Let AI Evaluate AI: Building an Automated Operations Agent System for Smart Customer Service

# AI-Native Customer Service Evolution and Evaluation
The rapid growth of **Large Language Models (LLMs)** and computing power is reshaping industries. Even though AI is still in an *assisted action stage*—primarily helping rather than acting fully autonomously—its potential and developmental trajectory are already clear.

One of the earliest fields to integrate intelligent capabilities is **Customer Service**, now revitalized by LLM advancements.
---
## Overview
We will explore:
1. **Traditional NLP-based customer service robots**
2. **RAG-based intelligent customer service**
3. **AI-native customer service workflows**
4. **Dialogue quality evaluation**
5. **Implementation considerations**
6. **Common challenges and lessons learned**
7. **Results and optimization impact**
8. **Opportunities for expanded AI service analysis**
9. **Final conclusions**
---
## 1. Traditional Robot Customer Service (NLP Era)
Early "robot customer service" used **NLP**, **rule engines**, and **knowledge bases**—a leap from human-only service but with notable weaknesses:
- **Poor intent understanding** (multi-intent recognition required heavy manual training)
- **High maintenance costs** (cold start complexity, constant updates)
- **Rigid dialogue flows** (low generalization, poor coreference resolution)
**Common Operations Tasks**:
- *Knowledge Base Construction*: Build FAQ Q–A pairs
- *Synonym & Rule Configuration*: Map multiple phrases to triggers
Example: “refund” → “return,” “get money back”
- *Dialogue flow design*: Complex SOPs & decision trees
- *Continuous monitoring*: Keyword tracking, rule updates
**Limitation:** Rules are finite; language is infinite—teams battled constant upkeep, with fixed intelligence ceilings defined by the initial rule set.
---
## 2. RAG-Powered Intelligent Customer Service
**RAG** (*Retrieval-Augmented Generation*) bridges retrieval and generation, enhancing accuracy while cutting knowledge maintenance costs.
### Workflow:
1. **Retrieve (R)** relevant knowledge snippets (vector or hybrid search surpasses ES keyword matching)


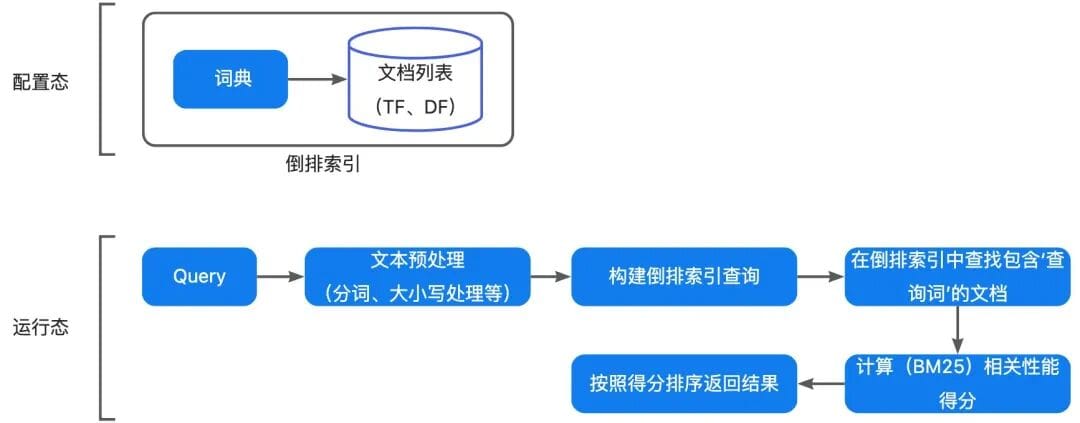
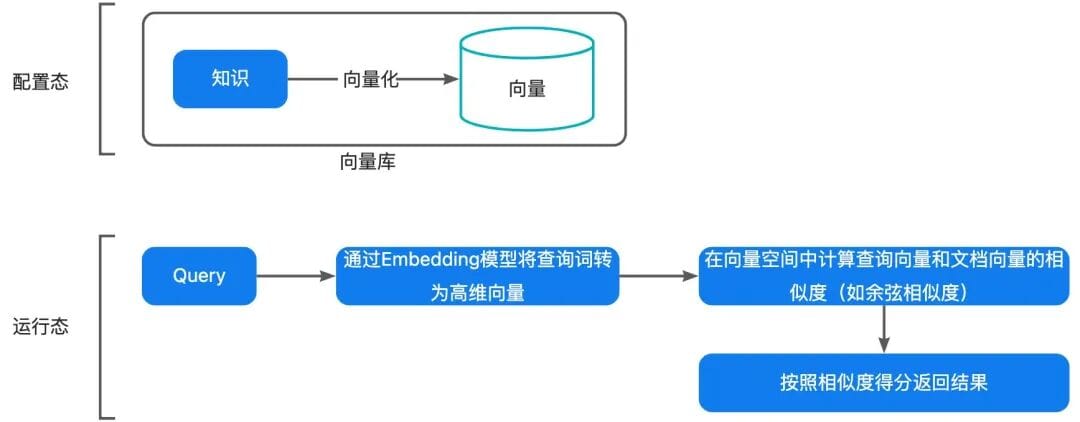
