NeurIPS 2025 Spotlight | NYU Introduces QSVD: Purely Mathematical Compression Makes Models Lighter, Faster, and More Stable
QSVD: Efficient Compression for Vision-Language Models
Date: 2025‑11‑15 17:20 · Location: Shandong
---
Key Insight:
Without altering architecture or retraining, mathematical compression alone can make large models lighter, faster, and more stable.

Research Team
- Authors: Wang Yutong (Master’s student) & Wang Haiyu (Ph.D. student), NYU SAI Lab
- Corresponding Author: Saiqian Zhang, Assistant Professor, NYU Computer Science; Director, SAI Lab
- Research Areas: Compression & acceleration of Vision-Language Models (VLMs), low-bit quantization, efficient inference, trustworthy AI systems
---
Why This Matters
Vision-Language Models are the engines for multimodal AI — powering image captioning, visual question answering, AI education, and interactive systems.
Challenge:
- Models often have tens of billions of parameters
- Heavy Key-Value (KV) cache during inference
- Deployment bottlenecks: slow speed, excessive memory consumption
---
QSVD at a Glance
Publication: NeurIPS 2025
- Title: QSVD: Efficient Low-rank Approximation for Unified Query-Key-Value Weight Compression in Low-Precision Vision-Language Models
- Paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/2510.16292
- Code: https://github.com/SAI-Lab-NYU/QSVD
Innovation:
A joint low-rank decomposition + quantization strategy to achieve “lightweight without loss of intelligence.”

---
1. Making Multimodal Models Lighter
Starting from the KV Cache
Attention mechanisms cause massive KV cache demands. Existing methods (Grouped-Query Attention, Multi-Query Attention, DeepSeek’s MLA) can reduce load — but at the cost of accuracy or retraining.
QSVD Goal:
> Without changing the architecture or retraining, compress mathematically for speed, stability, and reduced memory.
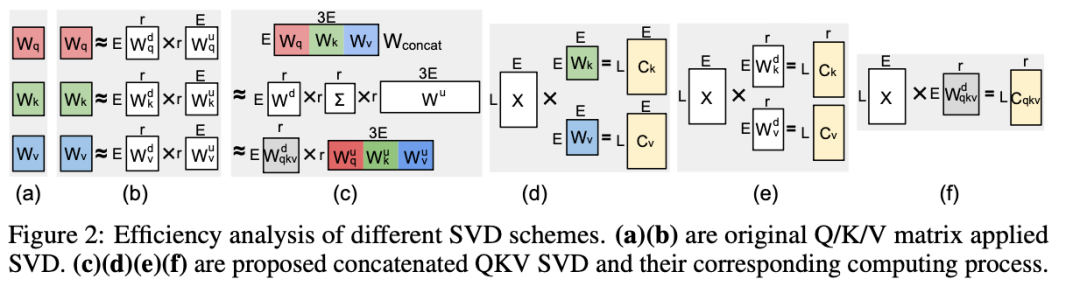
Core Concept: Joint SVD over QKV
- Traditionally, Q, K, V matrices are decomposed separately via SVD
- QSVD concatenates them into a single matrix
- Apply one decomposition → one shared down-projection + separate up-projections
- With rank `r < 0.75E` → major storage & computation savings
---
2. Inference Efficiency
Traditional: Store all K/V caches separately (Fig. 2‑d/e)
QSVD: Store only shared cache (Fig. 2‑f)
- Update once per generated token
- Recover K/V via their projections
Benefits:
- Less computation: Reduced matrix ops via dimensionality reduction
- Lower memory footprint: Halved KV cache size
- More stable representation: Preserves semantic coupling between Q/K/V
---
3. Adaptive Rank Allocation
Different layers have different importance → avoid uniform compression.
