# Language Ranker — Redefining LLM Decoding from a Recommendation System Perspective
**Date:** 2025-11-30 11:17
**Location:** Liaoning

---
## Introduction
**Language Ranker** offers a fresh perspective on **large language model (LLM) decoding**, treating it as analogous to the **ranking stage** in recommendation systems.

Traditionally, LLM research focuses on **optimizing output distributions** through:
- Scaling up models
- Enhancing distribution learning
- Improving reward signals
However, the **decoding stage**—converting probability distributions into *high-quality outputs*—has received less attention.
A research team from **Peking University** (Lin Zhoucheng, Wang Yisen) presents *Language Ranker: A Lightweight Ranking Framework for LLM Decoding*. Their approach applies **recommendation system ranking principles** to LLM decoding, exposing shortcomings in current methods and offering a **lightweight, efficient** improvement strategy.

---
**Paper Title:** *Language Ranker: A Lightweight Ranking Framework for LLM Decoding*
**Paper Link:** [https://www.arxiv.org/abs/2510.21883](https://www.arxiv.org/abs/2510.21883)
---
## 1. Rethinking LLMs as Recommendation Systems
LLMs can be conceptualized as recommendation systems:
- **Input** = User profile
- **Output** = Ranked recommendation from a large candidate space
**Mapping with Recommendation Systems:**
- **LM Backbone** → User feature extraction (**feature engineering**)
- **LM Head** → Initial candidate retrieval (**retriever stage**)
- **Decoding Method** → Selecting the best output (**ranking stage**)

