In-Depth Guide to LLM Fundamentals: Understanding the Transformer Architecture
# 👉 Table of Contents
1. **Preface**
2. **LLM Architecture Analysis**
3. **Current Open-Source Flagship LLM Architectures**
4. **Conclusion**
---
## Preface
This series of articles explains **Large Language Models (LLMs)** step by step — from how they are used, to their underlying principles, and finally to practical system implementation. Previous articles have won the *2025 Tencent Zhidian Award*.
In this installment, we explore the **source of intelligence** in LLMs, focusing on their foundational **Transformer** architecture. We will cover:
- **Tokenization**, **Word Embeddings**, and **Positional Encoding** — converting discrete text into continuous vectors.
- The **Attention Mechanism** — capturing complex dependency relationships in sequences.
- Decoder structures of self-attention layers + feed-forward networks.
- Cutting-edge designs like **MoE (Mixture of Experts)** architectures for efficiency and performance.
---
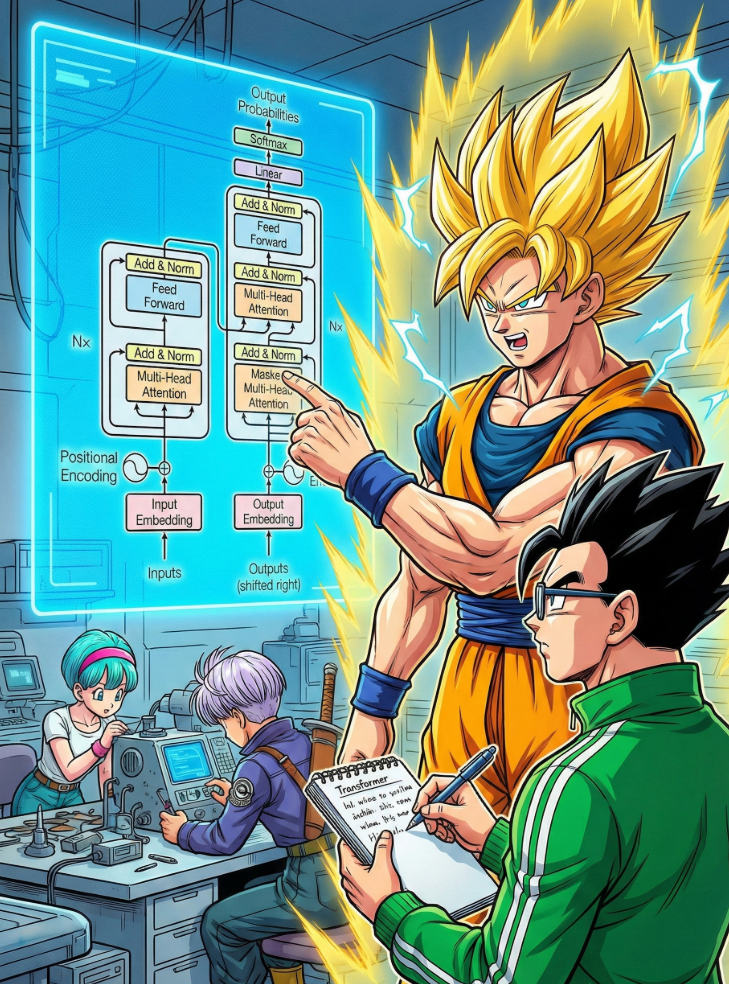
Recently, AI development has progressed rapidly. The above image — combining *Nano Banana Pro* with the classic *Attention Is All You Need* architecture diagram — shows *Sun Wukong* explaining the Transformer to *Sun Gohan*. Platforms such as **Bilibili** are trending with creative AI videos, e.g., *Journey to the West* characters singing.
This raises key questions:
- Why are LLMs so powerful?
- What principle drives the Transformer?
- How does its architecture work in detail?
After studying sources like *Building Large Models from Scratch*, *Illustrated Large Models*, and *Hands-On Transformer NLP Applications*, we will explain these principles using the example: translating
*"Transformer is powerful." → "Transformer 很强大。"*
---
### Core Challenges:
- **Understanding words** — Machines only understand numbers; how do they interpret words? → See **Tokenization**
- **Understanding word order** — Sequence changes meaning (“Dog bites man” vs “Man bites dog”). → See **Positional Encoding**
- **Understanding relationships** — “Powerful” modifies “Transformer”. → See **Attention Mechanism**

---
## LLM Architecture Analysis
The **Transformer** (introduced in *Attention Is All You Need*) revolutionized sequence modeling. It powers nearly all modern large language models, evolving from **BERT** and **GPT** to today's multimodal models.
Challenges in classic Transformers:
- Handling long texts
- Retrieving key info
- Avoiding hallucinations
Solutions include **DIFF Transformer**, **Energy-Based Transformer**, and hybrid **Transformer + MoE** designs. Over half of new releases now use hybrid models.
