Java Enters the Agentic AI Era: The Technical Evolution Behind Spring AI Alibaba 1.1 Release
Spring AI Alibaba 1.1: A New Era for Enterprise AI Agents
A few days ago, the Java Agent ecosystem welcomed a major release: Spring AI 1.1.0 GA, followed closely by the official Spring AI Alibaba 1.1 release.
This milestone builds on the enterprise experience from version 1.0, marking a new phase of production-ready AI Agent applications.
- 📄 Docs: https://java2ai.com/
- 💻 GitHub: https://github.com/alibaba/spring-ai-alibaba
---
🎯 Core Goals
- Simplify development: Build and run an agent with <10 lines of code.
- Enterprise support: Native multi-agent capabilities and workflow orchestration.
This guide explores version 1.1 — from a basic ReactAgent to advanced context engineering and multi-agent collaboration.
---
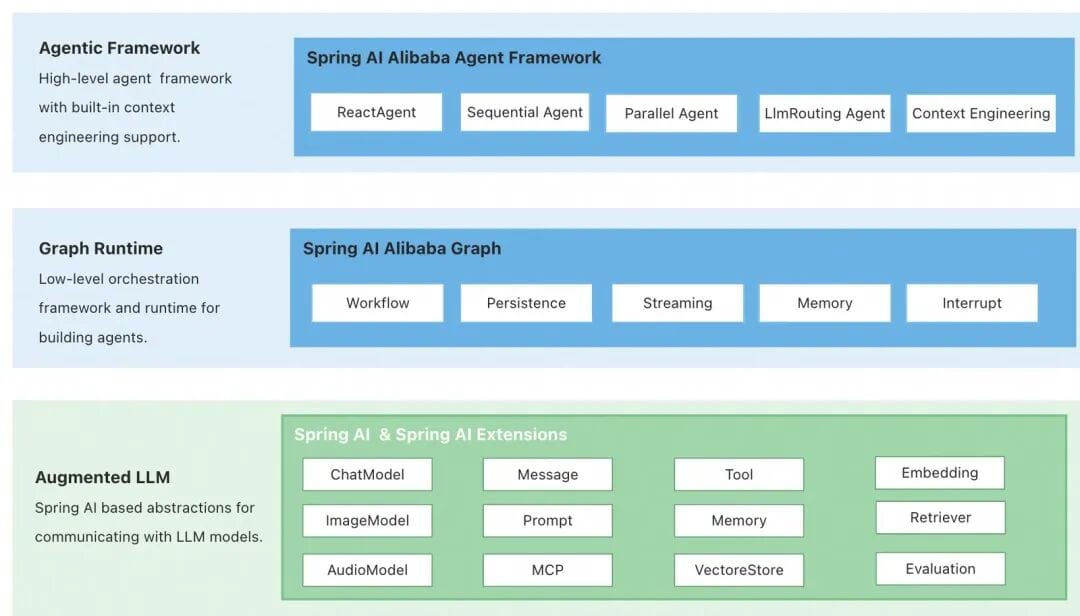
🏛 Architecture Overview
Spring AI Alibaba consists of three layers:
- Agent Framework: ReactAgent-based design with advanced features such as automatic context engineering and Human-In-The-Loop.
- Graph: Low-level workflow and multi-agent coordination framework; supports orchestration APIs.
- Augmented LLM: Atomic abstractions from the Spring AI framework for models, tools, messages, vector stores.