**Figure 1 — LLM-to-Recommendation System Mapping**
### Current Limitations
- **Static ranking methods** — Greedy decoding, beam search, self-consistency lack learning capability; gains are limited, task-specific.
- **Reward-model re-ranking** — Adds learning but duplicates feature extraction, increasing computational cost in both training and inference.
- **Scalability issues** — High-resource demands hinder universal decoding optimization.
---
## 2. Language Ranker Framework
### Key Idea
Borrowing from recommendation systems, **Language Ranker**:
- **Avoids heavy reward models**
- **Reuses hidden-layer features** from the main model
- Applies an **ultra-small ranking module** (<0.5M parameters)
This achieves **comparable or superior results** to large reward models across math reasoning, code generation, and function calling.
---
### Workflow Steps
1. **Candidate Recall**
Generate multiple candidate responses from the main model.
2. **Feature Extraction**
Gather hidden states of the last token from ~bottom 60% of layers as representation features.
3. **Candidate Ranking**
Re-rank using a lightweight Transformer or MLP.
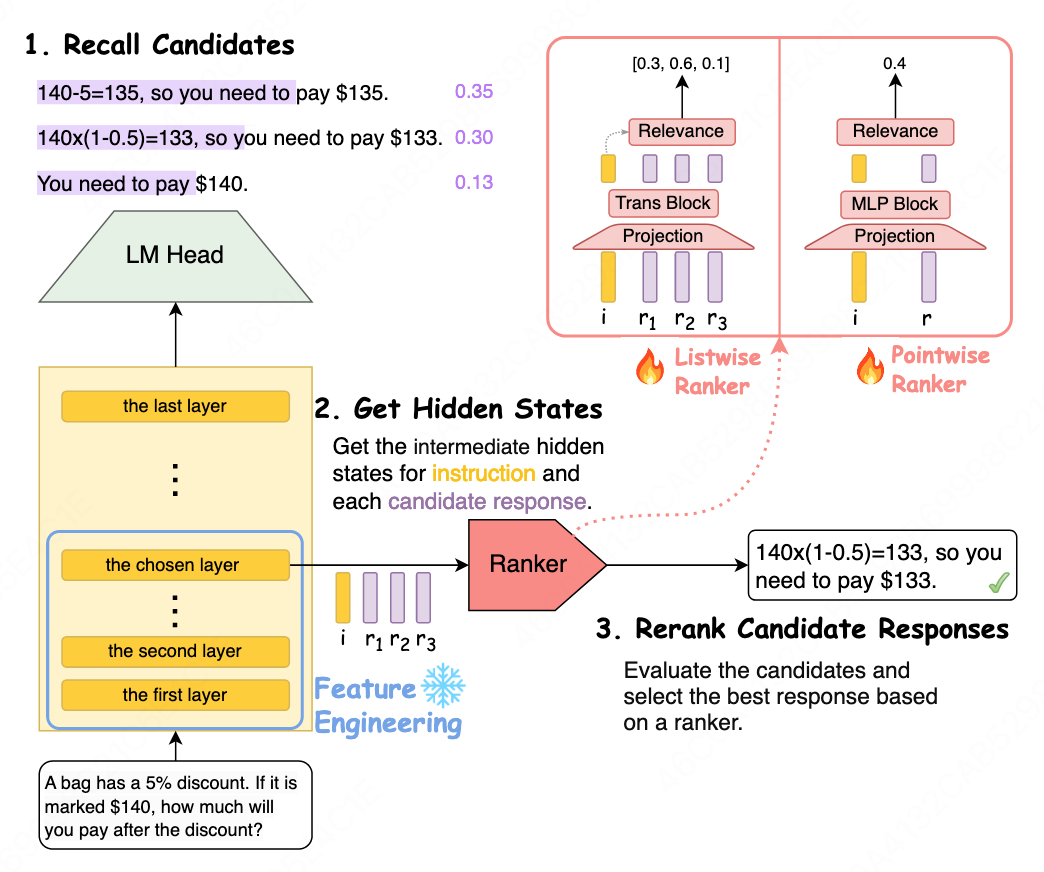
**Figure 2 — Language Ranker Framework**
### Benefits
- **Low overhead** — Train/infer on CPU
- **Plug-and-play** — No LLM structural changes
- **Modular deployment** — Main model and Ranker run independently
- **Personalization** — Multiple Rankers can be paired with one model to tailor responses
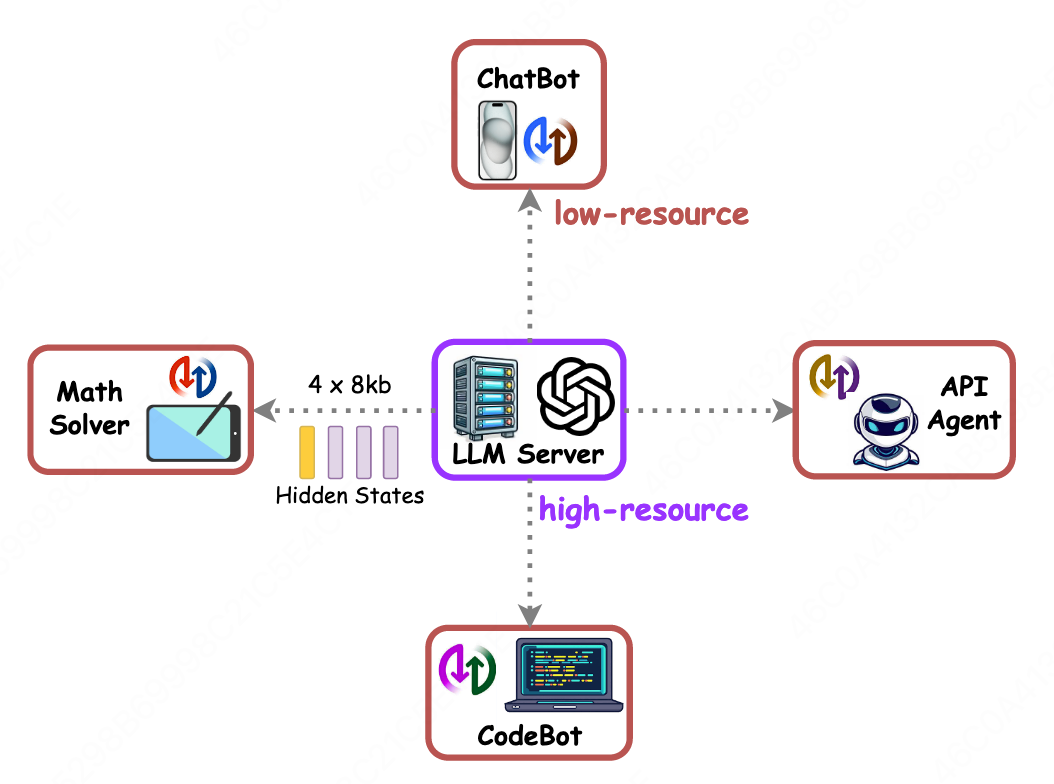
**Figure 3 — Personalized Enhancement with Multiple Rankers**
---
## 3. Experimental Results
### 3.1 Small Ranker, Big Gains
- **<0.5M parameters** = Performance on par with large reward models
- Outperforms 8B Reward Models in most tasks on 8B main models
- Nearly matches 32B Reward Models with only 0.36M parameters
- Consistently beats rule-based decoding strategies

**Figure 4 — Math, Coding, Tool-call Performance**
---
### 3.2 Speed & Efficiency
- **MBPP task**: CPU training in **67 seconds**
- **GPT-2 Reward Model**: >1 hour training
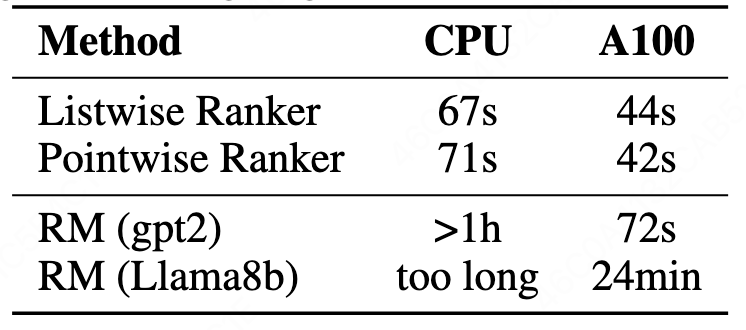
**Figure 5 — CPU Training Capability**
---
### 3.3 Transfer & Generalization
- **Cross-domain** within MATH tasks: performance drop <2%
- **Cross-task** (math → code): still beats GPT-2 Reward Models
- Single Ranker works across multiple tasks/models