---
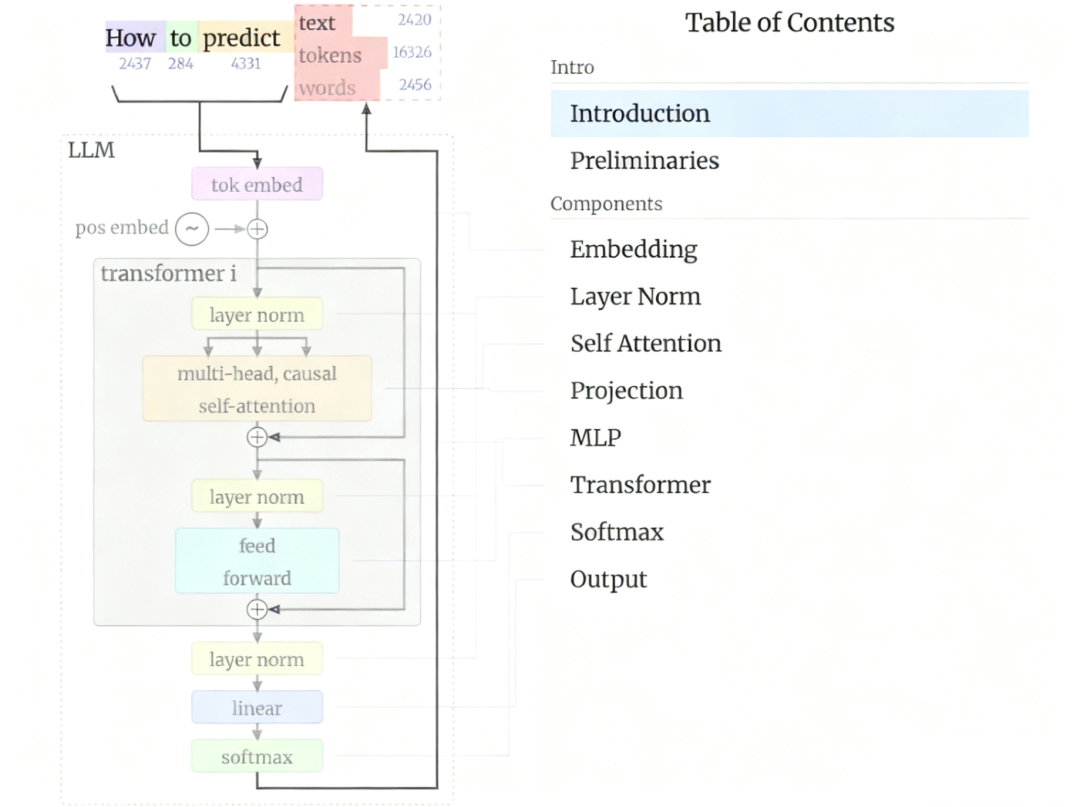
### Transformer Core: Encoder–Decoder Structure
- **Encoder**: Converts input sequences into contextual representations.
- **Decoder**: Generates outputs conditioned on encoder context + prior outputs.
Dominant today: **Decoder-only Transformers** with stacked layers of:
- **Self-Attention / Multi-Head Attention**
- **Feed-Forward Neural Networks (FFNs)**
Layer depth impacts performance vs. cost/training difficulty.
---
## Building the Model
**Three critical steps:**
1. **Data**
- Collect text
- Preprocess text
- Embed text
2. **Model**
- Design architecture
- Set parameters
3. **Training**
- Train
- Evaluate
- Optimize
Preprocessing = **Tokenization** + **Word Embedding**
---
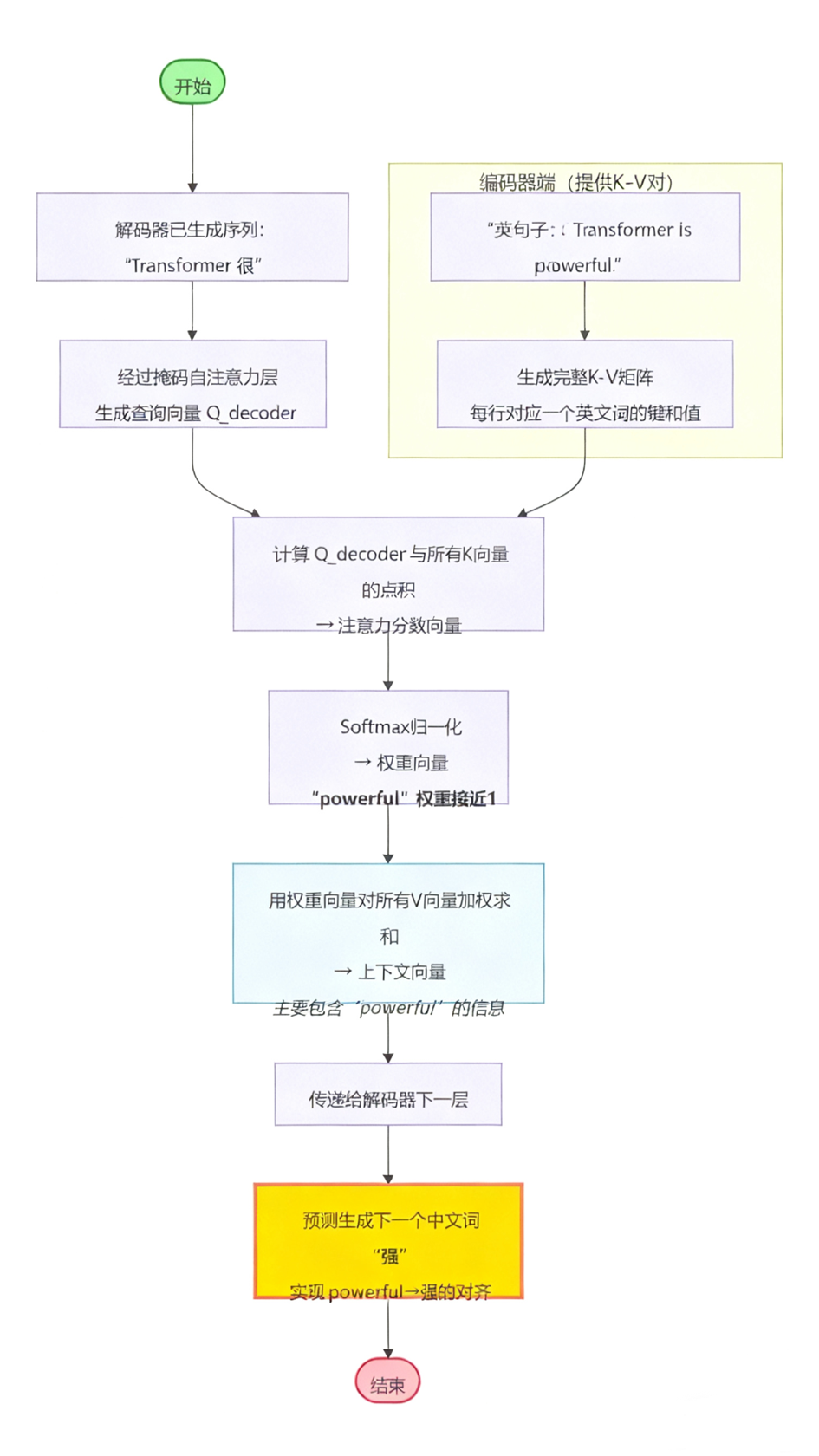
### Example: Token Flow in Translation
*"Transformer is powerful." → "Transformer 很强大。"*
**When generating “强”:**
1. **Generate Query (Q)** from partial output via masked self-attention.