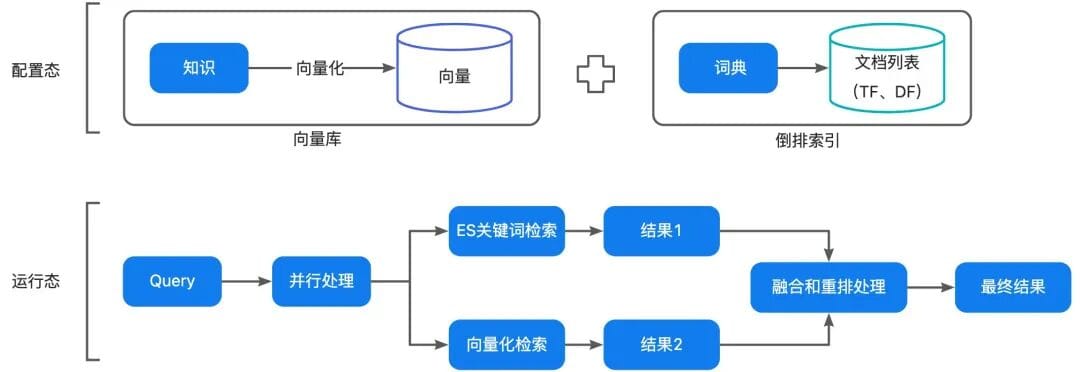
2. **Augment (A)**: Combine snippets + user query + conversation history into a structured prompt.
3. **Generate (G)**: LLM produces natural answers informed by retrieved content.
**Benefit:** Expands chatbot capability from FAQs to full-document intelligence (PDF, DOC, PPT).
---
## Prompt Engineering Essentials
A well-engineered prompt includes:
- **System role definition**: Sets LLM persona
- **Background instructions**: Explicit answer rules
- **Context content**: Retrieved snippets
- **User question**
- **Output format constraints** (Markdown, lists, JSON)
---
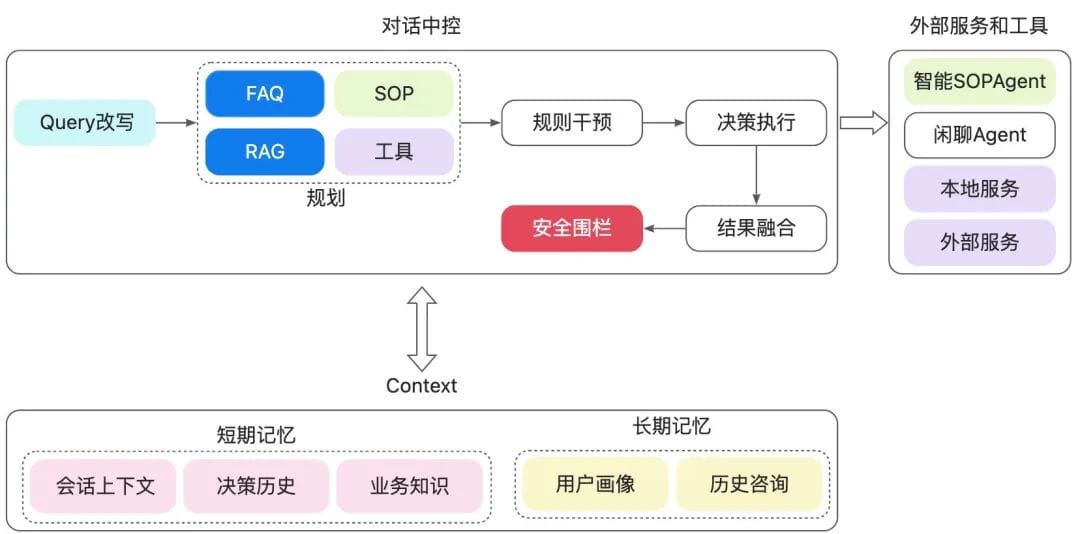
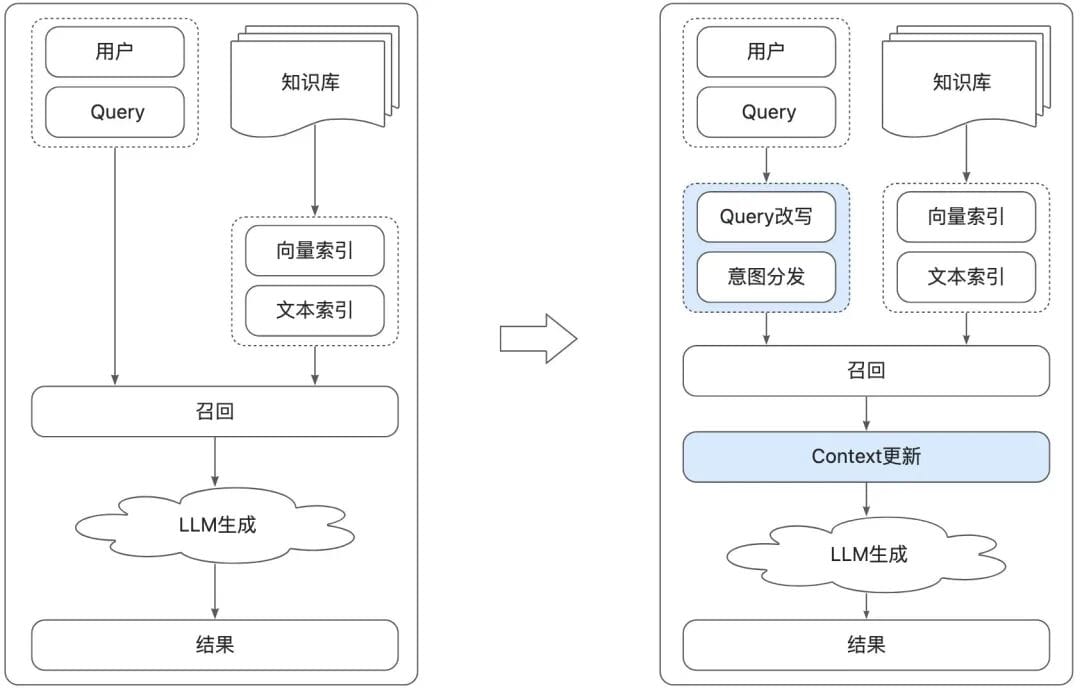
## 3. AI-Native Customer Service
By 2025, **AI-native agents** with **MCP** and **Function-Call** allow LLMs direct tool usage and dynamic integration of local data.
### Main Workflow:
- All model usage points replaced by LLM
- Model size tuned per task (small models for rewriting, large for planning)
- **Intelligent SOPs**: Natural language business logic with real-time branching decisions via Function-Call
