On My First Day at Work, a Data Sync Nearly Triggered a P0-Level Incident
Xiao Aba’s Data Synchronization Journey
You are Xiao Aba, fresh into your first job at an e-commerce company.
On day one, your boss hands you a mission: regularly sync order data to the analytics warehouse.
You immediately recall your brother Yupi’s tale — a failed sync on Singles’ Day cost over 100 million yuan in missed sales, and his job.

Determined not to fail, you clench your fists and promise to get it right.
---
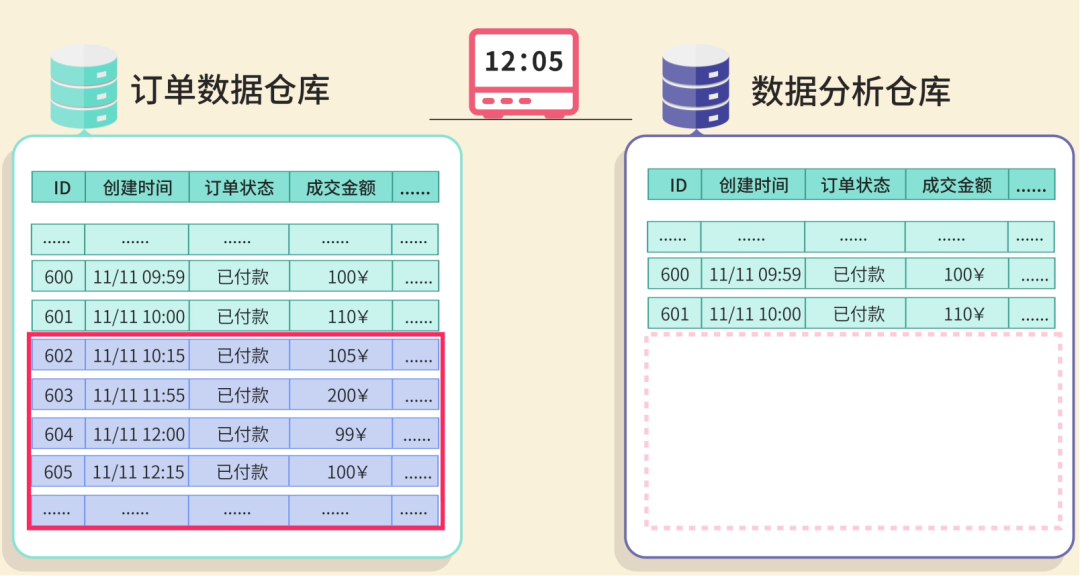
1. Full Synchronization
Data synchronization is like copying photos from one phone to another — regularly replicating data from one database to another.
Your first idea: every day, fetch the entire `orders` table and dump it into the warehouse.

Full synchronization copies all records whether they have changed or not.
# Fetch all orders
orders = db.query("SELECT * FROM orders")
# Clear old data
warehouse.execute("DELETE FROM orders")
# Insert new values
warehouse.insert(order)The first run takes 3 hours for 10,000 orders — success! The boss compliments your speed.
---
2. Basic Alerts
The next day, sync fails without warning, leaving the boss blind in a meeting.
Lesson: No alerts = bad idea.
You add error logging, email notifications to admins, and rollback on failure.
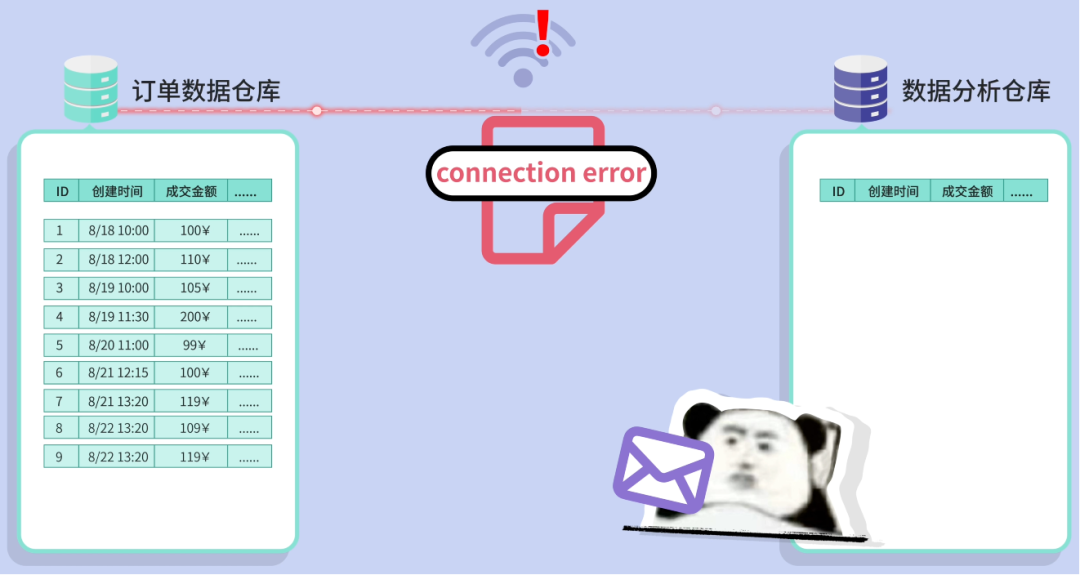
Now, if something breaks, you know immediately and can rerun the task.
---
3. Incremental Synchronization
With 100,000 orders, full sync takes 30 hours.
Scaling to millions becomes impossible.
Solution: Sync only new or updated orders since the last run — incremental synchronization.
Initially, you use `creation_time`, but status changes (like refunds) on old orders aren’t captured.
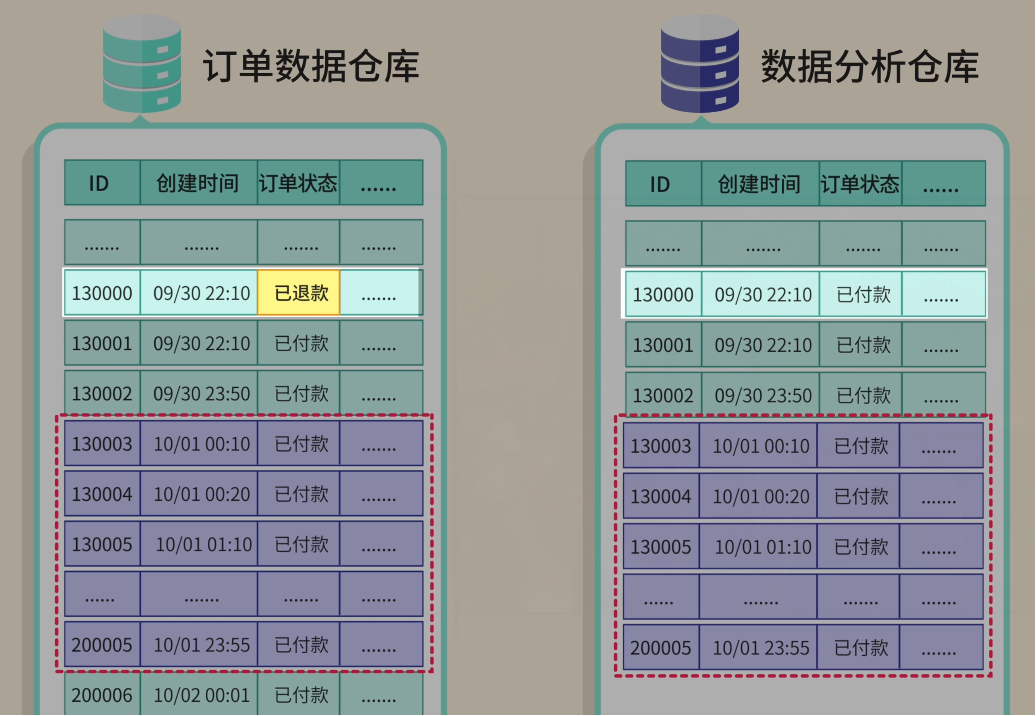
You switch to `updated_time`, which changes whenever data is modified.
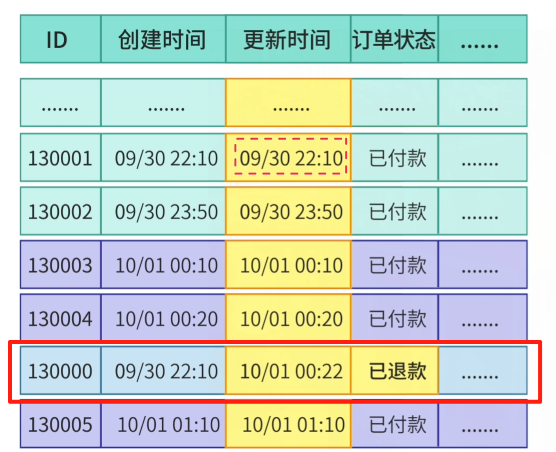
Problem solved — newly created and modified orders are included.
