NeurIPS 2025 Spotlight | China Unicom Accelerates Diffusion Models with Global Optimization

Author and Team Introduction
The first authors of this work are Huanlin Gao and Ping Chen, with corresponding authors Fang Zhao and Shiguo Lian.
Other contributors include Fuyuan Shi, Chao Tan, Zhaoxiang Liu, and Kai Wang.
All authors are part of the Yuanjing Large Model R&D Team at Unicom Data Intelligence Co., Ltd. (China Unicom Data Science and AI Research Institute).
---
Background: The Bottleneck in Video Diffusion Models
Recent DiT (Diffusion Transformer) models are achieving video generation quality close to real-world filming. Yet, they face a significant bottleneck:
- Long inference time
- High compute cost
- Difficulty accelerating generation speed
These issues worsen as video length and resolution increase, limiting their usability for fluid, high-quality video creation.
---
The LeMiCa Solution
A research team from the China Unicom Data Science and AI Research Institute has developed LeMiCa (Lexicographic Minimax Path Caching):
> A training-free, globally optimal caching acceleration framework that keeps quality and temporal consistency intact.
LeMiCa solves a long-standing challenge — avoiding local greedy decisions in caching — by adopting a global optimization approach.
Recognition
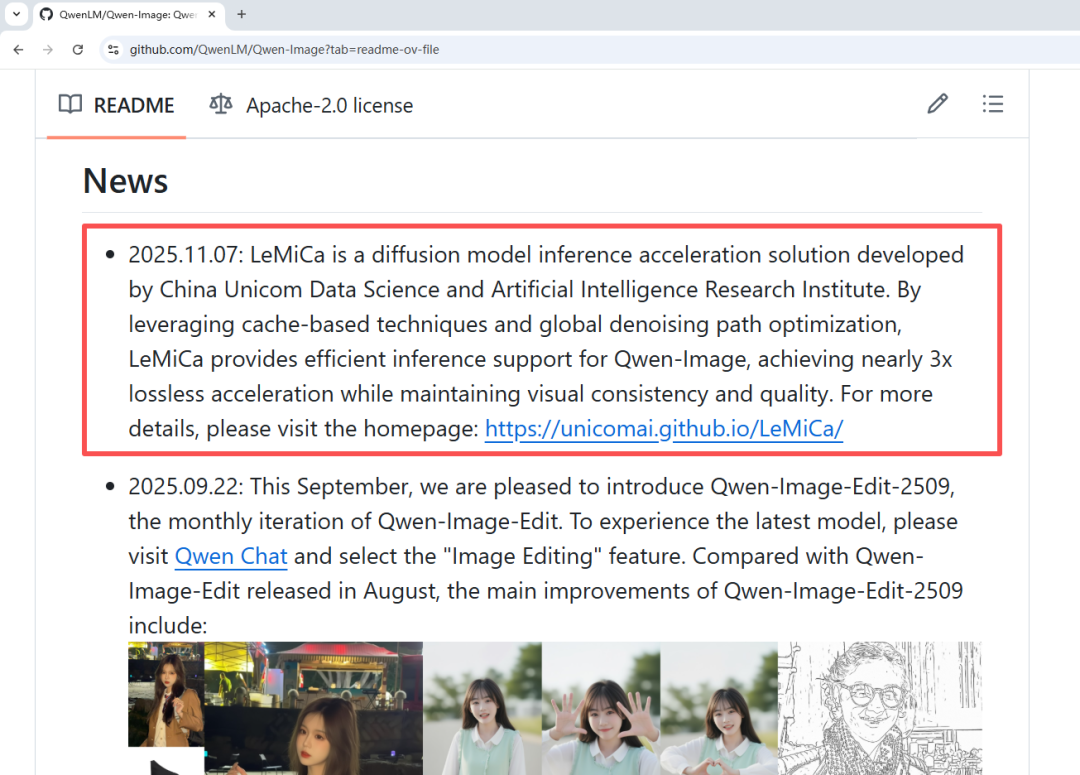
- Selected for NeurIPS 2025 Spotlight 🎉

Paper: LeMiCa: Lexicographic Minimax Path Caching for Efficient Diffusion-Based Video Generation
- Paper Link: https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.00090
- Project Homepage: https://unicomai.github.io/LeMiCa
- Code Repository: https://github.com/UnicomAI/LeMiCa
---
Key Highlights: Fast and Stable Inference
Problem with Existing Methods
Mainstream caching methods like TeaCache reuse results when adjacent timesteps have small differences.