2. **Keys (K) & Values (V)** come from encoder outputs for each source token.
3. **Compute Attention Weights**: Dot product of Q with all Ks, normalize via Softmax.
4. **Weighted Sum**: Combine Vs using weights to yield context vector → next decoder step predicts “强”.
---
## 2.2 Tokenization
Tokenizing → split sentence:"Transformer" , "is" , "powerful" , "."
Build **vocabularies** mapping tokens → IDs.
| Token | Index |
|-------------|-------|
| `` | 0 |
| `` | 1 |
| `` | 2 |
| `` | 3 |
| Transformer | 4 |
| is | 5 |
| powerful | 6 |
| . | 7 |


---
## 2.3 Embedding
Map tokens → continuous vectors (example dim=4):
| Token | Index | Vector |
|--------------|-------|-------------------------|
| Transformer | 4 | [0.2, -0.5, 0.8, 0.1] |
| is | 5 | [0.1, 0.0, -0.2, 0.9] |
| powerful | 6 | [0.3, -0.4, 0.7, 0.2] |
| . | 7 | [-0.1, 0.1, 0.0, 0.1] |
---
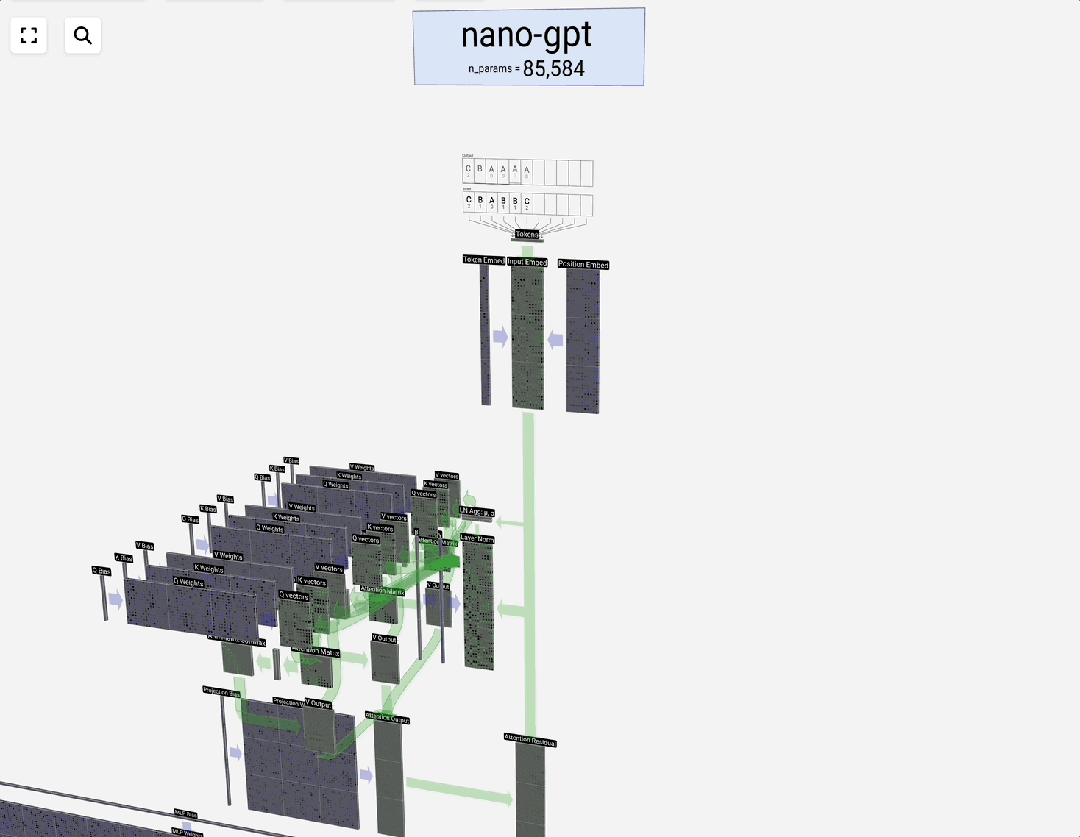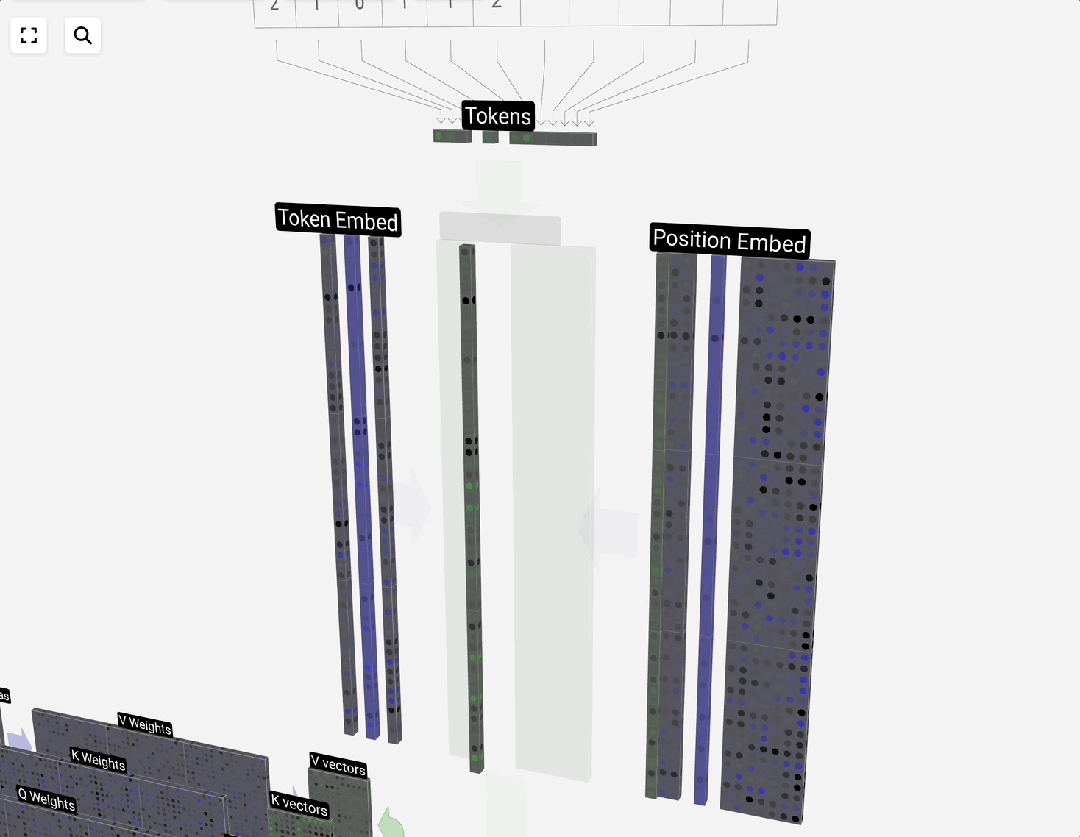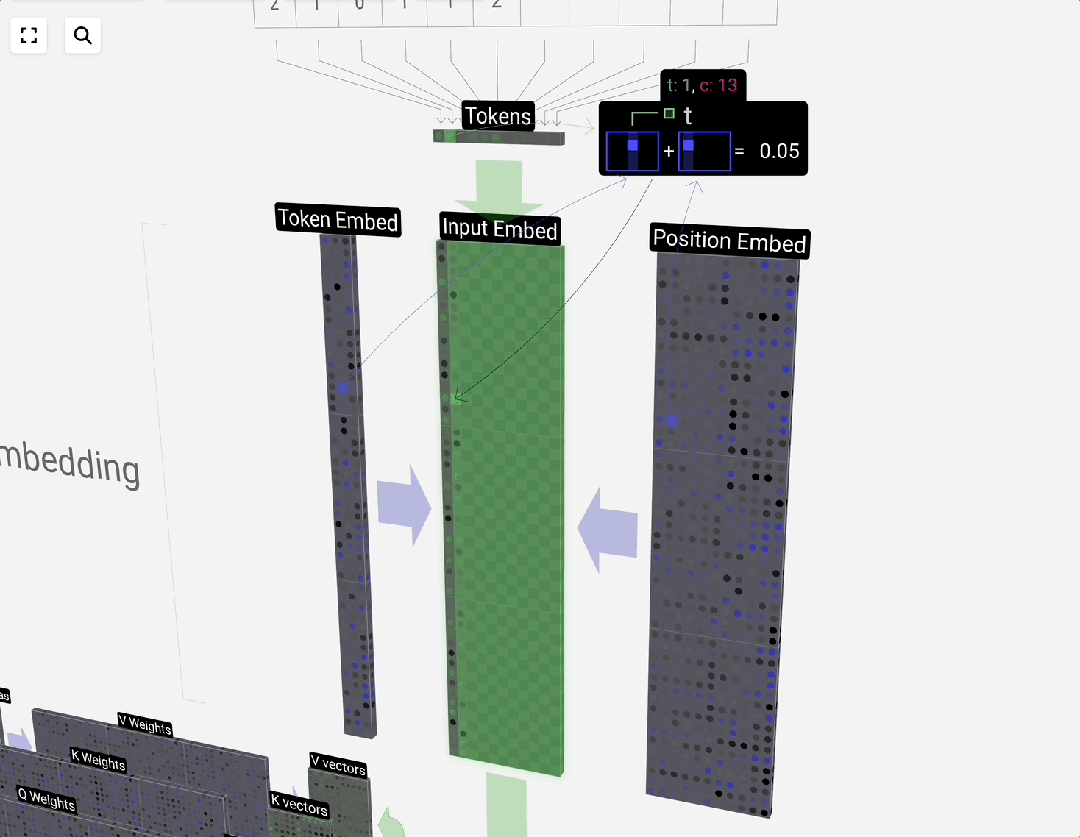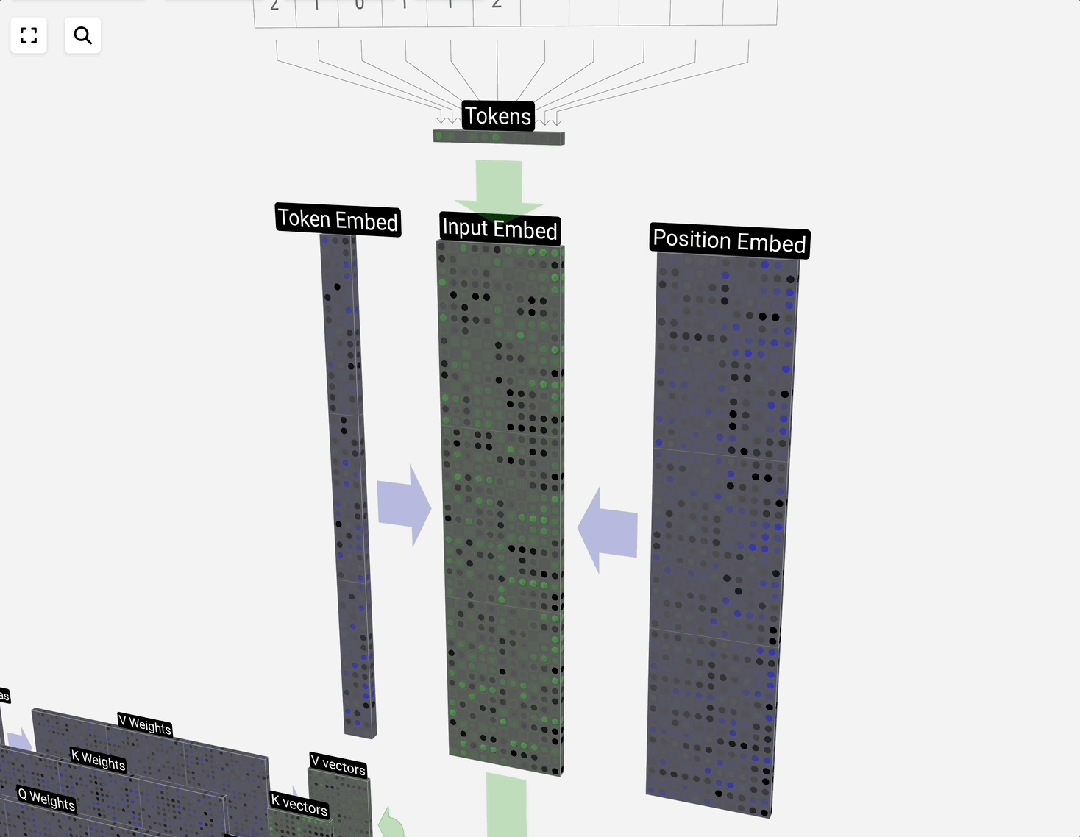
### Embedding Process & Scale
**GPT-3 example:**
- Vocab: 50,257
- Embedding dim: 12,288