---
4. Batch Processing
During a big promo, your midnight task crashes the server — Out Of Memory (OOM) — due to loading too many rows at once.
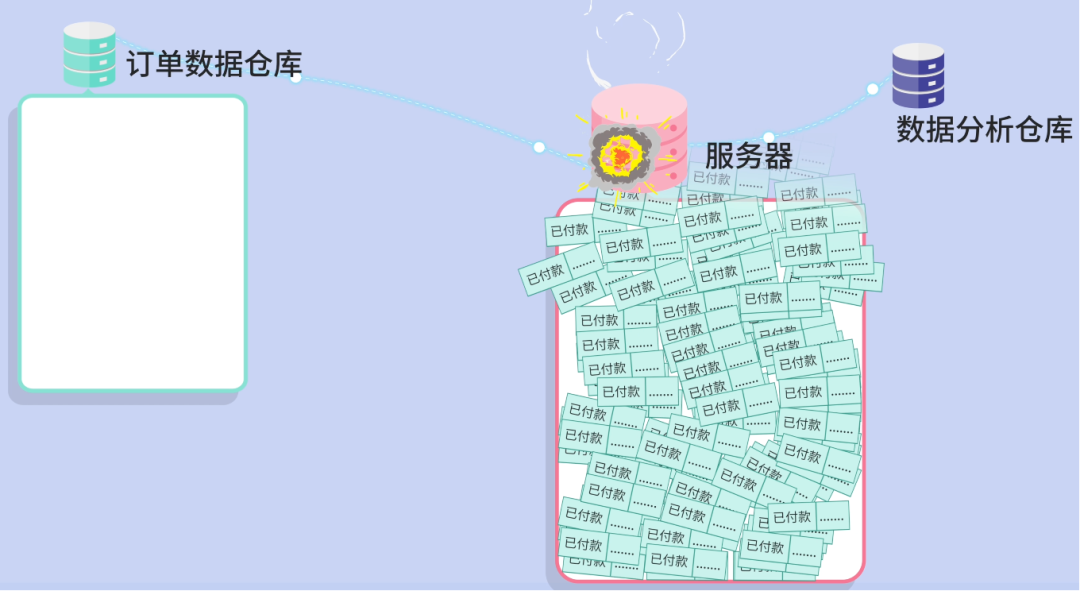
Fix: batch queries in small chunks (e.g., 100 rows), processing pages sequentially.

Benefits:
- Lower memory usage.
- Easier recovery from batch failures.
---
5. Cursor Mechanism
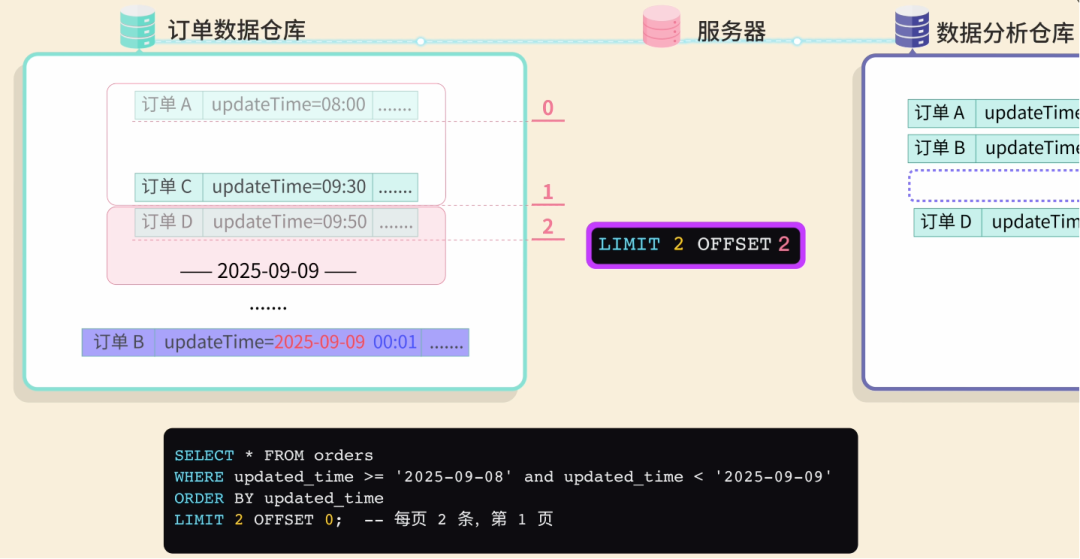
Paginated queries using `OFFSET` lose data when new updates occur mid-sync.
Example:
- Page 1: Orders A, B
- Before Page 2 runs, B’s `update_time` changes
- Page 2 skips C entirely — data loss
Fix: use a cursor (e.g., record `id` of last synced row).
Next query: `WHERE id > cursor`.
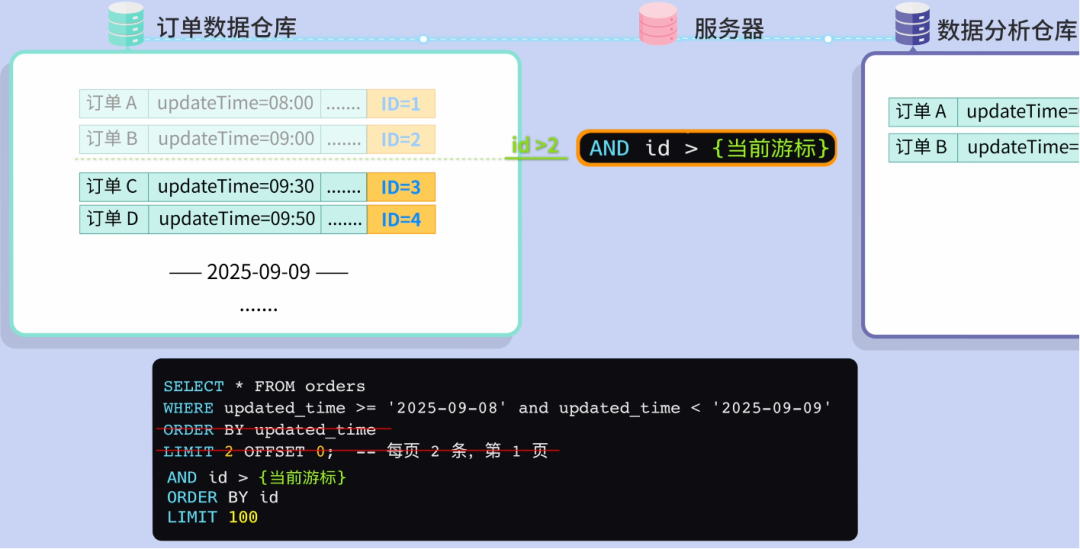
Advantages:
- No deep `OFFSET` performance hit.
- Acts as a progress checkpoint for restarts.
---
6. Performance Optimization
Orders reach millions per day; boss wants sync every 2 hours.
Optimizations:
- Bulk Inserts: insert multiple orders in one statement.
- Parallel Batches: process batches in multiple threads.

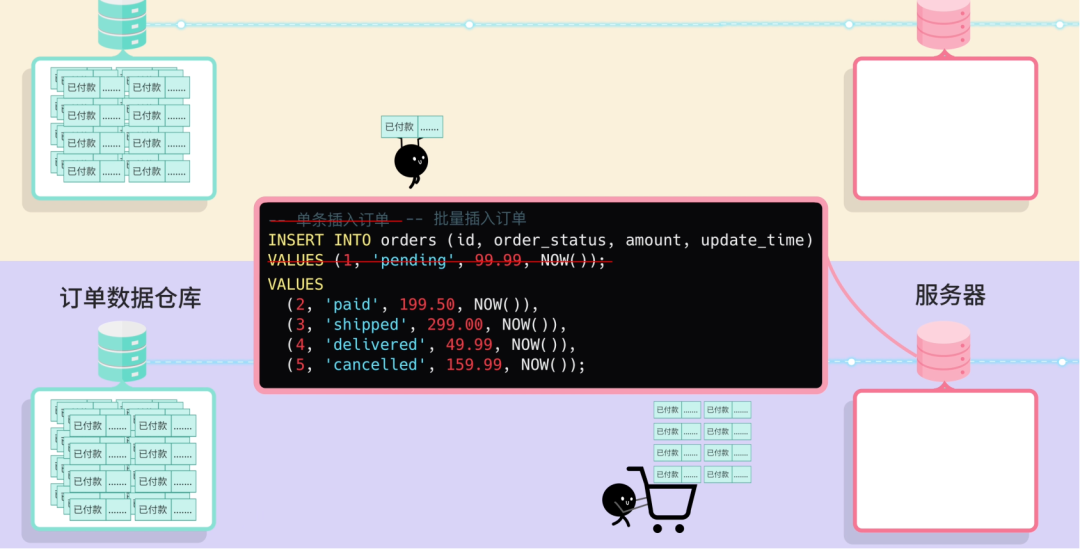
Result: sync runs much faster — and the boss promises promotion.