However:
- This local step-by-step strategy ignores early timestep sensitivity in diffusion models.
- Small early-stage errors accumulate and cause visible degradation.
- Some methods require online discrimination, adding compute overhead.
LeMiCa’s Core Insight
> Caching decisions require global path optimization, not local decisions.
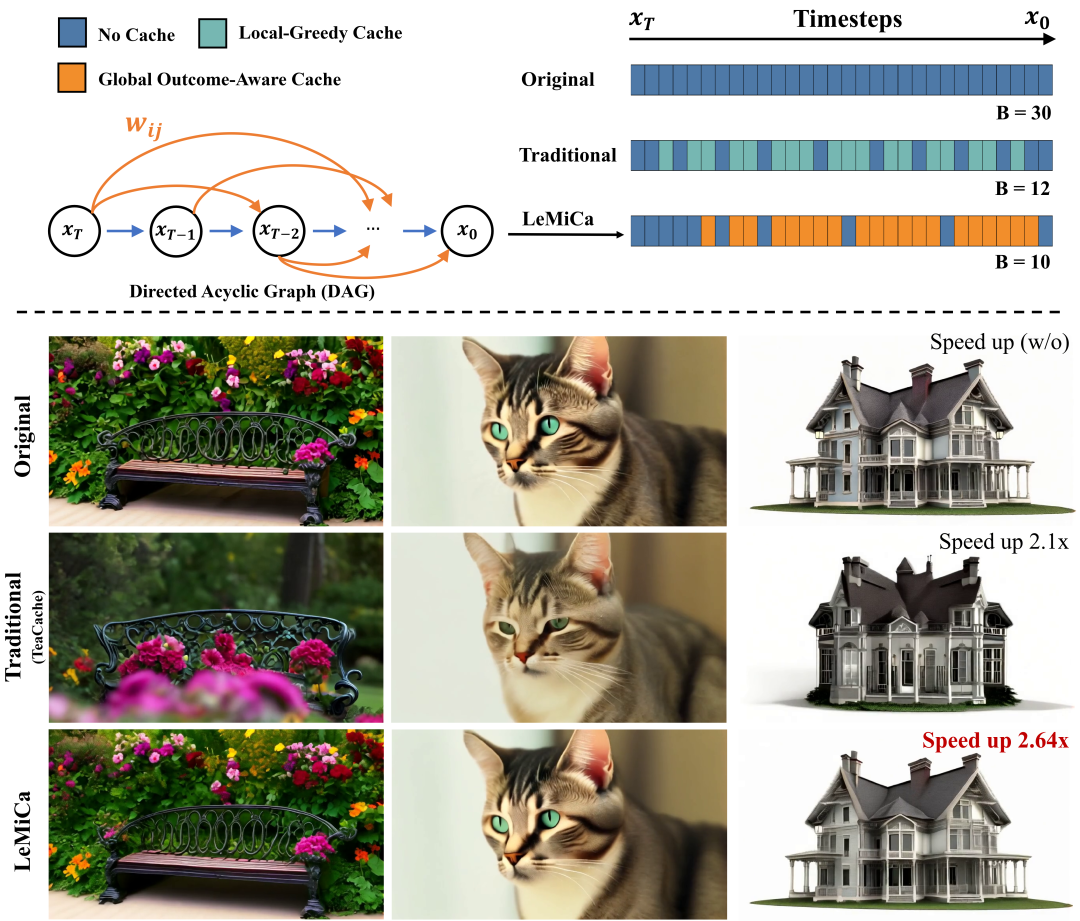
The team abstracts the generation process as a weighted Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG):
- Nodes: Timesteps
- Edges: Skip computation using cached results
- Weights: Global error introduced by caching
This turns cache scheduling into a shortest-path search problem, enabling globally optimal caching plans.
---
Technical Implementation
Step 1: Error Modeling and DAG Construction
LeMiCa introduces an error metric and builds a static, offline DAG:
- Nodes: Each timestep
- Edges: Possible cache reuse spans
- Weights: Global reconstruction error from caching
Example — for edge from i to j:
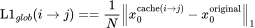
Weight = L1 loss between outputs before and after acceleration.