- RAG remains crucial for knowledge-based Q&A
---
## 4. Dialogue Quality Evaluation
**Goal:** Measure end-to-end **robot answer quality**.
Traditional evaluation:
- **Offline datasets + human annotation**
- **Manual cause identification and fix cycles**
- Time-consuming and resource-heavy
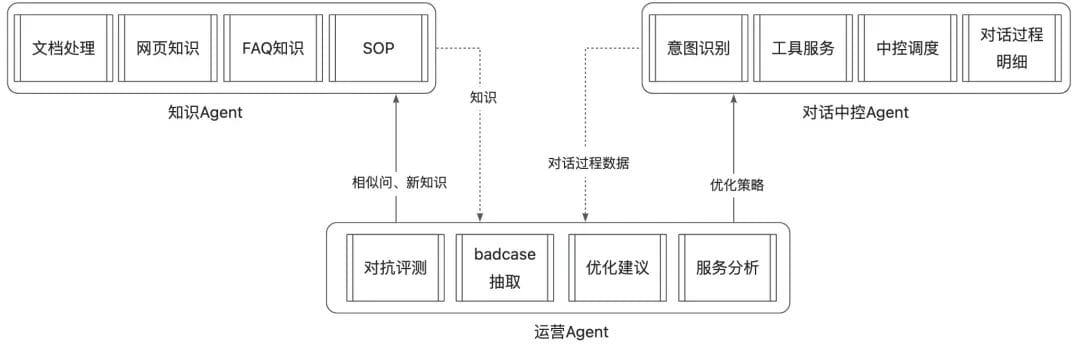
**AI-native upgrade:**
Introduce vertical-domain **Evaluate–Diagnose–Optimize (EDO) Agents** that:
- Detect **BadCases** (>85% accuracy)
- Identify root causes (>80% accuracy)
- Generate **optimization suggestions**
- Integrate with Knowledge/Conversation Agents

---
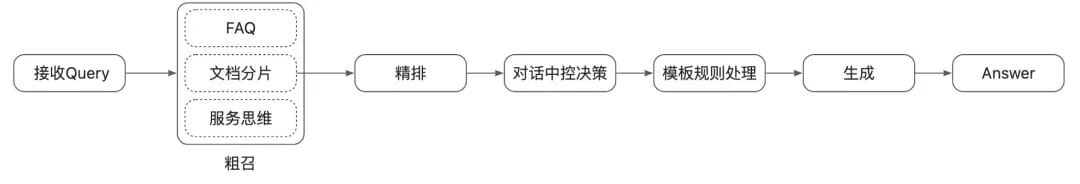
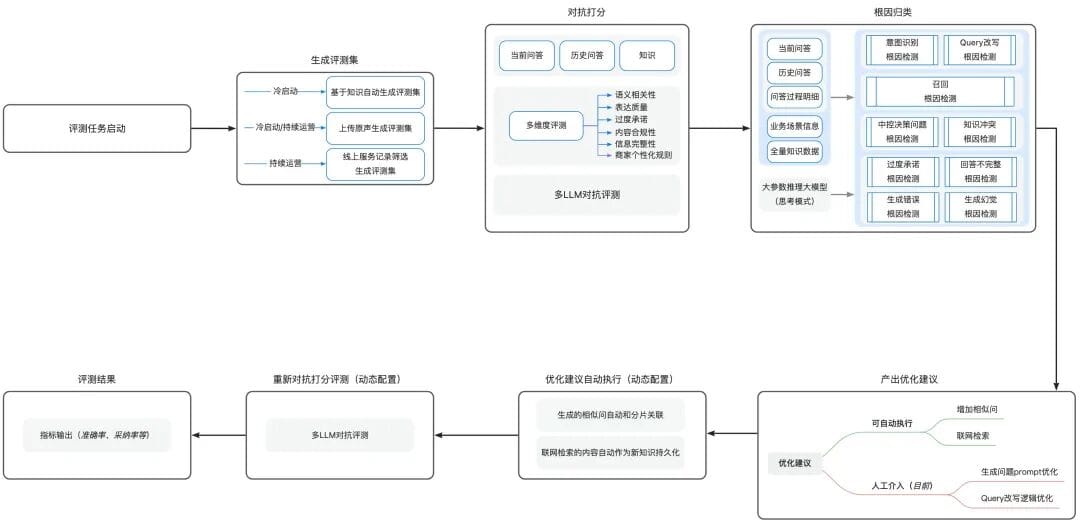
## 5. Implementation Framework
**Steps:**
1. **Confirm evaluation goals**
2. **Break down conversation workflow into modules**
3. **Record functional data**
4. **Build evaluation sets dynamically or via uploads**
5. **Apply multi-dimensional rules**:
- Semantic relevance
- Expression quality
- Content compliance
- Informational completeness
6. **Classify root causes**: retrieval issues, ranking errors, generation problems
7. **Automate optimization execution** where possible.