- Matrix size ≈ **2.34 GB** (FP32)
---
## 2.3.3 Positional Encoding
Transformers need position info for parallel sequence processing.
Example (dim=4):
| Token | Position | Embedding | Position Vector | Final Input |
|-------------|----------|---------------------|----------------------|----------------------|
| Transformer | 0 | [0.2,-0.5,0.8,0.1] | [0.0,1.0,0.0,1.0] | [0.2,0.5,0.8,1.1] |
| is | 1 | [0.1,0.0,-0.2,0.9] | [0.8,0.6,0.8,0.6] | [0.9,0.6,0.6,1.5] |
---
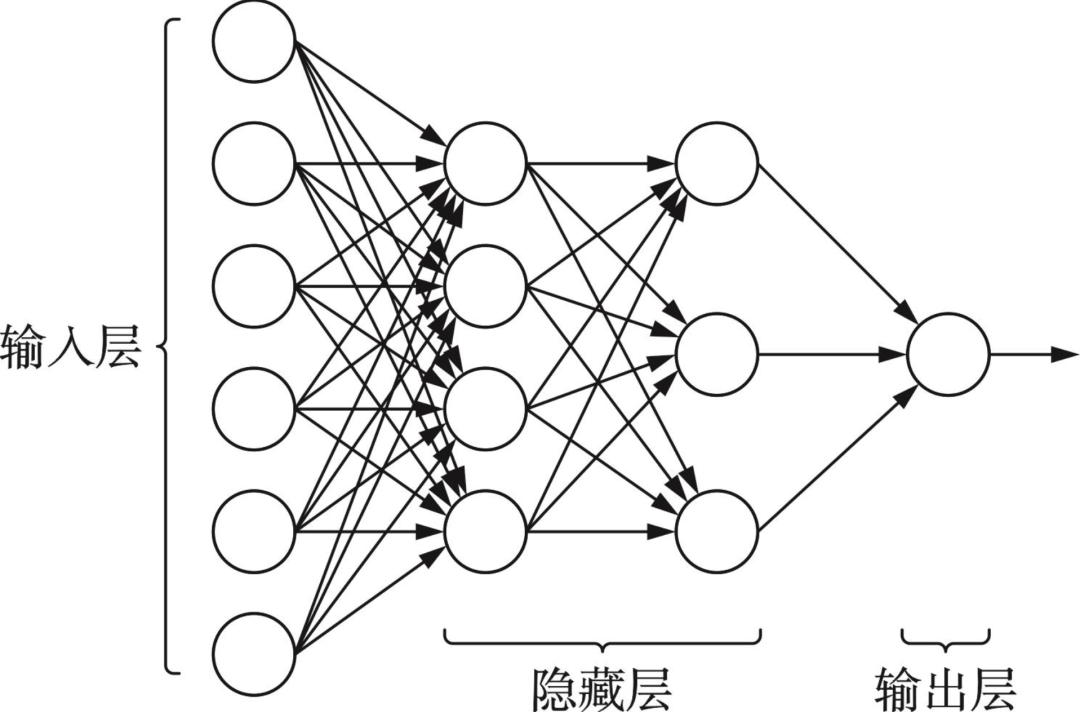
## 2.4 Neural Networks
Layers: **Input → Hidden → Output**.
