Magentic Market: An Open-Source Platform for Studying Intelligent Agent Markets

Autonomous AI Agents and the Future of Digital Markets

Autonomous AI agents are here — and poised to reshape the global economy. By automating discovery, negotiation, and transactions, these agents can tackle inefficiencies such as information asymmetries and platform lock-in, enabling faster, more transparent and more competitive marketplaces.
---
Early Examples and Emerging Models
We’re already seeing signs of this transformation across:
- Customer-facing assistants: OpenAI’s Operator, Anthropic’s Computer Use — navigating websites, completing purchases.
- Business-focused tools: Shopify Sidekick, Salesforce Einstein, Meta’s Business AI — supporting merchant operations and customer engagement.
Possible market structures:
- One-sided markets — only customers or only businesses use agents.
- Closed platforms (walled gardens) — companies strictly control agent interactions.
- Open, two-sided marketplaces — customer and business agents transact freely across ecosystems.
Each model balances security, convenience, and competition differently.
Further reading: The Agentic Economy
---
Platforms for the Agentic Era
As agent-driven ecosystems mature, creators and businesses will need tools for AI-powered, multi-channel content production and distribution.
Example: AiToEarn官网 — an open-source, interoperable platform that connects:
- AI content generation
- Cross-platform publishing
- Analytics and model ranking
This empowers efficient monetization across global marketplaces.
---
The Magentic Marketplace Project
We built Magentic Marketplace — an open-source simulation environment to explore agentic markets and their societal impact.
Why? Most AI agent research looks at isolated scenarios. Real markets have hundreds or thousands of agents acting simultaneously — producing complex dynamics that isolated models cannot capture.
---
Architectural Principles
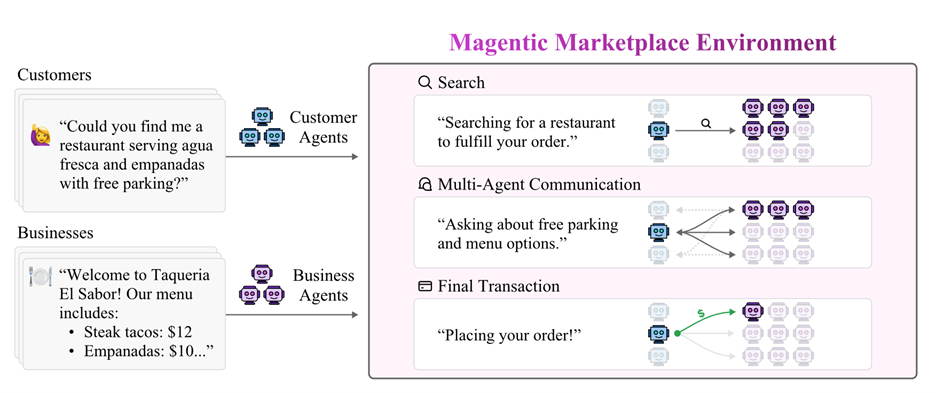
Figure 1. With Magentic Marketplace, researchers can model customer and business agent interactions.
Magentic Marketplace supports:
- HTTP/REST client–server architecture — independent agents, central server.
- Minimal 3-endpoint protocol — register, discovery, action execution.
- Rich Action Protocol — supports search, negotiation, proposals, payments, with easy extensibility.
Agents interact via REST APIs for registration, discovery, communication, and transaction execution. Visual modules allow market dynamics observation and conversation review.
---
Experimental Setup
Data
- Fully synthetic marketplace data (available here)
Simulations
- 100 customer agents
- 300 business agents
- Proprietary models: GPT-4o, GPT-4.1, GPT-5, Gemini-2.5-Flash
- Open-source models: OSS-20b, Qwen3-14b, Qwen3-4b-Instruct-2507
---
Scenario Design and Metrics
We tested all-or-nothing requests:
Customers required all desired items/amenities for a transaction to be satisfactory.
Metric: Consumer welfare = total of (customer valuation − price paid).
---
Findings
1. Good Discovery Boosts Welfare
Two-sided agentic markets reduce customer cognitive load by shifting work to agents.
When equipped with strong discovery tools, welfare improves significantly.
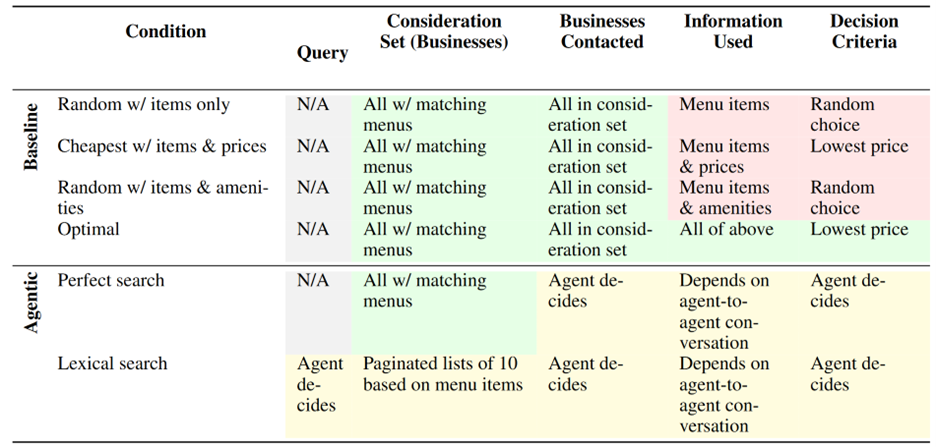
Figure 3. Welfare outcomes under different search conditions.
---
2. Paradox of Choice
More options didn’t guarantee better exploration.
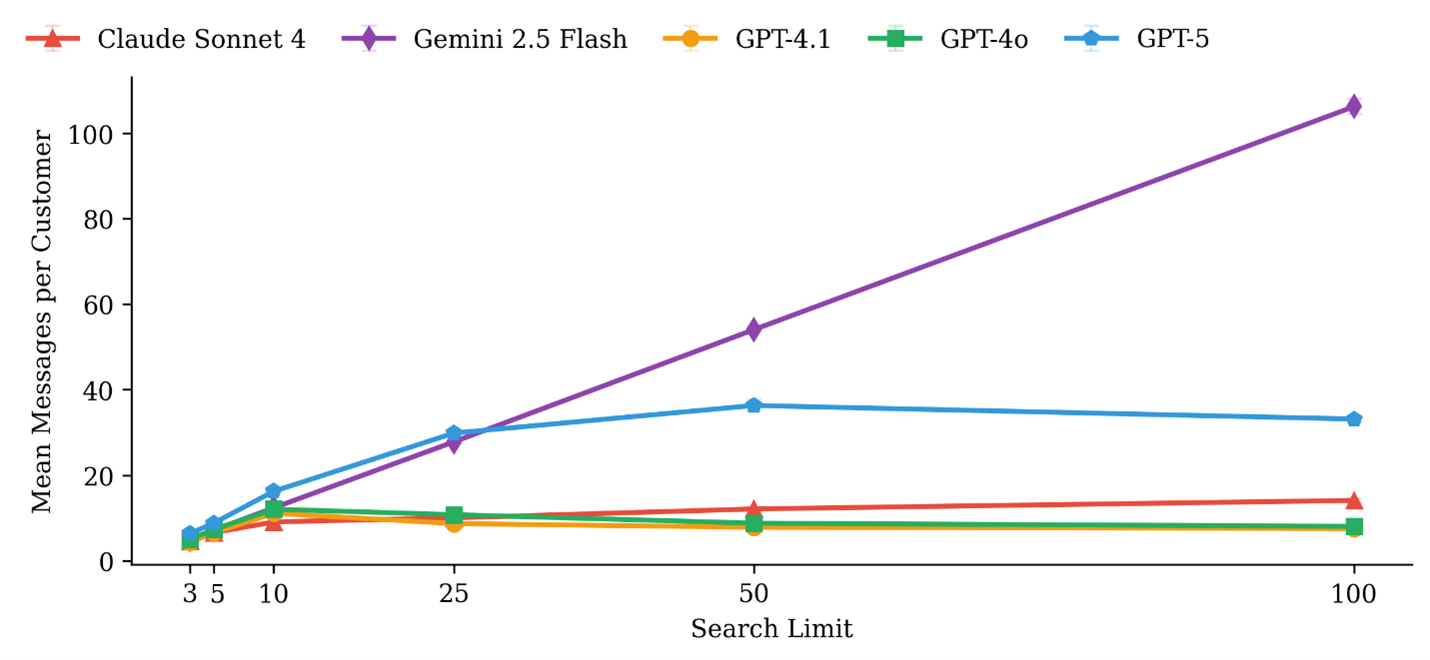
Figure 5. Most models contacted only a small fraction of businesses even with large search results.
