How to Use Twitter Search Filters for Accurate Results
Learn how to use Twitter search filters and advanced operators to refine results, find specific tweets, and improve social media research accuracy.
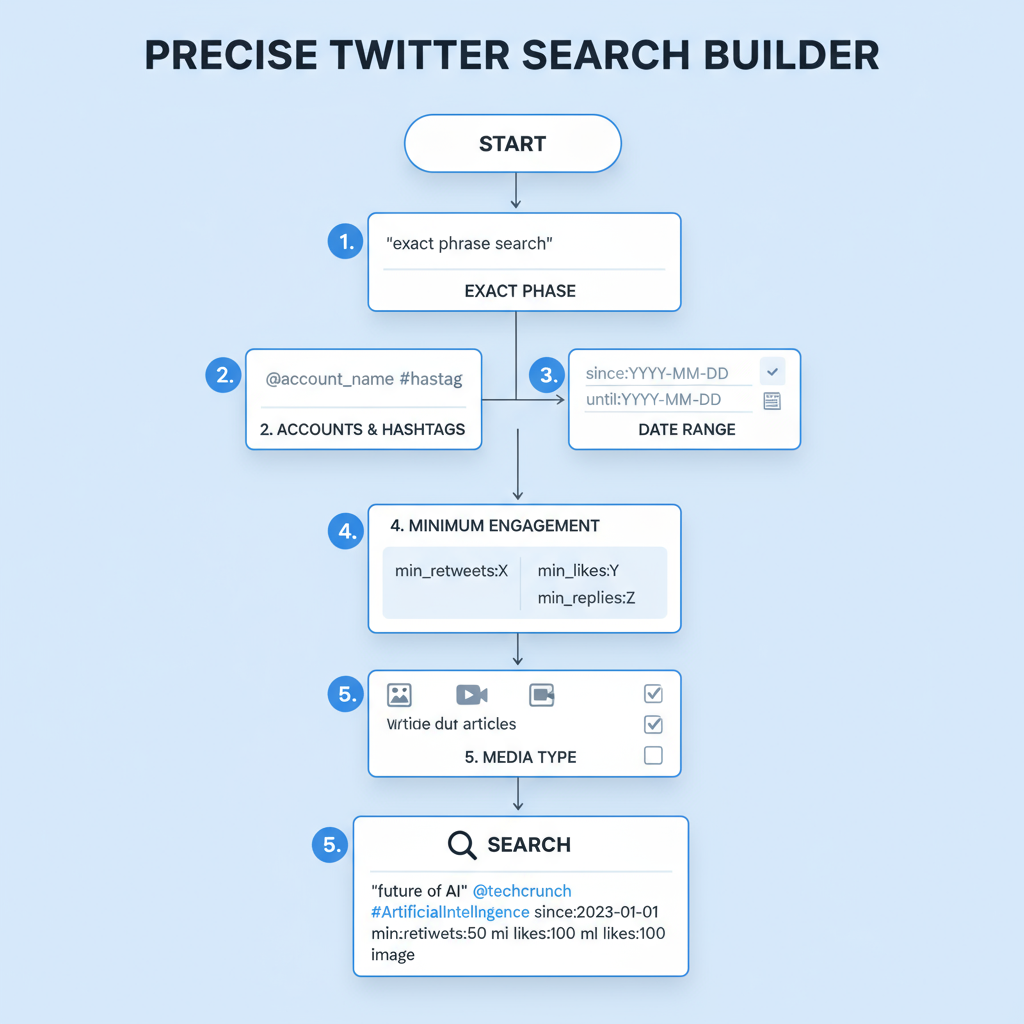
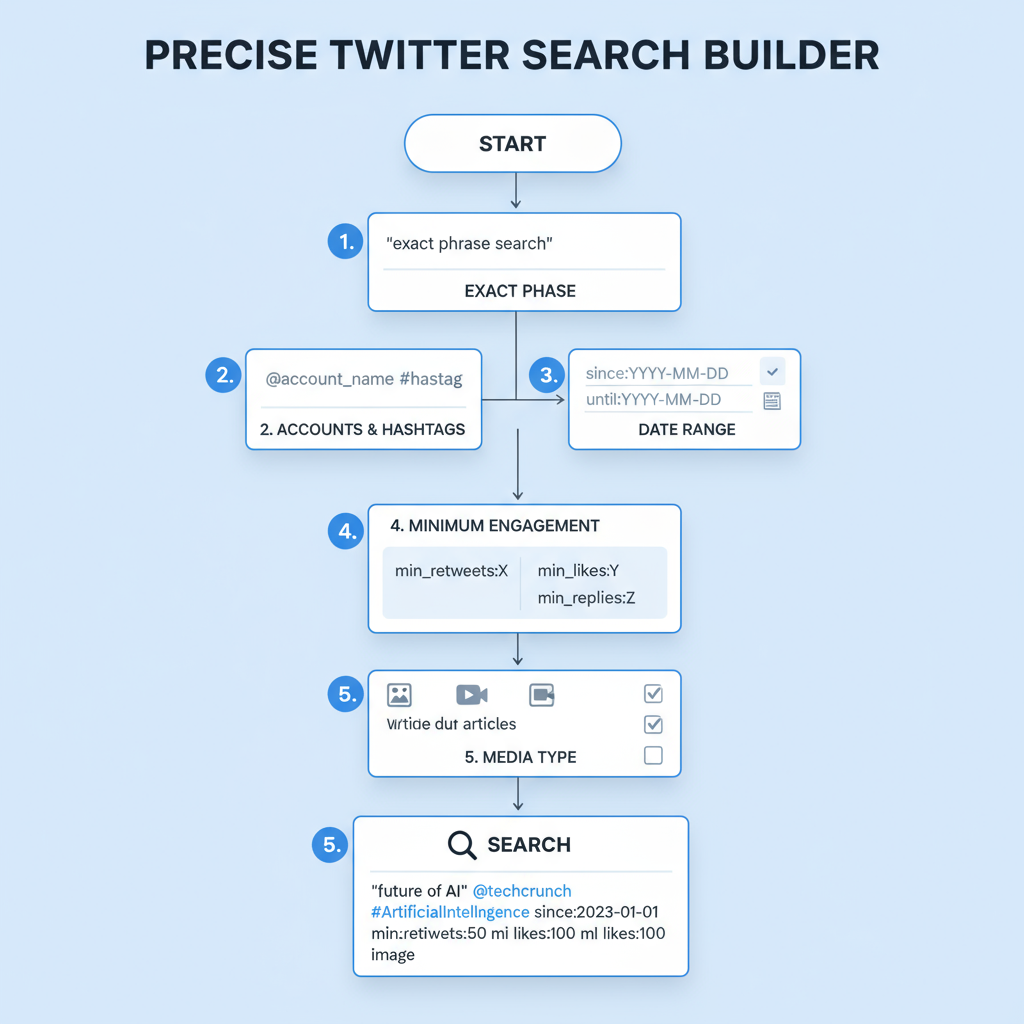
Introduction to Twitter Search Filters and Their Benefits
Mastering Twitter search filters is one of the fastest ways to cut through noise, uncover relevant tweets, and supercharge your social media research. Whether you’re a journalist seeking eyewitness accounts, a marketer monitoring brand sentiment, or simply curious about tweets from a specific era, search filters can save time and improve accuracy.
Instead of endlessly scrolling your feed, applying tailored filters helps you pinpoint relevant conversations, discover hidden content, and retrieve historical tweets with precision. Combined with Boolean operators, Twitter search filters bring laser focus to your results—making it easier to find exactly what you need.
