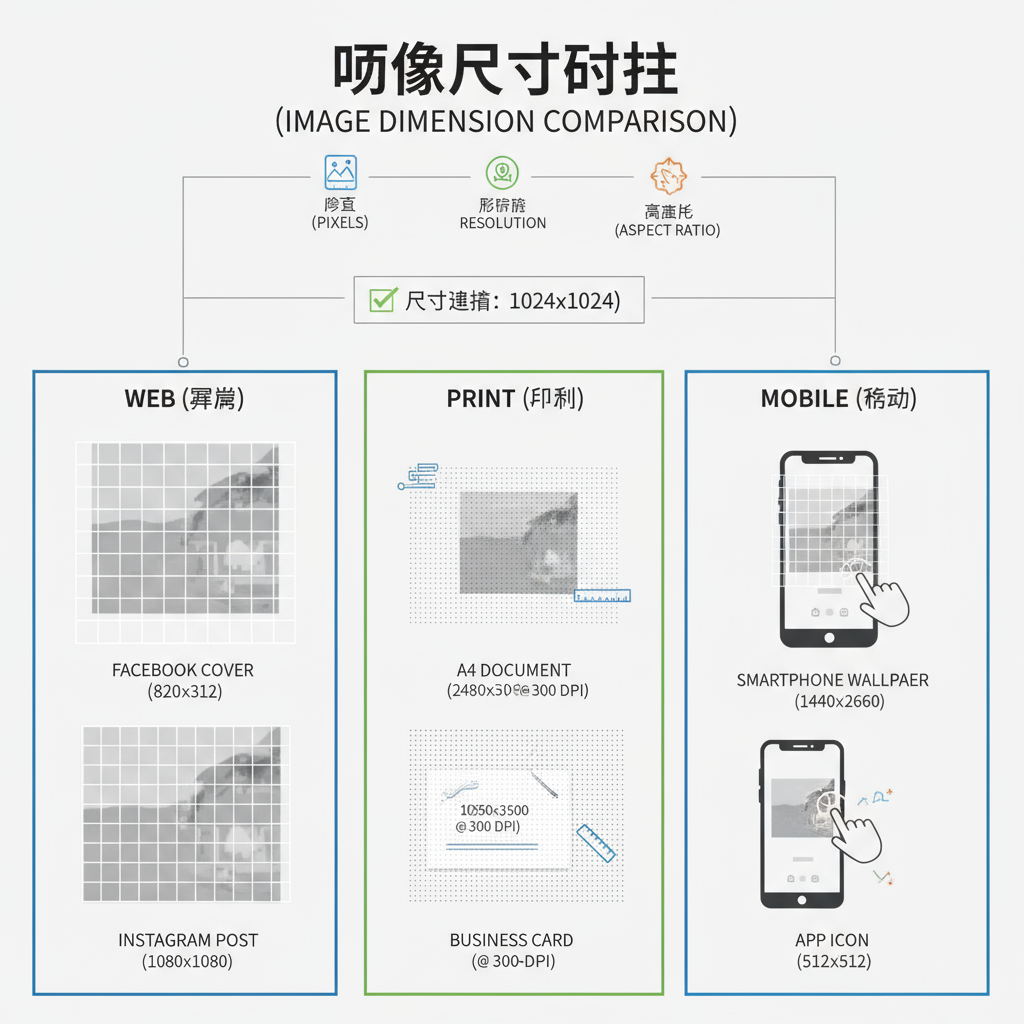
When working with digital images, dimensions are most commonly expressed in pixels, written as width × height, such as `1920×1080`.
Pixels, Resolution, and Aspect Ratio
- Pixels: The smallest discrete unit in a raster image.
- Resolution: Measured in PPI (pixels per inch) for screens and DPI (dots per inch) for print.
- Aspect Ratio: The proportional relationship between width and height (for example, 16:9, 4:3, 1:1).
Why Image Dimensions Matter
The right image dimensions directly affect:
- Website load speed
- Clarity and detail, especially in prints
- Display consistency across devices and screens
---
Dimensions in Photography and Graphic Design
In creative design, image dimensions go beyond technical measurements to impact composition and storytelling.
Composition and Layout
- Rule of thirds guides subject placement for visual appeal.
- Golden ratio leads to harmonious proportions.
- Grid systems underpin responsive web and print layouts.

In photography, choosing appropriate dimensions ensures quality when printing at various sizes. In graphic design, standard canvas formats (such as A4, poster sizes, or social media aspect ratios) ensure projects meet platform or print specifications.
---
Higher Dimensions in Mathematics
In mathematics, "dimension" specifies the number of variables needed to locate a point:
- 1D: A straight line (length only)
- 2D: A plane (length and width)
- 3D: Space (length, width, and height)
- 4D and higher: Add time or abstract coordinates
The image of a function is the complete set of points that a mathematical mapping produces. For example, `f(x, y)` mapping ℝ² to ℝ³ generates a surface in 3D.
## Example: plotting the image of a function in 3D
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
x = np.linspace(-5, 5, 50)
y = np.linspace(-5, 5, 50)
X, Y = np.meshgrid(x, y)
Z = np.sin(np.sqrt(X**2 + Y**2))
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z, cmap='viridis')
plt.show()---
Applications in Art, Architecture, and 3D Modeling
Spatial dimensions are fundamental in many creative and technical industries:
- Art: Artists manipulate perspective to create an illusion of depth.
- Architecture: Plans require exact 2D diagrams and 3D concept models.
- 3D Modeling: Used in film, gaming, simulation, and virtual reality.
Digital creators leverage images of dimensions for realistic rendering and proportionally accurate visualizations.
---
Measuring and Optimizing Image Dimensions for the Web
Balancing quality and file size is key for SEO, performance, and user experience. Oversized images slow sites, while undersized ones appear blurry.
Steps to Optimize
- Match to Display Size: Fit pixel dimensions to the expected display.
- Compress Smartly: Use WebP for modern browsers or optimized JPEG.
- Support Responsiveness: Implement HTML `srcset` for different device resolutions.
| Usage | Recommended Width | Format |
|---|---|---|
| Full-width banners | 1920px | JPEG/WebP |
| Blog inline image | 800px | JPEG/PNG |
| Thumbnail | 150px | JPEG/PNG |
| Icons | 32–64px | SVG/PNG |
Optimizing image dimensions contributes to better Core Web Vitals scores, increasingly important for search ranking.
---
Tools for Creating and Resizing Images of Specific Dimensions
Many software tools help tailor image dimensions to project needs:
- Adobe Photoshop – precision control with export presets
- GIMP – free tool with batch processing capabilities
- Canva – preset templates for marketing and social media
- ImageMagick – command line tool for automated resizing
Example ImageMagick command for batch resizing:
mogrify -resize 800x800 *.jpg---
Best Practices for Naming and Storing Dimension-Specific Images
Organized files enhance efficiency and support SEO.
Naming Conventions
- Include relevant keywords and pixel size:
- `sunset-beach-1920x1080.jpg`
- Use hyphens (not underscores) for readability and indexing.
- Keep names short yet descriptive.
Storage Practices
- Organize into directories by resolution or usage type.
- Pair with a CDN (content delivery network) to ensure fast global delivery.
---
Common Mistakes with Images of Dimensions
To maintain both aesthetics and performance, avoid:
- Distortion from non-uniform scaling (breaking aspect ratio)
- Excessive quality loss from repeated compression
- Ignoring high-resolution screens by omitting Retina-ready assets
- Overusing extra-large formats, hurting load times
Awareness of these pitfalls helps ensure a consistently high-quality visual experience.
---
Conclusion and Future Trends in Dimension Visualization
The concept of images of dimensions links abstract mathematics with tactile applications in media, design, and technology. Mastering it allows professionals to make informed decisions for efficiency, clarity, and impact.
Emerging trends include:
- Adaptive vector graphics that scale infinitely without loss
- Real-time browser-based 3D rendering with WebGL/WebGPU
- AI-powered scaling and upscaling that preserves fine detail
As display technologies evolve, the ability to manage and optimize image dimensions will remain a key skill for designers, developers, and content strategists alike.
---
Summary:
"Images of dimensions" encompass technical precision and creative artistry. By understanding how size, scale, and proportion work in different contexts, you can optimize digital assets for performance and clarity, improve SEO through intelligent file naming and optimization, and future-proof your visual content strategy.
Call to Action:
Start reviewing and optimizing your existing images today—measure, resize, and rename them for maximum impact across web, print, and interactive media.