---
🚀 Quick Start
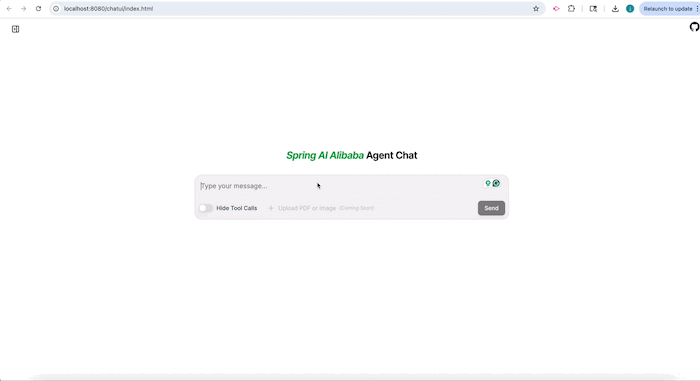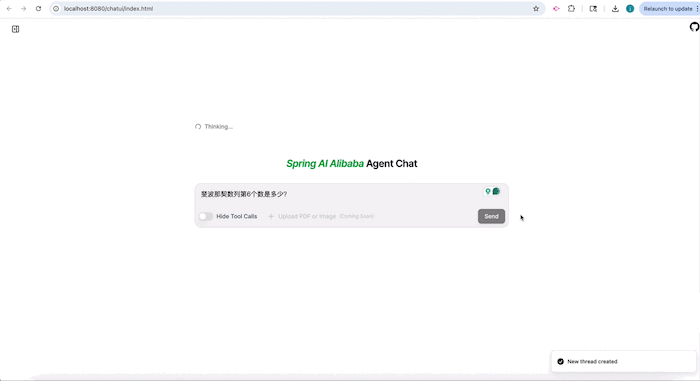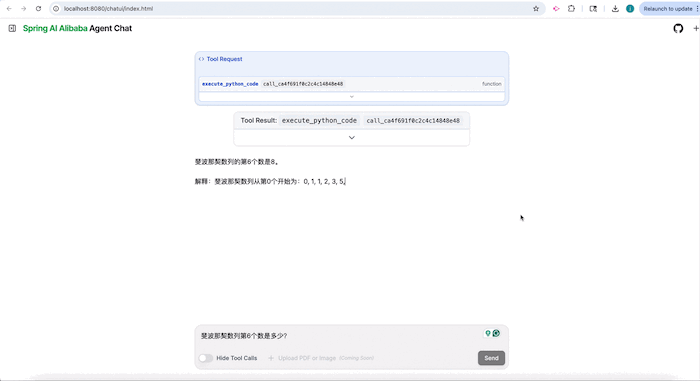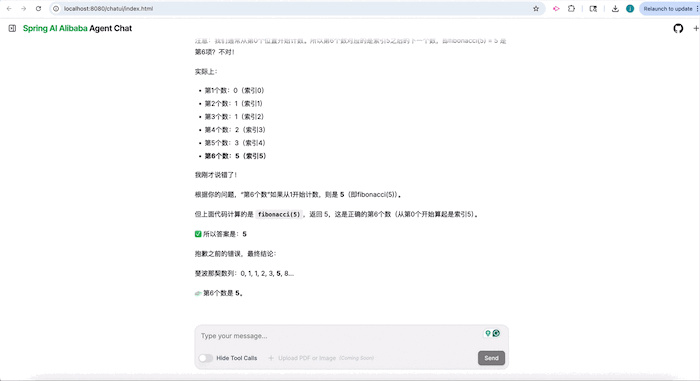
An example ChatBot agent is available in the repository. It supports Python scripts, shell commands, local file access, and more.
Step 1: Clone the Example
git clone https://github.com/alibaba/spring-ai-alibaba.git
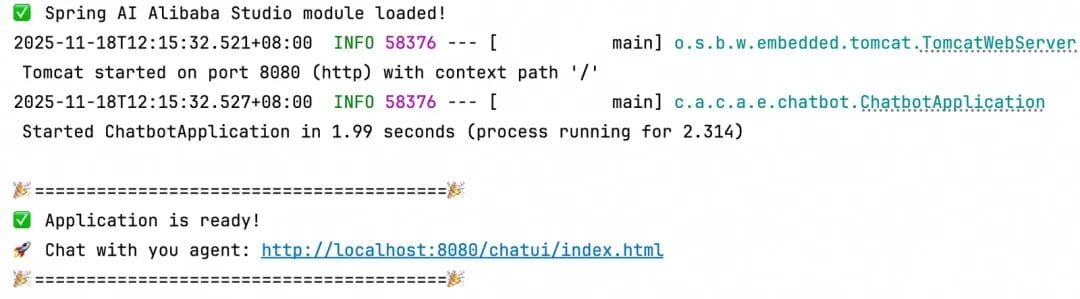
cd examples/chatbotStep 2: Run the Agent
mvn spring-boot:runStep 3: Access the UI
- Check the console output for the UI address
- Open it in your browser to chat and view reasoning steps
---
📦 Dependencies
Add the following POM dependencies:
com.alibaba.cloud.ai
spring-ai-alibaba-agent-framework
1.1.0.0-M5
com.alibaba.cloud.ai
spring-ai-alibaba-starter-dashscope
1.1.0.0-M5
com.alibaba.cloud.ai
spring-ai-alibaba-studio
1.1.0.0-M5
---
💬 Creating a ChatBot Agent
Example with Spring Boot:
@Bean
public ReactAgent chatbotReactAgent(ChatModel chatModel,
ToolCallback executeShellCommand,
ToolCallback executePythonCode,
ToolCallback viewTextFile) {
return ReactAgent.builder()
.name("SAA")
.model(chatModel)
.instruction(INSTRUCTION)
.enableLogging(true)
.tools(executeShellCommand, executePythonCode, viewTextFile)
.build();
}---
🐍 Python Tool Definition
Defined with GraalVM Python library:
@Bean
public ToolCallback executePythonCode() {
return FunctionToolCallback.builder("execute_python_code", new PythonTool())
.description(PythonTool.DESCRIPTION)
.inputType(PythonTool.PythonRequest.class)
.build();
}---
🧠 Core Concepts
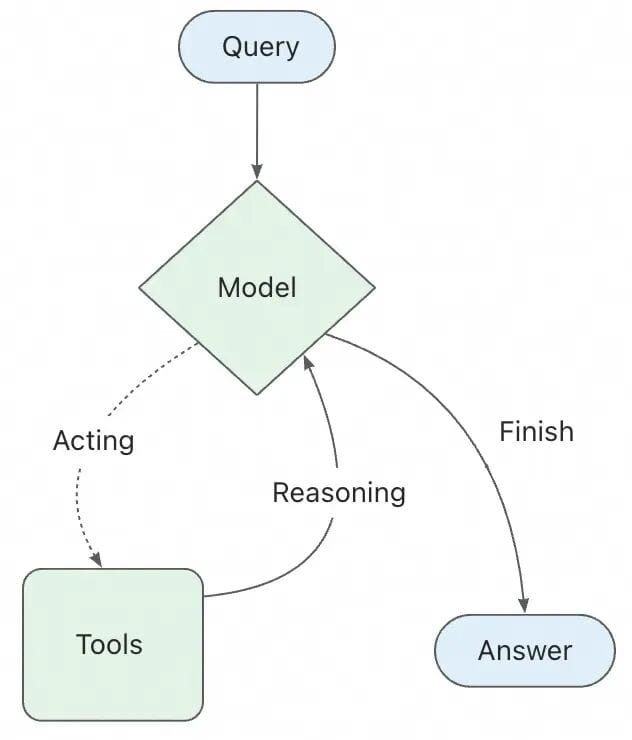
ReactAgent
Implements ReAct (Reasoning + Acting) loop:
- Reason: Analyze the task.
- Act: Choose and execute tools.
- Observe: Evaluate tool output.
- Repeat until completion.
Tool Definition
public class SearchTool implements BiFunction {
@Override
public String apply(String query, ToolContext toolContext) {
return "Search results: " + query;
}
}
ToolCallback searchTool = FunctionToolCallback
.builder("search", new SearchTool())
.description("Tool for searching")
.build();---
Graph Workflow
Low-level StateGraph with:
- State, Node, Edge
- Features: streaming, HITL, memory management
- APIs: Declarative (Agentic) & low-level (Graph)
Built-in orchestration patterns:
- SequentialAgent
- ParallelAgent
- LlmRoutingAgent
---
🛠 Context Engineering
Ensures correct and relevant context to the LLM.
Categories:
- Conversation history
- External data
- Tool metadata
Built-in hooks:
- Human-in-the-Loop
- Planning
- Model Call Limit
- Tool Retry
- Tool Selector & Emulator
- Context Editing
---
Example: Human-in-the-Loop
HumanInTheLoopHook humanReviewHook = HumanInTheLoopHook.builder()
.approvalOn("execute_sql", ToolConfig.builder().description("SQL execution requires approval").build())
.build();
ReactAgent agent = ReactAgent.builder()
.hooks(humanReviewHook)
.saver(new MemorySaver())
.tools(executeSqlTool)
.build();---
📏 Message Summarization
Avoid context overflow by compressing history:
SummarizationHook summarizationHook = SummarizationHook.builder()
.model(chatModel)
.maxTokensBeforeSummary(4000)
.messagesToKeep(20)
.build();---
🔍 Planning Interceptor
Force a planning phase before execution:
ReactAgent agent = ReactAgent.builder()
.interceptors(TodoListInterceptor.builder().build())---
🔒 Model Call Limit
hooks(ModelCallLimitHook.builder().runLimit(5).build())---
♻ Tool Retry
.interceptors(ToolRetryInterceptor.builder().maxRetries(2).build())---
🎯 Tool Selector
.interceptors(ToolSelectionInterceptor.builder().build())---
🧪 Tool Emulator
.interceptors(ToolEmulatorInterceptor.builder().model(chatModel).build())---
✏ Context Editing
.interceptors(ContextEditingInterceptor.builder().trigger(120000).build())---
🪝 Hooks & Interceptors
- Hooks: Insert logic at lifecycle points (`beforeModel`, `afterModel`)
- Interceptors: Wrap model/tool calls for retries, caching, safety
Examples:
- Content Moderation
- Performance Monitoring
- Tool Cache
---
🗄 Memory Management
Store short-term conversation state with `MemorySaver`.
Supports persistent savers like Redis/Mongo for production.
Access memory via `ToolContext` inside tools.
---
👥 Multi-Agent
Modes:
- Tool Invocation: Agent as a tool
- Workflow Orchestration: Sequential, Parallel, LLM Routing
- Agent as Workflow Node: Integrated with StateGraph
---
📌 Summary
Spring AI Alibaba 1.1:
- ReactAgent core with context engineering
- Hooks & Interceptors for fine-grained control
- Memory management for personalization
- Flexible multi-agent orchestration
---
More resources:



