One Code Across 8 Platforms: Is Vue3 Really That Powerful? A Detailed Look at Cross‑Platform Frameworks

📑 Table of Contents
- Origin
- What is a “Multi‑Platform Unified” Application
- Common Multi‑Platform Frameworks
- Truly Cross‑Platform Applications Across Eight Platforms
- Advantages of Cross‑Platform Frameworks
- Disadvantages of Cross‑Platform Frameworks
- Conclusion
---
Introduction
As the variety of application terminals grows, cross‑platform frameworks are becoming more common, aiming to save manpower and improve development efficiency.
This article covers:
- Major cross‑platform frameworks
- Their principles and architectures
- A real example that uses Vue3 to span eight different platforms — the Tencent Video Search Application
- Practical insights for teams implementing cross‑platform solutions
---
01 – Origin
Early Cross‑Platform Needs
Since the advent of multiple operating systems — Windows, Linux, macOS — software has needed adaptation for each OS’s underlying rules.
Without adaptation, apps cannot run natively across platforms.
Key facts:
- Dropping OS support abandons all its users.
- Web browsers are classic cross‑platform apps — each OS has its own install packages.
- Developers often cooperate with OS vendors for pre‑installation.
---
Rise of Web Apps and ERP
With C/S applications and ERP adoption, developers embraced web apps inside browsers.
Browser‑level cross‑OS compatibility meant fewer headaches for developers and users.
---
The Smartphone Disruption
Smartphones added another layer:
- Two dominant OS families: iOS and Android
- Requires separate app versions → doubled dev & maintenance costs
Using mobile browsers for web apps often led to:
- Poor performance
- Lagging UX
- Frequent freezes
---
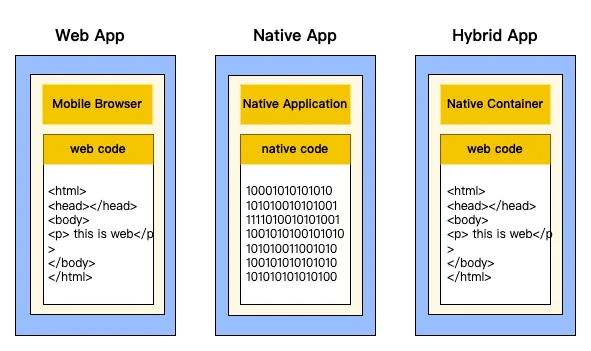
Native vs Web vs Hybrid
Native Apps
- Best performance & UX
- Require separate dev for iOS and Android
Web Apps
- Naturally cross‑platform via browsers
- Poorer UX & performance
Hybrid Apps
- Web tech + native container
- Single development effort
- UX close to native
Evolution diagram:
---
02 – What Is a “Unified Multi‑Platform” Application?
A unified multi‑platform app uses one codebase to run across all target platforms — delivering optimal UX everywhere.
---
Example — Search System Without Unification
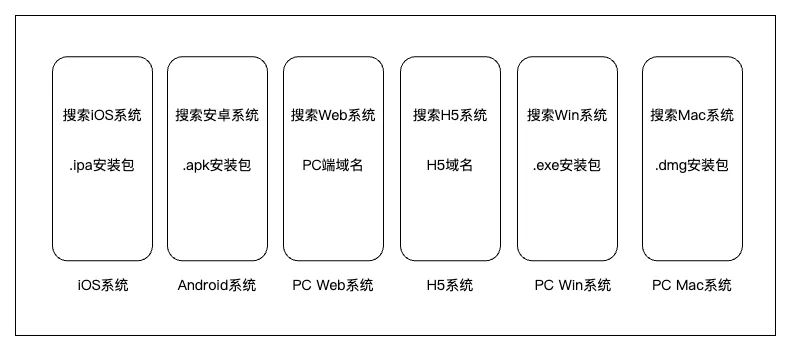
- Each platform: its own codebase
- Maintenance multiplies with each additional platform
---
With a Unified Framework
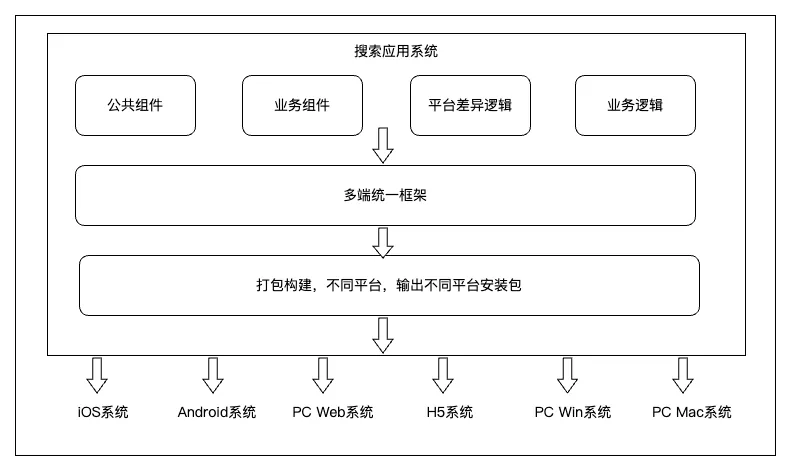
- One intermediate language for all
- Small platform‑specific adaptations
- Framework transforms code into native‑ready outputs
Result: Single codebase, multiple endpoints.
---
03 – Common Unified Multi‑Platform Frameworks
3.1 WebView Container–Based
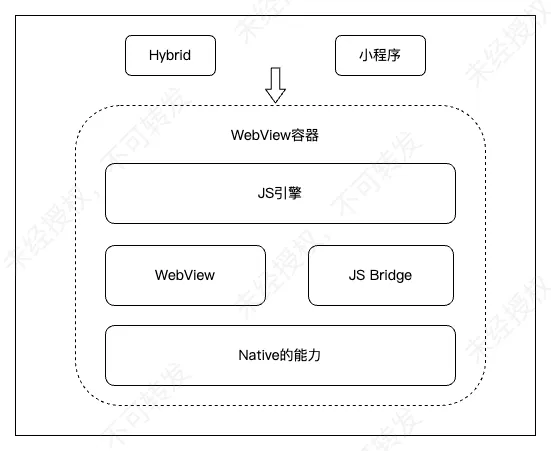
Examples: Ionic, Cordova, Taro.
Taro Highlights:
- Write once, produce mini‑programs for multiple platforms
- Own syntax, UI library, event handling
- Pure front‑end transformation middleware
- Architecture:
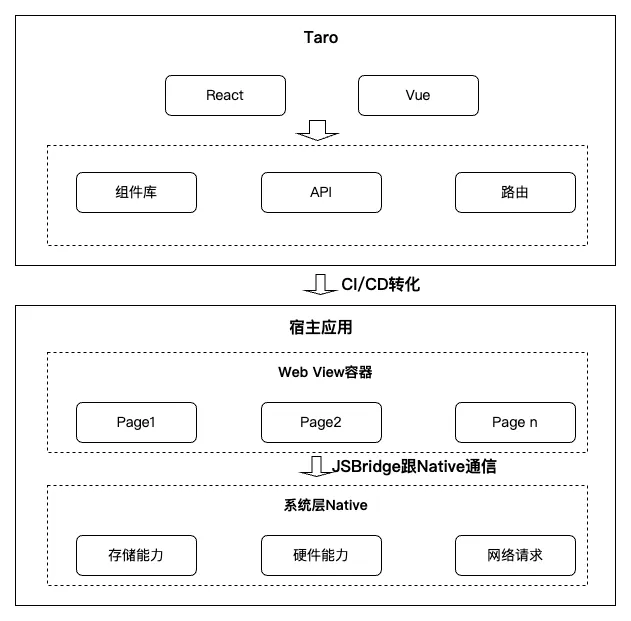
---
3.2 Generalized WebView / Native Rendering
React Native
- JS + React → Native components, not WebView
- Native rendering engine
- Architecture:
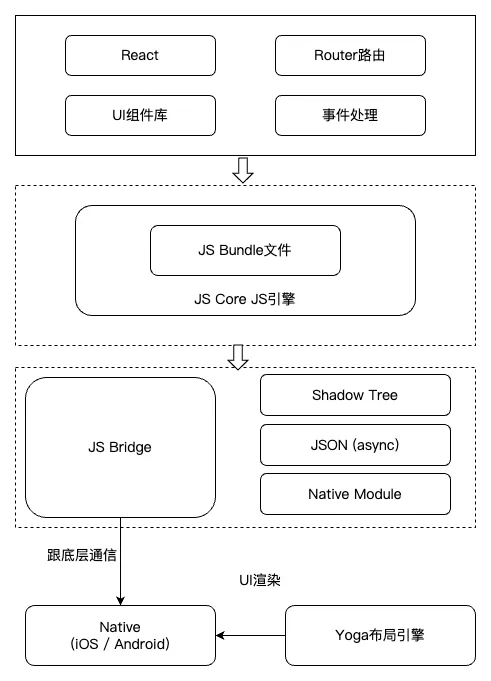
- Uses JS Bridge (optimized with JSI in next‑gen RN)
Hippy (Tencent)
- Widely used internally, open‑sourced
- Modular middleware: JS engine, layout engine, rendering
- Diagram:
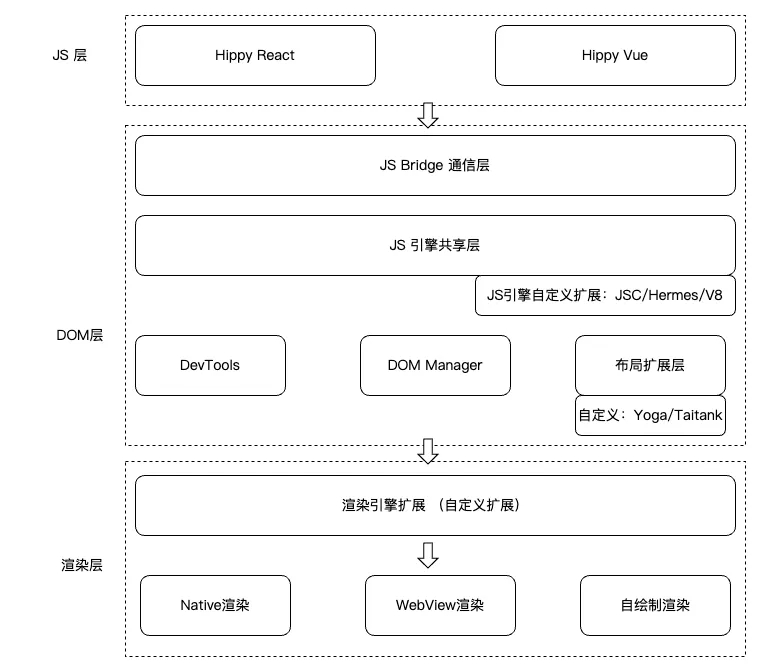
Highlights:
- Pluggable JS engine
- Custom layout engine (Yoga / Taitank)
- Extendable rendering engines
---
PC‑Side Cross‑Platform Frameworks
EVO
- Write client apps like web apps
- Supports Vue3, JS/TS, CSS
- Node.js integration for native API calls
- Native component rendering → consistent UX Win/Mac
- Flexible glue‑layer rendering design
- Architecture:
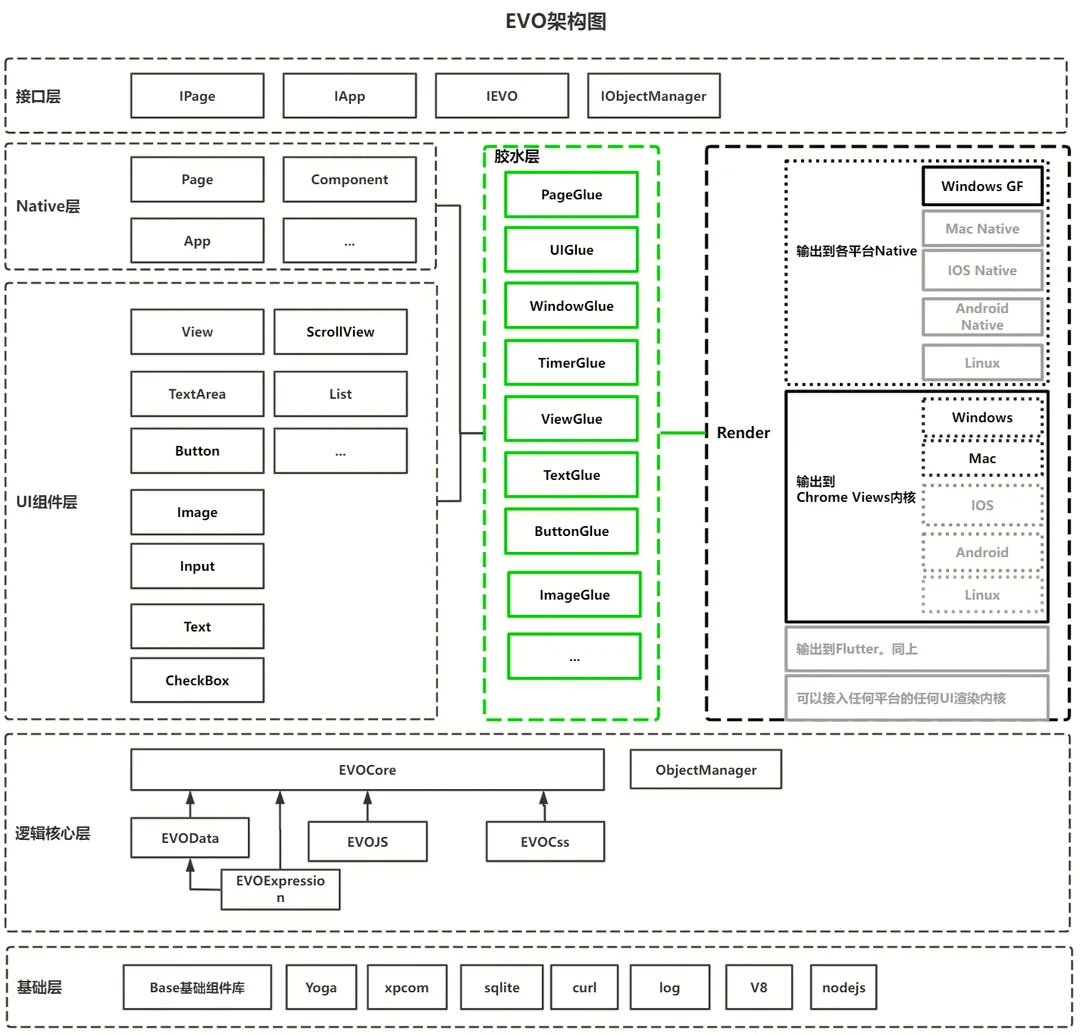
---
Code‑Sharing Approaches
KMM (Kotlin Multiplatform Mobile)
- Compile Kotlin to target platform code
Kuikly (Tencent)
- Declarative Kotlin UI mapped to native controls
- Native‑level performance
- One codebase → Android + iOS
- Architecture:
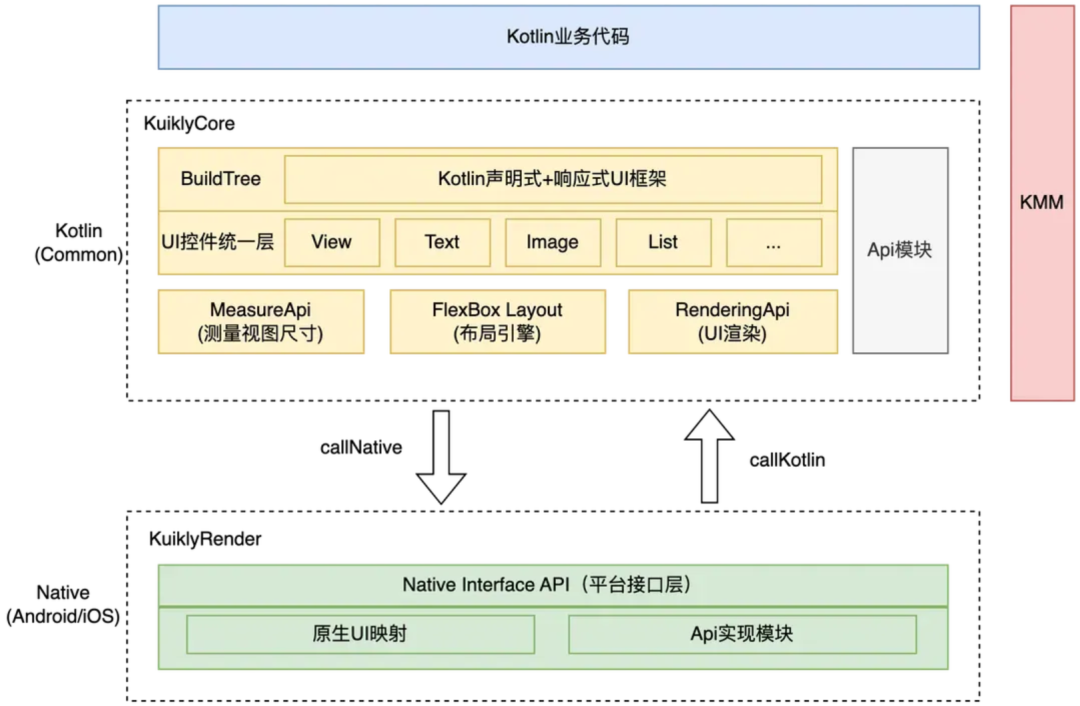
---
