Oh My, Someone Teach Me — In a Promotion Review, What Do Judges Really Care About? (Seeing It from Their Perspective Suddenly Makes It Clear!)

August Topic in the Planet: Promotion

Introduction
What makes a good question?
One that sparks thinking you hadn’t done before.
A question that significantly impacted my career was:
“During a promotion presentation, what do the reviewers actually pay attention to?”
Today, we’ll explore this in depth.
---
Reviewers’ Focus: Evaluation Criteria
The essence of this question lies in understanding the reviewers’ evaluation standard. From a corporate perspective, we can break it down as follows:
Q1. What defines the type of people a company needs?
- Answer: The job role — e.g., Java Engineer, Mobile Engineer, Operations Engineer.
Q2. How is a role’s capability model defined?
From the HR perspective, a competency model generally has three major dimensions:
- Knowledge
- Skills
- General Competencies
> Note: Each of these may contain sub-dimensions or more detailed elements.
Example — For a Java Engineer:
- Professional Knowledge: platform knowledge, business knowledge…
- Professional Skills: design ability, development ability, optimization ability…
- General Competencies: communication skills, innovation skills, project management skills…
Q3. How do competency models differ by level for the same role?
- Answer: For the same position, the behavioral standards (evaluation criteria) for each element vary by level.
---
The Competency Model Framework
This logical framework is a key internal tool at many companies.
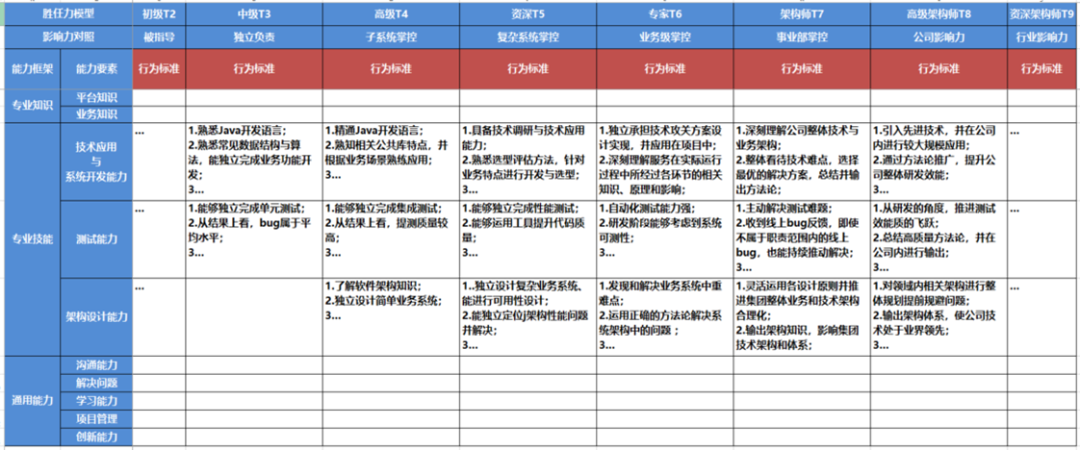
Structure of an Example Java Engineer Competency Model:
- First column: The three dimensions — knowledge, skills, general competencies.
- Second column: Specific competency elements under each dimension — development, testing, design…
- First row: The role, differentiated by levels (T2, T3, T4…).
- Cross cells: Behavioral standards for each level and element.
> Disclaimer: This example model is purely illustrative; actual corporate models may differ and are confidential.
---
Weight Classification by Level (Example)
- T2 → Guided
- T3 → Independent Responsibility
- T4 → Subsystem Ownership
- T5 → Complex System Ownership
- T6 → Business-level System Ownership
- T7 → Division-level Impact
- T8 → Company-level Impact
- T9 → Industry-level Impact
I had the privilege of co-creating the V1 competency models for all technical positions at 58.com, as the inaugural Chairman of the Technical Committee — giving me deep insight into their logic and application.
---
Why Competency Models Matter
A competency model is essential for systematic talent development — solving critical organizational issues.
Without it:
- Hiring: Interviewer’s gut feeling decides pass/fail and level.
- Promotion: Reviewer’s personal judgment dominates decisions.
- Career Development:
- No clear career path
- No clarity on expectations
- No guidance on skill improvement
- Training:
- No structure
- Not targeted to actual gaps
- Reinforces strengths only, without a full learning roadmap.
---
Benefits for Employees
- Clear target level and understanding of expectations.
- Ability to improve skills strategically.
- Awareness of promotion evaluation criteria used by reviewers.
---
Common Career Question
> “If I manage an entire business system (T6 impact) but don’t get opportunities to manage a division system (T7 impact), what should I do?”
In companies with strict “weight” requirements, promotion without meeting the level’s scope can be difficult.
Recommendations:
- Communicate with your leader to develop a plan for heavier responsibilities.
- Seek projects or systems that expand your scope and impact.
- If constrained (“too small a cage”), consider:
- Internal job rotation
- Transition to a new company or role
---
Summary
What do reviewers focus on in a promotion presentation?
- The role’s capability model and the behavioral standards of the target level.
What’s the use of a competency model?
For companies:
- Hiring standards
- Promotion standards
- Career development guides
- Training frameworks
For individuals:
- Clarity on needed capabilities
- Guidance for targeted skill development
- Roadmap to reach promotion goals
---
Reflection Questions:
- Do you understand your career path?
- Do you know the abilities required at each level?
- Are you actively improving those abilities?
---
> In the workplace, these “small things” might never be explained — but they can greatly impact your growth. I can’t give the exact answers for you, only share the logic and experience that worked for me.
---
P.S.
If you want to systematically build and monetize AI-assisted professional content across multiple platforms, tools like AiToEarn官网 provide:
- Open-source global AI content monetization framework
- Multi-platform publishing (WeChat, Douyin, Facebook, LinkedIn…)
- AI generation + analytics + model ranking (AI模型排名)
This can be particularly valuable for packaging career insights — like those above — into scalable multi-platform content.
---
Afterward: We enjoyed watching everyone’s performances.




