Open Source | 1×3 Pythonic Steps Toward Microservices in Python Applications
# **nacos-serving-python**: A Pythonic Approach to Microservices
**Article #112 of 2025 — Estimated reading time: 15 minutes**
---
## **Overview**
In today’s era of **microservice architectures**, Java — supported by frameworks like **Spring Cloud** — dominates with **non-intrusive service registration and discovery**. Python developers often face a trade-off: either accept heavy, intrusive coding or forgo many microservice benefits.
This article introduces **[nacos-serving-python](https://github.com/nacos-group/nacos-serving-python/)** — an open-source project based on *Nacos* — bringing **Java-like elegance** of microservice features to the Python world, in a fully **Pythonic way**.
---
## **01 — Pythonic Philosophy Meets Microservices**
### **1.1 What Does "Pythonic" Mean?**
"Pythonic" isn't just about following PEP8; it embraces principles like:
- **Readability counts**
- **Simple is better than complex**
- **Explicit is better than implicit**
In microservices, **Pythonic** should mean:
- **Non-intrusive** — no disruption to existing code structure
- **Low barrier to entry** — easy to learn and adopt
- **Flexible** — adaptable to any framework or scenario
---
### **1.2 Challenges for Python in Microservices**
Python excels in **web development**, **data analysis**, and **AI**, but in microservices it struggles with:
1. **Manual Service Registration** — no automated mechanism.
2. **Hardcoded Service Discovery** — often tied to load balancers.
3. **Static Configuration Management** — requires restarts to apply changes.
---
### **1.3 Java’s Non-intrusive Microservices**
In the Java world (particularly in China) using **Spring Cloud Alibaba**, developers enable full microservice functionality with minimal code:
@EnableDiscoveryClient
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}
@RestController
@RefreshScope
public class ConfigController {
@Value("${useLocalCache:false}")
private boolean useLocalCache;
}
Our goal: **bring this non-intrusive elegance to Python**.
---
## **02 — Low-Intrusion Service Discovery**
### **2.1 Usage Example**
`nacos-serving-python` enables **drop-in service discovery** for popular Python HTTP clients. Just swap imports:
Traditional hardcoded approach
import requests
def get_user_info_old(user_id):
response = requests.get(f"http://192.168.1.100:8080/api/users/{user_id}")
return response.json()
New service name approach — just change the import
from nacos.auto.discovery.ext import requests
def get_user_info_new(user_id):
response = requests.get(f"http://user-service/api/users/{user_id}")
return response.json()
**Supported Clients:**
- `requests` → `from nacos.auto.discovery.ext import requests`
- `httpx` → `from nacos.auto.discovery.ext.httpx import AsyncClient`
- `aiohttp` → `from nacos.auto.discovery.ext.aiohttp import get_session`
- `urllib` → `from nacos.auto.discovery.ext.urllib import urlopen`
---
### **2.2 Technical Principle**
**URL Interception & Route Conversion**:
An interceptor captures the outgoing request URL, resolves the service name, and dynamically replaces the host and port.
def resolve_url(self, url: str, strategy: LoadBalanceStrategy = LoadBalanceStrategy.ROUND_ROBIN) -> str:
service_name, parsed_url = self._parse_url(url)
if not service_name:
return url
try:
instance = self.service_discovery.get_instance_sync(service_name, strategy=strategy)
return self._replace_host_port(parsed_url, instance.ip, instance.port)
except NoAvailableInstanceError as e:
logger.error(f"No available instance for service '{service_name}': {e}")
raise
---
### **HTTP Client Adaptation**
Under `nacos.auto.discovery.ext`, clients are wrapped to support service discovery:
def request(method, url, **kwargs):
with _create_service_discovery_client() as client:
return client.request(method, url, **kwargs)
def get(url, **kwargs):
return request('GET', url, **kwargs)
__all__ = ["get", "request", ...]
---
### **Configuration-Driven Discovery**
Enable service discovery just by adding `nacos.yaml`:
nacos:
server: "127.0.0.1:8848"
namespace: "public"
discovery:
empty_protection: true # keep old list if no active instances
---
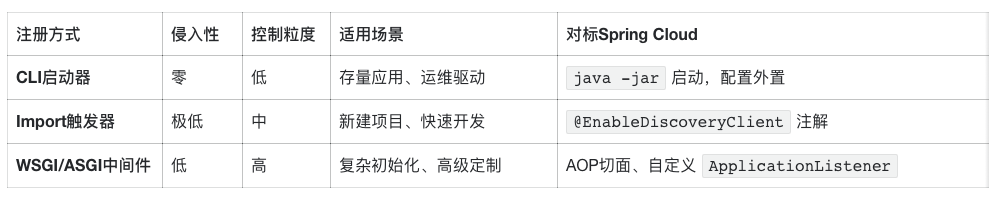
## **03 — Three Automatic Registration Methods**
Adaptable for scenarios from **legacy retrofits** to **new microservices**.