04 – True Cross‑Platform Across Eight Platforms
Goal: Single codebase for:
- App Android
- App iOS
- iPad
- aPad
- PC Web
- H5
- PC Windows Client
- PC Mac Client
Solution: Vue3 as common bridge
- Hippy3 + Vue3 → Mobile apps (Android, iOS, iPad, aPad)
- EVO + Vue3 → PC Win/Mac
- Vue3 itself → PC Web, H5
---
Experience Tencent Video Search:
- PC Web link
- For apps and PC: download Tencent Video, tap search bar
---
05 – Advantages of Cross‑Platform Frameworks
Business Perspective
- One codebase → consistent UI & data across platforms
- Simplified operations
- Single ticketing process for new features
Technical Perspective
- Greater dev efficiency
- Easier component reuse
- Centralized repo management
- Major manpower savings:
- One tech stack shared
- Lower dev costs
- Managers love the efficiency
---
06 – Disadvantages of Cross‑Platform Frameworks
Challenges:
- Multiple integrated frameworks → complexity
- Numerous compatibility checks
- Harder merges & code reviews
- Requires strong monorepo management discipline
---
07 – Conclusion
Cross‑platform frameworks are mature yet evolving. They offer clear efficiency gains but require careful platform selection and architecture planning to avoid pitfalls.
Combining such frameworks with multi‑platform content publishing tools — like AiToEarn官网 — can extend the “write once, run anywhere” philosophy to content as well as code. AiToEarn integrates:
- AI content generation
- Cross‑platform publishing
- Analytics
- Model ranking
Delivering reach across: Douyin, Kwai, WeChat, Bilibili, Rednote, Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, Threads, YouTube, Pinterest, and X (Twitter).
---
✅ Key takeaway: A well‑chosen unified multi‑platform framework can save time, save cost, and keep users happy across all devices. The right tools make the promise of “multi‑platform” achievable in both development and content delivery.
---
– End –