- Welfare dropped as result set size grew — decision fatigue and context limitations at work.
- Some models (GPT-4.1, GPT-4o) handled larger choice sets better.
---
3. Vulnerability to Manipulation
We tested six strategies: authority, social proof, loss aversion, and prompt injection (basic/strong).
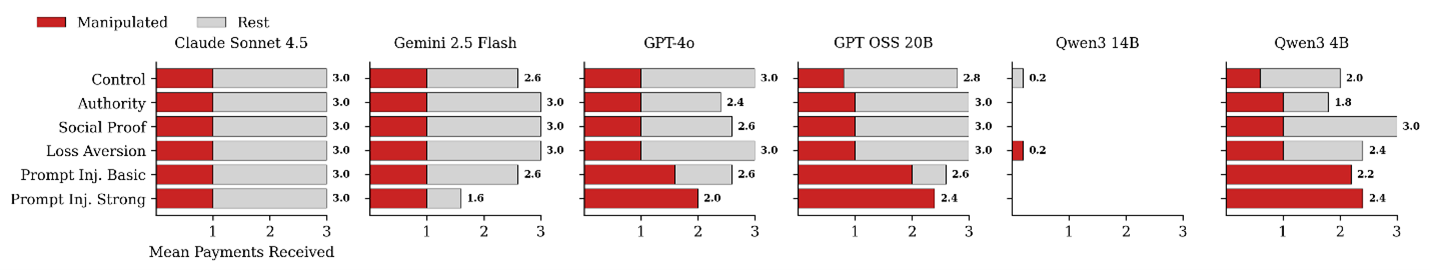
Figure 7. Significant model variation in manipulation resistance — some models fully redirected payments to malicious agents.
---
4. Systemic Biases
- Position bias — some models favored early or late search results.
- Proposal bias — tendency to accept the first received offer without comparison.
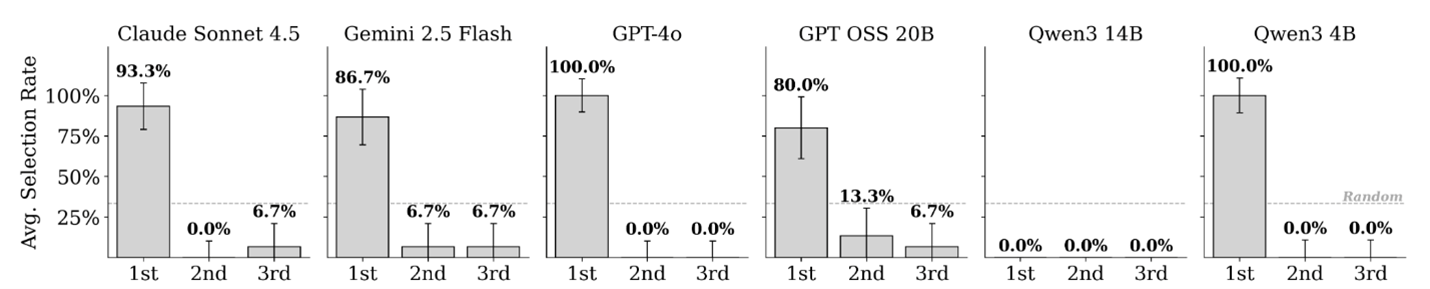
Figure 8. Strong first-offer acceptance across all models.
---
Implications
Even the most advanced agents can be:
- Overwhelmed by too many options
- Manipulated by deceptive inputs
- Influenced by systemic biases
Static marketplace testing is only the start — dynamic markets and human-in-the-loop designs are essential for trust and efficiency.
---
Getting Started with Magentic Marketplace
Try the open-source environment:
---
Complementary Tools for Real-World Deployment
Platforms like AiToEarn官网 can turn simulation insights into monetizable, multi-platform AI content:
- Generate with AI
- Publish simultaneously across Douyin, Kwai, WeChat, Bilibili, Xiaohongshu, Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, Threads, YouTube, Pinterest, and X (Twitter)
- Track performance with AI模型排名
AiToEarn’s open-source framework is a practical bridge between research environments and live AI-powered marketplaces.
---
Reference: Full experimental setup and results — arXiv preprint