---
7. Real-Time Synchronization
Boss demands instant updates for investor dashboards.
Solution:
Use CDC (Change Data Capture) + Message Queue.
- CDC: monitors the database for any changes.
- Message Queue: acts as a transfer station — stores changes until processed.

Now, new orders appear on dashboards within 100 ms.
Queue monitoring triggers alerts on backlog.
---
8. Refinement Challenges
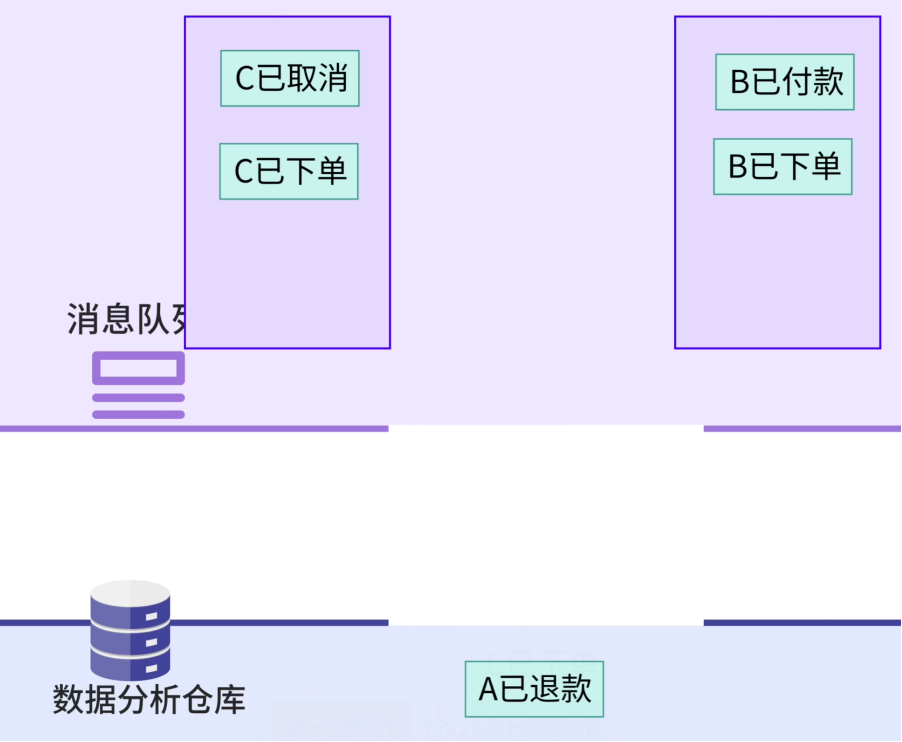
During Double 11:
- Duplicate messages
- Out-of-order updates
- Backlogs slowing processing

Intern Akun suggests:
- Idempotency: track processed message IDs to avoid duplicates.
- Partitioning: group related messages for sequential processing.
- Scaling: use clustering to handle peak loads.

Then asks:
"Why write all this from scratch? Use tools like DataX, Canal, or Debezium!"
Also: "Do periodic data reconciliation to check integrity."



Boss promotes Akun — and sends you to reflect.
---
Key Takeaways
When designing high-volume, real-time data sync:
- Use incremental + cursor-based logic to avoid waste & loss.
- Apply batch + parallel processing for speed.
- Ensure idempotency, ordering guarantees, and scaling with message queues.
- Consider enterprise tools instead of reinventing.
- Perform data reconciliation regularly.
---
> For creators & developers: Open-source platforms like AiToEarn unify AI content creation, cross-platform publishing, analytics, and monetization — syncing posts across Douyin, Kwai, WeChat, Bilibili, Rednote, Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, Threads, YouTube, Pinterest, and X.
> Learn technical workflows, publish tutorials, and rank models via AI模型排名.
---
Author: Programmer Yupi
Source: WeChat Official Account – Programmer Yupi (`coder_yupi`)
Submission Email: editor@dbaplus.cn



