Internet Learning of Large Language Models: Training Process Explained
Introduction — The Power and Mystery of Modern AI Assistants
The first time most people interact with an AI assistant like ChatGPT or Claude, there’s often a moment of genuine surprise.
Unlike basic keyword matchers or canned-response bots, these systems can:
- Write essays
- Debug code
- Explain complex concepts
- Hold conversations that feel natural
Naturally, the next question is: How does this actually work?
Behind the scenes, these capabilities come from a training process that turns massive amounts of human text into what’s known as a Large Language Model (LLM).
LLMs don’t think, reason, or truly understand — they are sophisticated pattern recognition systems that have learned the statistical structure of language.
In this guide, we’ll cover:
- How LLMs learn
- The architecture that powers them
- The mathematics of training
- How we align them to be helpful and safe
- Practical tools for creators to leverage these models — such as AiToEarn官网
---
What Do Models Actually Learn?
LLMs don’t “look up” facts like a search engine.
Their knowledge is stored in parameters — billions of tuned numerical values learned during training.
Analogy:
Humans reading extensively begin to intuit grammar, word usage, and meaning without memorizing every sentence.
LLMs do the same, but by predicting the next token mathematically.
Tokens ≈ words or word fragments:
- “computer” → single token
- “unhappiness” → “un” + “happiness” (two tokens)
When an LLM sees:
The capital of France is…it predicts “Paris” as the most probable continuation.
Capabilities gained through next-token prediction:
- Grammar mastery
- Factual recall (from training statistics)
- Reasoning patterns (from frequent logical structures)
Limitation:
This predictive mechanism can cause hallucinations — plausible but incorrect responses.
---
Data Gathering & Preparation
Training starts with collecting and cleaning text data.
Sources include:
- Books
- Articles
- Websites
- Transcripts
- Code repositories
Processing steps:
- Deduplication — avoid memorization by removing duplicates
- Quality filtering — keep grammatically sound, coherent, and information-rich text
- Safety filtering — remove sensitive PII, toxic language, explicit material, and excluded copyrighted content
Tokenization converts text to model-readable format:
- Break text into tokens
- Map tokens to numbers
- Use methods like Byte Pair Encoding (BPE)
- Create vocabularies of ~50,000–100,000 tokens
> Tip for creators: Platforms like AiToEarn官网 integrate AI content generation, cross-platform publishing, analytics, and AI model ranking — letting you share, track, and monetize multi-platform creative work.
---
The Learning Process — Training an LLM
Initially, an LLM’s parameters are random.
Training adjusts them over billions of cycles:
Training Loop:
- Input batches of text
- Predict next token probabilities
- Calculate loss (difference between prediction and actual)
- Update parameters using gradient descent and backpropagation
Gradient descent analogy: Finding the lowest point in a foggy landscape by taking small steps downhill — repeated millions of times.