---
## 6. Challenges & Lessons Learned
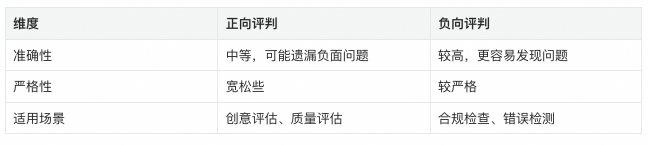
### 6.1 Balanced Positive/Negative Judgement
- Avoid purely negative (too harsh) or purely positive (too lenient)
- Use **hybrid scoring**: strengths → weaknesses → holistic weighing

---
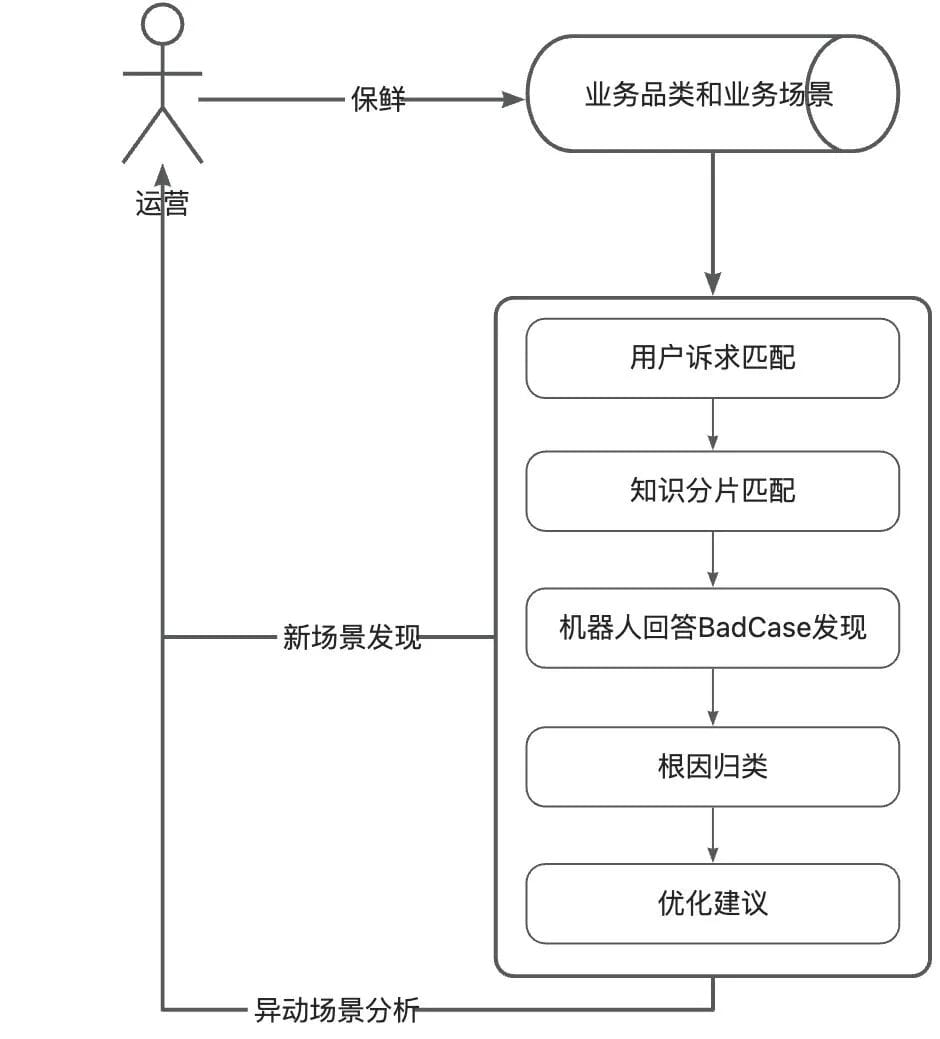
### 6.2 Strong Business Context Dependence
#### Intent Layering:
- **Business Category** (e.g., "Fitness membership cards")
- **Business Scenario** (e.g., "Membership card transfer")
Example JSON intent mapping:{
"customerDemand": "Membership card transfer inquiry",
"brand": "Fitness membership card",
"scene": "Membership card transfer scenario"
}
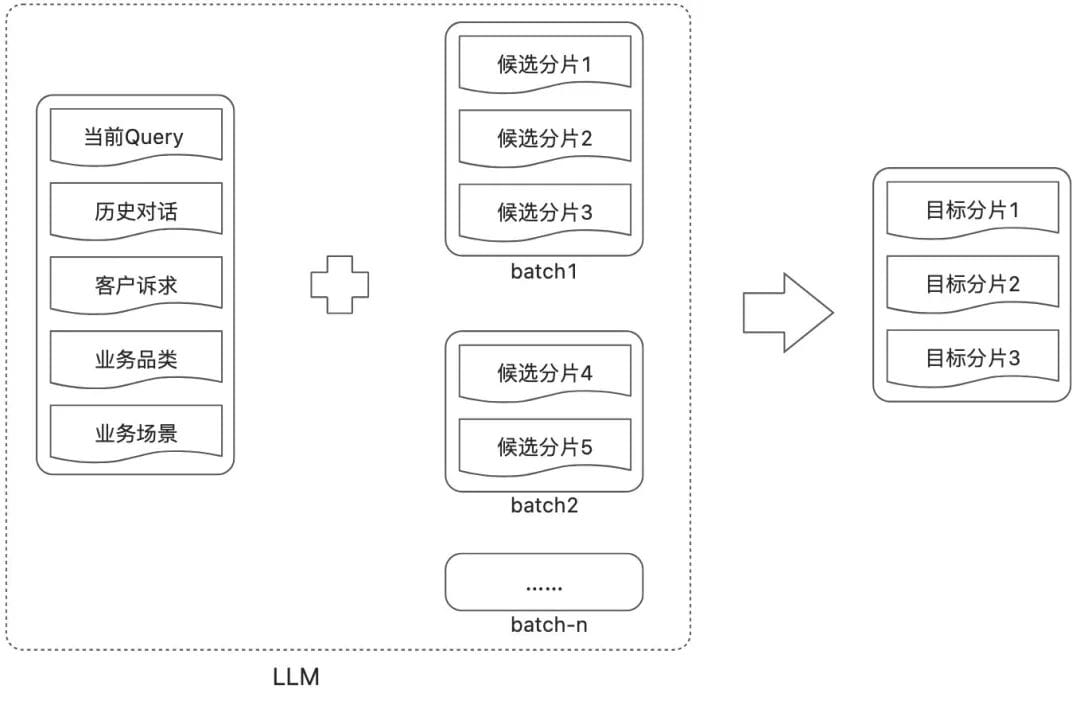
#### Reference Knowledge Validation:
- Store intermediate retrieval/ranking results
- Identify omissions in rough/fine retrieval stages
