# Next-Generation Industrial Search Systems: UniDex & UniSearch
## I. Introduction

When you type just a few words into a search bar — expecting the system to understand your **vague intentions** and find *that one perfect video among millions* — it feels effortless to you.
Yet, behind the scenes, this is a **complex challenge** for modern search technology.
Traditional search engines act like “librarians,” relying on rigid keyword matching. They struggle with nuances, like when "tastiest" implies something subjective, or when a "live game stream that just started" demands extreme timeliness.
**Modern search systems** use *deep semantic models* to represent both the **query** and **documents** (videos, pages, etc.). Document-side representation is critical — enabling not just *understanding*, but *anticipating* user intent. Next-generation search moves far beyond keyword matching, into **semantic representation** and **content generation**.
To match the intelligence of recommendation systems and understand even video content itself, the **Kuaishou team** pursued a new path:
Replacing traditional *Term-based* methods with **model-based semantic indexing**, and rebuilding the search pipeline with models that both **understand** and **generate**.
Two systems emerged:
- **UniDex** — The *world’s first* model-based inverted index solution, replacing term indexing entirely.
- Cuts compute and storage consumption
- Improves response speed **+25%**
- **UniSearch** — An innovative **generative search** framework; joint training for query encoding + generation.
- True end-to-end generative pipeline
- Significant increases in live-stream room entry rates
---
## II. Discriminative Paradigm — UniDex Semantic Inverted Index
### 2.0 Background

Traditional inverted indexes offer strong recall and matching, but have limitations:
- **High resource costs** for offline indexing
- **Expensive dynamic updates**
- **Poor generalization**
**UniDex** bridges this gap — maintaining inverted index strengths, while improving generalization with model-based semantic IDs.
📄 Research Paper: [https://arxiv.org/pdf/2509.24632](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2509.24632)
---
### 2.1 Technical Innovations

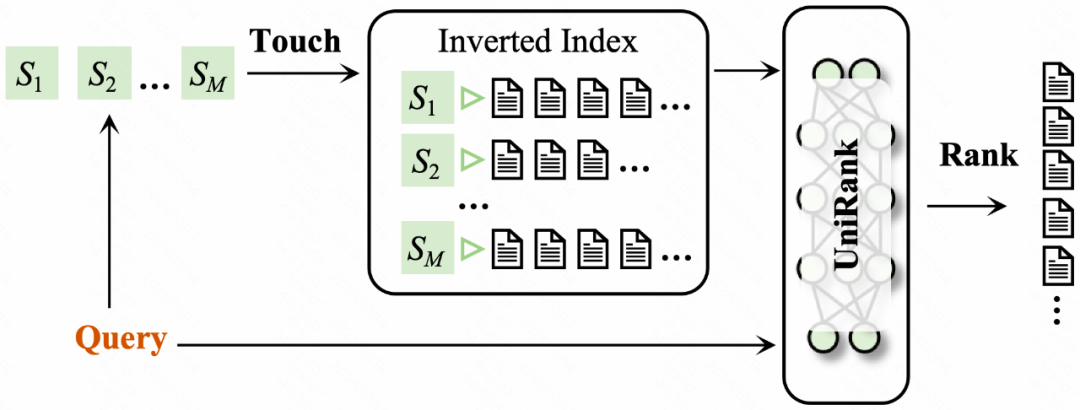
**Two core modules in classic inverted systems:**
1. **Touch** — recall via term-level matching
2. **Rank** — relevance scoring between Query and candidates
Legacy inverted recall used *hand-tuned methods* (synonym expansion, entity normalization, etc.) plus dozens of heuristic features.
**UniDex innovations:**
- **UniTouch** — Model-driven semantic recall
- **UniRank** — Unified semantic ranking
Both modules replace manual design with end-to-end learned components, reducing pipeline complexity and improving user experience.