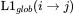
To keep the DAG manageable:
- Limit maximum skip length (longer skips add more error)
- Use few-shot samples to build reusable error graphs across tasks
---
Step 2: Lexicographic Minimax Path Optimization
Goal: Under a budget B (full inference steps), find the optimal start-to-end path.
Why not shortest path?
Errors are non-additive — summing them doesn’t reflect actual impact.
Solution:
LeMiCa uses lexicographic minimax:
- Minimize the maximum segment error
- Balance errors across the path
Formal Definition:
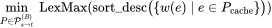
Where:
- !image = set of all valid paths (exact B full inference steps)
- !image = edges with cache reuse
- !image = error weight per edge
- !image = error vector sorted descending
Comparison rule:
- If Path A’s max error < Path B’s → A wins
- If equal → compare second largest, and so forth
---
Experimental Results
Performance on Mainstream Models
- Visual consistency preserved
- Acceleration factor: > 2.4×
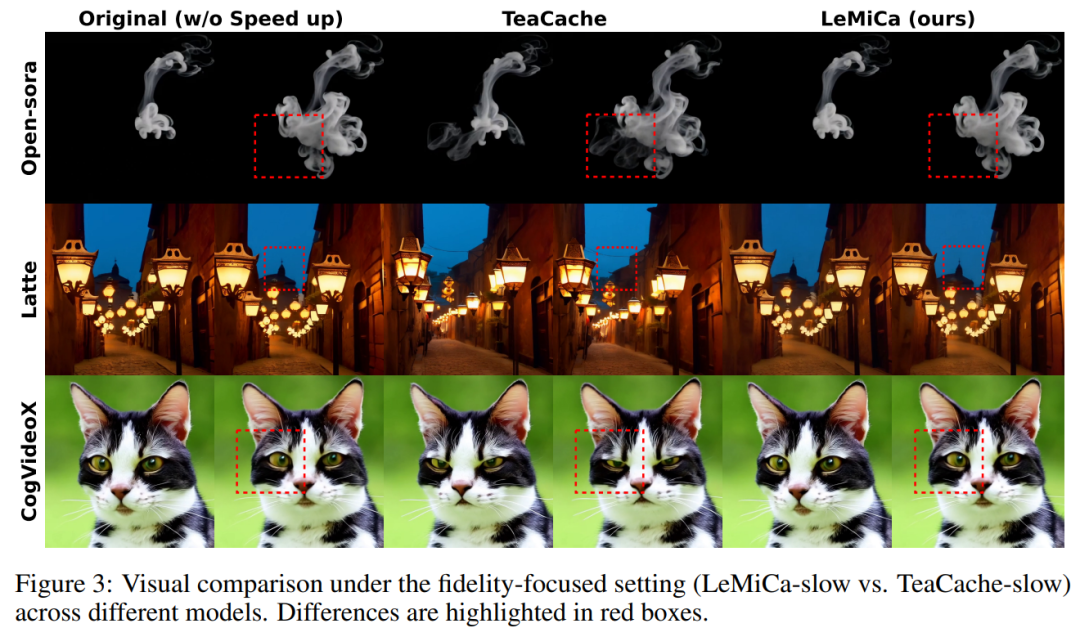
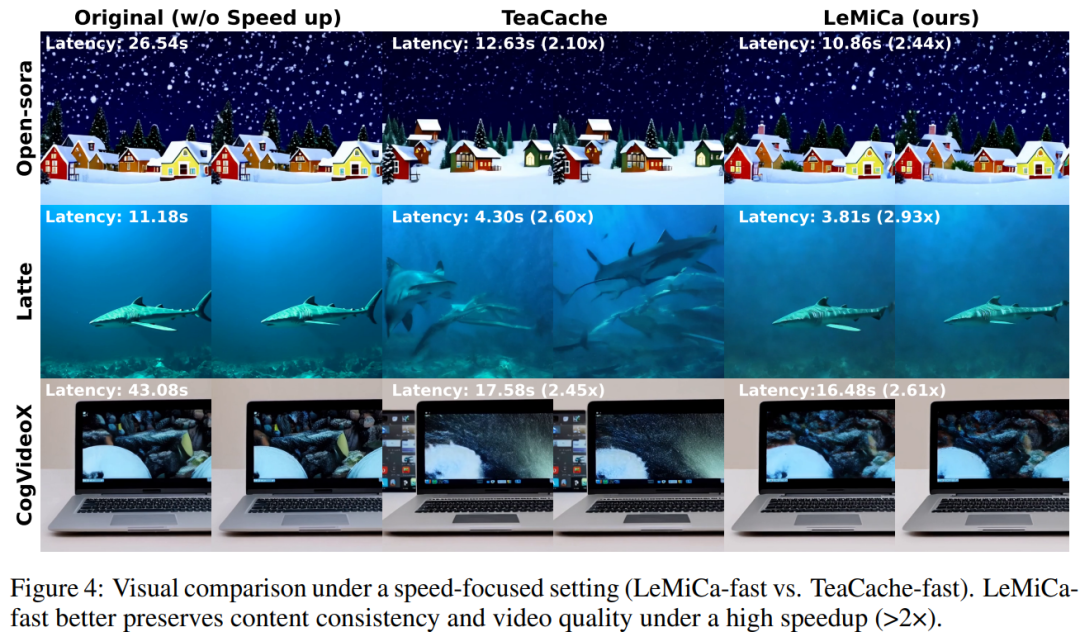
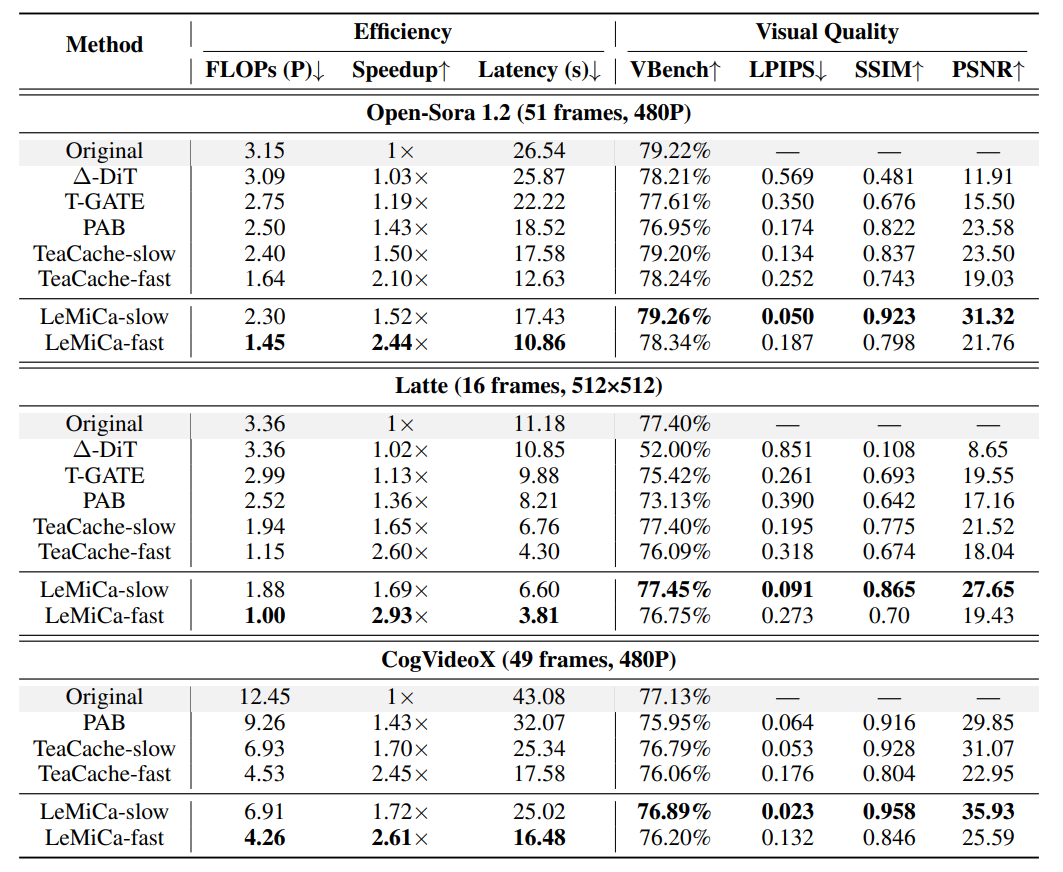


Advantages:
- Excellent structure, texture, content consistency
- Outstanding speed without quality loss
---
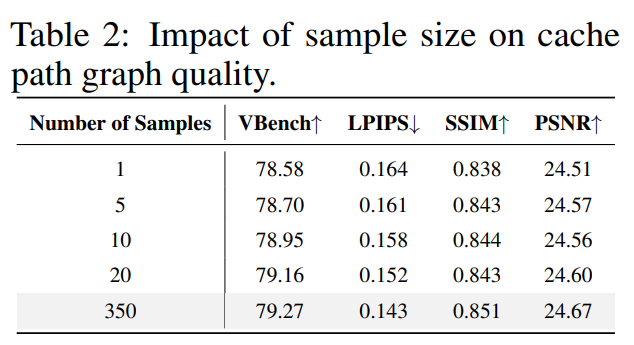
Ablation Studies
Few-Shot Graph Building