#### Exemptions:
- Recognize special-case dialogues as meeting business expectations.
---
### 6.3 LLM Randomness
#### Temperature & Top-P Control:
- **Temperature**: Adjust probability distribution sharpness
- **Top-P**: Filter token set by cumulative probability
**Solution:** Adjust parameters dynamically, or use **multi-LLM adversarial inference**.

---
### 6.4 Deep Thinking Mode
Enable in complex reasoning scenarios to improve:
- Step-by-step analysis
- Self-criticism & correction
- Ambiguity handling
---
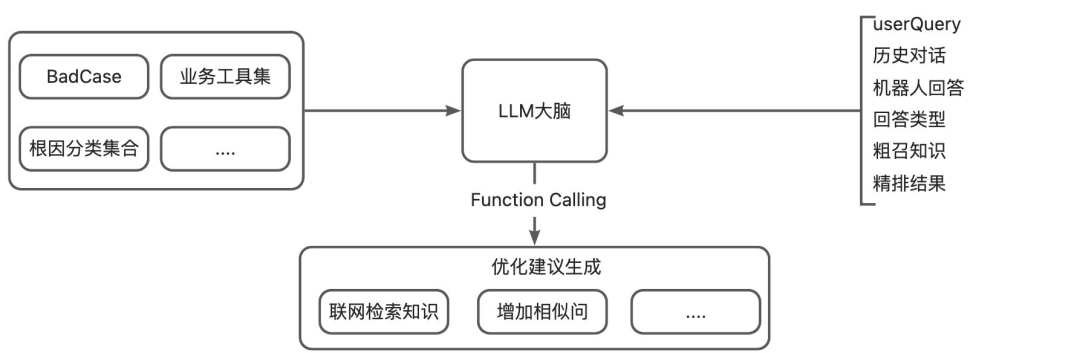
### 6.5 Context Engineering
Beyond prompt engineering:
- Manage **context length & relevance**
- Avoid dilution/confusion/conflict/loss
**Techniques:**
- Logical segmentation
- Content simplification
- Mandatory constraints (formatting rules)
- Few-shot examples
---
### 6.6 Concurrency & Rate Limiting
Control **QPM/TPM** limits to prevent throttling.
---
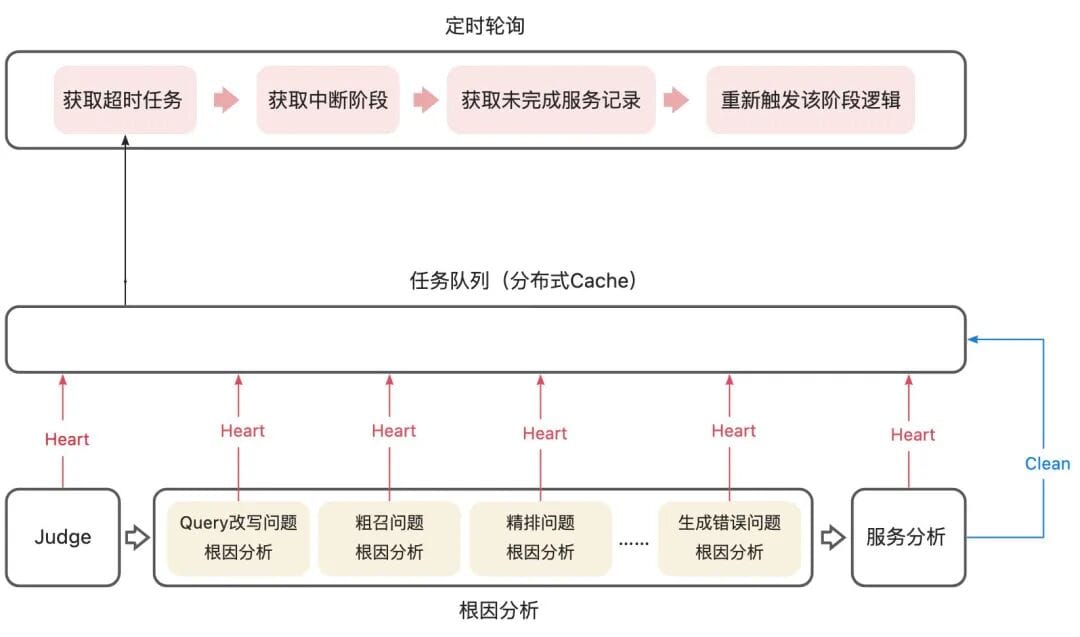
### 6.7 Interruption & Recovery
Use **task checkpointing** to resume long-running multi-stage evaluations without waste.
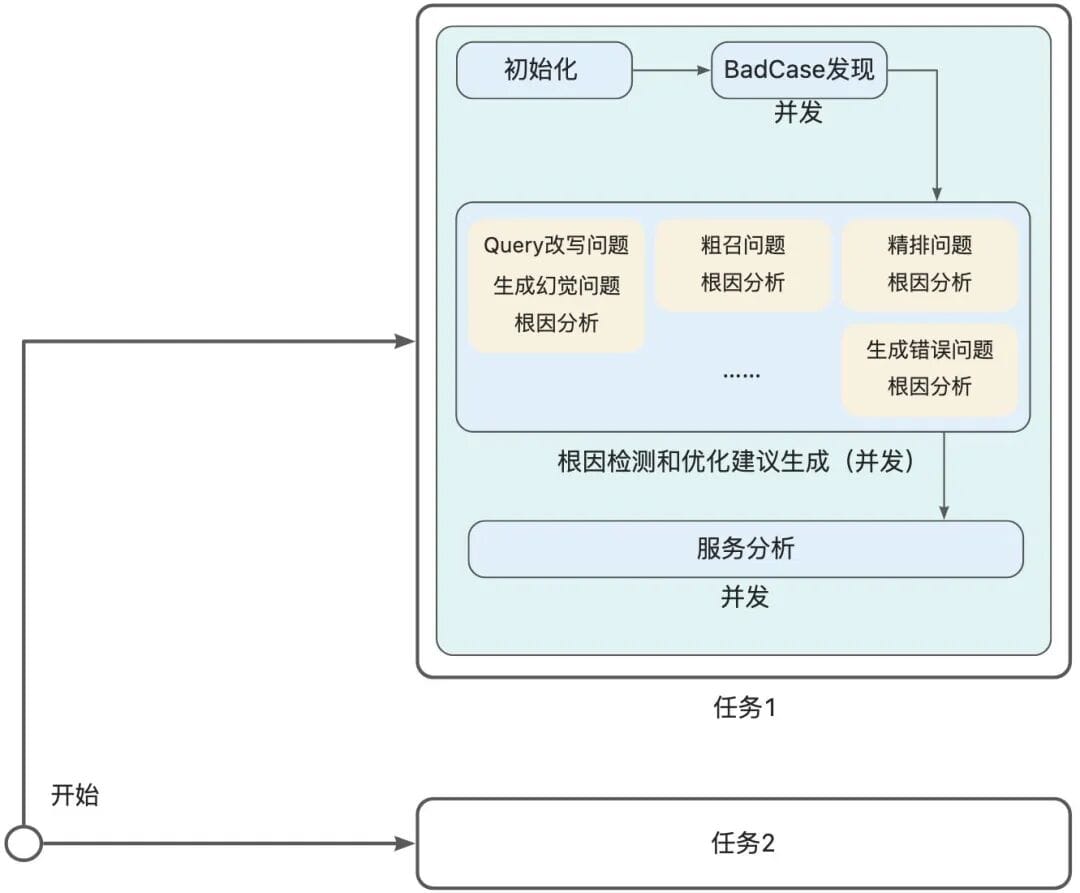
---
## 7. Results
- **BadCase detection**: 85%+
- **Root cause classification**: 80%+
- **Optimization suggestion accuracy**: 80%+
---
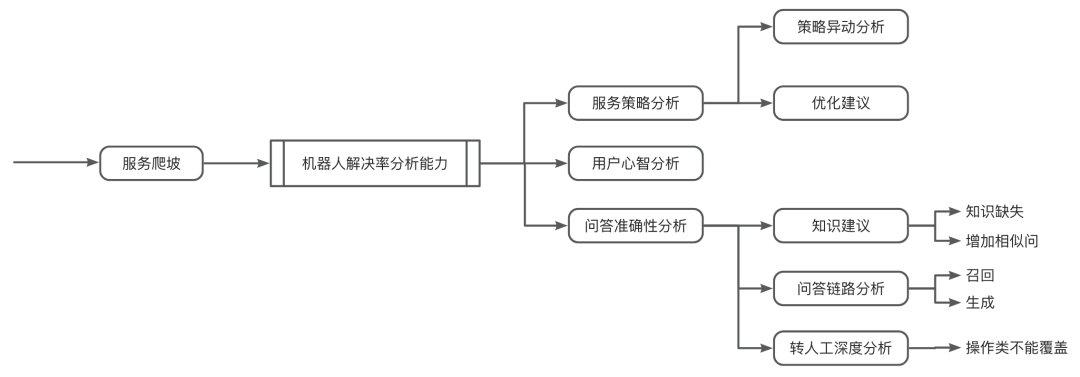
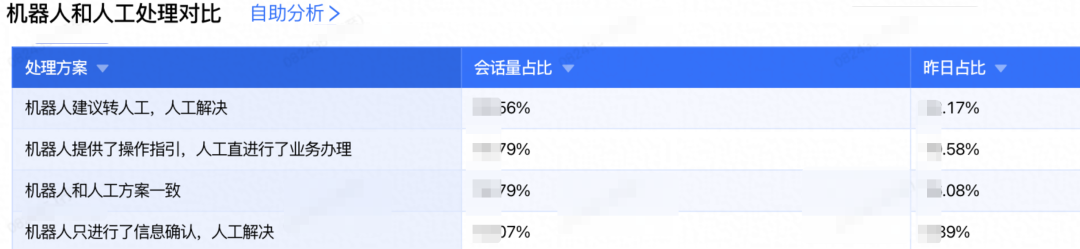
## 8. Beyond BadCases: Service Chain Analysis
Key metrics:
- **Robot Answer Accuracy**
- **Robot Resolution Rate**
Main escalation causes:
1. **Strategy-triggered escalation**
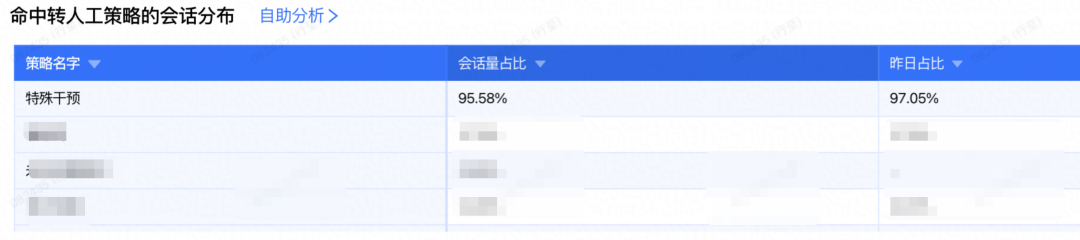

2. **Customer mindset issues**
3. **Robot content gaps**
---
## 9. Conclusion
**AI-native customer service**:
- Integrates **LLM reasoning, RAG retrieval**, and context management
- Employs **Agent ecosystems** for continuous evaluation and optimization
- Improves resolution rates & operational efficiency
- Benefits from scalable multi-platform analysis and deployment
---
**Tip:** Open-source ecosystems like [AiToEarn官网](https://aitoearn.ai/) can connect these concepts to monetizable **cross-platform workflows**, bundling AI content generation, publishing, analytics, and AI model rankings, enabling simultaneous distribution across Douyin, Kwai, WeChat, Bilibili, Xiaohongshu, Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, Threads, YouTube, Pinterest, and X/Twitter.



