Jensen Huang GTC Keynote: The "AI-XR Scientist" Has Arrived!
AI in the Lab: The Rise of LabOS, the AI Co‑Scientist
> AI has read countless papers — but can it actually perform experiments?
> LabOS is redefining that answer: an AI that can think, see, guide, and operate real-world experiments.
> This marks the dawn of human–machine co‑evolution in scientific discovery.
---
The Vision: Human–AI Collaboration in Real Laboratories
In what looks like a typical biology lab, a scientist prepares a solution wearing XR smart glasses.
A prompt appears: “Stem cell culture completed, please collect the sample.”
Immediately, a robot takes the test tube, activates a vortex mixer, and processes the sample.
Meanwhile, the CRISPR gene-editing workflow is overlaid in the scientist’s field of view.
Behind the scenes, LabOS — equipped with a “world model” of the lab — orchestrates humans, robots, and intelligent agents into a unified, reproducible workflow.
---
Highlights of the Launch
- Event: Washington GTC Conference, October 29
- Presented by: NVIDIA CEO Jensen Huang
- Developed by: Prof. Cong Le (Stanford), Prof. Wang Mengdi (Princeton), NVIDIA
- World’s First: Integration of AI + XR for a fully embodied Co‑Scientist
Useful Links
- 🌐 LabOS Official Site: https://ai4labos.com
- 📄 Research Paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/2510.14861
---
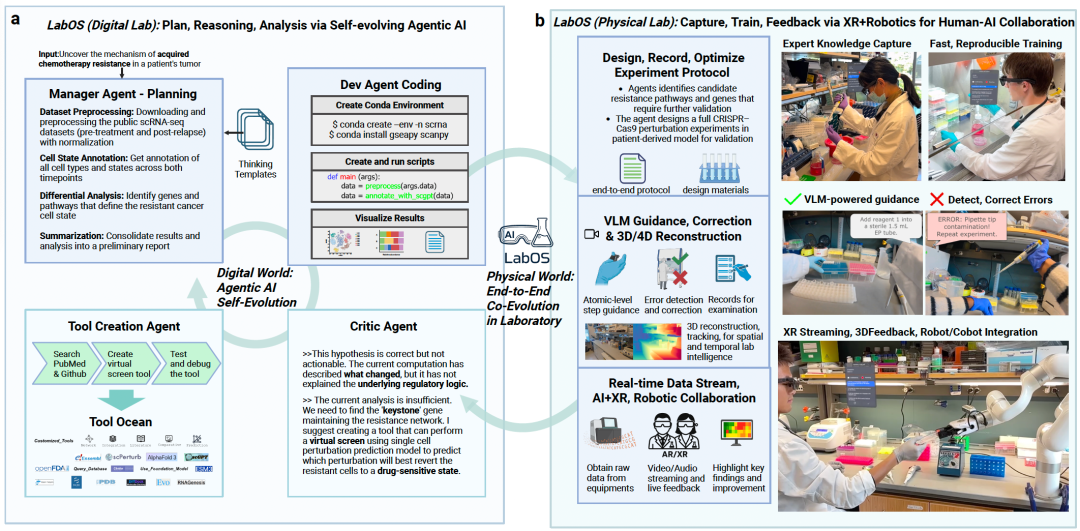
1. From Theory to Touch: Embodied AI Labs
Traditional research AI — e.g., AlphaFold or DeepMind’s “deep research” — remains digital-only.
Physical experiments still depend on human skill, limiting reproducibility and efficiency.
LabOS bridges this gap with brain–eye–hand synergy:
1. Brain — Self‑Evolving AI Agents
- Based on the STELLA framework
- Four intelligent agents: Planning, Development, Review, Tool Creation
- Ocean of Tools Module: Builds new tools from literature/data pools
- Reasoning-Time Extension: Continuously improves analytical ability
2. Eye — Laboratory Visual Reasoning
- Custom Vision–Language Model (LabOS‑VLM) built for lab workflows
- LabSuperVision (LSV) Benchmark: 200+ first-person experimental videos
- Trained to outperform general models in nuanced lab task recognition and error detection
3. Hand — Human–Robot Execution
- Lightweight AR Glasses capture video streams
- Real-time guidance, error alerts, and suggestions every 5–10 seconds
- LabOS Robot performs physical operations, coordinated via XR, hands-free in sterile conditions

Figure 2: 4D reconstruction of lab environment enabling real-time XR‑robot collaboration.
---
2. The LabOS “World Model” — Understanding Laboratory Space
Laboratories demand high-precision visual reasoning.
General VLMs scored poorly (2–3 / 5) in protocol alignment and error detection.
Building LabOS‑VLM
- Combined public/free lab videos with internal expert-annotated datasets
- Supervised Fine-Tuning + Reinforcement Learning
- Achieved > 90% accuracy in wet-lab SOP error detection
Spatial & Temporal Cognition
- AI identifies all lab items: glassware, instruments, samples
- Understands semantic flow: what’s completed, ongoing, pending
- Enables autonomous lab robot execution with precise context awareness

Figure 3: From LSV benchmark to real-time LabOS‑VLM deployment in live experiments.
---
3. Case Studies: AI–Human Scientific Breakthroughs
Case 1: Cancer Immunotherapy Target Discovery
- Dry Lab: CRISPR activation screen on melanoma cells → find CEACAM6
- Clinical Analysis: TCGA survival correlation
- Wet Lab Validation: CRISPR activation confirmed resistance to NK cell killing
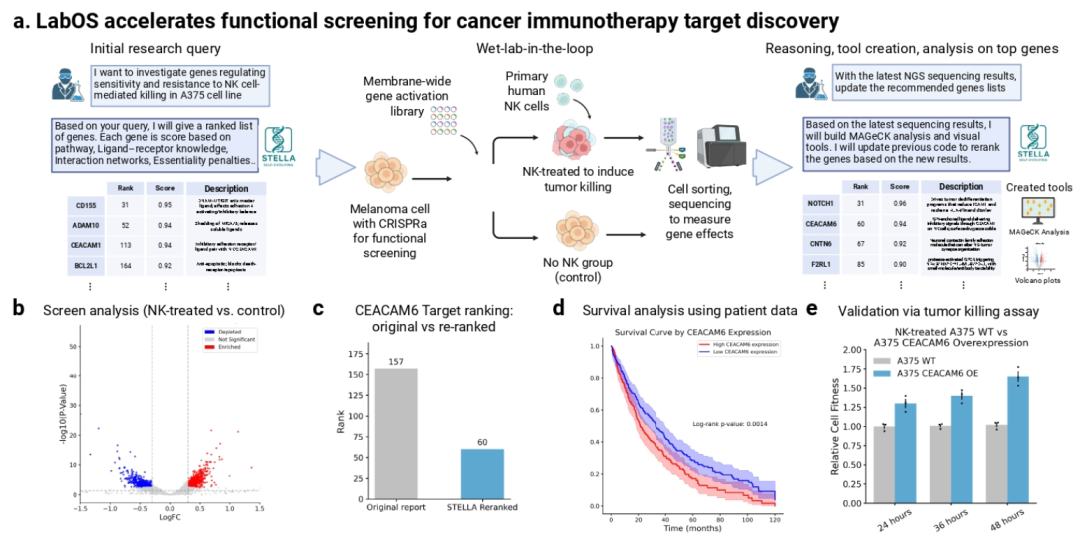
Figure 4: LabOS pipeline for target discovery.
---
Case 2: Mechanistic Study in Cell Fusion
- Hypothesis Generation: AI nominated ITSN1 as key regulator
- Validation: CRISPR interference in U2OS cells
- Result: ITSN1 knockdown significantly inhibited fusion
- Demonstrates complete closed-loop from idea to proof
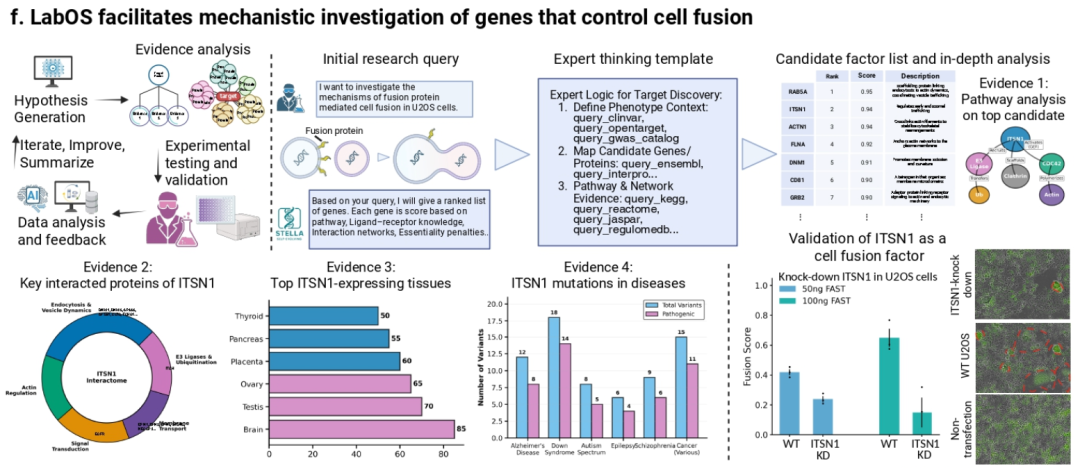
Figure 5: LabOS in mechanistic biology research.