- 1 sample → strong performance
- 20 samples → performance saturates
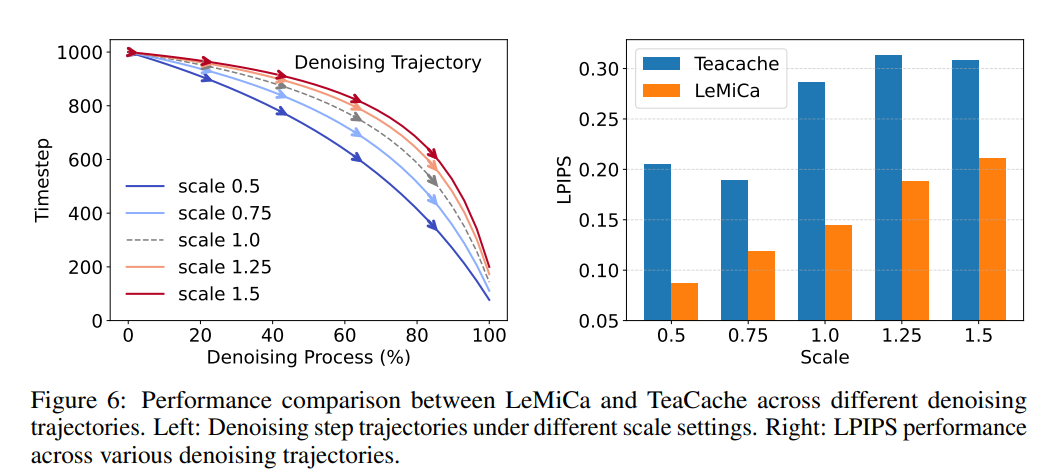
Robustness
- Works across different denoising trajectories
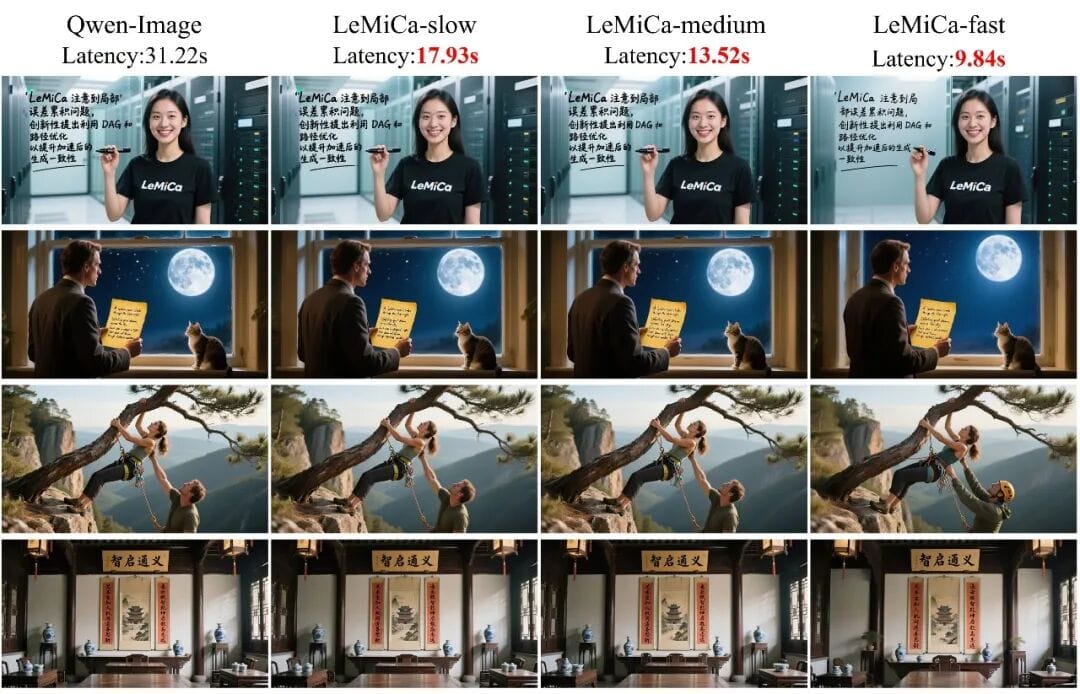
Text-to-Image Compatibility
- Works equally well with text-to-image models (e.g., QWen-Image)

---
Integration with AI Creative Workflows
Platforms like AiToEarn官网 complement LeMiCa:
- Generate, publish, monetize AI content
- Distribute to multiple platforms (Douyin, Kwai, Bilibili, Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, YouTube, Pinterest, X)
- Connect with analytics and AI model rankings (AI模型排名)
Benefit: Combines LeMiCa’s efficiency with multi-platform reach.