**Figure 6 — Cross-domain Generalization**
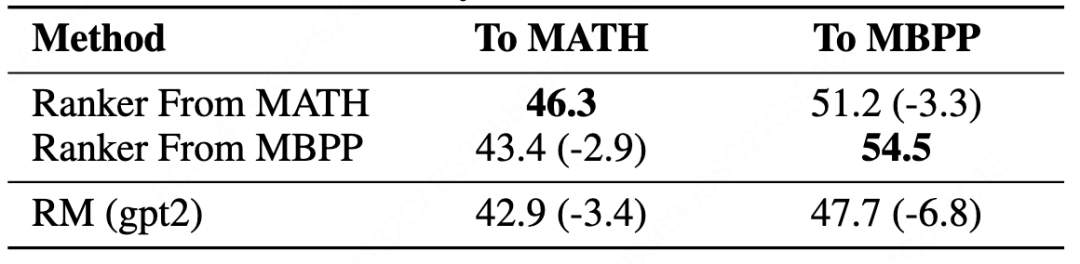
**Figure 7 — Cross-task Generalization**
---
### 3.4 Ranker Scaling Law
Increasing candidate samples from 1 → 100 steadily improves accuracy:
- **MATH:** 25% → 56%
- **MBPP:** 42% → 59%
- **xLAM Function Calls:** 11% → 47%
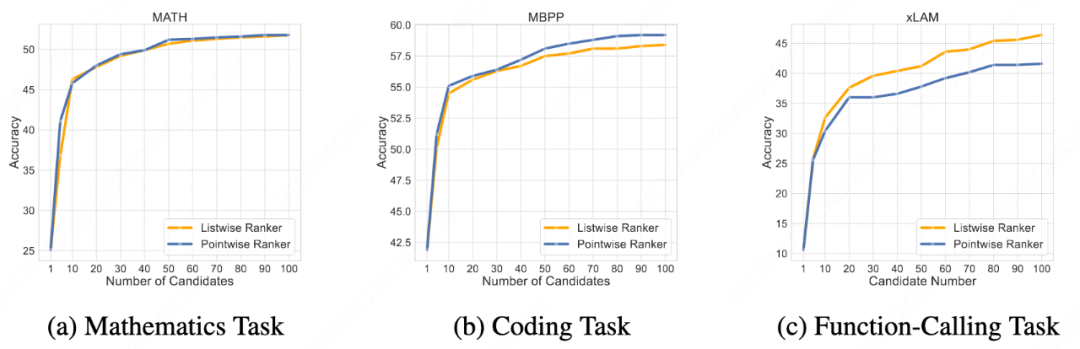
**Figure 8 — Ranker Scaling Law**
---
## 4. Summary & Outlook
**Language Ranker**:
- Redefines LLM decoding with a recommendation system mindset
- Reuses hidden-layer features to cut computation cost dramatically
- Matches large reward models while being **200× smaller**
- Trainable on CPUs and easy to deploy
- Flexible for personalization through modular Rankers
Experimental results confirm:
- Strong multi-task performance (math, coding, tool calling)
- Robust generalization in cross-task and cross-model scenarios
- Efficiency and scalability for real-world AI applications
---
## 5. Broader Context: AI Deployment Ecosystems
Platforms like **[AiToEarn官网](https://aitoearn.ai/)** complement innovations such as Language Ranker by:
- Connecting AI generation tools
- Publishing across Douyin, Kwai, WeChat, Bilibili, Rednote, Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, Threads, YouTube, Pinterest, and X
- Offering developer resources: [AI模型排名](https://rank.aitoearn.ai) and [AiToEarn文档](https://docs.aitoearn.ai)
- Applying scaling laws and modular AI agents to content monetization
This ecosystem demonstrates how **Ranker Scaling Law-powered workflows** can be deployed for greater reach and impact.
---
**References:**
- [Read Original](2651004903)
- [Open in WeChat](https://wechat2rss.bestblogs.dev/link-proxy/?k=b45c4dc4&r=1&u=https%3A%2F%2Fmp.weixin.qq.com%2Fs%3F__biz%3DMzA3MzI4MjgzMw%3D%3D%26mid%3D2651004903%26idx%3D3%26sn%3Db2abe2e61938c13f840fc2346dbc28c0)