---
#### 2.1.1 UniTouch

**Main Components:**
1. **Semantic Encoding**
- **FSQ Quantization** — Learnable tokens → Encoder → dense vectors → FSQ → offline semantic IDs (SIDs)
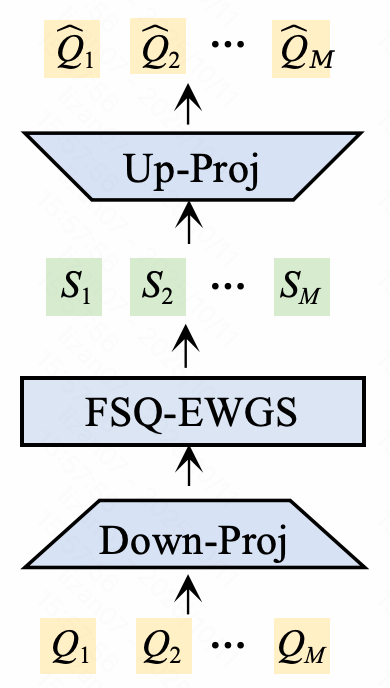
Encoded Query/Doc → low-dim projection → FSQ (K=2) → quantized SIDs
- **EWGS Gradient Optimization** — Improves FSQ training by addressing quantization error in backpropagation
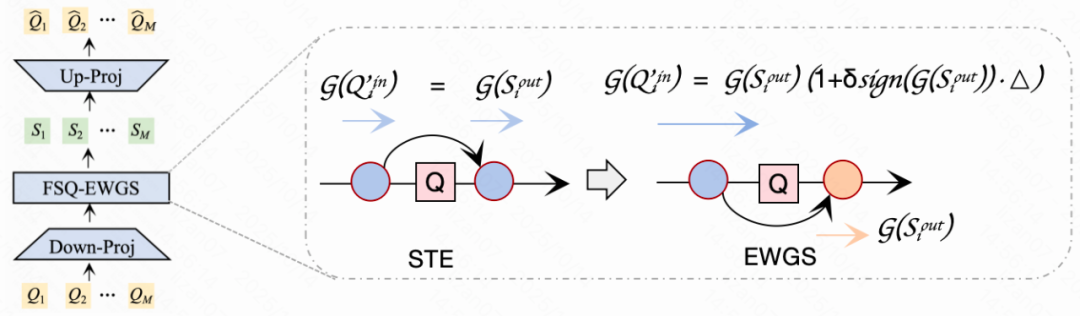
- **Token-Matching Mechanism** — Ensures retrieval consistency; retrieval triggers on *any* matched SID between Query & Doc.
2. **Learning Strategy**
- **Contrastive Learning (ListWise InfoNCE)** — Learns ranking order; uses same-bucket negatives + batch negatives.
- **Matching Loss** — Ensures identical SIDs for highly relevant Query–Doc pairs.
---
**Quantization Regularization**
To handle floating-point precision loss in inference acceleration, **Binary-Quant RegLoss** is introduced:
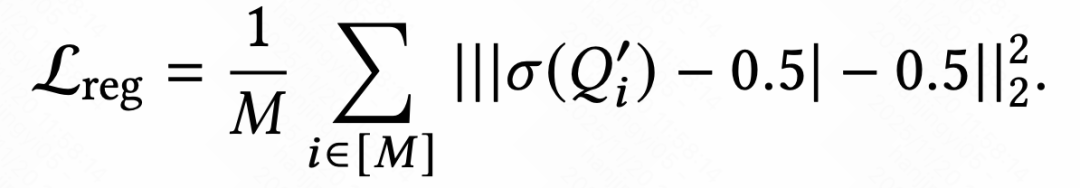
---