Training: backpropagation adjusting weights/biases.
---
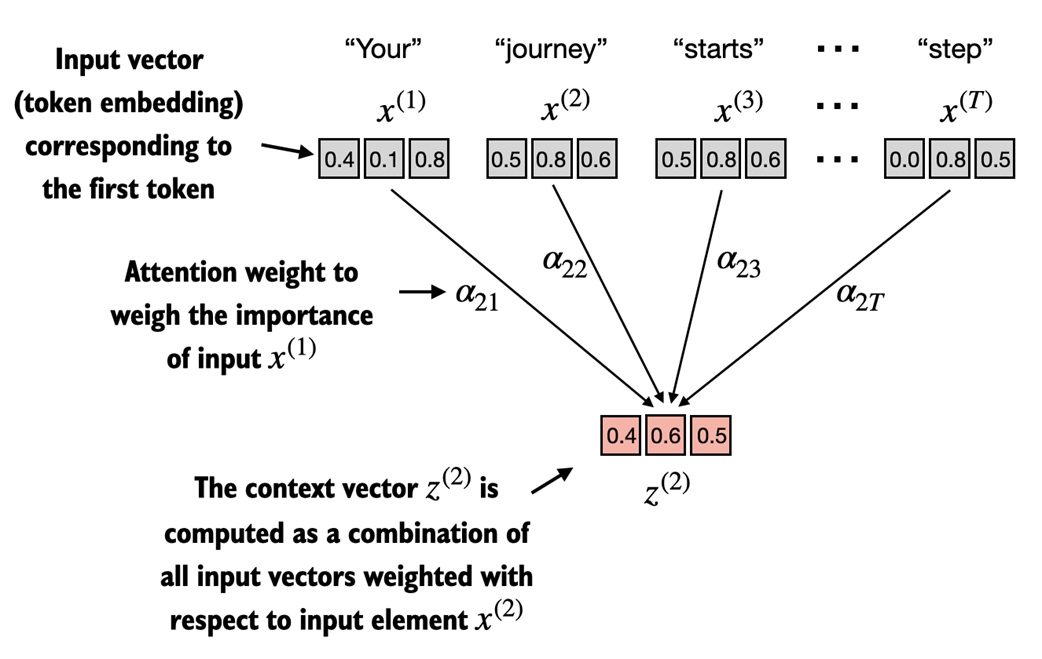
## 2.5 Attention Mechanism
**Goal:** Compute **context vectors** representing how tokens relate.
Steps:
1. Project inputs into Q, K, V
2. **Dot Product** Q•K → attention scores
3. **Softmax** normalize to weights
4. Weight V by scores → context vector
---
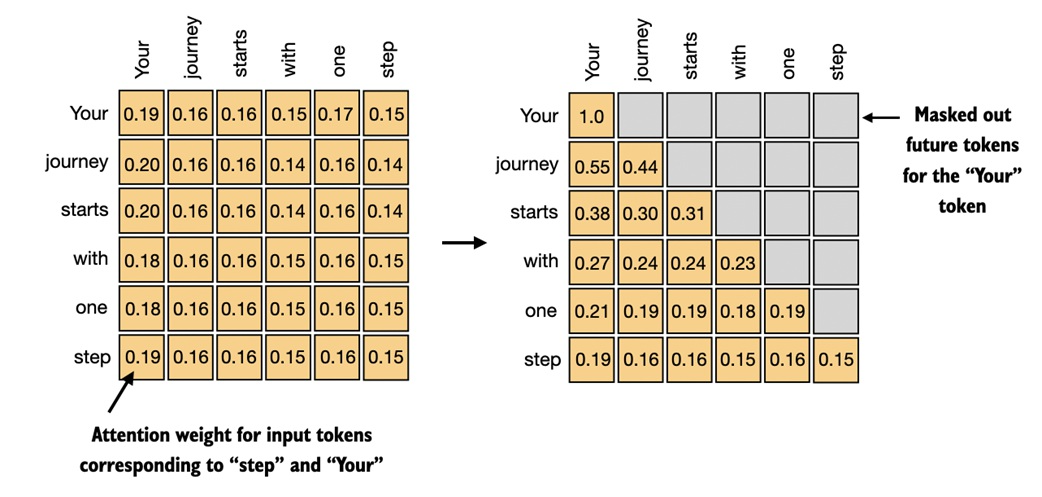
### Self-Attention vs Causal (Masked) Attention
- **Self-Attention**: Each token relates to all others.