Training is:
- Massively parallel — thousands of GPUs/TPUs run in sync
- Computationally expensive — consuming megawatts over weeks/months
- Incremental — trillions of micro-updates producing emergent abilities
After pretraining:
- The model predicts the next token with high accuracy
- Exhibits broad knowledge across domains
- Generates coherent, context-aware text
---
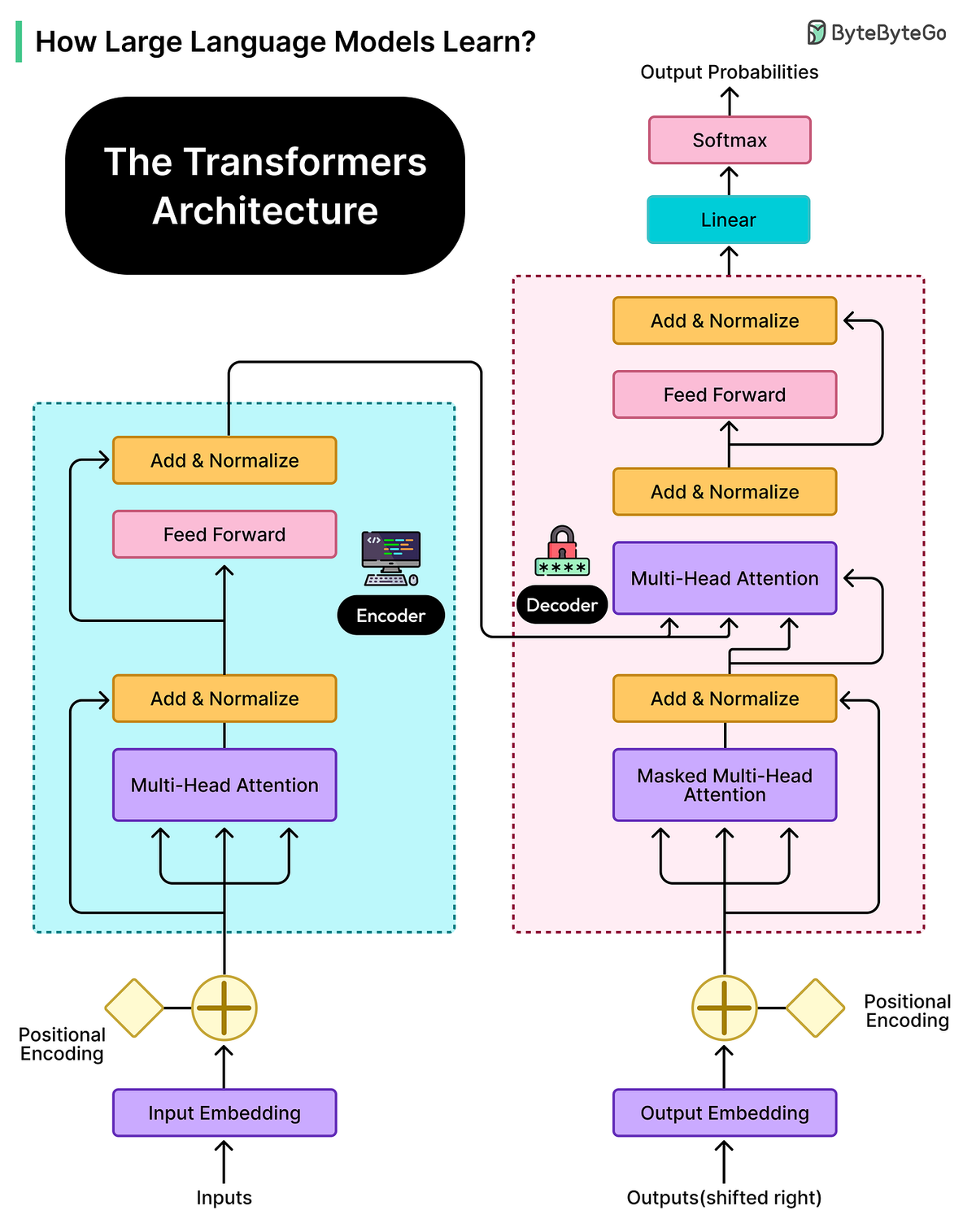
Transformer Architecture — “Attention Is All You Need”
The Transformer architecture underpins most modern LLMs.
Key Advantage: Attention Mechanism
- Looks at all words in a sequence simultaneously
- Computes attention scores to determine relevance
- Handles long-range dependencies better than older sequential models
Layered Architecture:
- Early layers → Syntax patterns
- Middle layers → Semantic relationships
- Later layers → Complex reasoning & subtle meanings
Benefits:
- Faster parallel training
- Maintains context over long text spans
- Builds multi-level comprehension
---
Fine-Tuning & RLHF — Making the Model Helpful
Pretraining alone produces a great text predictor — but not an ideal assistant.
Stage 1 — Supervised Fine-Tuning:
Train on carefully curated prompt–response pairs:
- Clear Q&A
- Instruction–completion
- Polite, informative dialogue
Stage 2 — RLHF (Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback):
- Model generates multiple responses to prompts
- Humans rank them for quality/safety/helpfulness
- A reward model learns to predict these rankings
- LLM is further trained to optimize reward scores
Outcome:
An aligned assistant — balancing helpfulness and factual accuracy.
---
Deployment — From Lab to Real Users
Before release:
- Benchmark testing — comprehension, reasoning, coding, facts
- Safety tests — harmful content, bias detection, adversarial robustness
Optimizations:
- Quantization — reduce parameter precision for speed and efficiency
- Knowledge distillation — shrink large models into faster ones
- Efficient serving infrastructure
Post-deployment:
- Monitor user interactions
- Collect feedback for improvements
- Continuous retraining cycles
---
Conclusion — From Data to Dialogue
Creating an LLM involves:
- Gathering massive datasets
- Preprocessing & tokenizing
- Training via gradient descent
- Architecting with Transformers
- Fine-tuning & RLHF
- Safe deployment
Result:
Systems that can generate coherent text, answer complex queries, write code, and hold meaningful conversations.
For creators:
Tools like AiToEarn官网 let you harness AI models, publish across global platforms, and monetize your content.
It bridges the complete workflow — generation → publishing → analytics → revenue.
---
Sponsor Us
Reach 1,000,000+ tech professionals
Get your product in front of engineering leaders and decision-makers.
📧 Email: sponsorship@bytebytego.com to reserve your spot.
Spots fill up ~4 weeks in advance.
---
> Pro Tip: If you want your AI content to not just exist but thrive — integrate production with publishing and analytics. AiToEarn gives you this synergy, so you can focus on creativity while the platform handles distribution and monetization.