#### 2.1.2 UniRank

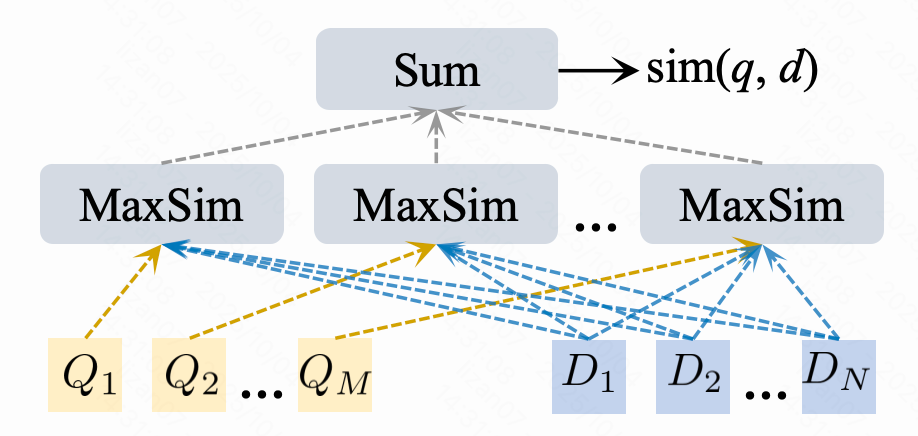
Focuses on **semantic ranking accuracy** with:
- **Dual-tower architecture**
- Multiple 128D semantic vectors
- **Token-level interactions** — every token contributes to ranking score
**Learning strategies:**
1. **Pointwise Relevance Loss** — distilled from fine-ranking model
2. **InfoNCE Loss** — same as UniTouch, reinforcing ranking chain
---
### 2.2 Real-Time Retrieval

Online pipeline:
1. Query → SID set via online inference
2. UniRank scores candidates
3. SIDs update via offline + real-time paths
---
### 2.3 Experimental Results
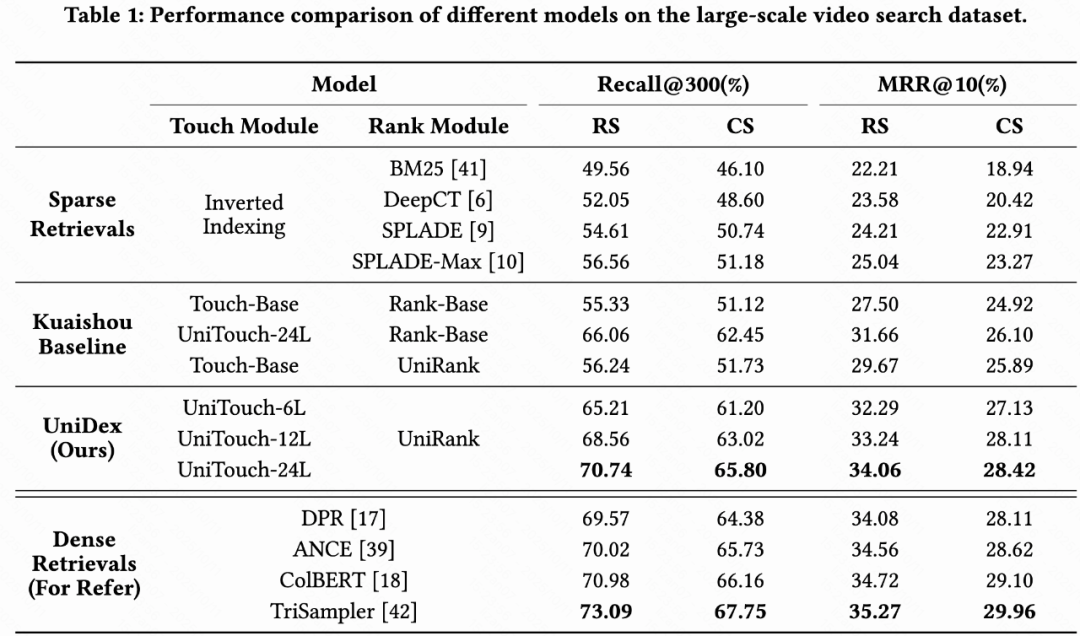
#### UniDex Offline
- **Recall@300** — +14.18% over Sparse baseline
- **MRR@10** — +10.02% improvements
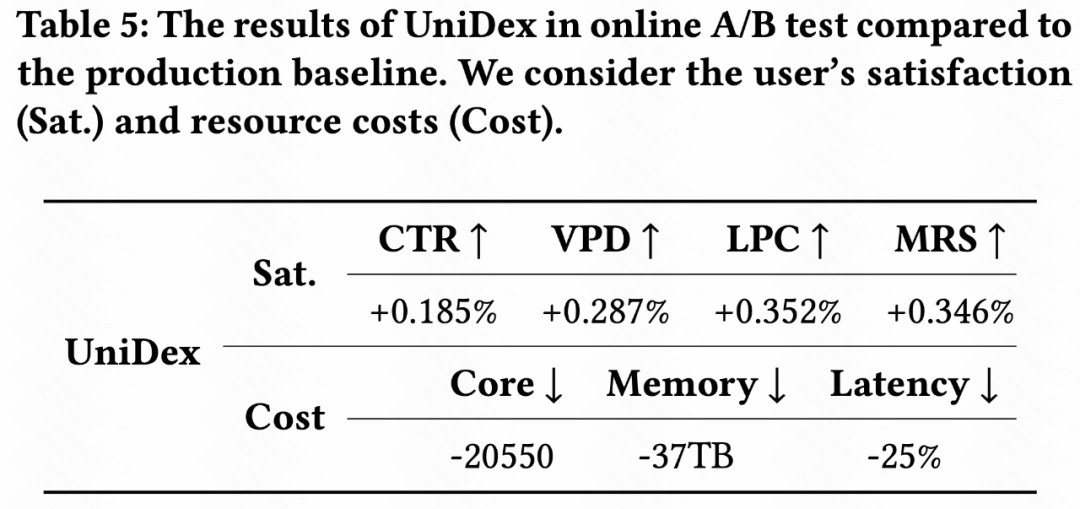
#### Online A/B Testing
- **Improved recall**
- **Reduced system load**
- **Better UX**
---
## III. Generative Paradigm — UniSearch

Live-stream search demands **extreme freshness**.