---
Case 3: Skill Transfer in Stem Cell Engineering
- Complex CRISPR stem cell workflows are hard to replicate
- LabOS uses XR + VLM to record expert protocols
- Automatically produces standardized digital SOPs
- Acts as an AI mentor for rapid skill onboarding
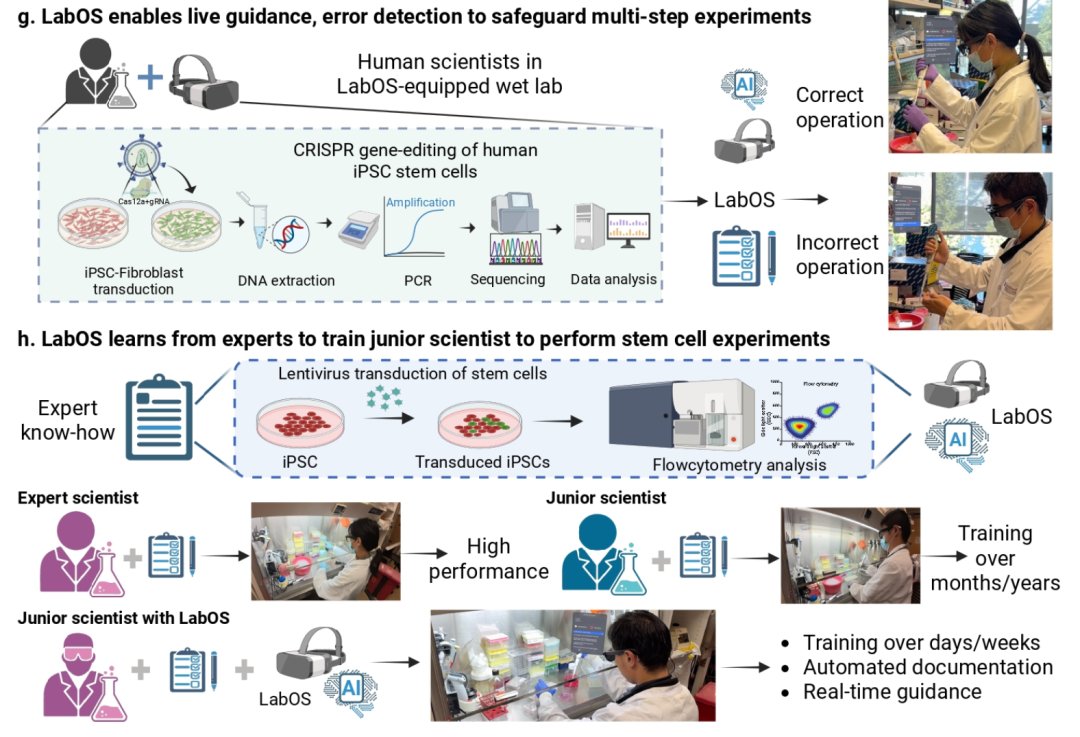
Figure 6: LabOS enhances reproducibility and tech transfer.
---
The Future: Scaling Science with AI
Professors Cong Le and Mengdi Wang envision a world where AI:
- Works inside the lab
- Understands each step of workflow
- Learns continuously from successes and failures
LabOS turns fragmented labs into integrated knowledge engines, accelerating discovery while lowering costs.
---
Bridging Science and Creative AI Ecosystems
Platforms like LabOS in science mirror creative AI ecosystems such as AiToEarn — an open-source global platform for AI‑driven content monetization.
Key Features of AiToEarn:
- Generate + publish simultaneously to Douyin, Kwai, WeChat, Bilibili, Xiaohongshu, Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, Threads, YouTube, Pinterest, X (Twitter)
- Built‑in analytics and AI model rankings
Resources:
---
Would you like me to now provide a publication‑ready title optimized for both tech media and academic audiences? That could make this Markdown immediately usable in professional outreach.



