Is 16:9 or 4:3 Better for Video and Photography Use
Learn the differences between 16:9 and 4:3 aspect ratios, their history, pros, cons, and best uses for video production and photography projects.
Introduction to Aspect Ratios: 16:9 vs 4:3
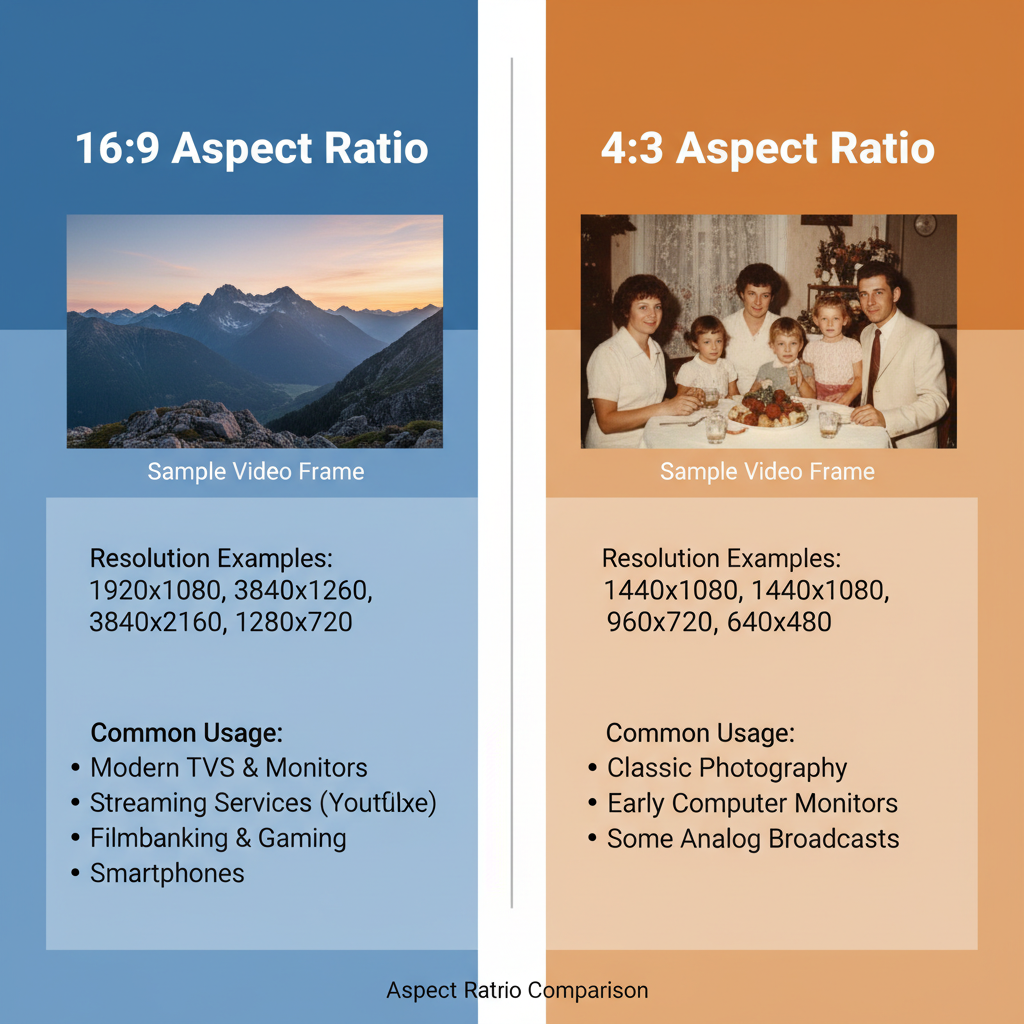
In the world of visual media — from video production to photography — choosing the right aspect ratio is critical to the quality and impact of your work. The aspect ratio defines the proportional relationship between width and height in an image or video frame. Two of the most widely discussed are 16:9 and 4:3.
If you’ve wondered “is 16:9 or 4:3 better?”, the answer hinges on your creative goals, technical setup, and where your content will be displayed. This guide explains each ratio’s meaning, history, pros and cons, and practical usage to help you decide.

---
Understanding 16:9 and 4:3
- 16:9 means 16 units wide and 9 units tall — producing a stretched rectangular, widescreen frame. Common in HDTV, modern computer monitors, and streaming video platforms.
- 4:3 means 4 units wide and 3 units tall — resembling a near-square frame. This was standard in older TV formats and classic photography.
Mathematical equivalents:
- 16:9 ≈ 1.78:1
- 4:3 ≈ 1.33:1
---
A Brief History of Aspect Ratios
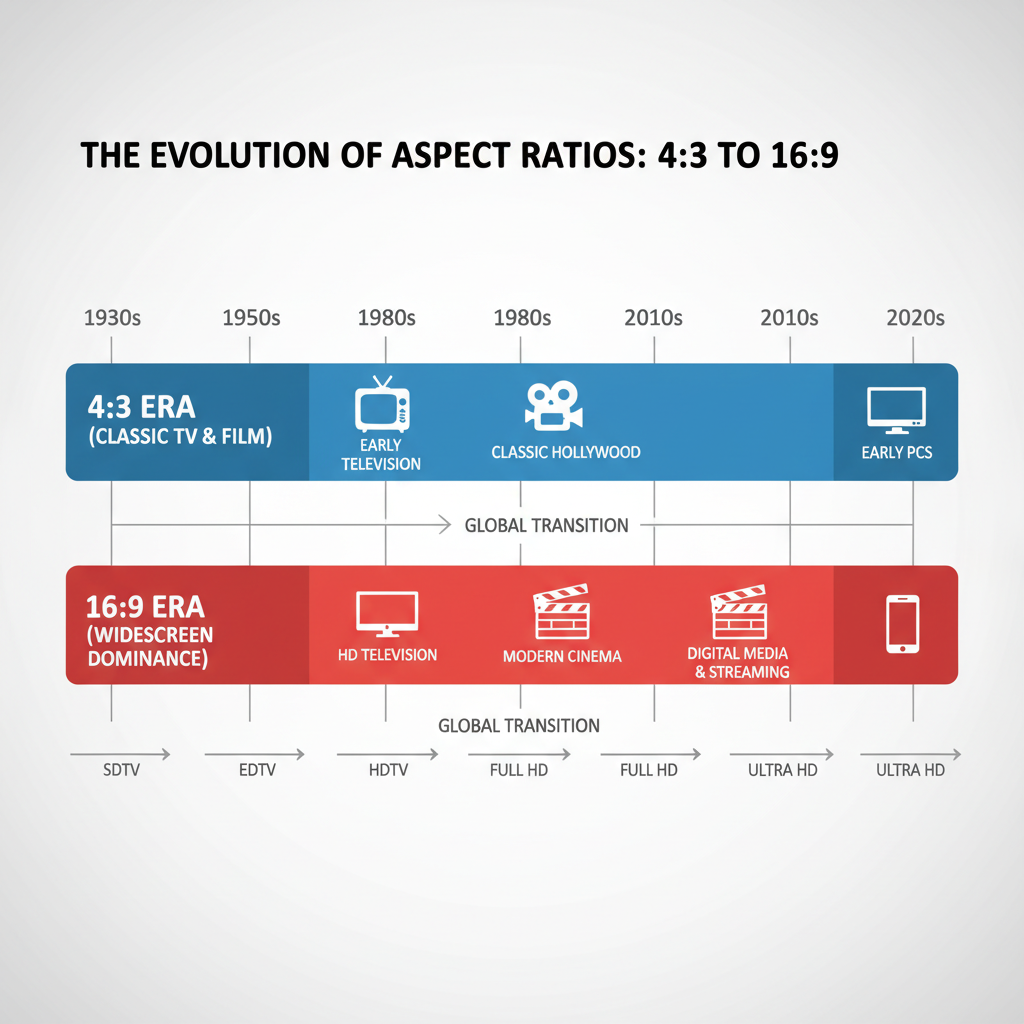
The Era of 4:3
From the 1950s until the late 1990s, most TV broadcasts and computer monitors adhered to the 4:3 aspect ratio.
It was favored for photographic film formats and early video cameras because it matched most print sizes and sensor dimensions.
Shift to 16:9
In the 1990s, HDTV standards introduced 16:9 as the preferred broadcast ratio. Its panoramic view matched digital cinema’s widescreen look and delivered a more immersive, human-eye-friendly field of vision.
---
Key Advantages of 16:9
Cinematic and Immersive Viewing
The panoramic nature of 16:9 enhances storytelling, particularly in action, travel, and documentary scenarios.
Native Fit for HD and 4K
Resolutions like 1280×720 (HD), 1920×1080 (Full HD), and 3840×2160 (4K) are optimized for 16:9, ensuring no need for cropping or scaling.
Gaming and Interactive Media
Most modern games and VR experiences are designed for 16:9 displays, preventing distortion and preserving interface layout.
---
Key Advantages of 4:3
Cropping Flexibility
While less rectangular than 16:9, the 4:3 frame adapts easily for square and vertical social media formats.
Retro and Nostalgic Appeal
Classic TV programs, vintage films, and legacy video game visuals are native to 4:3, maintaining authenticity when preserved.
Portrait Photography
Photographers sometimes prefer 4:3 when aiming for subject-focused compositions without excessive background space.
---
Side-by-Side Comparison
| Criteria | 16:9 | 4:3 |
|---|---|---|
| Common Resolutions | 1920×1080, 1280×720, 3840×2160 | 1024×768, 1600×1200, 2048×1536 |
| Viewer Experience | Immersive widescreen, cinematic look | Compact frame, focused storytelling |
| Editing Flexibility | Ideal for horizontal content | Easy to crop for multiple formats |
| Typical Use | Streaming, gaming, filmmaking | Portrait photography, retro media |
---
Platform and Industry Standards
YouTube & Streaming Services
YouTube defaults to 16:9 playback. Uploading 4:3 results in pillarboxing (black bars at the sides) unless the video is cropped or stretched.
Social Media Considerations
Instagram, TikTok, and Facebook prioritize vertical layouts. 4:3 can be cropped more easily into vertical/square formats, whereas 16:9 suits full-width videos.
Cinema & TV
Feature films may use even wider ratios such as 2.39:1, but most broadcast TV and consumer cameras today favor 16:9 for universal compatibility.
---
Aspect Ratio in Creative Composition

Framing impacts the emotional tone of media content:
- 16:9 maximizes horizontal space, perfect for landscapes, group scenes, and dynamic motion.
- 4:3 emphasizes verticality and can convey intimacy or tension.
Directors and photographers choose aspect ratio intentionally to influence how audiences perceive the scene.
---
Technical Factors to Consider
Cropping and Scaling Risks
Switching between ratios requires careful framing to avoid losing key visual elements or distorting proportions.
Letterboxing vs. Pillarboxing
- Letterboxing: black bars at top and bottom (common for 4:3 shown on 16:9 screens).
- Pillarboxing: black bars on sides (common for 16:9 shown on 4:3 screens).
Ensuring your content matches the display’s native ratio reduces these issues.
---
Practical Recommendations for Choosing the Best Ratio
Gaming
Go with 16:9 for native compatibility, proper field of view, and no borders.
Filmmaking
- For grand, sweeping cinematography → use 16:9 or wider aspect ratios.
- For intimate, character-centered narratives → 4:3 can emphasize focus and atmosphere.
Presentations
Modern projectors usually project in 16:9. Use 4:3 only if you know the venue supports it without widescreen distortion.
Social Content
- 4:3 works well if you plan to crop into vertical or square formats later.
- Use 16:9 for YouTube or horizontal streaming platforms.
---
Conclusion and Next Steps
So, is 16:9 or 4:3 better? The answer is situational:
- Choose 16:9 when targeting modern screens, cinematic storytelling, gaming, and HD/4K content.
- Choose 4:3 for retro authenticity, portrait photography, or flexible cropping for diverse social formats.
Pro tips for maintaining quality:
- Identify your primary distribution channel before shooting.
- Match camera settings to the output aspect ratio.
- Avoid stretching footage during post-processing.
- Consider extra framing space for later adjustments.
By understanding both ratios’ unique strengths and limitations, you can make intentional creative and technical choices that elevate your visual projects.
Ready to decide between 16:9 and 4:3? Align your choice with your project goals, and create content that resonates with your audience across every platform.




