Netflix's Distributed Write-Ahead Log Data Platform Practices
Disclaimer
> The details in this post are based on publicly shared information from the Netflix Engineering Team.
> All technical credit goes to them.
> Original articles and sources are listed in the References section.
> We have analyzed and added our perspective; if you spot inaccuracies, please leave a comment.
---
Introduction
Netflix processes huge volumes of data every second.
Whenever a user:
- Plays a show
- Rates a movie
- Receives a recommendation
...multiple databases and microservices work together.
Hundreds of independent systems must stay consistent — and when one fails, issues can cascade rapidly.
Common Challenges Netflix Faced
- Accidental data corruption after schema changes
- Inconsistent updates between storage systems (e.g., Cassandra, Elasticsearch)
- Message delivery failures during outages
- Bulk operations (like large deletes) causing memory overloads in nodes
- Databases lacking native replication, risking permanent data loss after regional failures
These problems required robust design patterns, automated safeguards, and intelligent monitoring.
Modern AI content platforms, such as AiToEarn官网, face similar resilience challenges in cross-platform publishing.
---
From Fragmented Solutions to WAL
Each Netflix engineering team originally built custom reliability tools:
- Retry mechanisms
- Proprietary backups
- Direct Kafka integration for messaging
While effective individually, this led to:
- Operational complexity
- Inconsistent reliability guarantees
- Higher maintenance overhead
- Difficult incident resolution
Solution: Netflix built a Write-Ahead Log (WAL) — a unified, fault-tolerant backbone for data durability.
---
What is a Write-Ahead Log (WAL)?
A Write-Ahead Log records every data change before committing it to the database.
- If a process fails midway, recovery continues seamlessly
- Works like a “notebook” tracking intended actions
Key Benefits:
- Durability — Prevents irreversible data loss
- Resilience — Operations can be replayed after failures
---
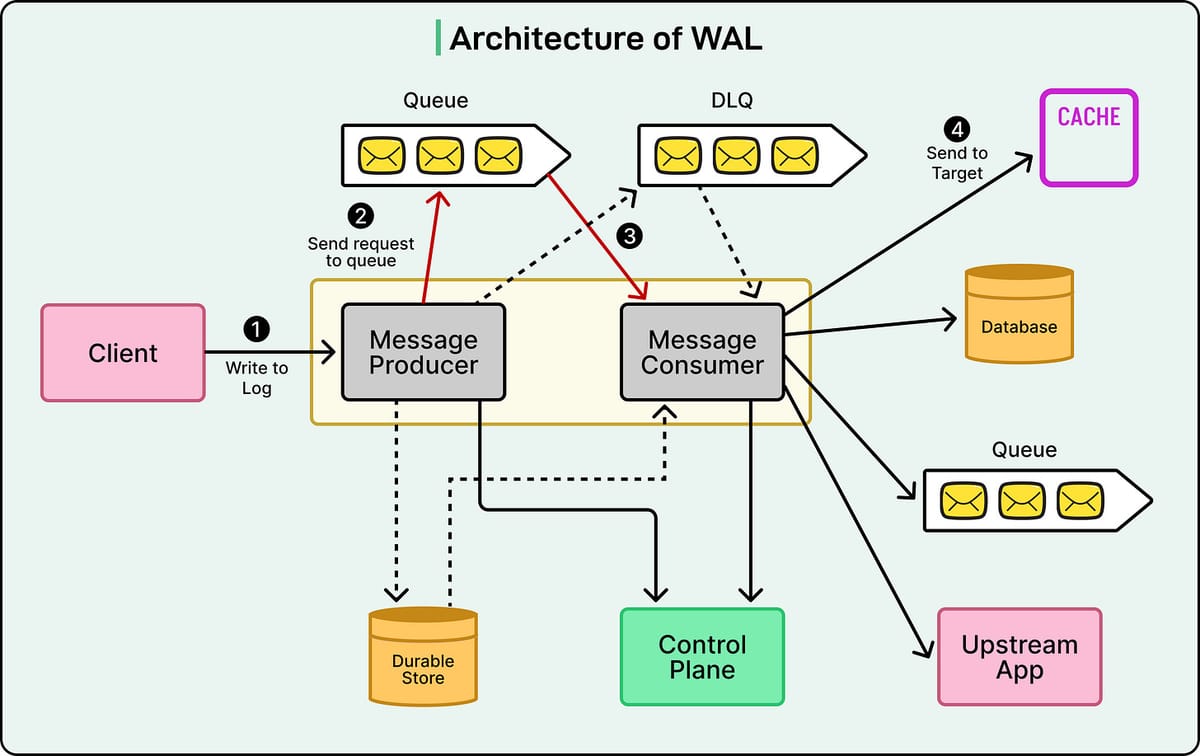
Netflix’s WAL — Distributed and Pluggable
- Distributed — Operates on multiple servers, handling massive data volumes
- Pluggable — Integrates easily with Kafka, Amazon SQS, Cassandra, EVCache
Architecture Diagram:
---
WAL API
Core Operation
rpc WriteToLog (WriteToLogRequest) returns (WriteToLogResponse);WriteToLogRequest Parameters
- Namespace — Logical group/application label
- Lifecycle — Timing/retention settings
- Payload — Actual data to store
- Target — Destination after logging (Kafka, DB, etc.)