---
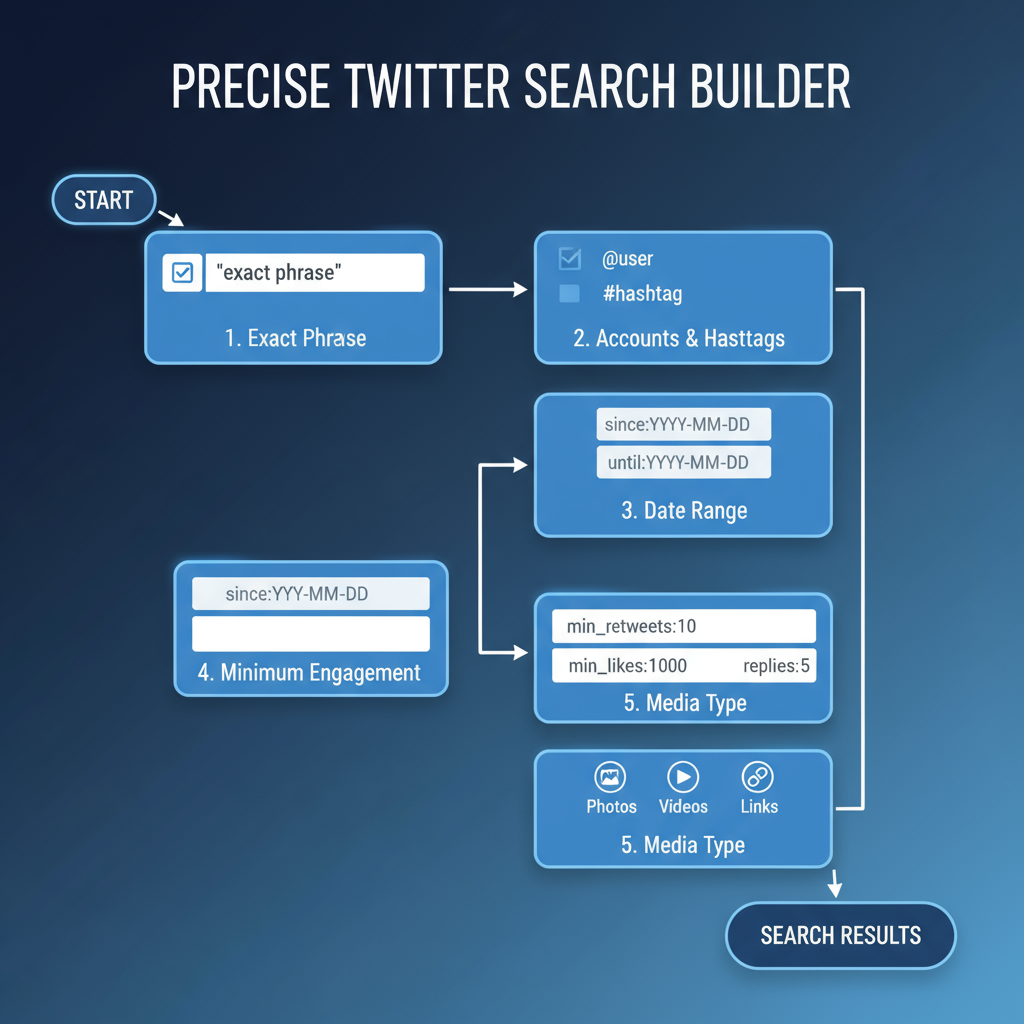
Twitter’s Advanced Search Page vs. Manual Filter Operators
Twitter offers two main methods to refine your searches:
- Advanced Search Page – A user-friendly interface with fields for keywords, hashtags, accounts, dates, and more. Ideal for beginners.
- Manual Filter Operators – Powerful text-based commands typed directly into the search bar for instant, highly targeted results. Favored by power users.
While the advanced search page is straightforward, manual operators provide greater flexibility—especially when combining multiple filters for complex queries.
---
Using Keywords and Phrases with Quotation Marks for Exact Matches
Without quotes, Twitter searches for tweets containing your words anywhere, regardless of order. Using quotation marks forces an exact phrase match.
Example:
"climate change policy"Returns tweets containing these words in that exact sequence.
To search for any one of several terms, use `OR`:
"climate change" OR "global warming"---
Filter by Hashtags, Mentions, and Specific Accounts
Target your searches by hashtag, username, or account origin:
#WorldCup → tweets with the hashtag #WorldCup
@OpenAI → tweets mentioning @OpenAI
from:NASA → tweets sent by @NASA
to:NASA → tweets sent to @NASAYou can combine filters:
from:NASA @SpaceXShows tweets from NASA mentioning SpaceX.
---
Searching Within Date Ranges Using since: and until: Operators
Date-based searches help you focus on specific time periods:
"electric cars" since:2022-01-01 until:2022-12-31- `since:` – tweets on or after the date.
- `until:` – tweets before the date.
Use both for a closed date range.
---
Narrowing by Engagement: min_retweets:, min_faves:, min_replies:
Target highly engaged tweets:
"AI tools" min_retweets:100Shows tweets with at least 100 retweets.
You can also search by likes or replies:
"AI tools" min_faves:500
"AI tools" min_replies:20---
Finding Media-Specific Tweets: filter:images, filter:videos, filter:links
Focus on tweets containing certain media types:
from:NASA filter:images
from:NASA filter:videosUse `filter:links` to find tweets containing hyperlinks.
---
Using -filter: to Exclude Content Types or Words
Exclude unwanted content:
from:NASA -filter:repliesShows only NASA's original tweets, excluding replies.
You can also omit words:
"AI tools" -beginnerFilters out tweets containing “beginner.”
---
Combining Multiple Filters for Hyper-Specific Results
Combine operators for maximum precision:
"machine learning" from:GoogleAI filter:links since:2023-01-01 min_retweets:50Finds “machine learning” tweets by @GoogleAI, with links, posted in 2023, retweeted 50+ times.
---
Locating Tweets by Language or Location (lang:, geocode:)
Filter by language:
"quantum computing" lang:enOr by proximity to specific coordinates:
"traffic" geocode:37.7749,-122.4194,10miThe following table summarizes these operators:
| Operator | Purpose | Example |
|---|---|---|
| lang: | Filter tweets by language code | lang:en |
| geocode: | Find tweets from a specific location and range | geocode:40.7128,-74.0060,5km |
---
Practical Real-World Examples for Journalists, Marketers, and Researchers
Journalists – Track breaking events with visuals:
"earthquake" filter:images since:2023-05-01Marketers – Monitor brand buzz:
"YourBrand" OR @YourBrand min_retweets:5 -filter:repliesResearchers – Analyze long-term trends:
"remote work" since:2020-01-01 until:2020-12-31 lang:en---
Tips for Discovering Trending Discussions and Old Tweets
- Apply `min_retweets:` to spot popular tweets on trending topics.
- Use `until:` to locate archival conversations.
- Combine hashtags with `since:` for event-based coverage.
Example:
#WorldCup since:2018-06-14 until:2018-07-15
---
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Irrelevant Results
- Skipping Quotes for Exact Phrases – Avoid loosely related results by using quotes.
- Wrong Date Formats – Always use `YYYY-MM-DD`.
- Overly Broad Keywords – Narrow them for manageable results.
- Ignoring Exclusion Filters – Use `-filter:` or `-word` to refine.
---
Summary and How to Save Frequent Searches for Quick Access
Twitter search filters transform Twitter into a precision information tool. Operators like `from:`, `since:`, `filter:images`, and their combinations help you find content faster and more accurately.
To save a search:
- Perform your filter-rich query.
- Click the overflow menu (`⋯`) on the results page.
- Select “Save search.”
Your saved queries will then be ready in the search bar for quick reuse—letting you re-run complex queries without retyping.
---
By adopting these approaches, you can unlock the full potential of Twitter search filters, streamline your workflow, and turn Twitter into a powerful engine for research, marketing, and trend discovery. Try combining multiple operators in your next search, and see how much more relevant your results can be.