Method:
- Use gradient approximation to estimate singular value impact on loss
- Score, globally sort & truncate
- Achieve globally optimal configuration

---
4. Low‑bit Quantization + Outlier Smoothing
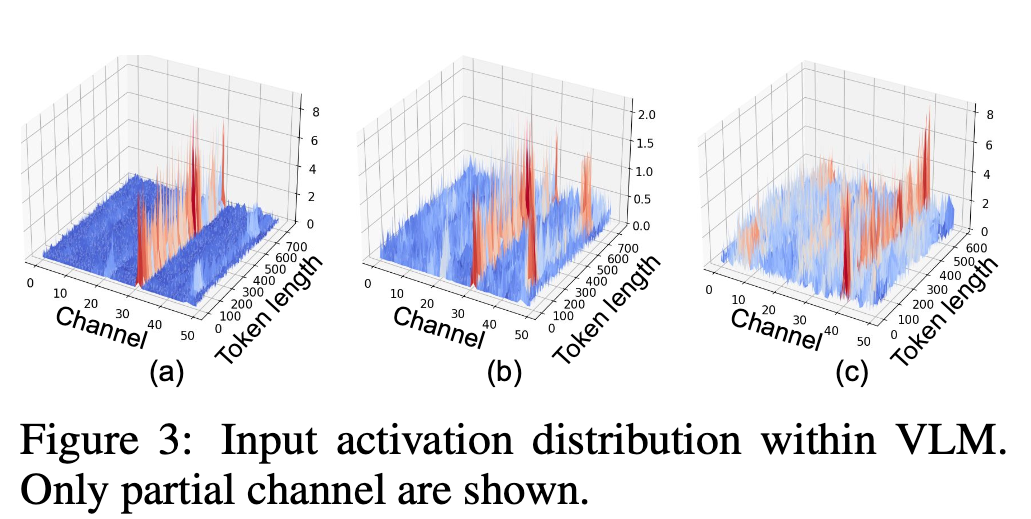
Problem: Channel outliers in VLM activations → quantization causes info loss.
Solution:
- Orthogonal transforms (rotation quantization idea) → smooth distributions
- High precision maintained even at 4‑bit or 8‑bit
- Learnable scaling parameter → balances dynamic range, reduces error
Figures:
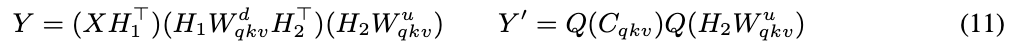
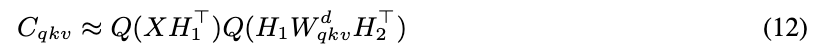
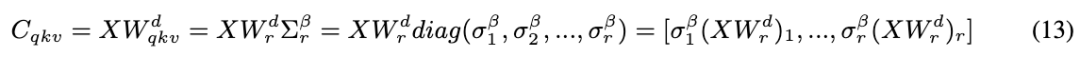
---
5. Experimental Results
- +10% accuracy over ASVD/SVD‑LLM at FP16
- W8A8: Almost no accuracy drop; W4A4 stable at ultra-low bit widths
- Speed: Up to 13× faster inference
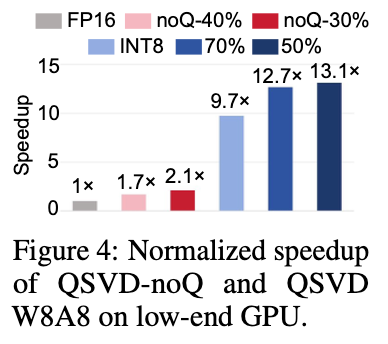
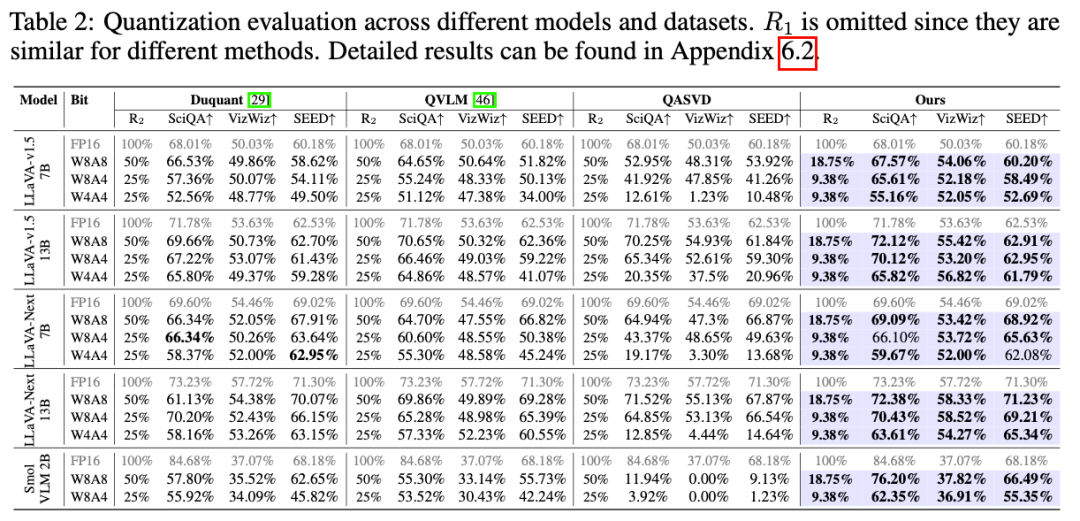
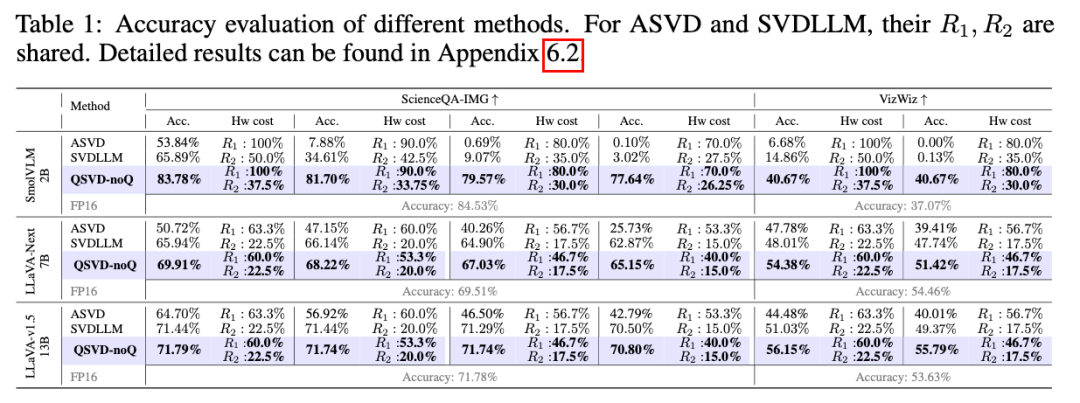
---
Technical Summary: Three Steps to Efficient Multimodal Inference
- Joint SVD over QKV – Unify decomposition for reduced dimensionality