---
### **3.1 CLI Launcher — Zero Intrusion**
#### **Usage:**Original
python app.py
With Nacos registration
python -m nacos.auto.registration \
--nacos-server 127.0.0.1:8848 \
--service-name user-service \
--service-port 8000 \
app.py
#### **How It Works:**
Detects Web framework → injects WSGI/ASGI middleware → starts service.
---
### **3.2 Import Trigger — Minimal Intrusion**
#### **Usage:**import nacos.auto.registration.enabled
from flask import Flask
app = Flask(__name__)
...
app.run(host='0.0.0.0', port=8080)
#### **Principle:**
Hooks Python's `import` to detect frameworks (`flask`, `fastapi`, `django`) and inject middleware:
def enable(self):
self.original_import = __builtins__['__import__']
__builtins__['__import__'] = self._hooked_import
---
### **3.3 WSGI/ASGI Middleware — Fine Control**
#### **Usage:**from nacos.auto.middleware.wsgi import inject_wsgi_middleware
app = Flask(__name__)
initialize_database_pool()
app = inject_wsgi_middleware(app)
app.run(host='0.0.0.0', port=8081)
---
### **3.4 Method Comparison**
---
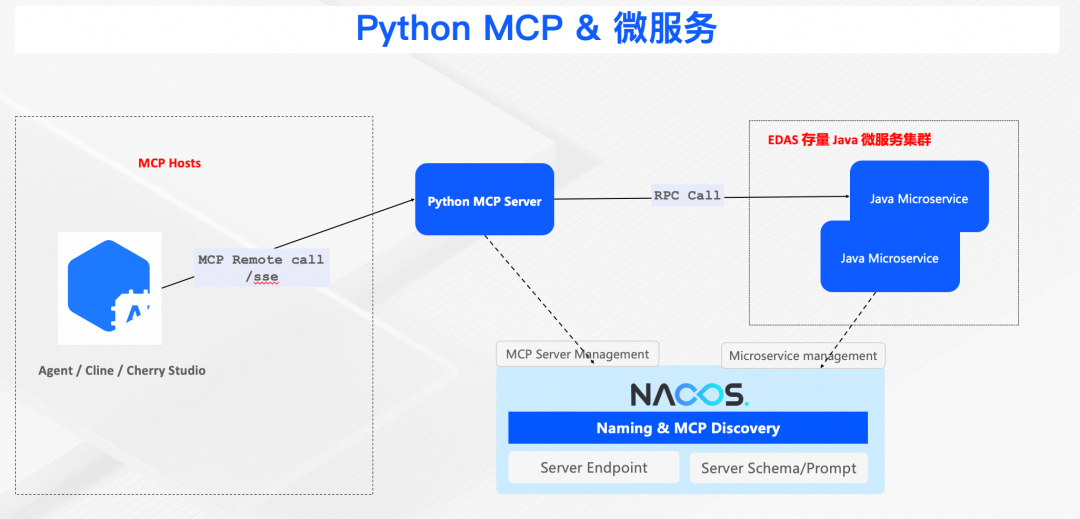
## **04 — Summary & Future**
- Python’s role in AI and microservices is growing.
- `nacos-serving-python` integrated with MCP enables **native microservice communication**.
- Future work: **graceful online/offline mgmt**, **zone routing**, **canary releases**.
---
**Join us:** DingTalk Group ID `21958624`
**Contribute:** [GitHub Repo](https://github.com/nacos-group/nacos-serving-python/)
---
**Tip:** For developers combining **microservices** with **multi-platform publishing** and **AI monetization**, platforms like [AiToEarn官网](https://aitoearn.ai/) provide integrated tools for **AI content creation**, **multi-platform publishing** (Douyin, Kwai, WeChat, Bilibili, Rednote, Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, Threads, YouTube, Pinterest, X), **analytics**, and **AI model rankings** — a natural complement to Pythonic microservice workflows.



