# A Unified Feature Attribution Framework — **DePass (Decomposed Forward Pass)**
**Date:** 2025-12-01 12:06 Beijing
---
## 1. Introduction

With the rapid advances in **Large Language Models (LLMs)**—demonstrating exceptional generative and reasoning abilities—AI interpretability research is increasingly focused on **tracing outputs back to internal computations**.
### 1.1 The Challenge
Current attribution methods often face:
- **High computational cost**
- **Limited tracing through intermediate layers**
- **Separate, siloed approaches** for different granularity levels (tokens, components, subspaces) instead of a unified method.
### 1.2 The Solution: DePass
A team from **Tsinghua University** and **Shanghai AI Lab** introduced **DePass (Decomposed Forward Pass)**:
- **Lossless decomposition** of each hidden state into additive sub-states.
- **Layer-by-layer propagation** with **fixed attention scores** and **MLP activations**.
- **Unified analysis** across tokens, attention heads, neurons, and residual stream subspaces.
---
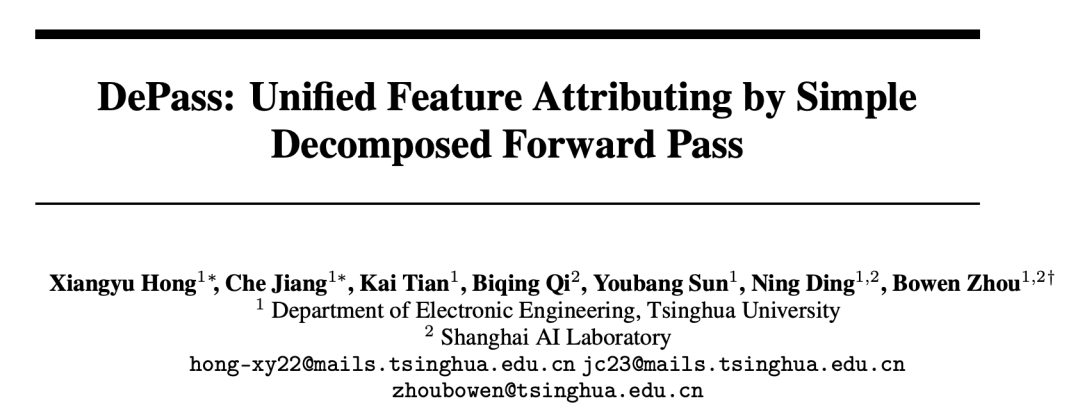
**Paper:** *DePass: Unified Feature Attributing by Simple Decomposed Forward Pass*
**[PDF](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2510.18462)** | **[Code](https://github.com/TsinghuaC3I/Decomposed-Forward-Pass)**
---
## 2. Problem Analysis
### 2.1 Limitations of Existing Attribution Methods
1. **Noise Ablation & Activation Patching**
- Inject noise or patch activations across modules.
- Pros: reveals dependencies
- Cons: computationally heavy, weak tracking of intermediate flow.
2. **Gradient-Based Attribution**
- Pros: easy to implement
- Cons: theoretical limitations, less fine-grained.
3. **Model Approximation / Abstraction**
- Pros: more human-aligned reasoning
- Cons: low granularity, risk in non-conservative approximations.
---
## 3. DePass Workflow
### 3.1 Core Idea
Decompose hidden state **X** into additive components:
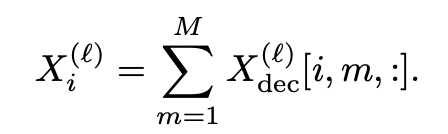
Propagate these components with:
- **Frozen attention scores**
- **Frozen MLP activations**
This yields **precise, fine-grained attribution** for Transformer behavior.
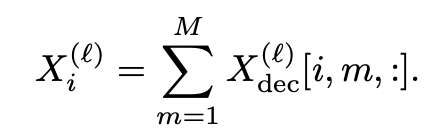
---
### 3.2 Attention Module
- **Step 1:** Each component undergoes a linear transformation.
- **Step 2:** Weighted & aggregated according to fixed attention scores.
- **Step 3:** Distribute exactly into each component.
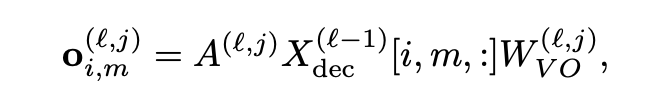
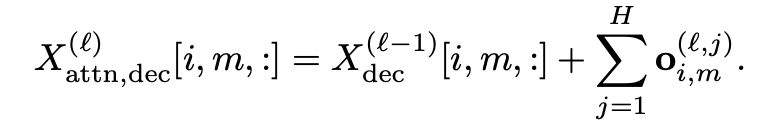
---
### 3.3 MLP Module
- Functions like a **neuron-level key-value store**.
- Different components influence key activations differently.
- Splits each neuron's output into component-specific values.
Formula:
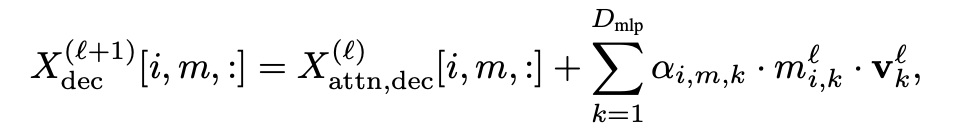
Where the weight assigns neuron *k* output to component *m*.
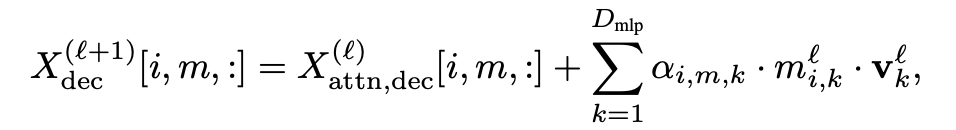
---
## 4. Experimental Validation
DePass enables **consistent attribution** at token, component, and subspace levels, aligning with human reasoning and sparse dictionary learning techniques (e.g., SAE).
### 4.1 Token-Level Attribution: Core Evidence Identification
**Experiment:** *Disrupt-top* & *Recover-top*
- *Disrupt-top:* Removing top contribution tokens → sharp drop in output probability.
- *Recover-top:* Retaining only top tokens → restores much prediction accuracy.

---
### 4.2 Token-Level Attribution: Subspace Origins Tracking
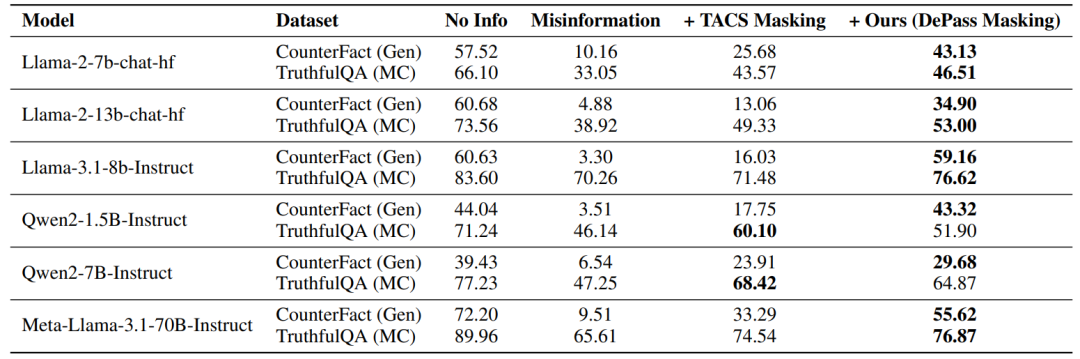
Example: **Truthfulness Subspace** & **False Information Subspace**
- Pinpoints input tokens activating specific semantic directions.
- Targeted masking of “false” tokens increased factual accuracy on CounterFact from ~10% → **>40%**.
---
### 4.3 Component-Level Attribution
Observes **actual roles** of attention heads and MLP neurons:
- **Top-k Masking:** Removing highly ranked components → faster accuracy drop.
- **Bottom-k Masking:** Keeping least important → preserves performance.
Outperforms metrics like AtP & Norm.

---
### 4.4 Subspace-Level Attribution: Language & Semantic
#### Language Subspace
- **Basis vector** via classifier weights.
- Hidden states projected into language vs. orthogonal semantic subspaces.
- Independent propagation & decoding.
**Findings:**
t-SNE visualization shows clear **language clusters** (English/French/German).
---
#### Semantic Subspace
- Decoding yields consistent factual answers across languages.
- Demonstrates preservation of subspace functionality.
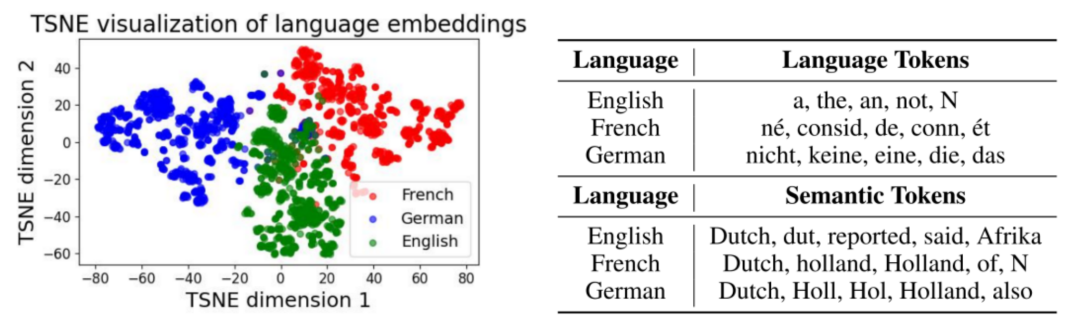
*(Left)* t-SNE projection onto language subspace.
*(Right)* Top five tokens decoded from each subspace under multilingual prompts.
---
## 5. Summary
**DePass** is:
- **Simple** & **efficient**
- **Lossless additive decomposition**
- Applicable to diverse Transformer architectures
**Advantages**:
- High faithfulness in attribution
- Multi-granularity analysis (tokens → subspaces)
- Potential to become a **general-purpose interpretability tool**

---
## 6. Beyond Research
Platforms like **[AiToEarn官网](https://aitoearn.ai/)** offer:
- Open-source AI content monetization
- AI generation + multi-platform publishing
- Cross-platform analytics & model ranking ([AI模型排名](https://rank.aitoearn.ai))
Ideal for sharing DePass insights via:
**Douyin, Kwai, WeChat, Bilibili, Rednote, Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, Threads, YouTube, Pinterest, X (Twitter)**.
---
**[Read the Original Article](2651004938)**
**[Open in WeChat](https://wechat2rss.bestblogs.dev/link-proxy/?k=307e735a&r=1&u=https%3A%2F%2Fmp.weixin.qq.com%2Fs%3F__biz%3DMzA3MzI4MjgzMw%3D%3D%26mid%3D2651004938%26idx%3D3%26sn%3D25484cb339fe684db22cf567767209ee)**