Kapasi's Large Model Comparison Is So Much Fun! Four Anonymous AI Contestants Rated, Unexpected Winner
Karpathy’s New Project: LLM Council
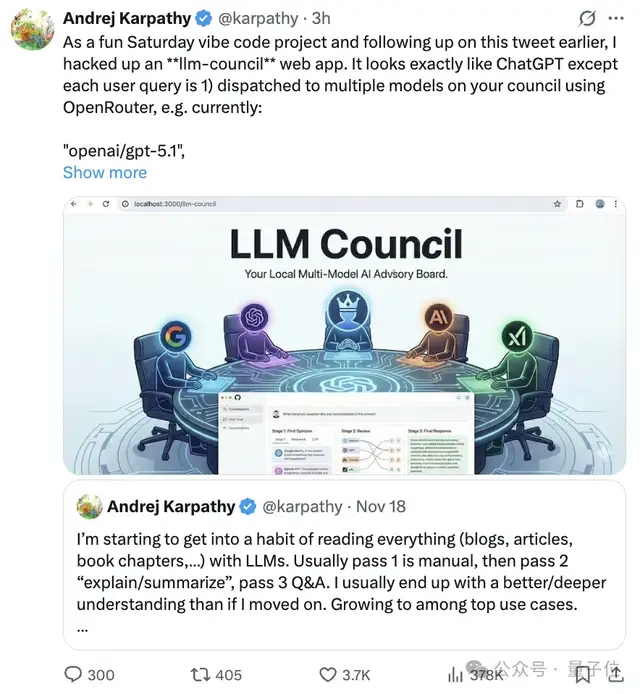
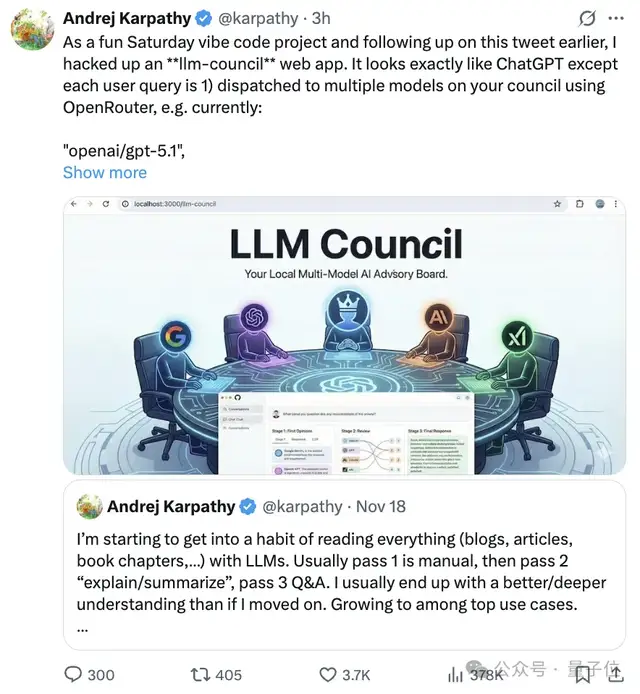
Andrej Karpathy is back with another entertaining and thought-provoking coding experiment—this time, he’s unveiled a “Large Language Model Council” (LLM Council) web app.
At first glance, the interface resembles a typical ChatGPT conversation.
But under the hood, when you submit a question, multiple LLMs are called via OpenRouter to hold a council-style discussion.
---
What Makes It Unique
The twist in this project is that the models don’t just answer your question—they also:
- Rate and rank each other’s responses anonymously.
- Designate a chair model to compile a final, unified answer.
Karpathy has shared clear installation and deployment instructions, immediately bookmarked by developers:
Some observers even suggested this peer-scoring method could evolve into a new type of automatic benchmark:

Author of Python Machine Learning also expressed enthusiasm for the approach:
---
How the LLM Council Works
Karpathy’s council operates in three main stages:
1. Multiple Models Respond to the Same Prompt
Using OpenRouter, several large models—such as:
- GPT-5.1
- Gemini 3 Pro Preview
- Claude Sonnet 4.5
- Grok-4
—answer your query at the same time. Their responses are shown in a tabbed interface for comparison.
2. Anonymous Peer Review
Every model receives the other models’ answers without knowing the identity of the author.
They score each answer for accuracy, clarity, and insight, along with written reasoning.

3. Chair Model Compiles a Final Answer
One designated LLM aggregates all of the responses, distills insights, and constructs a final reply for the user.
---
This structure makes it easy to:
- Compare different models’ writing styles side-by-side.
- Observe real-time cross-model evaluations.
---
Inspiration: Staged Deep Reading
This project builds on Karpathy’s earlier idea of using LLMs for staged deep reading:
That prior experiment (now with 1.8k GitHub stars):

The Three Phases of Deep Reading
- Human Read-Through — build a general sense and intuition.
- LLM Processing — extract structure, highlight difficult parts, summarize.
- Deep Questioning — probe the author’s intent and reasoning.
This shifts the target audience from humans to LLMs—allowing machines to comprehend first, then adapt content for various audiences.
---
Early Results from the Council
When testing, Karpathy found:
- GPT-5.1 was consistently rated the most insightful by peers.
- Claude Sonnet 4.5 ranked lowest.
- Gemini 3 and Grok-4 scored in the middle.

Karpathy’s personal judgments differed—GPT-5.1 was rich in content but less structured, Gemini 3 had better processing and concise style, while Claude’s answers were too brief.
Surprisingly: The models exhibited very little bias—often admitting another’s response was better.
---
Why It Matters
Karpathy believes that while AI self-evaluation may not perfectly match human opinions, multi-model collaboration is an exciting research path—possibly a future breakthrough in AI product design.
Such model council frameworks could complement emerging ecosystems like AiToEarn:
An open-source global AI content monetization platform that integrates:
- AI content tools with multi-platform publishing.
- Analytics and model rankings (AI模型排名).
A council-driven approach could help creators optimize and monetize AI outputs cross-platform.
---
Overview: LLM Council for AI Model Decision-Making
Karpathy’s LLM Council is an open-source experiment in collaborative deliberation among LLMs, exploring:
- Consensus-building
- Role assignment
- Biased vs unbiased evaluation
Core Concept
Several LLMs act as “participants” in a discussion—offering opinions and reasoning.
A meta-controller then organizes these responses into a final decision, much like a human committee.
Potential applications include:
- Content moderation
- Creative collaboration
- AI peer review
- Business and policy decision support
Tech Implementation
The GitHub repo contains:
- Scripts for spinning up multiple model instances.
- Tools for assigning roles to models.
- Methods for aggregating and weighting final outcomes.
Broader Context
LLM Council is part of the multi-agent AI trend—models collaborating, debating, and synthesizing outputs rather than working alone.
This parallels ensemble learning but emphasizes dialogue and reasoning.
---
References:
[1] https://x.com/karpathy/status/1992381094667411768?s=20
[2] https://github.com/karpathy/llm-council
[3] https://x.com/karpathy/status/1990577951671509438