---
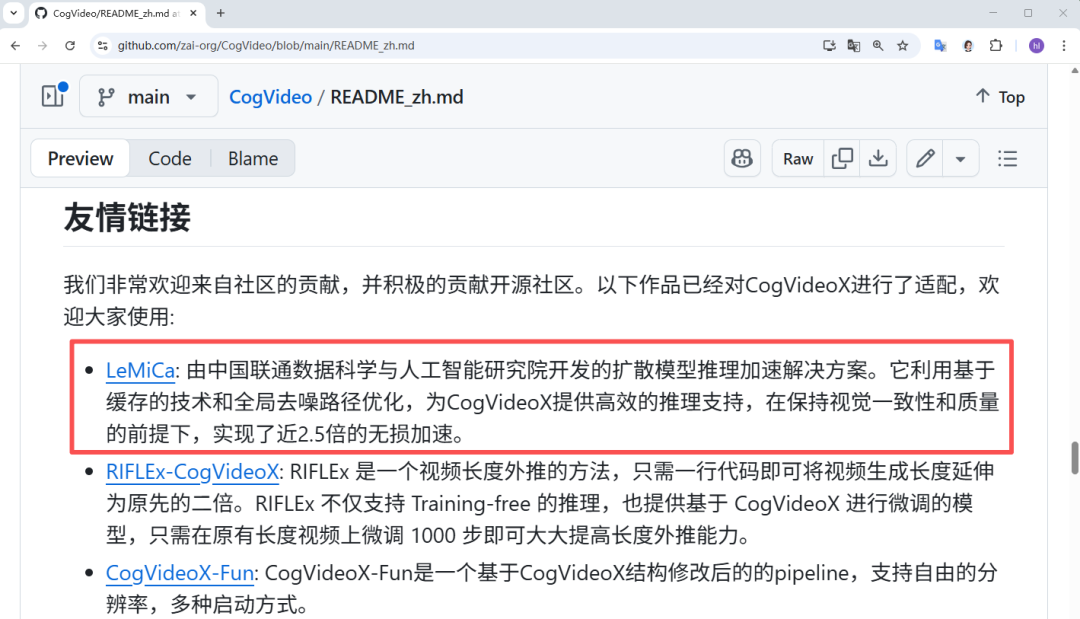
Industry Endorsements
LeMiCa has been officially recommended by:
- Alibaba Tongyi Qianwen
- Zhipu AI
---
Summary and Outlook
LeMiCa:
- Global DAG-based optimization for caching acceleration
- Training-free and model-agnostic
- Achieves fast yet stable diffusion-based video generation
Future vision:
Serve as a foundation for high-efficiency AI creativity, enhanced by integrated publishing and monetization platforms like AiToEarn.
---
In short:
LeMiCa shifts caching from local greed to global foresight, opening the path to faster, better AI content — from videos to cross-platform creative campaigns.