- **Causal Attention**: No "future" tokens allowed.
---
### Multi-Head Attention
Parallel attention heads focus on **different relationships** (syntax, semantics).
---
## 2.6 FFN / MLP
Two linear layers + nonlinear **GELU**, residual connections.
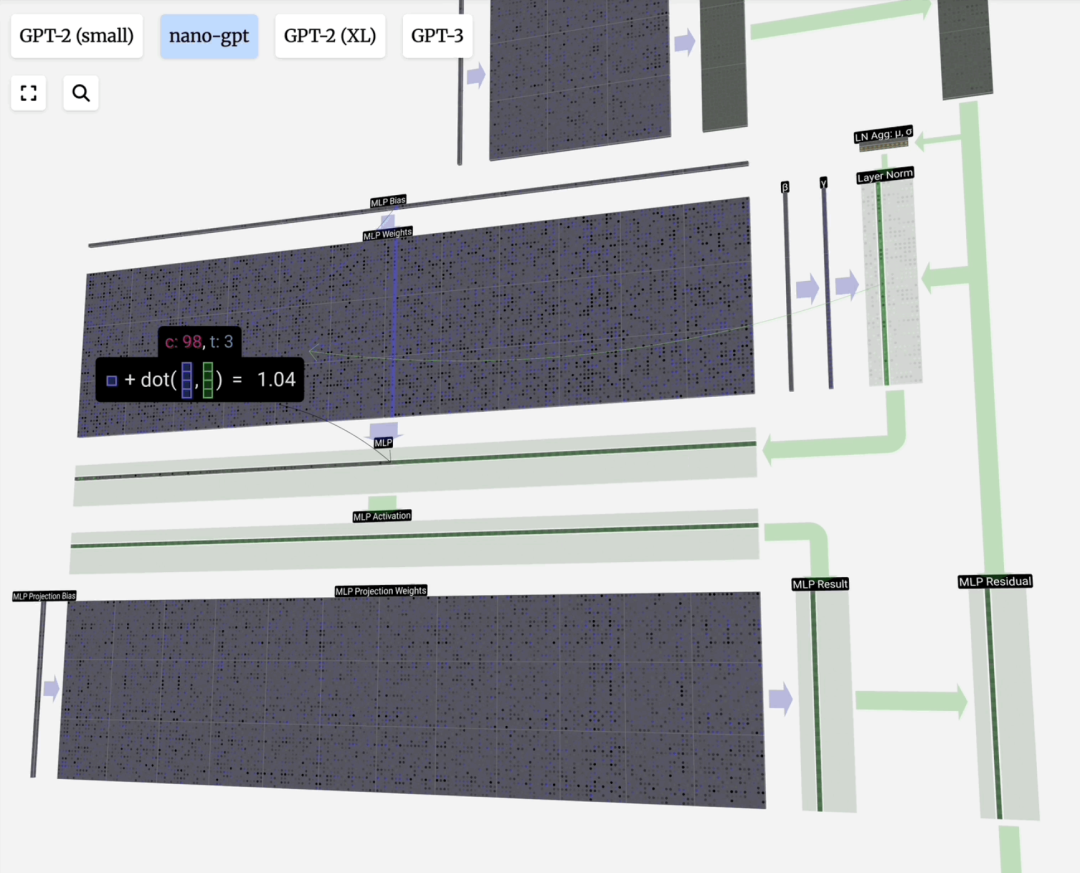
---
## 2.7 Stacking Transformer Layers
Lower layers → basic features
Higher layers → complex semantics
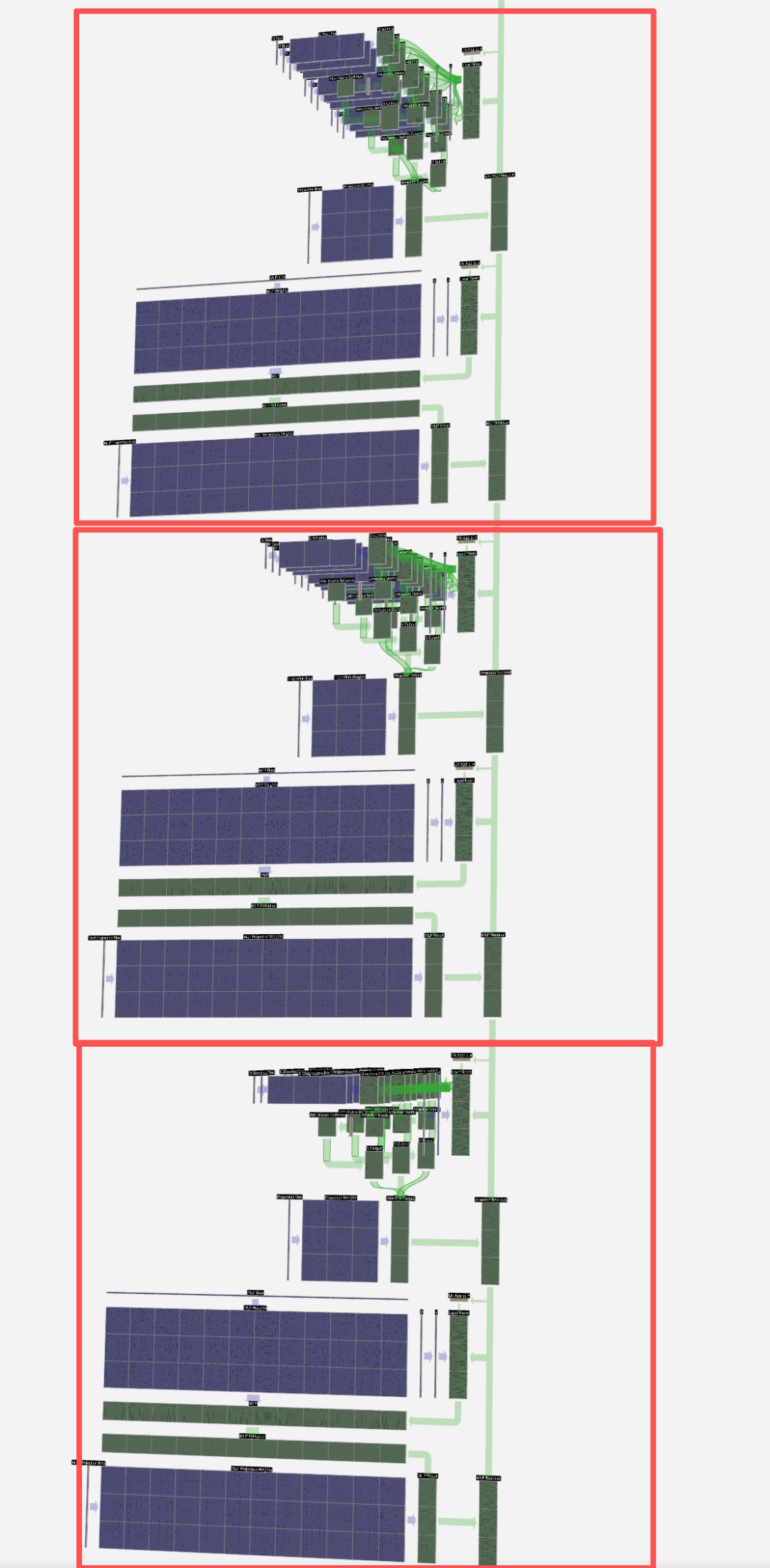
---
## 2.8 Example Translation Walkthrough
### Steps:
1. `` → "Transformer"
2. Add "很" (copula → adverb)
3. Add "强" (first char of "powerful")
4. Add "大" (to complete "强大")
5. End with "。" (period)

---
## Visualizing Attention
Heatmap shows alignment:
- "Transformer" ↔ "Transformer"
- "is" ↔ "很"
- "powerful" ↔ "强大"
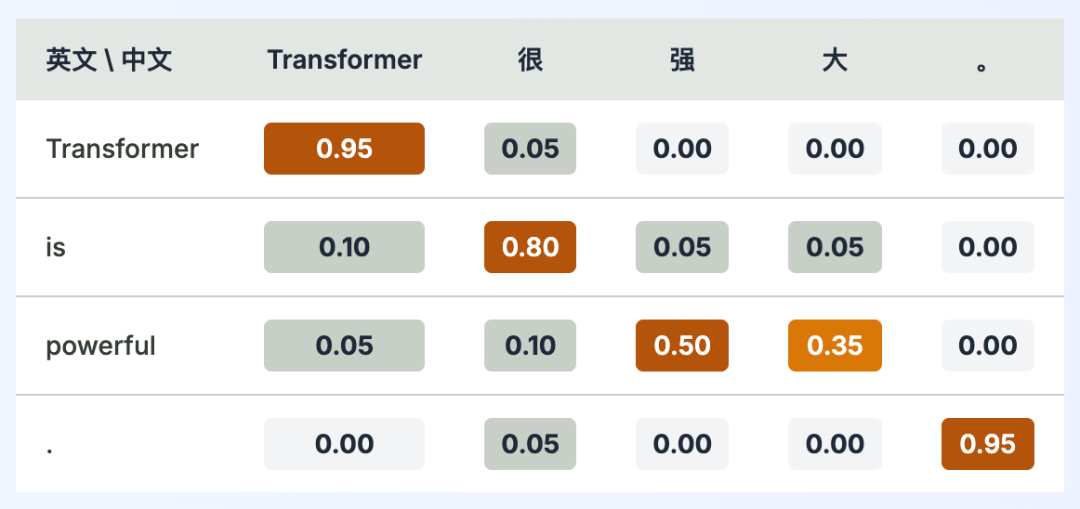
---
## 03 Current Open-Source Flagship LLM Architectures
2025 trends:
- **Hybrid** architectures (Transformer + Mamba)
- **MoE** widespread
- **Specialized attention** like MLA
Examples:
- **DeepSeek V3**: MoE + MLA
- **OLMo2**: RMSNorm + GQA
- **Gemma 3**: Sliding window attention
---
## Conclusion
**Key idea:** *Model capability is the foundation; application patterns are the superstructure.*
Strong models reduce need for complex application scaffolding.
Focus both on **improving capabilities** and watching how **application forms evolve**.
---
## References
- [Attention Is All You Need (2017)](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1706.03762)
- [Modular RAG (2024)](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2407.21059)
- [Animals vs Ghosts](https://karpathy.bearblog.dev/animals-vs-ghosts/)
- [Let's Build GPT from Scratch](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kCc8FmEb1nY)
- [nanochat](https://github.com/karpathy/nanochat)
- [LLM Visualization](https://bbycroft.net/llm)
- [LLM Open Source Ecosystem Report](https://github.com/antgroup/llm-oss-landscape/blob/main/reports/250913_llm_landscape/250913_llm_report_cn.md)
---
**- End -**