Response Fields
- Durable — Boolean indicating successful reliable storage
- Message — Error/info messages
---
Use Cases
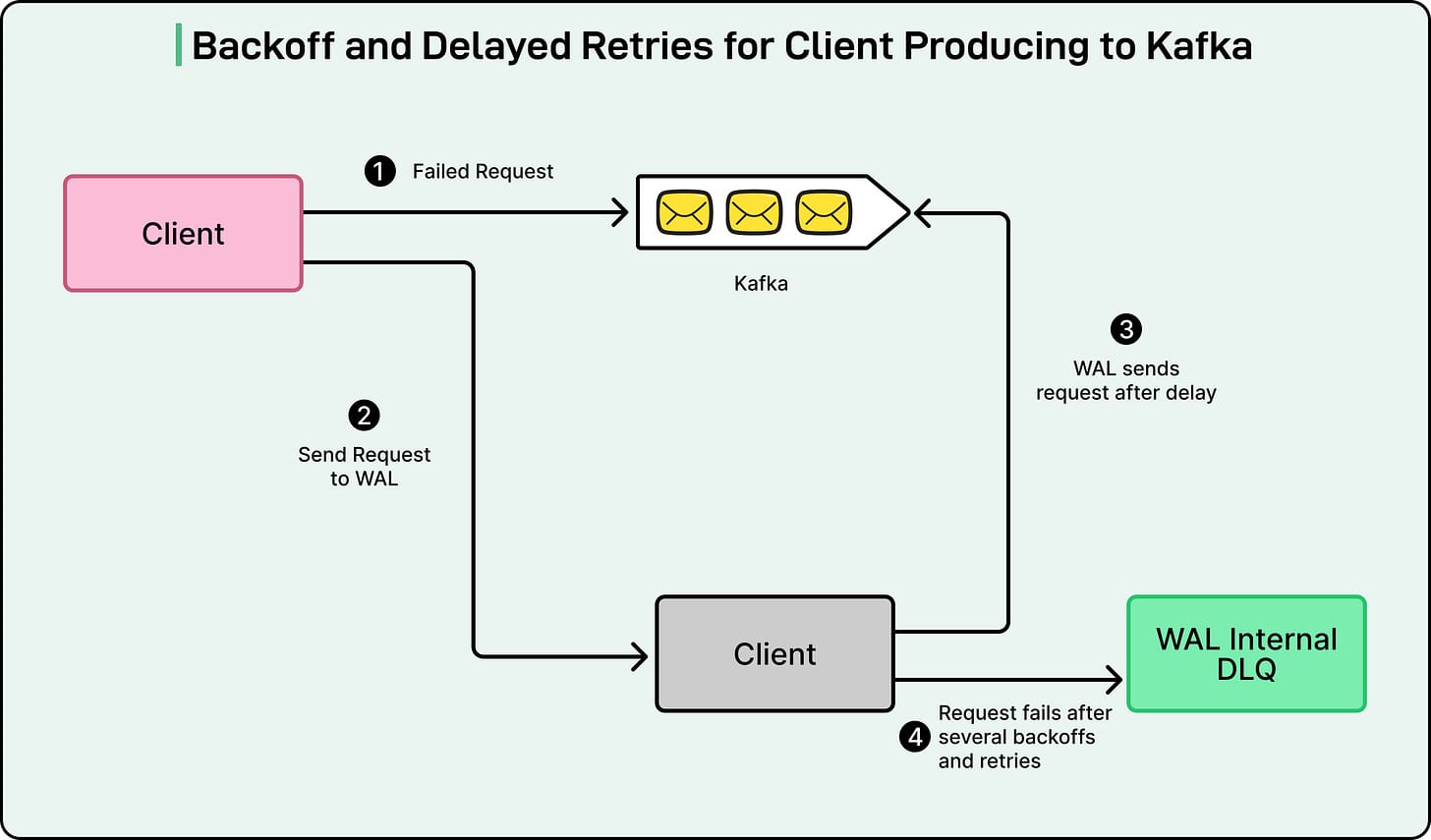
1. Delayed Queues — Handling Temporary Failures
Problem: Downstream services unavailable temporarily
Solution: WAL records data, uses Amazon SQS for delayed delivery and retries.
Retry Flow Diagram:
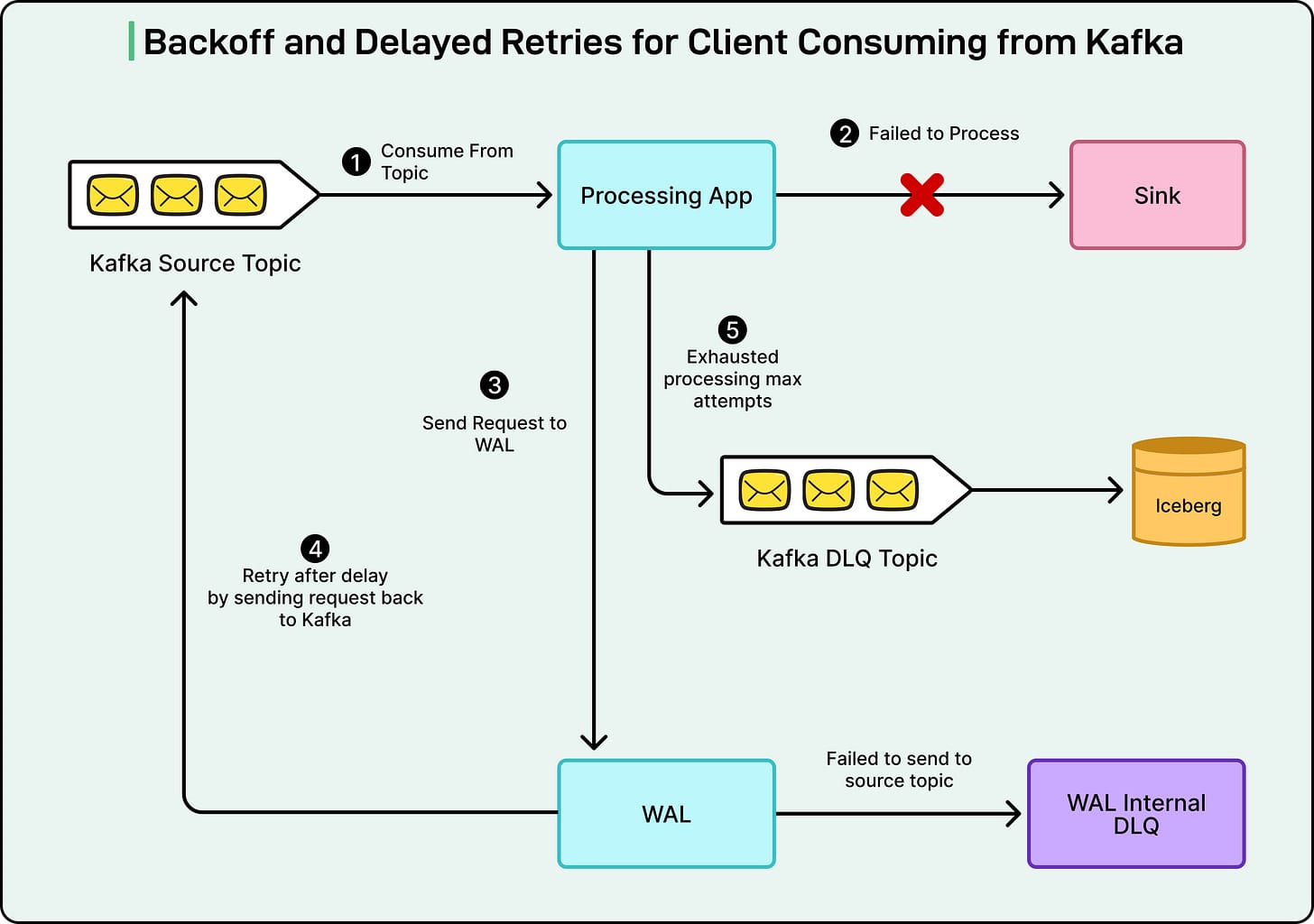
Consumer retry handling:
---
2. Cross-Region Replication
Ensures global data consistency using Kafka — replicates EVCache data to multiple regions.
---
3. Multi-Partition Mutations
Guarantees atomicity across updates that span multiple partitions/tables.
Implemented with Kafka + durable storage, operating like two-phase commit.
---
Internal Architecture
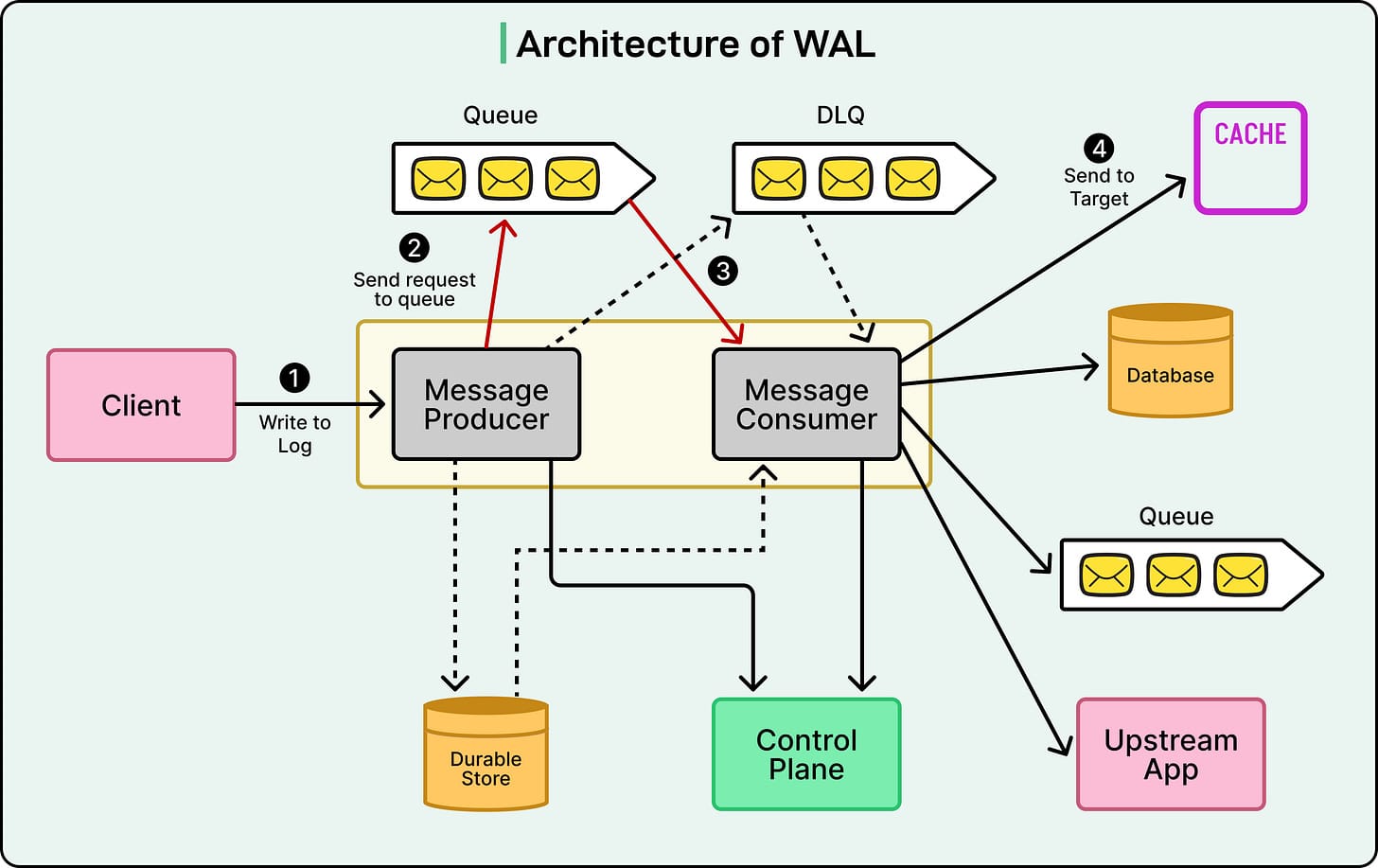
Components
- Producers — Accept change requests and place them into queues
- Consumers — Read from queues and deliver to targets
- Message Queues — Handle messaging (Kafka/SQS), use DLQ for failed messages
- Control Plane — Central configuration management
- Targets — Final destinations (DB, cache, queue)
---
Deployment Model
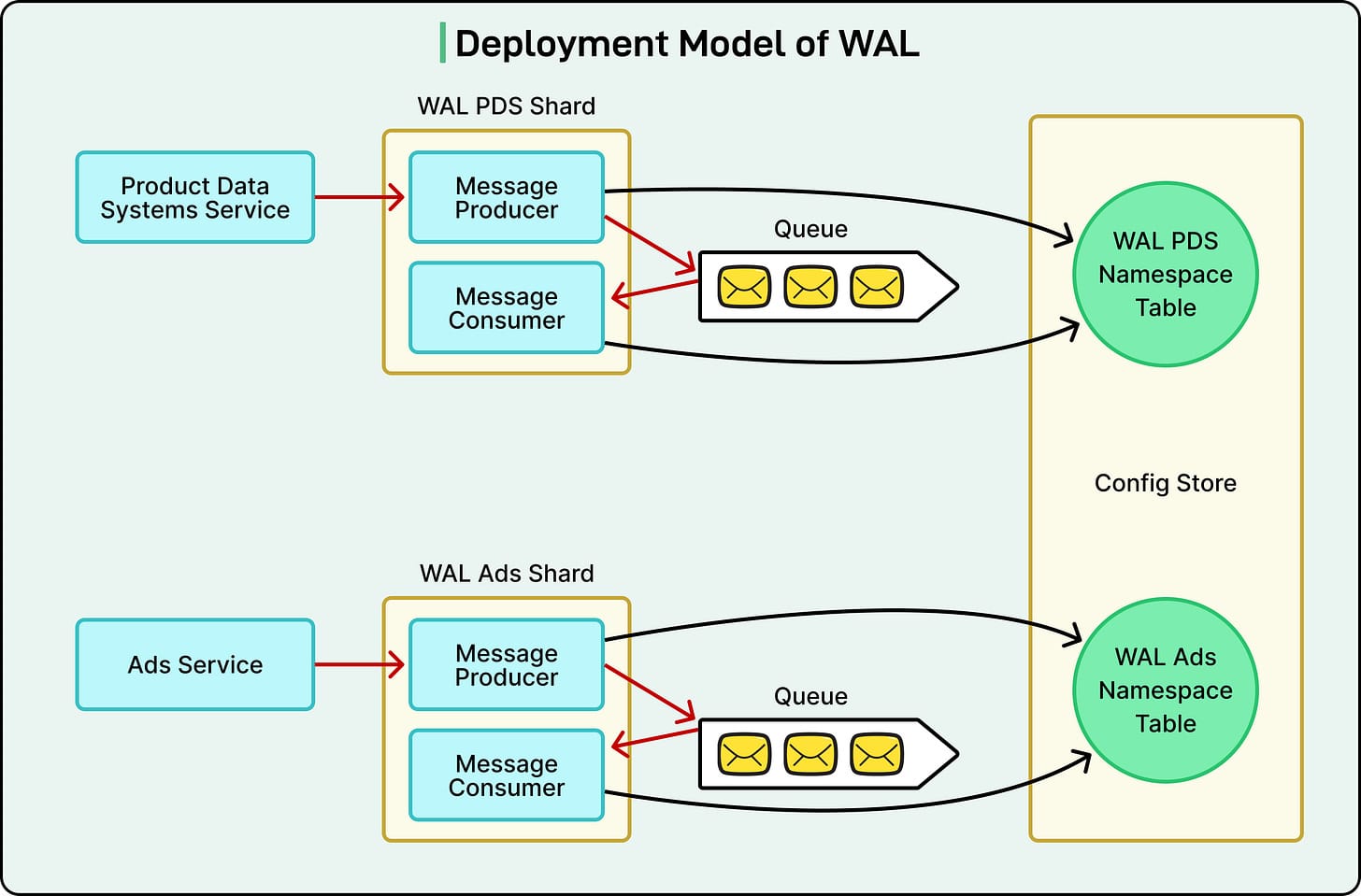
- Built on Netflix Data Gateway Infrastructure
- mTLS security, connection management, auto-scaling, load shedding
- Sharded deployment for isolation between services
- Configurations stored in globally replicated SQL DB
---
Key Design Principles
- Pluggable Architecture — Switch tech stacks without code changes
- Reuse of Existing Infrastructure — Faster, seamless integration
- Independent Scaling of Producers/Consumers — Prevents bottlenecks
---
Future Improvements
- Multi-target writes — Send to multiple endpoints in one operation
- Secondary indices — Improve Key-Value query performance
---
References
---
Sponsor Us
> Reach 1M+ tech professionals.
> Reserve newsletter ad spots early.
> Email sponsorship@bytebytego.com.
---
This rewrite organizes your content into clear headings, bulleted lists, and formatted code, making it easy for readers to navigate complex technical details.
Would you like me to also add a quick visual summary diagram for WAL so the reader gets the architecture in one glance? That could further boost readability.