UniSearch is a **unified generative architecture** for end-to-end search.
📄 Paper: [https://arxiv.org/pdf/2509.06887](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2509.06887)
---
### 3.1 Technical Innovations

Traditional generative systems had **multi-stage** training → stage mismatch.
**UniSearch** trains generator + encoder jointly, ensuring end-to-end consistency.
#### 3.1.1 True End-to-End Architecture
- **Search Generator** — Encoder–Decoder; autoregressively predicts video SIDs from queries
- **Video Encoder** — Learns latent embeddings & SIDs; uses **VQ Codebook** for discretization
- Joint training removes representation–generation gap
---
#### 3.1.2 Offline Training
**Steps:**
1. **Residual Contrastive Semantic Learning** — Similar to RQ-Kmeans, but integrated into end-to-end training.
2. **Progressive Coarse-to-Fine Objective** — Mirrors "recall → coarse rank → fine rank" pipeline.
3. **Codebook Learning via VQ-VAE** — Discretizes videos into SIDs without offline clustering; prevents collapse via **SimVQ**.
4. **Generative Constraints + Rejection Sampling** — Filters low-quality samples; weighted losses by quality tier.
---
#### 3.1.3 Online Training — Search Preference Optimization (SPO)
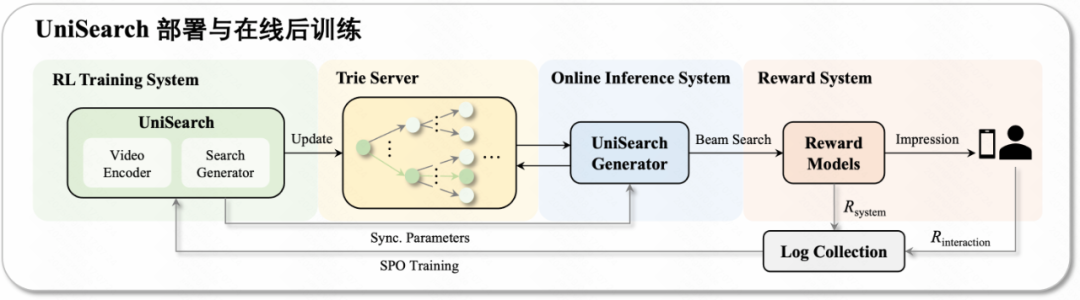
Two reward types:
1. **Online fine-rank reward**
2. **User behavior feedback reward**
Continuous update optimizes generation preferences for live-use.
---
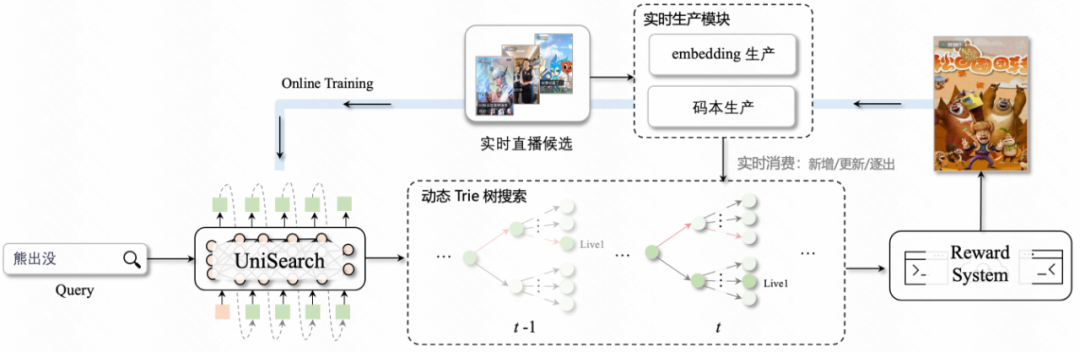
#### 3.1.4 Inference — Dynamic Trie Constraints
**Key for live-stream search freshness:**
1. **Generation Model** — Produces probability distribution over codebook IDs
2. **Dynamic Trie** — Updates every minute with live room data; beam search ensures valid outputs
3. **Reward Feedback** — Guides ongoing online tuning
---
### 3.2 Experimental Results
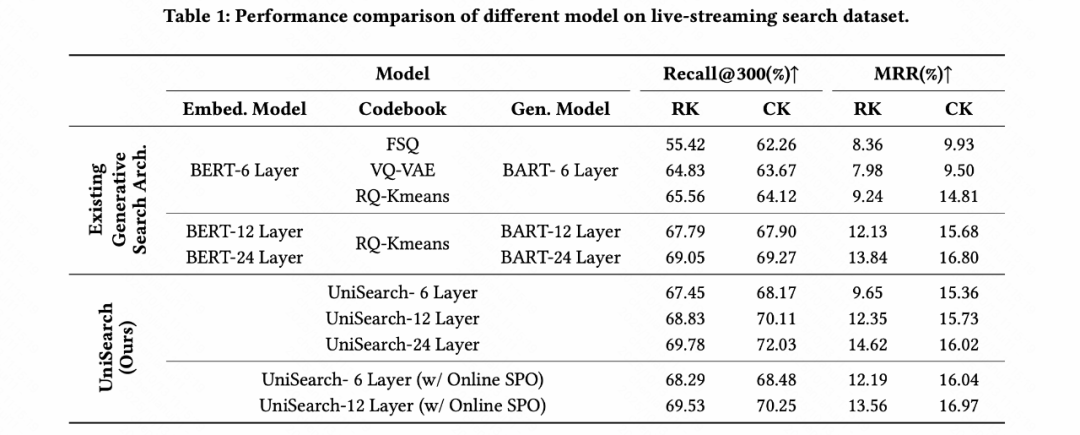
#### Offline
- UniSearch-6 surpasses other 6-layer baselines (MRR)
- Recall@300 ~ 12-layer baselines, at smaller scale
#### Online
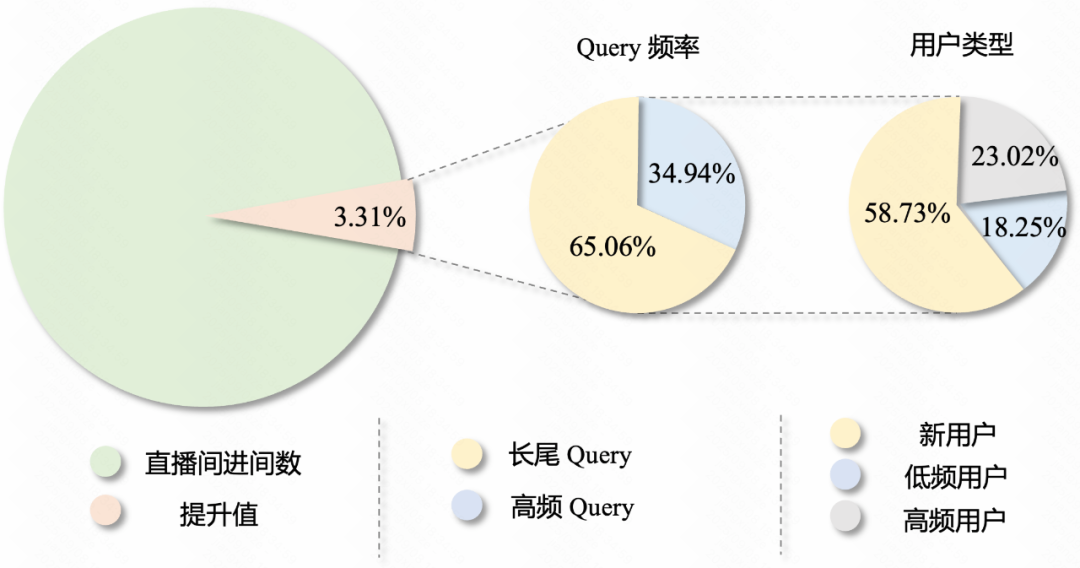
- **+3.31% live-room entries** — biggest increase in 2 years
- **-0.382% query change rate** — improved search quality
- **58.73% of gain from new users** — strong acquisition potential
---
## IV. Conclusion
UniDex and UniSearch demonstrate complementary strengths:
- **UniDex (Discriminative)** — Precise SID matching replaces keyword search entirely
- **UniSearch (Generative)** — Produces SIDs directly, unified training, freshness-aware
Kuaishou’s approach shows that **AI-driven semantic representation + generation** can reshape industrial search — enhancing **precision**, **efficiency**, and **user engagement**.
For content creators and AI developers, open-source ecosystems like [AiToEarn官网](https://aitoearn.ai/) enable practical use of similar technologies for:
- AI content generation
- Cross-platform publishing
- Analytics + monetization
…across Douyin, Kwai, WeChat, Bilibili, Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, Threads, YouTube, Pinterest, X (Twitter), and more.
---
**References:**
- [UniDex Paper](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2509.24632)
- [UniSearch Paper](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2509.06887)
- [AiToEarn官网](https://aitoearn.ai/)