- Cross‑layer Rank Allocation – Compress by layer importance
- Quantization with Outlier Smoothing – Rotate + scale to suppress outliers
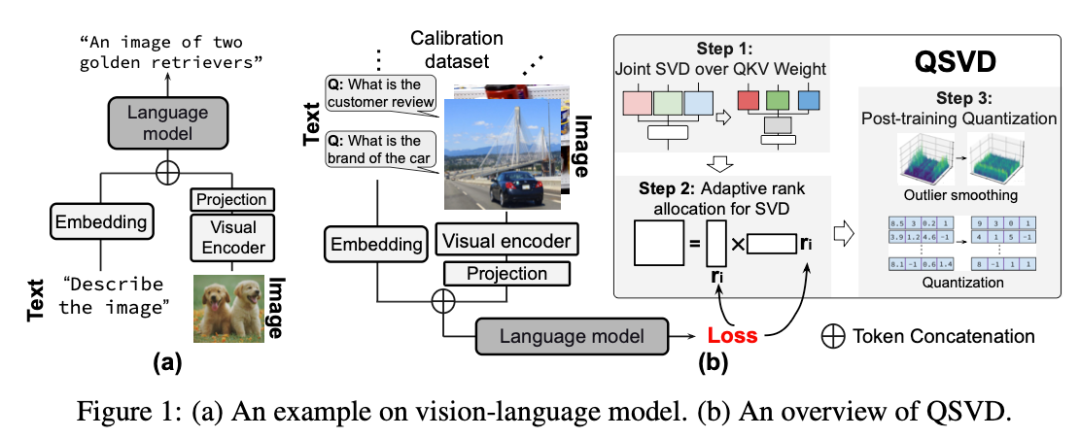
Result:
Low‑memory, high‑precision, and fast multimodal models.
---
6. Integration with AI Publishing Ecosystems
Optimizations like QSVD can supercharge cross-platform AI content generation.
Example: AiToEarn官网
- Open-source AI content monetization
- Multi-platform publishing (Douyin, Kwai, Bilibili, Xiaohongshu, Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, Threads, YouTube, Pinterest, X/Twitter)
- Tools for generation, analytics, ranking
Repo: AiToEarn开源地址
---
Conclusion
QSVD = SVD + Quantization for efficient compression of VLM QKV weights.
Key Impacts:
- Cuts computational load, KV cache size, storage cost
- Minimal accuracy loss
- Enhances deployability → wider accessibility
Future Directions:
- Cross-module joint compression
- Adaptive optimization for full-system lightweighting
- Balancing openness & safety amidst potential risks (privacy, misinformation)
Resources:




